Can microorganisms be used to treat sewage and water?
That’s because waste from humans and pets are a source of several types of waterborne diseases and bacterial contamination. Thanks in part to microorganisms, treating wastewater and sewage is possible.
What are the advantages of anaerobic microorganisms in sewage treatment?
Another advantage of anaerobic microorganisms in sewage treatment is that they remove phosphorus from wastewater. Most common anaerobic forms belong to Actinomyces, Bifidobacterium, Clostridium, Propionibacterium and Peptostreptococcus genera.
What is the role of bacteria in wastewater treatment?
This bacterium uses the free oxygen within the water to degrade the pollutants in the wastewater and then converts it into energy that it can use to grow and reproduce. For this type of bacteria to be used correctly, it must have oxygen added mechanically.
Why is sewage treatment important?
The sewage contains organic materials and harmful fecal pathogens, which can spread deadly diseases by the disposal of water bodies. It is also capable of making the water bodies poisonous and can cause the death of aquatic animals. Hence, sewage treatment is crucial.
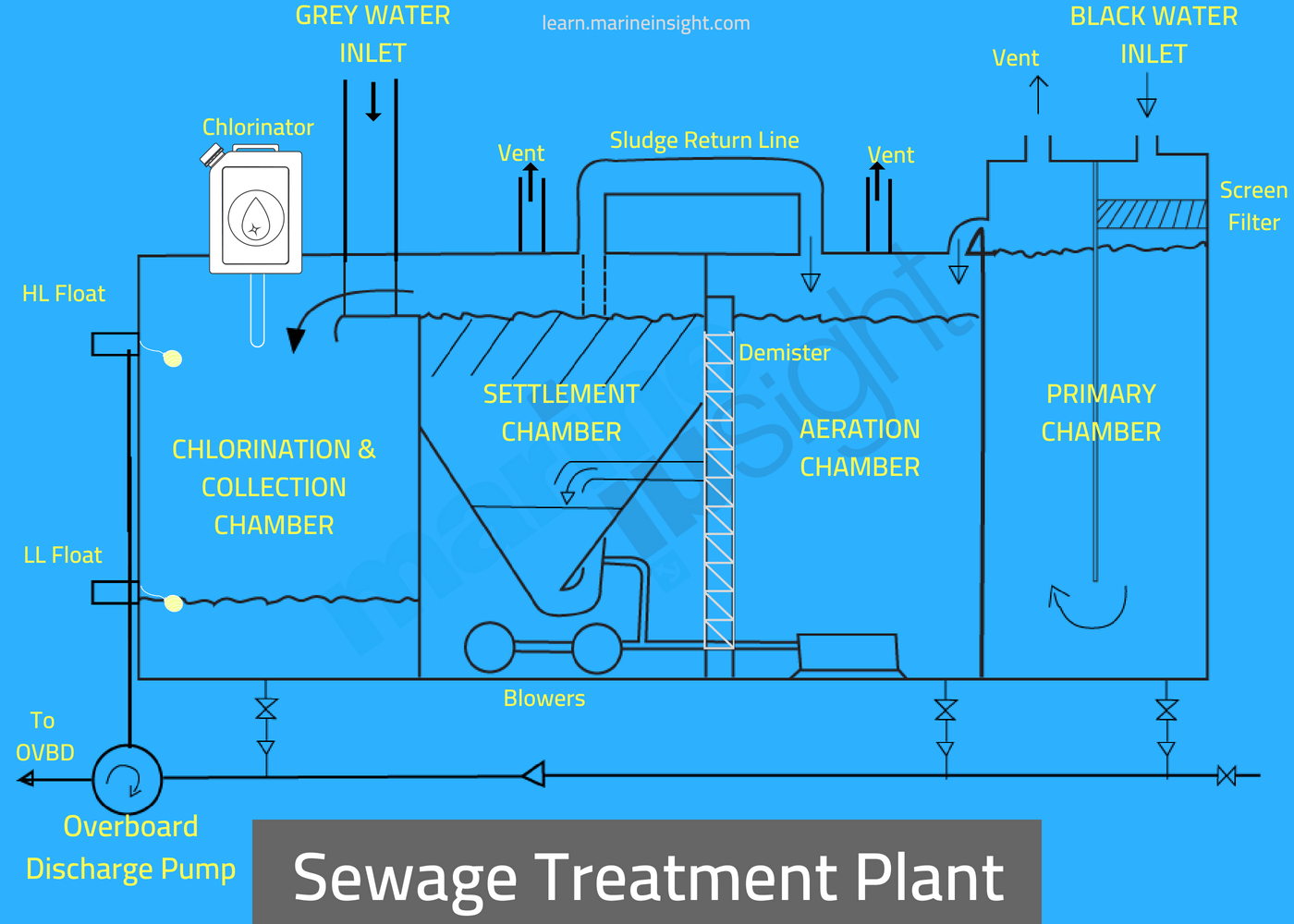
What is a sewage treatment plant and how does it work?
A semi-solid waste or slurry byproduct of sewage treatment is called sewage sludge. Different processes like physical, chemical and biological meth...
What are the main steps in sewage treatment?
a. Primary treatment or Physical process b. Secondary treatment or Biological process
What is the major function of Microbes in Sewage Treatment?
Sewage is treated in sewage treatment plants (STPs) by the heterotrophic microbes present in the sewage before being disposed of in water bodies. M...
Explain types of microbes used in sewage treatment?
Aerobic Bacteria: These bacteria degrade the contaminants in the wastewater using free oxygen in the water, then turn into the energy that can be u...
Why is sewage treatment important?
Sewage treatment helps in reducing the rate of harmful contaminants that cause pollution of water and soil. Wastewater that is treated in these STP...
How does sewage treatment help the environment?
Wastewater that is treated in these STPs can be reused for several purposes. Thus, sewage treatment helps in conservation of water as well as the environment.
How is sewage treated?
Sewage sludge is treated in a separate process called sludge digestion.
What is the name of the tank that sludge is pumped back into?
The remaining part of the sludge is pumped back into large tanks called anaerobic sludge digesters. Here, other anaerobic bacteria like methanogens are also present. Along with organic mass, these microbes also digest aerobic microbes (bacteria and fungi) of the sludge.
What are the most common forms of anaerobic bacteria?
Most common anaerobic forms belong to Actinomyces, Bifidobacterium, Clostridium, Propionibacterium and Peptostreptococcus genera. Facultative Bacteria: In sewage treatment, facultative microorganisms are bacteria that can switch between aerobic and anaerobic states depending on their surroundings.
What are the different types of bacteria in wastewater treatment?
Which Microbes are Used in Sewage Treatment? 1 Aerobic Bacteria: Aerobic bacteria are most commonly used in aerated environments in modern treatment plants. These bacteria degrade the contaminants in the wastewater using free oxygen in the water, then turn into the energy that can be used to grow and reproduce. This helps the bacteria to complete their tasks, continue to grow and reproduce. 2 Anaerobic Bacteria: Anaerobic microorganisms are commonly employed in wastewater treatment. Primary function of these bacterias in sewage treatment is to reduce sludge volume and create methane gas from it. This gas can be used as an alternative energy source when properly cleaned and managed. This type of bacterias can utilize enough oxygen from its food supply and does not require additional supply of oxygen. Another advantage of anaerobic microorganisms in sewage treatment is that they remove phosphorus from wastewater. Most common anaerobic forms belong to Actinomyces, Bifidobacterium, Clostridium, Propionibacterium and Peptostreptococcus genera. 3 Facultative Bacteria: In sewage treatment, facultative microorganisms are bacteria that can switch between aerobic and anaerobic states depending on their surroundings. These bacteria like to reside in an aerobic environment.
Why is sewage mixed with air?
The sewage is often mixed with air to facilitate decomposition as oxygen is critical for the growth of bacteria. This air helps in the growth of useful aerobic microbes into flocs (masses of bacteria associated with fungal filament to form mesh-like structures).
What is sewage water?
Sewage refers to the municipal wastewater that is generated in cities and towns on daily basis. Researchers estimate the indicator species, such as coliform bacteria or Pseudomonas aeruginosa in the sewage water.
What is sewage treatment?
Sewage treatment is a process in which the pollutants are removed. The ultimate goal of sewage treatment is to produce an effluent that will not impact the environment [1] . In the absence of sewage treatment, the results can be devastating as sewage can disrupt the environment. The general processes of sewage treatment are primary, ...
Why is the environment of sewage treatment plant controlled?
The environment of the sewage treatment plant has to be controlled precisely because bacteria are sensitive to the oxygen level, pH level, temperature, and level of nutrient. In order for efficient degradation of biological matter to occur, these factors are controlled manually.
Why is oxygen important?
Oxygen level. Oxygen level is an important factor to secondary and tertiary treatment processes. Secondary treatment, oxygen is required as a terminal electron acceptor in organic matter degradation. For example, nitrification by Nitrosomonas and Nitrobacter species requires dissolved oxygen to occur [4].
What are the two processes that occur after primary treatment?
The liquid phase is treated with aeration to allow aerobic degradation of the nutrients. The two important microbial processes at this stage are nitrification and phosphorous removal. Nitrification occurs in two discrete steps.
How is oxygen provided in secondary treatment?
Oxygen in secondary treatment is provided manually by pumping oxygen into the sewage continuously which occurs in an aeration tank [5]. In tertiary treatment, the removal of excess organic matter is enhanced by settling the sewage in a lagoon. This process is also aerobic, but it depends on the diffusion of oxygen because most organic matter has ...
How is sewage transferred to secondary treatment?
The liquid sewage is then transferred to secondary treatment which focuses on removing the dissolved biological compound by the use of micro-organisms. The micro-organisms usually use aerobic metabolism to degrade the biological matter in the liquid sludge. Then tertiary treatment is required to disinfect the sewage so that it can be released ...
Why are nutrients available in sewage?
Nutrients availability. There are a lot of nutrients available in the sewage because of human waste and agricultural runoff [3]. Bacteria can harvest the electron from organic matter and transfer it to a terminal electron acceptor which results in the break down of organic matter and energy conservation [10] .
Why is wastewater treatment important?
Wastewater treatment is as essential to human health as it is to the protection of the environment. The use of these bacteria accelerates the process of treating pollution on a small surface: the wastewater treatment plant.
What is biological wastewater treatment?
Biological wastewater treatment is the most common sanitation method in the world. This technology uses different types of bacteria and other microorganisms for the treatment and purification of polluted water. Wastewater treatment is as essential to human health as it is to the protection of the environment.
How does floc work?
The technique consists in recirculating a well-adapted combination of substrate and selected bacteria so that they settle very quickly. Under these favorable conditions, bacteria develop flocs or biofilms very quickly. Under these favorable conditions, bacteria develop flocs or biofilms very quickly.
How long does it take for bacteria to colonize the environment?
The colonization of an environment by the needed bacteria and microorganisms necessary for the purification generally lasts between 4 and 8 weeks. Once again, it is the temperature that has the most influence on this growth time.
What is lipophilic bacteria?
Lipophilic bacteria are specialized in the decomposition of animal and vegetable fats and oils in urban WWTPs and industrial treatment plants. These bacteria are easily adaptable to all current treatment systems.
How to solve the presence of undesirable bacteria?
First, the solution consists of extracting as much sludge as possible and increasing aeration. The good bacteria can take several days to recover the environment.
What are the parameters that influence a plant's growth?
First, before we know who they are, we need to understand the parameters that influence their growth. Firstly, geographical location. Secondly, the type of pond in which bacteria will be grown. Thirdly, the characteristics of the wastewater entering the plant.
Why are microbes important in sewage treatment?
In today’s world, microbes became essential for any kind of industrial process, and thus, various techniques are discovered where microorganisms are utilized for solving multiple problems. In that way, the role of microbes in sewage treatment is critical.
What is the purpose of sewage treatment?
Purpose of Sewage Treatment 1 To remove pollutants 2 Destruction of the deadly pathogens 3 To counterbalance coarse particles. 4 Elimination of poisonous substances
What is the most exciting part of sewage treatment?
However, the most exciting part of sewage treatment is that those microbes we need to eradicate ...
What is secondary treatment?
Secondary Treatment. So after the preliminary and primary wastewater treatment , let’s move to the actual point that is secondary treatment. Secondary sewage treatment is otherwise known as the biological process as microorganisms are utilized to treat the sewage.
How many steps are there in sewage treatment?
And the large-scale treatment involves lots of other physical, chemical, and biological processes. Besides these two parts, the entire sewage treatment process comprises four significant steps and various sub-steps. These four steps are: Also Check: Ways to prevent ocean acidification.
What are the three types of microbes?
Generally, three types of microbes, bacteria, fungi, and protozoa, are utilized for different functions. Bacteria decompose the sewage and convert them into settleable solids; fungi can degrade some constituents that cannot decompose by bacteria, and protozoa are the predators that help control the bacterial population.
What is tertiary wastewater treatment?
Tertiary wastewater treatment. Tertiary or the final step is concerned with subtracting non-biodegradable organic materials, heavy metals, and minerals. After processing in the secondary treatment plant, the effluent undergoes into the tertiary wastewater treatment, where mostly chemicals are used.
What are the microbes that live in sludge?
The sludge itself is inhabited by a diverse community of microbes, including bacteria, protozoans and even some eukaryotes like tardigrades, that have hitched a ride (perhaps through us) along the sewers connecting our homes to the waste management facility.
What is the last sludge that survives primary and secondary microbial digestion?
The very last of the activated sludge that survives primary and secondary microbial digestion is then dried. This “waste activated sludge” is ready to leave the facility as fertilizer or smoke, depending on its composition. Here, many weeks and microbial assists later, is the final destination of our modern sewage.
Why are biofilms important?
These biofilms help microbiologists monitor when a healthy consortium of bacteria are actively working to digest waste, while signs like excessive foam point to microbes that aren’t team players. If the wrong microbes show up or the process goes off track, then we intervene chemically or remove excess sludge.
What bacteria are in blue?
All bacteria were stained green, and Candidatus Accumulibacter Phosphatis, which accumulates phosphorus, were stained in blue. Courtesy of Connor Skennerton. When things are going well, it’s easy to see. C lumps of bacteria, called flocs, form in the sludge as these microbes help us reclaim the water within.
What is the process of forming a C lump in sludge?
C lumps of bacteria, called flocs, form in the sludge as these microbes help us reclaim the water within. Similar to its homophone, flocculation is a process where these aerobic bacteria produce biofilms composed of extracellular polymeric substances that allow them to stick together.
What is activated sludge?
Sludge comprises an incredibly rich medium, full of organic matter that we find unappetizing, but bacteria find delicious. Once this sludge has been processed by bacteria, it is called activated sludge, which can refer to both the material itself and the waste management process.
What is the process of reducing nitrates and nitrites into nitrogen gas?
Anaerobic bacteria further break down the sludge and reduce nitrate and nitrite into nitrogen gas through a process called denitrification. Biogas (primarily methane and carbon dioxide) produced during this anaerobic digestion is burned off or further purified for sale to energy companies.
Where does organic matter end up in sewage?
While some of the organic matter in sewage is eaten and respired during secondary treatment or when released to a receiving water body, the rest of the organic matter in sewage ends up as sludge that falls to the bottom of tanks in the treatment system.
What are the most common microorganisms in sludge?
The most predominant microorganisms are aerobic bacteria, but there are also substantial populations of fungi and protozoa. Rotifers and nematodes are most frequently found in systems with long aeration periods. Seman (n.d.) reports (p. 36) that protozoa "Make up about 3 percent of activated sludge microorganisms".
What is a biofilm?
Biofilms of bacteria, protozoa and fungi form on the media’s surfaces and eat or otherwise reduce the organic content. The filter removes a small percentage of the suspended organic matter, while the majority of the organic matter supports microorganism reproduction and cell growth from the biological oxidation and nitrification taking place in the filter. With this aerobic oxidation and nitrification, the organic solids are converted into biofilm grazed by insect larvae, snails, and worms which help maintain an optimal thickness.
What is activated sludge made of?
Wikipedia ("Activated sludge") says that the biological floc in activated-sludge systems "is largely composed of saprotrophic bacteria but also has an important protozoan flora component mainly composed of amoebae , Spirotrichs, Peritrichs including Vorticellids and a range of other filter-feeding species.
What is a WSP?
Babu (2011) reports (p. 3): "Wastewater stabilization ponds (WSP) are the most common wastewater treatment technologies used in developing nations, especially in tropical regions. [...] The major disadvantage of wastewater stabilization ponds is the requirement of relatively large areas for construction." From the perspective of minimizing invertebrate populations, covering a large area with water isn't obviously bad, since covering land with water means that terrestrial plants can't grow on that land. Unfortunately, more aquatic plants and algae can grow in a larger area of water.
Why is vegetation growth prevented?
Preventing vegetation growth reduces food and habitat for soil critters and thus prevents some invertebrates from being born . However, relative to the volumes of organic matter processed by a wastewater plant, prevented vegetation growth is negligible, as the following calculation shows.
What is lagoon treatment?
Wikipedia ("Sewage treatment" ): "Lagoons or ponds provide settlement and further biological improvement through storage in large man-made ponds or lagoons. These lagoons are highly aerobic and colonization by native macrophytes, especially reeds, is often encouraged. Small filter-feeding invertebrates such as Daphnia and species of Rotifera greatly assist in treatment by removing fine particulates."

Introduction
Physical Environment
- The environment of the sewage treatment plant has to be controlled precisely because bacteria are sensitive to the oxygen level, pH level, temperature, and level of nutrient. In order for efficient degradation of biological matter to occur, these factors are controlled manually.
Microbial Processes
- There are several microbial processes, and the microbial processes can be catergorized into aerobic and anaerobic.
Current Research
- A research has shown the correlation between nutrient removal efficiency, light wavelength and light intensity. Xu et al. discovered that red and high intensity light maximizes the nutrient removal efficiency . Also, the use of pre-treated sludge is found to generate electricity in a microbial fuel cell . This can potentially lead to production of renewable energy.
References
- (1) Zhao, H., Duan, X., Stewart, B., You, B., Jiang, X., “Spatial correlations between urbanization and river water pollution in the heavily polluted area of Taihu Lake Basin, China.” Journal of Geographical Sciences, 2013, 23(4):735-752.(2) Canler, J.P., Perret, J. M., “Biological aerated filters: assessment of the process based on 12 sewage treatment plants.” Water Science and Te…