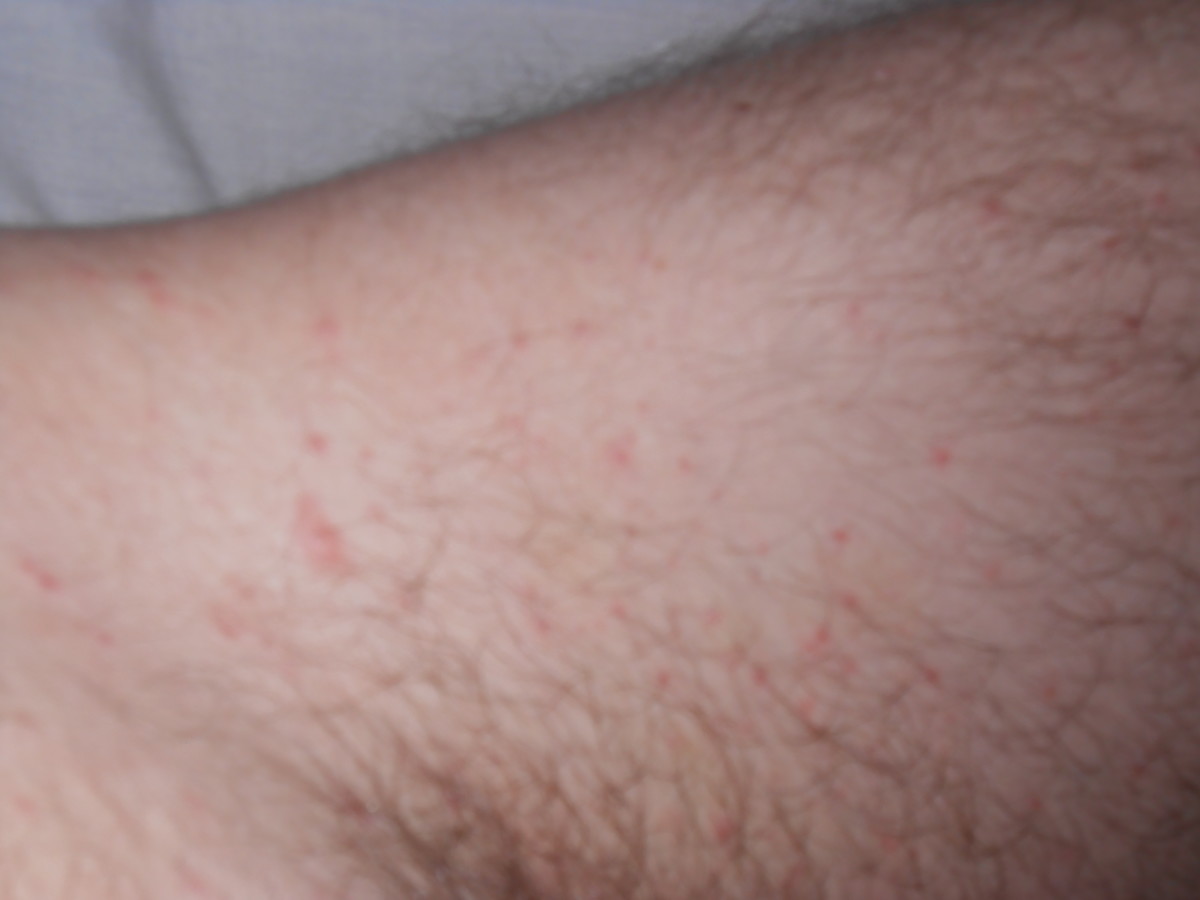
Symptoms
Unfortunately, nothing kills scabies instantly. Successful treatment usually takes multiple weeks, but if you do it properly, and use the right treatments, you will be cured. As for what kills the mites the fastest, here’s the rundown:
Causes
What Is The Life Expectancy Of Scabies? On a person, scabies mites can live for as long as 1-2 months . Off a person, scabies mites usually do not survive more than 48-72 hours .
Prevention
Symptoms and signs of scabies include the following:
- Intense itching, especially at night
- Pimple -like itchy rash Rash may affect most of the body or may be limited to sites such as the wrists, webbing between the fingers, elbows, armpits, nipples, waist, penis ...
- Tiny burrows seen on the skin that appear as tiny raised and crooked grayish-white or skin-colored lines on the skin
Complications
- People with chronic health conditions that weaken the immune system, such as HIV or chronic leukemia
- People who are very ill, such as people in hospitals or nursing facilities
- Older people in nursing homes
What kills scabies instantly?
What is the life expectancy of scabies?
What are the first signs of scabies?
How to know when scabies are not contagious?

Can you still get scabies bites after treatment?
After several treatments, he/she still has symptoms while I am cured. Why? The rash and itching of scabies can persist for several weeks to a month after treatment, even if the treatment was successful and all the mites and eggs have been killed.
How do you know scabies is gone after treatment?
This is to make sure the infection has fully gone away. Medicines work quickly to kill the mites, but the itchy rash may last for several weeks after treatment. Marks on the skin from scabies usually go away in 1 to 2 weeks, but sometimes take a few months to go away.
How do you know if you need a second treatment for scabies?
If itching still is present more than 2 to 4 weeks after treatment or if new burrows or pimple-like rash lesions continue to appear, retreatment may be necessary. Skin sores that become infected should be treated with an appropriate antibiotic prescribed by a doctor.
How do you know if scabies come back?
See a doctor if the itch persists longer than 2-3 weeks after treatment. Sometimes the first treatment does not work, and a different one is then needed. The most common reasons why treatment fails, and scabies returns, are: The cream or lotion is not applied correctly for the recommended time.
How do I know if permethrin worked?
After 8-14 hours have passed, wash off the cream by bathing or showering. Your skin may be itchy after treatment with permethrin cream. This does not mean your treatment did not work. If you see live mites 14 days or more after treatment, then you will need to repeat the treatment process.
How many times can you use permethrin cream?
Use two applications of permethrin cream, seven days apart. Your whole body must be treated with the cream. Leave each application on for 8-12 hours, then wash the cream off with soap and water.
Why won't my scabies go away?
If your skin has not healed within 4 weeks, you may still have mites. Some people need to treat two or three times to get rid of the mites. Be sure to see your dermatologist for treatment. You should never use a scabicide used to treat crops or livestock.
Can you feel scabies crawling?
You can't feel the mite crawling as they are very tiny. Scabies itching is more at night.. Lice and nits itching occurs in the day too.
How do you get rid of scabies completely?
Scabies treatment involves eliminating the infestation with medications. Several creams and lotions are available with a doctor's prescription....TreatmentPermethrin cream. Permethrin is a topical cream that contains chemicals that kill scabies mites and their eggs. ... Ivermectin (Stromectol). ... Crotamiton (Eurax, Crotan).
How long does scabies last after treatment?
The rash will heal up and go away in 2 weeks. There shouldn't be any new rash after treatment. The itching may last up to 4 weeks. Reason: It's an allergic reaction to the dead scabies.
How do you prevent scabies from coming back?
The only way to keep scabies away is to avoid prolonged, direct skin-to-skin contact with a person who has them. You also want to avoid touching items, like bedding or clothing, that the person has used. If you, or someone in your home, has scabies or has been exposed to it, seek treatment right away.
What happens if you use permethrin too much?
Get emergency medical help if you have signs of an allergic reaction: hives; difficult breathing; swelling of your face, lips, tongue, or throat. Call your doctor at once if you have severe burning, stinging, redness, or swelling after applying permethrin topical.
What Is Crusted (Norwegian) Scabies?
Crusted scabies is a severe form of scabies that can occur in some persons who are immunocompromised (have a weak immune system), elderly, disabled...
How Soon After Infestation Do Symptoms of Scabies Begin?
If a person has never had scabies before, symptoms may take as long as 4-6 weeks to begin. It is important to remember that an infested person can...
What Are The Signs and Symptoms of Scabies Infestation?
The most common signs and symptoms of scabies are intense itching (pruritus), especially at night, and a pimple-like (papular) itchy rash. The itch...
How Is Scabies Infestation Diagnosed?
Diagnosis of a scabies infestation usually is made based on the customary appearance and distribution of the rash and the presence of burrows. When...
How Long Can Scabies Mites Live?
On a person, scabies mites can live for as long as 1-2 months. Off a person, scabies mites usually do not survive more than 48-72 hours. Scabies mi...
Who Should Be Treated For Scabies?
Anyone who is diagnosed with scabies, as well as his or her sexual partners and other contacts who have had prolonged skin-to-skin contact with the...
How Soon After Treatment Will I Feel Better?
If itching continues more than 2-4 weeks after initial treatment or if new burrows or rash continue to appear (if initial treatment includes more t...
How do you know if you have scabies?
The most common symptoms of scabies are intense itching and a pimple-like skin rash. The scabies mite usually is spread by direct, prolonged, skin-to-skin contact with a person who has scabies. Scabies is found worldwide and affects people of all races and social classes. Scabies can spread rapidly under crowded conditions where close body ...
What to do if you think you have scabies?
If a person thinks he or she might have scabies, he/she should contact a doctor. The doctor can examine the person, confirm the diagnosis of scabies, and prescribe an appropriate treatment. Products used to treat scabies in humans are available only with a doctor’s prescription.
What is scabicide used for?
Products used to treat scabies are called scabicides because they kill scabies mites; some also kill eggs. Scabicides to treat human scabies are available only with a doctor’s prescription; no “over-the-counter” (non-prescription) products have been tested and approved for humans.
What is a crusted scaby?
Crusted scabies is a severe form of scabies that can occur in some persons who are immunocompromised (have a weak immune system), elderly, disabled, or debilitated. It is also called Norwegian scabies. Persons with crusted scabies have thick crusts of skin that contain large numbers of scabies mites and eggs.
What is a scabies mite?
Scabies is an infestation of the skin by the human itch mite ( Sarco ptes scabiei var. hominis ). The microscopic scabies mite burrows into the upper layer of the skin where it lives and lays its eggs. The most common symptoms of scabies are intense itching and a pimple-like skin rash. The scabies mite usually is spread by direct, prolonged, ...
Why is crusted scabies not treated?
Treatment failure of crusted scabies because of poor penetration of scabicide into thick scaly skin containing large numbers of scabies mites; repeated treatment with a combination of both topical and oral medication may be necessary to treat crusted scabies successfully.
How is scabies spread?
Scabies usually is spread by direct, prolonged, skin-to-skin contact with a person who has scabies. Contact generally must be prolonged; a quick handshake or hug usually will not spread scabies. Scabies is spread easily to sexual partners and household members. Scabies in adults frequently is sexually acquired. Scabies sometimes is spread indirectly by sharing articles such as clothing, towels, or bedding used by an infested person; however, such indirect spread can occur much more easily when the infested person has crusted scabies.
How long does it take for scabies to go away?
Your skin may continue to itch for 2 or 3 weeks, even after the scabies mites are gone. Over-the-counter antihistamines or cortisone cream may help relieve itching. Trim your fingernails so you do not spread any mites that are still alive after treatment. Do not scratch your skin. Scratches may cause a skin infection.
How long after scabies can you go back to school?
You may return to school or work 24 hours after using scabies medicine.
How long should you dry scabies mites?
Dry them for at least 20 minutes on the hot cycle of a dryer. Take items to be dry cleaned that cannot be washed in a washing machine. Place any clothing or bedding that cannot be washed or dry cleaned in a closed plastic bag for 1 week. Do not have close body contact with anyone until the scabies mites are gone.
How to prevent scabies?
Prevent the spread of scabies: Have all family members use scabies medicine. Tell all sex partners and anyone who has shared your clothing or bed for the past month about the scabies. Tell them to ask their healthcare provider for scabies medicine even if they have no itching, rash, or burrow marks.
What happens if you bite a scab?
The bites become crusty or filled with pus. You have worsening itching after scabies treatment. You have new bite or burrow marks after treatment. You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
How to treat scabies in the neck?
Medicines: Prescription creams are used to treat scabies. You will need to apply them over all of your body from the neck down. Do not swallow this medicine. An oral medication may be ordered if scabies is severe. Take your medicine as directed.
What is scabies mites?
Scabies is a skin condition that is caused by scabies mites. Scabies mites are tiny bugs that burrow, lay eggs, and live underneath the skin. Scabies is spread through close contact with a person who has scabies. This includes having sex, sleeping in the same bed, or sharing towels or clothing.
Why does scabies itch after treatment?
Because the symptoms of scabies are due to a hypersensitivity reaction (allergy) to mites and their feces (scybala), itching still may continue for several weeks after treatment even if all the mites and eggs are killed.
How long does it take for scabies to develop?
It is important to remember that the first time a person gets scabies they usually have no symptoms. Symptoms can typically take 4-8 weeks to develop after they are infested; however they can still spread scabies during this time. In addition to the infested person, treatment also is recommended for household members ...
What is scabicide used for?
Products used to treat scabies are called scabicides because they kill scabies mites; some also kill mite eggs. Scabicides used to treat human scabies are available only with a doctor’s prescription. No “over-the-counter” (non-prescription) products have been tested and approved to treat scabies.
How long does it take for a pimple to heal after a rash?
If itching still is present more than 2 to 4 weeks after treatment or if new burrows or pimple-like rash lesions continue to appear, retreatment may be necessary. Skin sores that become infected should be treated with an appropriate antibiotic prescribed by a doctor. Page last reviewed: October 31, 2018.
Where to apply scabicide lotion?
Scabicide lotion or cream should be applied to all areas of the body from the neck down to the feet and toes.
Can scabies be sexually acquired?
All persons should be treated at the same time to prevent reinfestation. Scabies may sometimes be sexually-acquired in adults, but is rarely sexually-acquired in children.
Can you use scabicide on your head?
In addition, when treating infants and young children, scabicide lotion or cream also should be applied to their entire head and neck because scabies can affect their face, scalp, and neck, as well as the rest of their body. Only permethrin or sulfur ointment may be used in infants.
How to know if scabies is gone?
If your scabies isn’t gone, these symptoms will reoccur, accompanied by blisters and bumps in the affected area.
What to do after scabies treatment?
After completing the treatment, follow up with your doctor. Even if symptoms are gone, a doctor should still examine you to ensure the scabies infection is eliminated.
How to prevent scabies from spreading?
Minimize your chances of additional outbreaks. Scabies can be prevented by avoiding physical contact, such as holding hands. Wash your bed linens in hot water, because scabies can live in a variety of linens, including sheets and towels.
How long does it take to cure scabies?
Treat your skin for one week 1. People infected with scabies often worry that treatment methods aren’t working. But treatment methods often take a week to be effective. Repeat the course of treatment. If symptoms haven’t subsided in a week, you’ll need to ask your doctor about repeating the treatment.
What is scabies rash?
Scabies is a skin infection caused by mites that burrow into the skin and lay eggs. Most people will notice they have a rash around the wrists, fingers or private areas. This infection is extremely contagious and transferred easily through skin-to-skin contact.
What to do if symptoms don't go away?
If symptoms haven’t subsided in a week, you’ll need to ask your doctor about repeating the treatment. With most patients, a second course of treatment will eliminate the problem for good 1. Follow up with your doctor. After completing the treatment, follow up with your doctor. Even if symptoms are gone, a doctor should still examine you ...
Is scabies easy to treat?
Although scabies is relatively easy to treat, sometimes it takes more than one course of medication. Examine your skin carefully.
How to diagnose scabies?
A dermatologist can often diagnose scabies by visually examining a patient’s skin from head to toe. To make sure that a patient has scabies, a dermatologist may remove some skin. This is painless. Your dermatologist will put the skin on a glass slide and look at the slide under a microscope.
How to get rid of scabies?
To get rid of the mites and prevent getting scabies again, you have to do more than treat the skin or take a pill. You will need to wash clothes, bedding, and towels to get rid of mites that may have fallen off your skin. You also should vacuum your entire home. Centers for Disease Control.
How do dermatologists treat scabies?
To get rid of scabies, treatment is essential. Medicine that treats scabies is only available with a doctor’s prescription.
How many times should you treat crusted scabies?
Some people need to treat two or three times to get rid of the mites. Be sure to see your dermatologist for treatment. You should never use a scabicide used to treat crops or livestock. People who develop crusted scabies, also known as Norwegian scabies, often need repeat treatments to get rid of the mites.
What is the best treatment for scabies?
Treating the skin more often than instructed can worsen the rash and itching. Medicines that may be prescribed include: 5% permethrin cream: This is the most common treatment for scabies. It is used to treat patients 2 months of age and older and women who are pregnant. 10% crotamiton cream.
When to apply meds to skin?
A dermatologist will provide specific instructions to follow. Most medicine is applied at bedtime. The medicine is then washed off when the patient wakes up.
Can ivermectin be prescribed for scabies?
When scabies infects many people at a nursing home, extended-care facility, and other institution, ivermectin may be prescribed to everyone who has a risk of catching scabies.