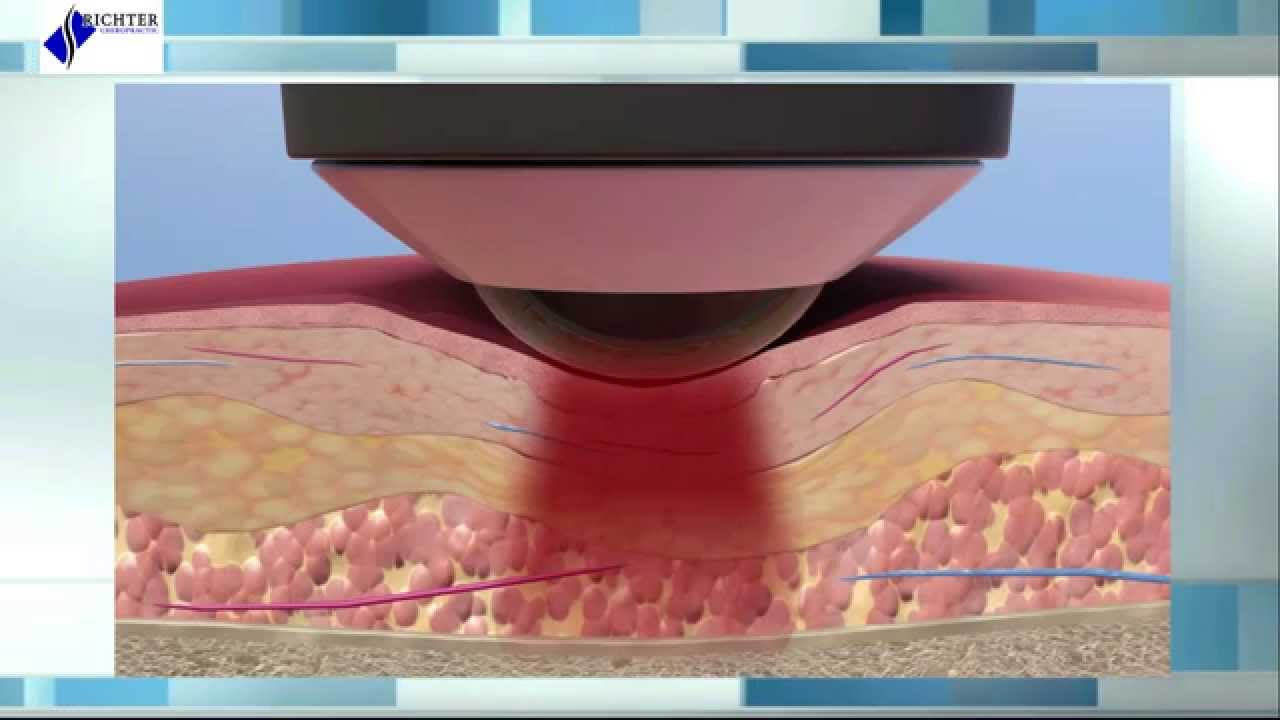
The device uses low levels of energy, or photons. Unlike higher-frequency lasers used for surgery, they don’t heat or cut your skin. Photons penetrate deep into a painful joint. The light triggers chemical changes that help damaged cells and tissues heal and regrow.
Full Answer
How does laser therapy work for pain relief?
· Deep tissue laser therapy may sound a little bit like science fiction. But in reality, it’s a great tool that can help your body heal and recover fast from all types of injuries. Laser therapy is used to alleviate pain isolated down deep in the muscle tissue — and best of all it has none of the side effects that come with invasive surgery or medications!
Can deep tissue laser therapy treat neuropathic pain in type 2 diabetes?
How Does Deep Tissue Laser Therapy Work? More or less, deep tissue laser therapy works similar to deep tissue massage. One of its greatest pros is that it concentrates directly on the exact damaged cells/ tissues. Therefore, it works by focusing high-energy light on the affected area that stimulates photobiomodulation process.
What is low level laser therapy (LLLT) for pain?
· Utilising LCT 1000 Deep Tissue (Class IV) Laser Technology, the treatment works by penetrating tissue with photoenergy in a process called photobiostimulation. This energises the damaged cells, encouraging an increase in circulation to the affected area and significantly reduces or eliminates pain.
What is the role of laser therapy in the treatment of burn?
· Some of the benefits of the class IV laser include: Compression removes superficial absorbers and reaches targeted tissues. Therapists can manually work tissue while delivering energy; The tighter beam of the class IV laser minimizes energy loss and. A refractive index that minimizes light loss due to skins and lens composition similarity.

Why do we use deep tissue lasers?
At Moss Rehabilitation Center, we use deep tissue laser therapy because it’s a non-invasive, non-chemical-dependent method to stimulate “ microcirculation ” within the damaged tissue.
Why do we use laser therapy?
At Moss Rehabilitation Center, we use deep tissue laser therapy because it’s a non-invasive, non-chemical-dependent method to stimulate “ microcirculation ” within the damaged tissue. A great physical therapy practice should not be looking to mask problems with painkillers or suggest invasive surgical treatment.
How long does it take to get relief from neck pain?
It’s torturous. Suffering patients may feel relief after just a 5 or 10-minute deep tissue laser session!
Is laser technology real?
In fact, there are many real-world applications of laser technology, despite the many fictional depictions we’re used to seeing.
How does laser therapy work?
Therefore, it works by focusing high-energy light on the affected area that stimulates photobiomodulation process. Through this process, photons enter your tissues then are absorbed into the mitochondria through the cell membrane. These photons are then converted into chemical energy in the form of ATP. This ATP energy starts the healing process in the affected area, increasing your body’s cellular metabolism. It also stimulates cytochrome oxidase enzymes that fasten regeneration and healing of tissues. This helps to repair and heal any torn or strained tissues that cause inflammation, discomfort, or pain. It also enhances your body’s natural ability to heal.
How does laser therapy help discs?
Disc problems: Laser therapy accelerates healing by activating the cells inside the tissue. Note this is the tissue around the disc. This subsequently decreases inflammation, hence giving pain relief.
How does laser therapy help sports injuries?
Laser Therapy is quite successful for such ailments. It speeds up the healing process by up to four times. It does so by decreasing swelling and inflammation. This encourages rapid repair of injured tissues while alleviating pain.
Is there pain with laser therapy?
It’s soothing: Besides effectiveness , there is no pain or discomfort during deep tissue laser therapy treatment. In fact, it brings out a soothing, warm and gentle feeling that makes you enjoy the experience. This is as a result of your body cells response to laser therapy light.
Is laser therapy cheaper than surgery?
Therefore, this non-invasive treatment has provided a cheaper alternative to surgery thus saving on treatment cost.
Does deep tissue laser therapy help with inflammation?
Deep tissue laser therapy also encourages circulation of red blood cells towards the injured area. This increases oxygenation to that damaged area which in turn heals inflammation as well as reducing the pain.
Is deep tissue less painful?
Note that the process is so painless, safe, warming, fast and effective. In this article, we dive into Deep Tissue Lesser Therapy and how it works. Also, you will know the conditions that it treats.
Deep tissue laser therapy – An Overview
Deep tissue laser therapy is an FDA (Federal Drug Administration) approved method to treat various neuromuscular illnesses. Acute and chronic sports injuries are treated using laser therapy.
Who can go for deep tissue laser therapy?
There are many common conditions like arthritis, plantar fasciitis, Achilles tendonitis, ulcers, sores, neuromuscular conditions and joint pain; treatable with cold laser.
Deep tissue laser therapy in Pakistan
If you’re in Pakistan and looking for a reliable pain management clinic then BioFlex Pakistan is the best choice for you.
What are the effects of lasers on tissue repair?
Also, some molecules that increase inflammation are reduced, and beneficial antioxidants like superoxide dismutase are increased. Accelerated Tissue Repair and Cell Growth: “Photons of light from lasers penetrate deeply into tissue and accelerate cellular reproduction and growth.
How does laser therapy help with cell damage?
Laser also causes a widening of the arteries and veins around the injury which helps to remove damaged cellular debris and increase nutrients and oxygen. White blood cell activity is enhanced leading to a more rapid repair process.
Can a sprain be treated with laser?
Strains, sprains, and repetitive motion injuries all have an inflammatory component and can be successfully treated with laser,” he commented. “There is no particular condition that responds more quickly to laser.
Why is laser healing so fast?
Faster Wound Healing: “Laser light stimulates the building blocks of collagen, which is important in the wound healing of damaged tissues. Collagen is the essential protein required to replace old tissue or to repair injuries. As a result, the laser is effective on open wounds and burns.”. Stem Cell Activation: “Laser increases the number ...
Does laser light help with wound healing?
Improved Vascular Activity: “Laser light increases the formation of new capillaries in damaged tissue, which speeds up the healing process, and closes wounds quickly.”
What is class 3 laser?
Class 3 lasers are sometimes referred to as cold lasers, and the therapy may be called LLLT for low-level laser therapy. In contrast, class 4 laser therapy is sometimes called HPLT for high-power laser therapy. “The majority of neuro-musculoskeletal conditions respond better to a higher power and a higher dosage, ...
What are the different types of lasers used in physical therapy?
Two Types or Classes Used in Physical Therapy. There are two classes of lasers being used in physical therapy; class 3 and 4. “Class 3 lasers are less than 500 milliwatts (mw) in power while class 4 lasers are greater than 500 mw,” Dr. Coren said. Class 3 lasers are sometimes referred to as cold lasers, and the therapy may be called LLLT ...
What is laser therapy?
Laser therapy is an alternative treatment for some types of pain, such as that often associated with the knee. Research on laser therapy is preliminary, and most insurers still consider it to be experimental. However, some studies show it can alleviate pain, including knee pain. Laser therapy is also known as cold laser therapy, ...
Why are lasers used in medicine?
Surgical lasers are increasingly common in medicine and cut more precisely than traditional surgical equipment, reducing the risk of injury and helping speed up surgery.
Can lasers cause health issues?
When studies do find side effects, they are minor and similar to the side effect of a placebo. As the lasers are cold and less powerful than other medical lasers, it is unlikely that they can cause serious health issues. Little research has shown that laser therapy offers long-term relief.
Why is laser therapy so difficult?
One of the problems with laser therapy is that different studies look at different wavelengths of light. This makes it difficult to compare one laser to another. Likewise, different manufacturers make different recommendations about treatment frequency and duration.
How long does laser neck pain last?
A 2009 analysis looked at previous research on laser therapy for neck pain. The study found significant pain relief ,lasting up to 22 weeks. While some people experienced side effects, ...
Can laser therapy be applied to knees?
Because it is unclear how laser therapy works, it is not known whether the results of these studies can be applied to the knee.
Does LLT help with knee pain?
A 2005 Cochrane review assessed the ability of LLT to reduce the pain of rheumatoid arthritis, a common cause of knee pain. It found evidence for moderate short-term pain relief with few side effects.
What is low level laser therapy?
Low Level Laser Therapy (LLLT) sometimes known as Low Level Light Therapy or Photobiomodulation (PBM) is a low intensity light therapy. The effect is photochemical not thermal. The light triggers biochemical changes within cells and can be compared to the process of photosynthesis in plants, where the photons are absorbed by cellular photoreceptors and triggers chemical changes.
What is laser light?
A laser is a device that generates light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. There are four main classes of lasers as defined by the International Engineering Consortium (IEC standard 60825.) These classes indicate potential danger the radiation is to the eye.
When did the North American Association for Laser Therapy conference hold a consensus meeting on safety and contraindications?
The North American Association for Laser Therapy conference in 2010 held a consensus meeting on safety and contraindications. Their main recommendations were:
What is the purpose of the site of injury?
The site of injury to promote healing, remodeling and reduce inflammation.
Where are the nerve endings of nociceptors located?
The peripheral nerve endings of nociceptors, consisting of the thinly myelinated A∂ and unmyelinated, slow-conducting C fibers, lie within the epidermis. This complex network transduces noxious stimuli into action potentials. Moreover these nerve endings are very superficial in nature and thus are easily within the penetration depths of the wavelengths used in LLLT (Figure 4). The cell bodies of neurons lie within the dorsal nerve root ganglion, but the elongated cytoplasm (axons) of the neurons extends from the cell body to the bare nerve endings in the surface of the skin. The direct effect of LLLT are initially at the level of the epidermal neural network, but the effects move to nerves in subcutaneous tissues, sympathetic ganglia, and the neuromuscular junctions within muscles and nerve trunks.
What is LLLT laser?
LLLT is the application of light (usually a low powered laser or LED typically power range of (10mW–500mW). Light with a wavelength in the red to near infrared region of the spectrum (660nm–905nm), is generally employed because these wavelengths have the ability to penetrate skin, and soft/hard tissues (Figure 2) and are proven in clinical trials to have a good effect on pain, inflammation and tissue repair. The power density (irradiance) is usually between 5W/cm2and is applied to an injury or to a painful site for 30–60 seconds a few times a week for several weeks. The result is a reduction of inflammation, pain relief and accelerated tissue regeneration. In most cases the lasers/LEDs used for LLLT emit a divergent beam (not focused or collimated) because collimation is lost in tissue, but as a consequence ocular risks are also diminished over distance.
Who invented the red ruby laser?
In 1960, Professor Maiman TH [12] built the first working red ruby laser [12], but it was not until 1967 when Mester E et al. [13,14] was able to demonstrate the phenomenon of “laser bio stimulation” [13,14]. In 1999, Whelan H et al. [15] presented his work on the medical applications of light emitting diodes (LED) for use on the NASA space station [15]. Subsequently over 400 Phase III randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials have been published, with over 4000 laboratory studies of LLLT. (Pubmed.gov)
