
Reverse osmosis
Reverse osmosis (RO) is a water purification technology that uses a semipermeable membrane to remove ions, molecules, and larger particles from drinking water. In reverse osmosis, an applied pressure is used to overcome osmotic pressure, a colligative property, that is driven by c…
What is a reverse osmosis system and how does it work?
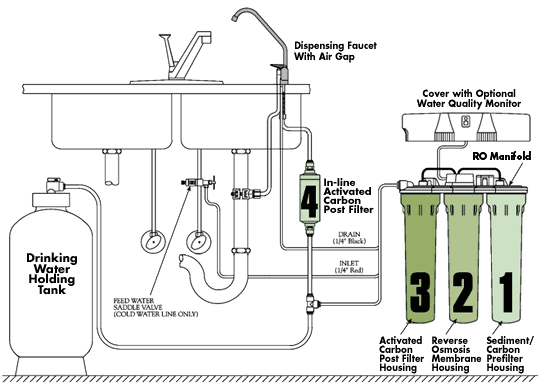
A reverse osmosis system removes sediment and chlorine from water using a pre-filter before the water is forced through a semipermeable membrane to eliminate total dissolved solids. After filtered water comes through RO, it passes through a postfilter to improve taste and appearance.
What are the pros and cons of reverse osmosis?
May 08, 2008 · A reverse osmosis system is connected to the water supply under your sink, where the water passes through three to five filters to achieve purity. The filtered water is then stored in a storage tank (also under the sink). An entirely separate faucet is then installed on your sink, fed from the storage tank below.
What are the stages of reverse osmosis?
In simple terms, a reverse osmosis water filter works as water is forced across a semi-permeable membrane, leaving contaminants behind that are flushed down the drain. The clean drinking water collects in a holding tank. Millions of American households install Reverse Osmosis (RO) because: Reverse Osmosis produces healthy, great-tasting water
How to build your own reverse osmosis system?
The Reverse Osmosis Process A reverse osmosis system forces water through a very fine, semi-permeable membrane at high pressures. Any molecules that are larger than a typical water molecule are unable to physically pass through the membrane and are trapped, resulting in water that is almost completely pure after treatment.
How reverse osmosis works step by step?
1:334:02How does reverse osmosis work? - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipWater passes through the membrane surface. Into the permeate channel it flows in a spiral. DirectionMoreWater passes through the membrane surface. Into the permeate channel it flows in a spiral. Direction and collects in the core tube. This water is the final recycled water product or permeate.
Does reverse osmosis really purify water?
RO systems remove contaminants from water including nitrates, sulfates, fluoride, arsenic and much more. But it also removes healthy minerals such as magnesium, calcium, potassium and sodium. Overall they remove 100s of substances from tap water with a 99% or higher filtration effiency rate.
Why should you not drink reverse osmosis water?
RO water which doesn't contain enough minerals, when consumed, leaches minerals from the body. This means that the minerals being consumed in food and vitamins are being urinated away. Less minerals consumed plus more minerals being excreted causes serious negative side effects and big health problems.Aug 9, 2020
What are the disadvantages of reverse osmosis?
One of the major disadvantages of RO systems for the home is that they remove most of the minerals from the water leaving it with an acidic pH. Also, during the purification process, up to 20 gal of water is flushed down the drain for every gallon of filtered water produced.May 18, 2012
What is the healthiest water to drink?
What Is The Healthiest Water To Drink? When sourced and stored safely, spring water is typically the healthiest option. When spring water is tested, and minimally processed, it offers the rich mineral profile that our bodies desperately crave.
Is bottled water reverse osmosis?
bottled water can actually be RO water. As of publishing, many major bottled water companies run their water through a filtration process that includes reverse osmosis — including Dasani, Nestle and Aquafina.Apr 7, 2021
How do you Remineralize reverse osmosis water?
Add mineral salt Natural salt, such as Himalayan salt, instead of common table salt, contains all the necessary trace minerals that are removed during the reverse osmosis process. This is one of the most cost-effective means of remineralizing water.May 25, 2021
Does Brita use reverse osmosis?
The Brita PRO Under-Sink Reverse Osmosis System: Combines micron/carbon/membrane filtration with state-of-the-art reverse osmosis technology for taste and quality. Removes impurities while improving the taste, color and smell of your drinking and cooking water.
Does reverse osmosis remove E coli?
Reverse Osmosis Systems have a very high effectiveness in removing bacteria (for example, Campylobacter, Salmonella, Shigella, E. coli); Reverse Osmosis Systems have a very high effectiveness in removing viruses (for example, Enteric, Hepatitis A, Norovirus, Rotavirus);
Which is better filtered water or reverse osmosis?
The difference between reverse osmosis and carbon filtration is the presence of the high-quality reverse osmosis membrane. Activated carbon filtration is most effective at removing or reducing impurities and contaminants such as chlorine, sediment, volatile organic compounds, poor taste and odour from water.
What is not removed by reverse osmosis?
Reverse osmosis units do not effectively remove most organic compounds, bacterial microorganisms, chlorine by-products, or dissolved gases like carbon dioxide, methane, and radon.
What are the pros and cons of reverse osmosis water?
The Benefits of Reverse Osmosis water FiltrationPro #1: Reverse Osmosis filters the most contaminants.Pro #2: Reverse Osmosis is a safe, environmentally friendly alternative to bottled water.Pro #3: Reverse osmosis provides better water for cooking.Con #1: More water wasted.Con #2: Some noticeable pressure drop.More items...
What is reverse osmosis?
Reverse Osmosis is the reversal of this natural phenomenon, by the application of external pressure on the solution that contains the higher concentration of dissolved ions, this forces water through the semi-permeable membrane in the opposite direction, leaving behind the dissolved ions and the suspended solids.
How does osmosis work?
In natural osmosis, the solvent or water in this application travels through the membrane from the solution with the lower concentration of ionic materials to the solution with the higher ionic concentration. This process continues until the ionic concentration of both solutions is equal or until the resultant passage of the water through the membrane reaches the osmotic pressure of the solution if the solutions are trapped in a container as illustrated in Figure 1.
What is the water that passes through the membrane called?
In the reverse osmosis process, the water that passes through the membrane is commonly referred to as permeate, or product water , the water that remains behind the membrane along with the dissolved and suspended solids is referred to as the concentrate, brine or reject water. Figure 2.
What are the dissolved solids in RO?
The presence of some dissolved solids such as silica, barium, strontium, or calcium and magnesium when present with carbonate or sulfate ions restricts the recovery of an RO unit more than other dissolved solids, due to their limited solubility in water.
What happens when water comes into contact with a substance?
When water comes into contact with substances they either become dissolved solids, such as minerals, gases and organic compounds or they become suspended solids such as clay, silt, and microorganisms.
What factors affect the flux rate of a membrane?
The flux rate of a particular membrane is generally limited by several factors including, temperature, operating pressure, and the requirement of surface flushing action to keep the membrane surface clean of suspended solids. Typically higher flux rates cause higher fouling rates.
Can you recover all of the water in a membrane?
If all of the water that was processed were converte d to product water, there would be no water available to flush the membrane surface area free of remaining suspended solids.
How does reverse osmosis work?
In simple terms, a reverse osmosis water filter works as water is forced across a semi-permeable membrane, leaving contaminants behind that are flushed down the drain. The clean drinking water collects in a holding tank.
What is reverse osmosis water filter?
If you’re looking for a water filter that will provide great-tasting, fresh drinking water for your home or business, Reverse Osmosis (RO) water filtration is one of the most popular and cost-effective water filtration methods available. In simple terms, a reverse osmosis water filter works as water is forced across a semi-permeable membrane, ...
Why don't we need a whole house RO water filter?
Whole-house reverse osmosis consumes a lot of water. Whole-house RO flushes a lot of filtered water down the drain.
What are the pre-filters used in reverse osmosis?
There may be more than one pre-filter used in a Reverse Osmosis system, the most common being sediment and carbon filters . These pre-filters are used to PROTECT the RO membranes by removing sand silt, dirt, and other sediment that could clog the system.
How much does a RO system cost?
Absolutely. Looking at cost alone, RO systems generally cost less than 30-cents per day to own and operate for a family of four. From a cost-savings perspective, since most Americans spend $100/year on bottled water translating to $400/year for the household, and an RO system would save nearly $300/year as it operates for roughly $100/year. And the number crunching doesn’t reveal anything about the health benefits of RO! RO systems can remove harmful contaminants such as pesticides, herbicides, chlorine, chloramine, and arsenic---certainly making an RO system “worth it.”
What is the post filter in RO?
The post filter is usually a carbon filter.
Why is public water not regulated?
The problem is that there are many contaminants, especially those that cause taste and odor issues, which are simply not EPA regulated. These contaminants can easily penetrate aquifers, streams and rivers, bringing impurities straight to your water lines.
The Reverse Osmosis Process
A reverse osmosis system forces water through a very fine, semi-permeable membrane at high pressures. Any molecules that are larger than a typical water molecule are unable to physically pass through the membrane and are trapped, resulting in water that is almost completely pure after treatment.
Components of a Reverse Osmosis System
Most reverse osmosis systems include pre-filters to protect the membrane and improve the treatment results. A typical system will feature:
Reverse Osmosis Systems in Maryland
At Water Doctor, we sell, install, and service reverse osmosis systems, as well as a variety of other water treatment solutions, such as whole-home filtration systems, water softening systems, UV sterilization systems, and more.
What is reverse osmosis?
Reverse osmosis is a process of purifying water by removing unwanted materials and ions through the use of a semi-permeable membrane. The resulting product is purified water suitable for drinking or industrial use.
How much water is removed by reverse osmosis?
Reverse osmosis removes up to 99.8% of contaminants in water in order to create clean, potable water, but the quality of the individual components used in any RO system is the key to creating a truly high-performing, cost-effective system. Particularly when it comes to portable, containerized RO systems, it’s imperative that every component is top-of-the-line in order for the system to successfully operate.
What is the most important part of a RO system?
Pretreatment may be the single most important part of an RO system. In many cases, it is not unusual for the pretreatment system to cost more than the RO itself. Reverse Osmosis via the RO membrane. After pre-treatment, the water is then moved through the reverse osmosis membrane by means of a high pressure pump.
Is reverse osmosis a good method of purification?
Reverse osmosis has long been considered one of the best methods for purifying water due to its ability to remove such a wide range of contaminants including dissolved solids. If applied correctly, it has proven to be cost effective and dependable. It is energy efficient, compact, and relatively easy to operate as compared to other desalination technologies.
Does desalination require chemical treatment?
In some cases, the permeate (product) from the RO process will require post-treatment before it can be used for its intended purpose. In the case of desalination for potable water, the permeate may require chemical treatment to make it less corrosive. It will also require disinfection.
Why use reverse osmosis?
Reverse osmosis systems are ones that should be used as a last resort when it comes to cleaning your water. There are many reasons for this, one being the cost, they are expensive and the second being that you are left with pure water without minerals. The human body requires minerals in order to fulfil basic biological needs, so by removing iron, magnesium and other minerals, you will need to make sure that you are getting them from other sources, such as supplements or bottled mineral water. Prior to installation it will always be worth having the quality of your water checked. Not only will it show what contaminants are in you water course, it will also show you the density and prevalence. Reverse osmosis doesn’t sound as complicated as it seems. It is simply water being forced through a semi permeable membrane. It is this forcing the molecules that leaves the contaminants on one side and purified water on the other. The process is simple, but you will need to make sure that you maintain the system to a high standard to ensure the best possible results.
Can you use reverse osmosis water in a kitchen sink?
Like other water filtration systems there are an array of installation options if you are looking at a reverse osmosis system. Reverse osmosis systems can be as small or as large as you like. Some can easily be fitted under the kitchen sink if you want to make sure that your drinking water is at a particular standard. You can also opt for whole house systems. These are a lot more expensive and a lot larger than under the counter systems, however they make sure that your entire home is fed with water that has gone through this system. The benefit of whole house systems is that you won’t need any additional filtration devices in any rooms, as all the water into your home will be free from contaminants. In cases where lead is extremely prevalent in your water system, this is very important, as sustained exposure to lead can hamper brain development in children, along with a whole host of other issues. As we aforementioned, before committing to a system, it is worth having your water tested.
What is reverse osmosis water?
A reverse osmosis system is one of the most extensive methods of filtration. It removes 98% of dissolved solids, which makes it healthier to drink. A water distiller is the only other drinking water system that also reduces TDS, but it's less efficient than an RO system.
What is the purpose of reverse osmosis?
A reverse osmosis system removes dissolved solids like arsenic and fluoride through the RO membrane. An RO system also includes sediment and carbon filtration for a broad spectrum of reduction. The carbon filters in an RO system remove chlorine and bad taste and odors, and the sediment filter removes dirt and debris.
What is the RO membrane?
The RO membrane is the focal point of a reverse osmosis system, but an RO system also includes other types of filtration. RO systems are made up of 3, 4, or 5 stages of filtration. Every reverse osmosis water system contains a sediment filter and a carbon filter in addition to the RO membrane. The filters are called either prefilters ...
How long does it take for a reverse osmosis system to make water?
A reverse osmosis system makes water slowly. It takes one minute to produce two to three ounces of RO water. If you were to turn on your faucet for a glass of water at the actual membrane production rate, then you would have to wait at least 5 minutes for it to fill. With a storage tank, your glass fills instantly.
What is a semi-permeable membrane?
Semi-permeable membrane: Removes up to 98% of total dissolved solids (TDS) When water first enters an RO system, it goes through prefiltration. Prefiltration typically includes a carbon filter and a sediment filter to remove sediment and chlorine that could clog or damage the RO membrane.
How is bottled water purified?
Most bottled water is purified through reverse osmosis, but producing bottled water wastes more water than a reverse osmosis system. Think about all the water required to make one bottle of water. When bottled water is purified, wastewater is sent to the drain, and producing the bottle uses water and petroleum. Petroleum is used again to deliver the bottled water to the store. Afterward, the truck may get washed, using even more water. A reverse osmosis system provides water just as pure as bottled water that tastes just as refreshing without as great of a cost to the environment.
What is needed to disinfect water in a whole house?
In addition to a large water pump and storage tank, a UV system is needed to disinfect the water once it leaves the tank.
Water
Dissolved Solids
Suspended Solids
Dissolved Ionic Content and Water Quality
Osmosis
Reverse Osmosis
- Reverse Osmosisis the reversal of this natural phenomenon, by the application of external pressure on the solution that contains the higher concentration of dissolved ions, this forces water through the semi-permeable membrane in the opposite direction, leaving behind the dissolved ions and the suspended solids. This is illustrated in Figure 2. In ...
Practical Applications
Recovery Limitations