Medication
The symptoms of HD can vary a lot from person to person, but they usually include:
- Personality changes, mood swings & depression
- Forgetfulness & impaired judgment
- Unsteady gait & involuntary movements (chorea)
- Slurred speech, difficulty in swallowing & significant weight loss
Therapy
Surgeries and Specialist-Driven Procedures
- Active Therapy. There are a number of types of therapy that you can actively participate in. ...
- Muscle Injections or Surgery. If your medical treatment of muscle spasms is not effective, you may benefit from botulinum toxin injections or even surgical release of the muscle.
- Counseling. ...
- Caregiver Support. ...
Self-care
While Huntington's disease is a stressful experience with an uncertain prognosis, it's not a reason to give up on life. It's possible to treat some of the symptoms and try to lead a healthy life for as long as possible. If you've been diagnosed, you don't need to let the disease take over.
See more
For some animals, it may be a year or more before symptoms develop, which can include drastic weight loss (wasting), stumbling, listlessness, and other neurologic symptoms. Infected animals shed prions through saliva, feces, blood, and urine.
How does Huntington disease affect the brain?
What is the treatment for Huntington disease?
What is the prognosis of Huntington disease (HD)?
What are the symptoms of hunting disease?

What is the most common treatment for Huntington's disease?
Xenazine (tetrabenazine) is the only medication specifically approved for Huntington's chorea. Others, such as antipsychotics and benzodiazepines, have also demonstrated a benefit and can be used off-label. Physical therapy can help maintain mobility and prevent falls through tailored exercises for the patient.
How Does gene therapy work for Huntington's disease?
However, in the case of Huntington's disease, the goal is to use gene therapy to limit the production of the toxic huntingtin protein. Less toxic protein in the brain would mean a slower breakdown of neurons. These genetic instructions are delivered to cells using vectors.
Can Huntington's disease be prevented or treated?
Can you prevent Huntington's disease (HD)? HD is caused by having a mutation on the HTT gene. You can't change your genes or prevent the disease from developing. Currently, there isn't a treatment that can slow or stop the progression of HD.
What is the latest treatment for Huntington's disease?
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) today approved SD-809 (deutetrabenazine), the second drug approved for use in the United States to treat chorea in Huntington disease (HD), a rare, inherited neurodegenerative disorder.
How Does gene therapy work?
With gene therapy, doctors deliver a healthy copy of a gene to cells inside the body. This healthy gene may replace a damaged (mutated) gene, inactivate a mutated gene or introduce an entirely new gene. Carriers, called vectors, transport these healthy genes into cells.
How close is a cure for Huntingtons?
There is no cure, and symptoms on average begin in the mid-40s (it then usually takes about 15 years to kill). Indeed, for more than 100 years after the disease was characterised, those at 50:50 risk of inheriting it had no way of ending the uncertainty until the symptoms started.
Why can't Huntington's disease cured?
The disease is genetic, which means it is inherited from your parents. There is no cure, and it is fatal. People are born with the defective gene that causes the disease. But symptoms usually don't appear until middle age.
Is Huntington's disease painful?
A large worldwide study on the prevalence of pain in Huntington's Disease (HD). The outcomes are pain interference, painful conditions and analgesic use. The prevalence of pain interference increases up to 42% in the middle stage of HD. The prevalence of painful conditions and analgesic use decrease as HD progresses.
How does tetrabenazine treat Huntington's disease?
Tetrabenazine (TBZ) is a dopamine depleter. It works by inhibiting the vesicular monoamine transporter 2 (VMAT2). Neurons are connected to each other by synapses and communicate through chemical signals called neurotransmitters.
What are the 5 stages of Huntington's disease?
5 Stages of Huntington's DiseaseHD Stage 1: Preclinical stage.HD Stage 2: Early stage.HD Stage 3: Middle stage.HD Stage 4: Late stage.HD Stage 5: End-of-life stage.
What should you watch for in a person with Huntington's?
Emotional symptoms include:Depression (around one third of people with Huntington's disease experience depression)Mood swings, apathy and aggression.Personality changes.
What is the first treatment for Huntington's disease?
If you have severe muscle stiffness that causes pain or inhibits your movements, medication adjustment is usually the first type of treatment, because some of the antipsychotic medication used in the treatment of Huntington’s disease can cause muscle stiffness. 6 . Physical therapy may help as well.
How to reduce Huntington's symptoms?
And, as your behavioral symptoms and mood changes emerge, keeping a familiar schedule and avoiding unexpected or sudden changes in your life can help reduce the impact of these symptoms on your day-to-day life. The Signs and Symptoms of Huntington's Disease.
What is physical therapy?
5 . Physical therapy is focused on improving your muscle strength, control, and coordination.
How to reduce the effects of your condition?
You can reduce the effects of your condition with some at home strategies. As your motor control and coordination decline, you can optimize your safety by doing things like avoiding stairs, using a walker, and having supportive handrails while you shower.
Why is swallow therapy important?
Swallow therapy is very important as Huntington’s disease advances. Eating safety involves learning how to chew and swallow with better muscle control, and also selecting food and liquids that aren’t choking hazards.
Can a therapist help with Huntington's disease?
In the early stages of Huntington’s disease, you may have trouble thinking, problem-solving, and remembering things. Your therapist can help you with strategies so you can still maintain the best quality of life possible as some of these cognitive skills are declining.
Can Huntington's disease cause anxiety?
Depression is the most common mood symptom associated with Huntington’s disease, although anxiety can occur as well. These symptoms can be treated with antidepressants or anti-anxiety medications, with careful monitoring of side effects and consideration of potential drug interactions. 2
How long does it take to die from Huntington's disease?
People usually die from the disease within 15 to 20 years of developing symptoms.
What type of test is used to determine if you have Huntington's disease?
Special blood tests can help your healthcare provider determine your likelihood of developing Huntington disease. A computed tomography (CT) scan of the head can evaluate the scope and scale of brain cell damage and loss of brain tissue. A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan or a positron emission tomography (PET) scan may also be used.
How much chance of developing Huntington's disease?
The goal of treatment is to manage your symptoms so that you can function as long as possible. If you have Huntington disease, your child has a 50% chance of developing the disease. Huntington disease affects your emotional, physical, and intellectual abilities.
Can you cure Huntington's disease?
You can’t cure or slow the progression of Huntington disease, but health care providers can offer medications to help with certain symptoms. Drugs like haloperidol, tetrabenazine, and amantadine are especially helpful for controlling the unusual movements caused by Huntington disease.
Can Huntington's disease be caused by other diseases?
Because many of these symptoms can be caused by other diseases, a detailed physical and neurological exam is usually needed. Not surprisingly, a family history of the disorder is often the biggest clue that you may have Huntington disease.
What kind of doctor is needed for Huntington's disease?
To effectively manage Huntington’s disease you will need a neurologist, psychiatrist, social worker and geneticist.
What is the treatment for chorea?
Symptomatic treatment for chorea involves medications that deplete dopamine (such as tetrabenazine) or block dopamine (such as antipsychotics). Symptomatic treatment for psychiatric, behavioral, and cognitive symptoms are variable and include SSRIs, antipsychotics, and other treatments.
What is the treatment for Huntington's disease?
For now, treating Huntington's involves managing symptoms: Medications, Speech or language therapy, occupational or physical therapy, and assistive devices can all help.
Is Huntington's disease a substitute for medical advice?
THIS TOOL DOES NOT PROVIDE MEDICAL ADVICE. It is intended for general informational purposes only and does not address individual circumstances. It is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment and should not be relied on to make decisions about your health.
What is the best treatment for Huntington's disease?
Chorea (involuntary movements): Some experts believe beginning treatment with an atypical antipsychotic drug, such as olanzapine, is best. Others start with another type of drug recently approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) specifically for Huntington's, called tetrabenazine.
What is the function of huntingtin?
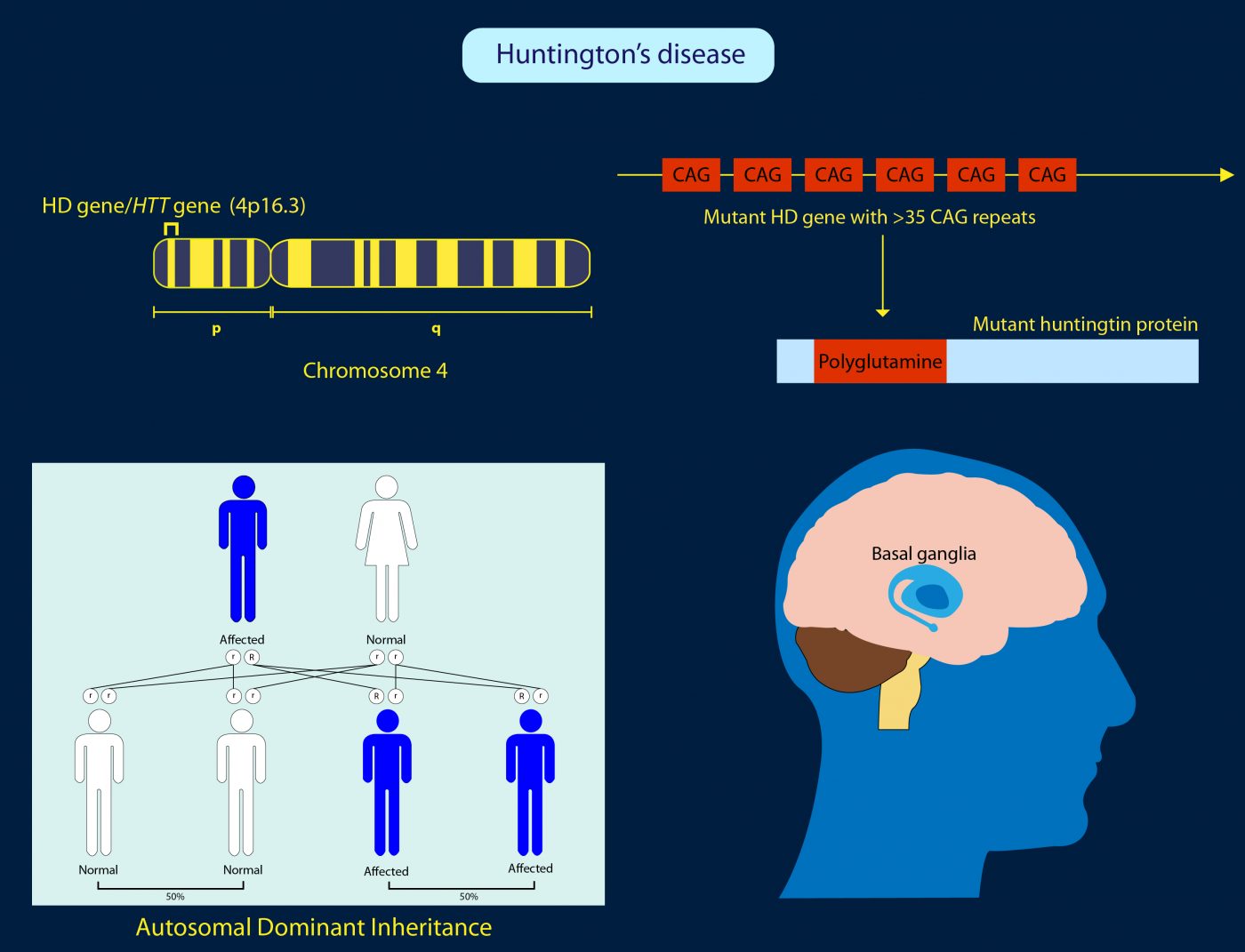
The defective gene codes the blueprint for a protein called huntingtin. This protein's normal function isn't yet known, but it's called "huntingtin" because scientists identified its defective form as the cause of Huntington's disease. Defective huntingtin protein leads to brain changes that cause abnormal involuntary movements, ...
What is the genetic disorder Huntington's disease?
The defective gene codes the blueprint for a protein called huntingtin.
How early can you get Huntington's disease?
Symptoms of Huntington's disease usually develop between ages 30 and 50, but they can appear as early as age 2 or as late as 80. The hallmark symptom of Huntington's disease is uncontrolled movement of the arms, legs, head, face and upper body. Huntington's disease also causes a decline in thinking and reasoning skills, including memory, concentration, judgment, and ability to plan and organize.
When was Huntington's disease discovered?
Diagnosis. Scientists identified the defective gene that causes Huntington's disease in 1993. A diagnostic genetic test is now available. The test can confirm that the defective gene for huntingtin protein is the cause of symptoms in people with suspected Huntington's disease and can detect the defective gene in people who don't yet have symptoms ...
Why is huntingtin called huntingtin?
This protein's normal function isn't yet known, but it's called "huntingtin" because scientists identified its defective form as the cause of Huntington's disease.
How long does Huntington's disease last?
The rate of disease progression and duration varies. The time from disease emergence to death is often about 10 to 30 years. Juvenile Huntington's disease usually results in death within 10 years after symptoms develop.
What causes Huntington's disease?
Common causes of death include: Pneumonia or other infections. Injuries related to falls. Complications related to the inability to swallow.
What are the movement disorders associated with Huntington's disease?
The movement disorders associated with Huntington's disease can include both involuntary movement problems and impairments in voluntary movements, such as: Involuntary jerking or writhing movements (chorea) Muscle problems, such as rigidity or muscle contracture (dystonia) Slow or abnormal eye movements.
What is the difference between Huntington's disease and Bipolar Disorder?
Mania, which can cause elevated mood, overactivity, impulsive behavior and inflated self-esteem. Bipolar disorder, a condition with alternating episodes of depression and mania. In addition to the above disorders, weight loss is common in people with Huntington's disease, especially as the disease progresses.
How many copies of each gene are there in Huntington's disease?
Huntington's disease is an autosomal dominant disorder, which means that a person needs only one copy of the defective gene to develop the disorder. With the exception of genes on the sex chromosomes, a person inherits two copies of every gene — one copy from each parent.
Where are Huntington's embryos implanted?
The embryos are tested for presence of the Huntington gene, and only those testing negative for the Huntington gene are implanted in the mother's uterus. By Mayo Clinic Staff. Huntington's disease care at Mayo Clinic.
When to see a doctor for Huntington's disease?
When to see a doctor. See your doctor if you notice changes in your movements, emotional state or mental ability. The signs and symptoms of Huntington's disease can be caused by a number of different conditions. Therefore, it's important to get a prompt, thorough diagnosis.
What is Huntington disease?
Listen. Huntington disease (HD) is an inherited condition that causes progressive degeneration of neurons in the brain. Signs and symptoms usually develop between ages 35 to 44 years and may include uncontrolled movements, loss of intellectual abilities, and various emotional and psychiatric problems. People with HD usually live for about 15 ...
What age do you start Huntington's disease?
On average, most people begin developing features of HD between ages 35 and 44. Signs and symptoms vary by stage and may include: [2] [3]
How many times does the HTT gene repeat?
This segment is made up of three DNA building blocks that repeat multiple times in a row. The CAG segment in a normal HTT gene repeats about 10 to 35 times. In people with HD, it may repeat from 36 to over 120 times.
What causes HD in humans?
In rare cases, HD is caused by a new ( de novo) mutation in the HTT gene, in which case the disease occurs for the first time in the affected person and is not inherited from a parent. [2] As HD is passed through generations, the size of the mutation in the HTT gene (called a trinucleotide repeat) often increases.
What causes HD?
It is caused by changes ( mutations) in the H TT gene and is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. Treatment is based on the symptoms present in each person and may include various medications. [1] [2] There is also a less common, early-onset form of HD which begins in childhood or adolescence.
How long does HD last?
The duration of the disease (from onset until death) varies considerably, with an average of approximately 19 years. Most people with HD survive for 10-25 years after the onset of symptoms. The average age at death ranges from 51-57 years, but the range may be broader.
Is Huntington disease progressive?
Huntington disease (HD) is progressive, eventually leading to disability and death (usually from a coexisting illness or infection). However, the disease affects everyone differently; the age of onset, specific symptoms, and rate of progression varies for each person with HD.
Preclinical Stage
The preclinical stage of a disease is a period when the disease can be detected through screening or biological testing, but there are no obvious physical symptoms yet. During this time, damage can occur at the cellular level, but there is not enough damage yet for a person to notice it in their daily life.
Early Stage
During the preclinical stage of HD, neurologic damage occurs but you will not have any noticeable physical signs. As cells are gradually destroyed, the symptoms slowly begin to appear in your 30s to 50s.
Early Intermediate Stage
In the early intermediate stage (stage II) of HD, the physical signs of the disease are more noticeable and may begin to affect your daily life.
Late Intermediate Stage
In the late intermediate stage of HD, the disease's effect on your life becomes more pronounced. Sometimes referred to as stage III, many people at this stage of the disease can no longer work and struggle to complete basic daily tasks. 8
Early Advanced Stage
The early advanced stage of HD usually begins about a decade after the onset of the disease but can range from nine to 21 years after symptoms start. 8
Advanced Stage
At the most advanced stage of HD (stage V), many people with the disease require around-the-clock skilled nursing care. Their movement is severely limited, and it can be difficult to complete any basic motor function.
Summary
Huntington's disease is a neurodegenerative disease that causes emotional, behavioral, cognitive, and physical problems.

Diagnosis
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Coping and Support
Preparing For Your Appointment
Specialist to consult
Home Remedies and Lifestyle
- A preliminary diagnosis of Huntington's disease is based primarily on your answers to questions, a general physical exam, a review of your family medical history, and neurological and psychiatric examinations.
Prescriptions
- Managing Huntington's disease affects the person with the disorder, family members and other in-home caregivers. As the disease progresses, the person will become more dependent on caregivers. Several issues will need to be addressed, and the ways to cope with them will change over time.
Surgeries and Specialist-Driven Procedures
- A number of strategies may help people with Huntington's disease and their families cope with the challenges of the disease.
Emerging Treatment
- If you have any signs or symptoms associated with Huntington's disease, you'll likely be referred to a neurologist after an initial visit to your provider. A review of your symptoms, mental state, medical history and family medical history can all be important in the clinical assessment of a potential neurological disorder.
Complementary and Alternative Medicine
A Word from Verywell
- There are a number of prescription therapies used to alleviate some of the symptoms of Huntington’s disease. These treatments do not reverse the disease itself or stop its progression. You might need several different medications to manage each of the different symptoms, and sometimes one or more of your medications may exacerbate the effects of Huntington’s diseas…