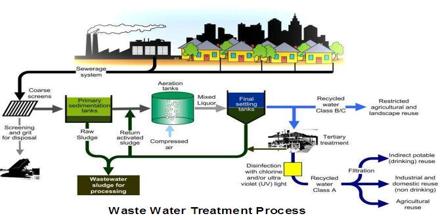
How does sewage treatment plant works?
- Primary treatment:. Usually, it is anaerobic. The solids separates from the sewage first. Wastewater is fed to a screen...
- Secondary treatment:. This is usually aerobic. The solvent from the primary treatment consists of dissolved biological...
- Tertiary treatment:. This is the third stage of wastewater treatment. This is also known...
What are the main steps in sewage treatment?
Jan 16, 2020 · In the combined sewer system, domestic and commercial wastewater is fed into a sewer together with rainwater that accumulates on sealed surfaces (e.g. streets and roofs). The separate sewer system divides the media. Dirty water …
What are the primary stages of sewage treatment?
Sewer pipes fit together simply, with a bell joint, and tiny root hairs find their way to the nutrient-rich flow, then grow larger, eventually growing large enough to shatter the vitreous clay pipe...
Where does your sewage go and how is it treated?
Primary Treatment As sewage enters a plant for treatment, it flows through a screen, which removes large floating objects such as rags and sticks that might clog pipes or damage equipment. After sewage has been screened, it passes into a grit chamber, where cinders, sand, and small stones settle to the bottom.
How expensive is sewage treatment?
Sewage treatment works by employing numerous physical, chemical, and biological treatment processes. A typical sewage treatment plant, in most cases, will first employ preliminary treatment involving screens and/or grit chambers to remove larger and …

What are the 3 stages of sewage treatment?
There are three main stages of the wastewater treatment process, aptly known as primary, secondary and tertiary water treatment.Dec 6, 2018
How does a sewage treatment plant work?
0:523:31How do wastewater treatment plants work? - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAnd soil settle down at the bottom the sewage flows into the settling tank or sedimentation tankMoreAnd soil settle down at the bottom the sewage flows into the settling tank or sedimentation tank where the solid wastes like feces are allowed to settle down waste such as soaps oils.
Where does human waste go after a sewage treatment plant?
The treated wastewater is released into local waterways where it's used again for any number of purposes, such as supplying drinking water, irrigating crops, and sustaining aquatic life.
What are the 5 stages of sewage treatment?
Treatment StepsStep 1: Screening and Pumping. ... Step 2: Grit Removal. ... Step 3: Primary Settling. ... Step 4: Aeration / Activated Sludge. ... Step 5: Secondary Settling. ... Step 8: Oxygen Uptake. ... Sludge Treatment.
What happens to poop at the water treatment plant?
The wastewater flows through bar screens to remove trash and debris, then slowly moves through a grit tank where sand and heavy particles settle and are removed.
What are the methods of sewage treatment?
Majorly, four methods of sewage water treatment are followed – physical, biological, chemical, and sludge water treatment. By following these methods, the wastewater is disinfected from all the sewage materials and converted into treated water that is safe for both human usage and the environment.
Do we drink toilet water?
Indirect potable reuse of treated wastewater that's sent into rivers or underground to mingle with surface or groundwater, and later purified and used for drinking. Direct potable reuse of treated and purified wastewater for drinking. Indirect potable reuse has been used throughout the country for decades.Jul 16, 2021
Do we drink poop water?
That separates water vapor from the solid waste, and then the two part ways. Water vapor travels up and through a cleaning system that uses a cyclone and several filters to remove harmful particles. A little condensation takes place and voila — out comes clean drinking water!Jan 10, 2015
What do they do with human poop?
Some of our poop gets used as fuel, heating the very facilities that process our waste. And the rest eventually reaches landfills. But before the fate of your poop is sealed, a long series of steps ensures it's free from disease, and safe for farms and waterways.Jan 25, 2020
What are the 7 steps in wastewater treatment?
The Wastewater Treatment ProcessStage One — Bar Screening. ... Stage Two — Screening. ... Stage Three — Primary Clarifier. ... Stage Four — Aeration. ... Stage Five — Secondary Clarifier. ... Stage Six — Chlorination (Disinfection) ... Stage Seven — Water Analysis & Testing. ... Stage Eight — Effluent Disposal.Mar 5, 2021
What materials Cannot be removed from wastewater?
When wastewater arrives at the treatment plant, it contains many solids that cannot be removed by the wastewater treatment process. This can include rags, paper, wood, food particles, egg shells, plastic, and even toys and money.
What happens to waste water drainage?
Wastewater is passed through a septic tank, filtered, and disinfected with ozone treatment; it is then reused for non-consumptive uses, such as toilets and laundry. These conservation measures allow them to reuse up to 55 percent of wastewater, while decreasing pressure on wastewater treatment and storage processes.Jan 23, 2017
How many miles of sewer did Boston have?
Boston, still largely building sewers privately, had about 100 miles of sewers in 1869; by 1885 that had expanded to 226 miles, and new houses were expected to connect to the system both for pump and washbasin waste and for the human waste now going into flush toilets instead of privies.
When did Philadelphia start putting sewers underground?
Philadelphia had a system of culverts and some underground sewers by 1750 , and New York City started putting a few sewers underground later in the century. Human waste, though, remained mostly a personal matter of cesspits and privies.
Why did the Romans use portable toilets?
Because Roman sewers lacked ventilation, the only egress for sewer gas was those same drains and latrines. On the plus side, Romans also invented portable toilets, setting urns by the side of the road near the entrances to the city (vendors would rent you what Schladweiler calls "a modesty cape").
How many times can bacteria go around the cycle?
Bacteria can go around the cycle half a dozen times, Lynch says, but eventually they become WAS--waste activated sludge. In the WAS stream, the bacteria go to four big covered tanks called aerobic sludge digesters, in which instead of wastewater nutrients they eat each other.
How much slope does a sewer need?
Stanley says a sewer is a simple thing: The pipe needs to drop about half a foot per 100 feet of length, a slope of 0.5 percent, which is fast enough to keep everything moving, but not so fast that the liquid races away from the solids. Bigger pipes--30 inches or larger--can slope even less.
What is a weir dam?
A weir is nothing more than a low barrier for steering water. When flow is routine, the dam routes it through pipes to the treatment plant; during large rain events, the flow of mixed stormwater and wastewater rises high, overtops the weirs, and flows directly through outfalls to rivers or lakes.
How often did the tides flood Boston?
Some of Boston's sewers had outfalls dammed by the tide 12 hours of every 24; others, built by unscrupulous contractors in land reclamation projects like the Back Bay, sagged and lost their downhill slope, causing settling, clogs, and backups.
Why is sewage treated?
Sewage treatment is a process that is followed for the purification of used water that is often rich in contaminants. The treatment process is followed so that treated wastewater can be safely returned to the water cycle as environmentally friendly effluent.
What is a sewage water treatment plant?
Sewage water treatment plants are an essential aspect of sanitation and water infrastructure. Collection and treatment of sewage, along with purifying and returning the water to the environment in safe and environmentally friendly manner, is a keystone to adhering to the environment agency regulations and to protecting public health.
The working principle of a sewage treatment plant
Sewage treatment works by employing numerous physical, chemical, and biological treatment processes. A typical sewage treatment plant, in most cases, will first employ preliminary treatment involving screens and/or grit chambers to remove larger and heavier, often inert organic matter.
How does sewage get to the treatment plant?
The sewage enters the plants either via gravity (used water is flowing directly to the treatment plant), or under pressure/pumping (wastewater is collected in a chamber and a pump is to direct the wastewater to the tank).
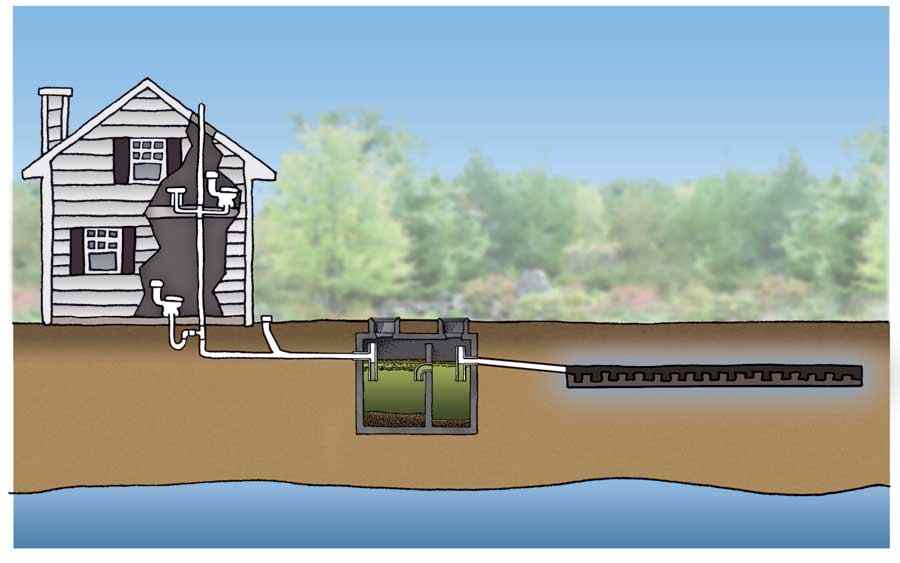
Drainage fields for sewage treatment plants
Water after treatment can be discharged either on a surface water body or in the ground via drainage fields. Drainage fields are an important part of the process, especially for compact sewage treatment plants. A drainage field allows infiltration of the often partially treated effluent into the ground at a controlled rate.
See our sewage treatment plants
Now that you know the basics of what wastewater is and how sewage treatment plants work, view our range of solutions to find out how they can protect your property, our environment and the planet we all share.
Overview
Sewage Treatment Plants (STP) requires physical, biological and often chemical processes in order to eliminate contaminants. Its purpose is to produce sewage water that is environmentally friendly and suitable for disposal or reuse. By circulating air, a sewage treatment plant works to facilitate bacteria’s growth to break down sewage.
Advantages and disaDVANTAGES of sewage treatment plant?
The main purpose of having a sewage treatment plant is to handle the wastewater as thoroughly as possible. While such plants can often cope with more waste than a septic tank, they will still require emptying from time to time. Sludge can also be developed over time in the system.
The Sewage Treatment Plant process comes into 2 main types
Anaerobic bacteria partially decompose sewage in a tank without oxygen. This leads to the removal of methane, hydrogen sulphide, carbon dioxide, etc., from organic matter. We commonly use them to treat sludge from wastewater since it offers a significant amount of volume and mass reduction in the raw material.
How does sewage treatment plant works?
The main objective of STP is to leave all solid particles back before the effluent discharges into the atmosphere. Conventional wastewater treatment includes mainly three phases. They are primary, secondary, and tertiary treatment
Bottom Line
Sewage water treatment is a combination of waste and water which contains organic or inorganic solids from various formations. Cleaning up wastewater is hence very important. In the most economical way, a sewage treatment plant (STP) removes hazardous pollutants and provides a healthy environment. We Jateen Trading Co.
What is chemical sewage treatment?
The preliminary chamber is equipped with coarse and fine mesh of screen as filters to remove large solid particles from getting into the system. In many designs it stay set at the top of the primary chamber with flow measurement device recording and filtering waste water inlet at the same time.
What is the process used to break down sewage into small parts?
The process used to systematically break the sewage into small parts; using biological and chemical method is known as sewage treatment.
What happens when you discharge sewage in open water?
In the absence of sewage treatment plant when we discharge the waste in open water; the waste starts to attract aerobic bacteria and decompose on its own. Not just it suck up the necessary oxygen from the water but also lead to widespread risks of health epidemic if discharged near port.
What is sewage treatment plant?
A sewage treatment plant is designed to treat and process raw sewage over different steps involving breaking, filtering, settling, controlled aerobic decomposition and chemical treatment. One of the most common things that come in our mind regarding human waste; is to dump it to the sewers and let the government take care of it.
How long does it take to remove the smell of chlorine from a water tank?
This is done by adding a 5 % solution of chlorine to kill of bacteria within a period of 30 minutes. Further chemical treatment is done to remove the smell and get rid of the pale colour.
Why use an air driven ejector pump?
To reduce the need to add fresh set of bacteria and increase plant efficiency; many new designs came with air driven ejector pump. They pumps 1/4th of the sludge back to aeration chamber for further treatment and growth of bacteria in the fresh lot of sewage.
How many crews are required to have a sewage treatment plant?
The law requires all ships and water vessels above 4000 Gross tonnage dead weight or carrying more than 15 crew / personal in international waters is required to have dedicated sewage treatment plant or sludge tank to hold sewage for appropriate time.
How is sewage treated?
While most sewage is treated by local municipalities, it is done so in various ways. In the United States, these local municipal facilities must follow both federal and local regulations in terms of the purity requirements for the treated effluent, and although they are treating roughly the same types of human waste, ...
What is biological sewage treatment?
Biological sewage treatment systems are a small part of a larger process that treat human wastes by using bacteria and other microbial accomplices to break them down into other byproducts such as sludge.
Why is nitrification used in sewage treatment?
Because there is ammonia now, the sewage treatment is going to include biological nitrification to remove the ammonia, which gives you nitrates. And after all the ammonia is converted to nitrates, bacteria—either anaerobic or anoxic—reduce all the nitrate and create nitrogen gas, which dissipates into the atmosphere.
Can bacteria settle in a secondary clarifier?
It might, however, get a little difficult when the bacteria in the secondary clarifier do not settle. The whole process really depends upon the bacteria settling in the clarifier, because if they don’t settle you can’t RAS and control MLSS and you’ll see your system’s performance start to drop.
What is a sewage treatment plant?
A sewage treatment plant is designed to take wastewater from a building (wastewater is defined as water from showers, baths, toilets, washing machines, dishwashers and sinks) and treat it to take out contaminants that are harmful to the environment.
How do you add oxygen to sewage water?
Most systems add oxygen to the water using a small air blower which bubbles air up through the water in the tank . Bacteria also need food, this comes from the waste in the sewage water.
Why is fixed biology important?
Fixed biology. Fixed biology treatment plants grow bacteria on some filter material. The filter material will often be lots of small plastic balls with grooves cut in to allow a large surface area. The large surface area is important as it allows lots of room for bacteria to colonise.
What happens when water enters the treatment zone?
When the water enters the treatment zone, it has much less solids in it than the original water, but still has harmful pathogens and am monia (which is poisonous to fish and plant life). This is where bacteria come in. Unlike in the primary chamber, the treatment zone is designed to grow Aerobic Bacteria which does a much better job ...
What is the settlement zone in wastewater treatment?
When wastewater first arrives at the treatment plant it enters an initial settlement zone. This is designed to allow solids to settle down to the bottom of the tank. Often a crust will form on the top which is a build up of lighter solids that float on the water.
What happens to water after settlement?
Following the settlement stage, cleaned water is then free from solids and has undergone a massive reduction in Ammonia and contaminants and can be discharged into a stream or river.
What is the final settlement stage in a tank?
Final Settlement. Once bacteria has done its job and broken down the waste , you will have a final settlement stage. This is designed to allow any remaining small particles (suspended solids) to drop to the bottom of the tank.
Overview
Advantages and Disadvantages of Sewage Treatment Plant?
- The main purpose of having a sewage treatment plant is to handle the wastewater as thoroughly as possible. While such plants can often cope with more waste than a septic tank, they will still require emptying from time to time. Sludge can also be developed over time in the system. Therefore, it is essential to maintain a sewage treatment plant on a regular basis at least once a …
The Sewage Treatment Plant Process Comes Into 2 Main Types
- Anaerobic sewage treatment:
Anaerobic bacteria partially decompose sewage in a tank without oxygen. This leads to the removal of methane, hydrogen sulphide, carbon dioxide, etc., from organic matter. We commonly use them to treat sludge from wastewater since it offers a significant amount of volume and ma… - Aerobic sewage treatment:
Aerobic bacteria digest the contaminants in this process. Air is continuously supplied to the biozone in a sewage treatment plant by either direct surface aeration or submerged diffused aeration. These achieve nearly full oxidation and digestion of carbon dioxide, water, and nitroge…
How Does Sewage Treatment Plant Works?
- Primary treatment:
Usually, it is anaerobic. The solids separates from the sewage first. Wastewater is fed to a screen during primary treatment to extract any large objects suspended in the water. They settle at the base of a primary settlement tank. After this, the water enters a chamber of grit where the grit is … - Secondary treatment:
This is usually aerobic. The solvent from the primary treatment consists of dissolved biological matter and particulate matter. eventually, it will be converting into clean water by the use of indigenous, water-borne aerobic microorganisms and bacteria. These bacteria digest pollutants…
Bottom Line
- Sewage water treatment is a combination of waste and water which contains organic or inorganic solids from various formations. Cleaning up wastewater is hence very important. In the most economical way, a sewage treatment plant (STP) removes hazardous pollutants and provides a healthy environment. We Jateen Trading Co. are experts in supplying your sewage treatment pla…