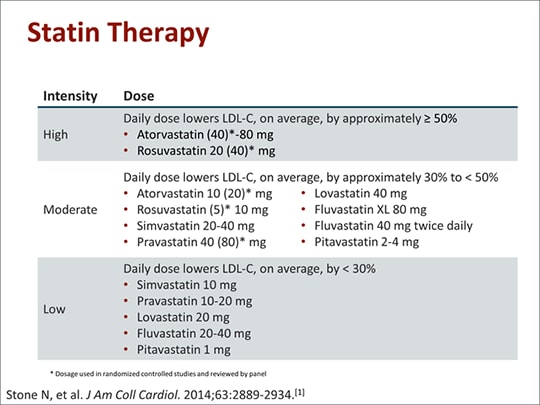
Medication
Smoking: Smoking may raise LDL cholesterol while lowering HDL cholesterol. Stress: When a person feels stressed, they produce certain hormones that may cause their body to make more cholesterol. Drinking too much alcohol: Binge drinking may raise cholesterol. the risk of developing high LDL cholesterol, including type 2 diabetes and obesity.
Self-care
A person can prevent their LDL cholesterol from getting too high by eating foods low in saturated fat and avoiding tropical oils, such as palm oil, when cooking. They can also choose high-fiber foods to increase HDL cholesterol while lowering LDL cholesterol. Learn more about high-fiber foods here. Taking time to stay active
Nutrition
Very high HDL levels could slow the process of clearing LDL cholesterolfrom your arteries. When LDL cholesterol builds up in these blood vessels, it forms clumps called plaques that slow or block blood flow. Eventually a chunk of plaque can break free and form a clot, which could lead to a heart attack or stroke.
What are the causes of high LDL cholesterol?
Everyone with high cholesterol should start with heart-healthy lifestyle changes like diet, exercise, quitting smoking, and weight loss. But if your cardiac risk is high, you may need treatment with medications, too.
How can I prevent my LDL cholesterol from getting high?
What happens if HDL cholesterol is too high?
What are the treatment options for high cholesterol?
See more

How do you treat high LDL cholesterol?
AdvertisementReduce saturated fats. Saturated fats, found primarily in red meat and full-fat dairy products, raise your total cholesterol. ... Eliminate trans fats. ... Eat foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids. ... Increase soluble fiber. ... Add whey protein.
When should you treat high LDL?
Your health care provider may prescribe medicine if: You have already had a heart attack or stroke, or you have peripheral arterial disease. Your LDL cholesterol level is 190 mg/dL or higher. You are 40–75 years old with diabetes and an LDL cholesterol level of 70 mg/dL or higher.
What can happen to a person who has a high LDL cholesterol level?
With high cholesterol, you can develop fatty deposits in your blood vessels. Eventually, these deposits grow, making it difficult for enough blood to flow through your arteries. Sometimes, those deposits can break suddenly and form a clot that causes a heart attack or stroke.
What level of cholesterol requires treatment?
LDL cholesterol: less than 130 mg/dL, or less than 100 mg/dL if you have heart disease or diabetes, or less than 70 mg/dL if you've had a heart attack or stroke. HDL cholesterol: above 50 mg/dL for females and 40 mg/dL for males. Triglycerides: below 150 mg/dL.
Does high cholesterol need to be treated?
Lifestyle changes such as exercising and eating a healthy diet are the first line of defense against high cholesterol. But, if you've made these important lifestyle changes and your cholesterol levels remain high, your doctor might recommend medication.
What does high LDL cholesterol mean?
When you have high LDL cholesterol levels, it means you are at greater risk for cardiovascular disease like heart attack and stroke. The plaque formed by this fatty substance on the inner walls of arteries can block or restrict blood flow.
Does high LDL cause heart disease?
Myth: All cholesterol is bad for you. Two types of lipoproteins carry cholesterol throughout the body: LDL (low-density lipoprotein), sometimes called “bad” cholesterol, makes up most of your body's cholesterol. High levels of LDL cholesterol raise your risk for heart disease and stroke.
Is high cholesterol hereditary?
High Cholesterol: Is It Hereditary? Cholesterol comes in several different forms, some good and some bad. Many factors, including genetics, can play a role in the levels of cholesterol in your blood. If a close relative has high cholesterol, you're more likely to have it yourself.
How to treat high cholesterol?
Treatment. Lifestyle changes such as exercising and eating a healthy diet are the first line of defense against high cholesterol. But, if you've made these important lifestyle changes and your cholesterol levels remain high, your doctor might recommend medication.
What is the best treatment for high cholesterol in children?
Diet and exercise are the best initial treatment for children age 2 and older who have high cholesterol or who are obese. Children age 10 and older who have extremely high cholesterol levels might be prescribed cholesterol-lowering drugs, such as statins.
How is cholesterol measured?
In the United States, cholesterol levels are measured in milligrams (mg) of cholesterol per deciliter (dL) of blood. In Canada and many European countries, cholesterol levels are measured in millimoles per liter (mmol/L). To interpret your test results, use these general guidelines.
How old do you have to be to get a cholesterol test?
For most children, the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute recommends one cholesterol screening test between the ages of 9 and 11, and another cholesterol screening test between the ages of 17 and 21.
What are the side effects of statins?
The common side effects of statins are muscle pains and muscle damage, reversible memory loss and confusion, and elevated blood sugar. If you decide to take cholesterol medication, your doctor might recommend liver function tests to monitor the medication's effect on your liver.
What is the best medicine for high triglycerides?
If you also have high triglycerides, your doctor might prescribe: Fibrates. The medications fenofibrate (TriCor, Fenoglide, others) and gemfibrozil (Lopid) reduce your liver's production of very-low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) cholesterol and speed the removal of triglycerides from your blood.
What medications lower cholesterol?
The medications cholestyramine (Prevalite), colesevelam (Welchol) and colestipol (Colestid) lower cholesterol indirectly by binding to bile acids. This prompts your liver to use excess cholesterol to make more bile acids, which reduces the level of cholesterol in your blood. Cholesterol absorption inhibitors.
How to prevent high cholesterol?
To help prevent high cholesterol, you can: Eat a low-salt diet that emphasizes fruits, vegetables and whole grains. Limit the amount of animal fats and use good fats in moderation. Lose extra pounds and maintain a healthy weight. Quit smoking.
What happens if you have too much cholesterol?
If you have too many cholesterol particles in your blood, cholesterol may accumulate on your artery walls. Eventually, deposits called plaques may form. The deposits may narrow — or block — your arteries. These plaques can also burst, causing a blood clot to form. High cholesterol can cause a dangerous accumulation of cholesterol ...
What is the difference between HDL and LDL?
LDL , the "bad" cholesterol, transports cholesterol particles throughout your body. LDL cholesterol builds up in the walls of your arteries, making them hard and narrow. High-density lipoprotein (HDL). HDL, the "good" cholesterol, picks up excess cholesterol and takes it back to your liver.
What is the combination of proteins and cholesterol called?
Cholesterol is carried through your blood, attached to proteins. This combination of proteins and cholesterol is called a lipoprotein. There are different types of cholesterol, based on what the lipoprotein carries. They are:
What are the health risks of eating too much saturated fat?
Eating too much saturated fat or trans fats can result in unhealthy cholesterol levels. Saturated fats are found in fatty cuts of meat and full-fat dairy products. Trans fats are often found in packaged snacks or desserts. Obesity. Having a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or greater puts you at risk of high cholesterol. Lack of exercise.
What are some examples of unhealthy cholesterol?
Medical conditions that can cause unhealthy cholesterol levels include: Chronic kidney disease. Diabetes.
How often should I check my cholesterol?
According to the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI), a person's first cholesterol screening should occur between the ages of 9 and 11, and then be repeated every five years after that.
What happens if you have too much LDL cholesterol?
If a person’s LDL cholesterol is too high, they may develop atherosclerotic plaque in their blood vessels, which over time can cause cardiovascular disease. People sometimes refer to LDL cholesterol as “bad cholesterol” and HDL cholesterol as “good cholesterol.” HDL cholesterol transports cholesterol to the liver, where it breaks down.
Why is LDL cholesterol considered bad cholesterol?
Because LDL cholesterol may narrow blood vessels. Trusted Source. over time and elevate the risk of heart disease, people sometimes refer to it as “bad cholesterol.”. HDL cholesterol, on the other hand, takes cholesterol to the liver for removal, rather than allowing it to accumulate in the blood vessels.
How does cholesterol build up as you get older?
As people get older, cholesterol naturally builds up as the body is no longer as efficient at clearing it. In general, males have lower levels of HDL cholesterol, and females have lower levels of LDL cholesterol until they reach menopause or are about age 55.
What foods can cause high LDL cholesterol?
Foods high in saturated fat include fatty cuts of meat and rich dairy products.
Why is it important to avoid fatty foods?
Sometimes people inherit a gene that causes high LDL cholesterol, so it is important they avoid fatty foods and remain active. High levels of LDL cholesterol could lead to conditions such as heart attack, stroke, and angina. If someone is concerned about their cholesterol levels, they should get in touch with their doctor.
What is the best medicine for lowering cholesterol?
Bile acid sequestrants: This medicine removes bile acids, which prompts the body to make bile acids from LDL cholesterol. Niacin : This B vitamin raises HDL cholesterol while lowering LDL cholesterol.
Can LDL run in families?
High levels of LDL cholesterol may run in families. If there is a change in a gene relating to cholesterol, a person may develop familial hypercholesterolemia. When someone has this condition, their body struggles to remove LDL cholesterol.
What is the purpose of high density lipoprotein?
High-density lipoprotein (HDL) is sometimes called “good cholesterol.” It helps return LDL cholesterol to your liver to be removed from your body. This helps prevent cholesterol plaque from building up in your arteries.
What is the name of the cholesterol that builds up in the walls of the arteries?
Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) is often called “bad cholesterol.” It carries cholesterol to your arteries. If your levels of LDL cholesterol are too high, it can build up on the walls of your arteries.
Why is cholesterol important to the body?
It’s vital for the formation of cell membranes, certain hormones, and vitamin D. Cholesterol doesn’t dissolve in water, so it can’t travel through your blood on its own. To help transport cholesterol, your liver produces lipoproteins. Lipoproteins are particles made from fat and protein.
What is the normal cholesterol level for a person with a high LDL?
According to the National Human Genome Research Institute, most adults with this condition have total cholesterol levels above 300 mg/dL and LDL levels above 200 mg/dL. Other health conditions, such as diabetes and hypothyroidism, may also increase your risk of developing high cholesterol and related complications.
How to measure cholesterol?
To measure your cholesterol levels, your doctor will use a simple blood test. It’s known as a lipid panel. They can use it to assess your levels of total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, and triglycerides. To conduct this test, your doctor or other healthcare professional will take a sample of your blood.
How does the body use triglycerides?
They’re different from cholesterol. While your body uses cholesterol to build cells and certain hormones, it uses triglycerides as a source of energy. When you eat more calories than your body can use right away, it converts those calories into triglycerides. It stores triglycerides in your fat cells.
Why is my cholesterol high?
Causes of high cholesterol. Eating too many foods that are high in cholesterol, saturated fats, and trans fats may increase your risk of developing high cholesterol. Other lifestyle factors can also contribute to high cholesterol. These factors include inactivity and smoking.
How to lower cholesterol?
Other ways that can help you maintain healthy cholesterol and triglyceride levels include: eating skinless poultry with no visible fat. eating lean meats, in moderate portions. eating low-fat or fat-free dairy products.
Why is my cholesterol high?
Other causes of high cholesterol levels include: Lack of exercise. Not getting enough exercise can increase your LDL levels. Not only that, exercise has been shown to boost your healthy HDL levels. Smoking. Smoking can also increase your bad cholesterol, causing plaque to build up in your arteries.
How to check cholesterol levels?
To check your cholesterol levels, your doctor will order a blood test called a lipid profile, or lipid panel. This test measures your total cholesterol (both LDL and HDL) and triglycerides. Before this test, your doctor will likely ask you to avoid eating and drinking liquids other than water for at least 8 to 12 hours.
What does it mean when you have a lipid disorder?
What is a lipid disorder? If your doctor says you have a lipid disorder, that means you have high blood levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, and fats called triglycerides, or both. High levels of these substances increase your risk for developing heart disease.
What are the effects of LDL?
LDL can combine with other fats and substances in your blood, creating blockages in your arteries. Blockages in your arteries can reduce your blood flow and cause serious health problems such as heart disease, heart attack, or stroke. Because of its potential effects, doctors recommend lower levels of LDL.
What are the two main forms of cholesterol?
The two major forms of cholesterol found in your body are low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and high-density lipoprotein (HDL). LDL, sometimes known as “bad cholesterol,” is made by your body and also absorbed by your body from cholesterol-rich foods such as red meat and dairy products. LDL can combine with other fats and substances in your blood, ...
What are some medications that help with lipids?
Several types of medications are used to treat lipid disorders. Statins: These drugs block a substance created in your liver that produces cholesterol. Your liver then removes cholesterol from your blood. Statins can also absorb cholesterol trapped in your arteries. Commonly prescribed statins include:
What does it mean when you have high LDL cholesterol?
When you have high LDL cholesterol levels, it means you are at greater risk for cardiovascular disease like heart attack and stroke. The plaque formed by this fatty substance on the inner walls of arteries can block or restrict blood flow.
What is considered high cholesterol?
Levels above 200 mg/dL are considered high and mean a higher risk for developing heart disease. LDL cholesterol below 130 mg/dL. LDL should be lower than this for those at risk of heart attacks or stroke. HDL cholesterol above 60 mg/dL. HDL levels of 60 mg/dL and higher can help reduce the risk for heart disease.
What is the risk of developing heart disease?
HDL levels of 40 mg/dL and lower are considered a risk factor for developing heart disease. Triglycerides below 150 mg/dL. Levels higher than 150 mg/dL increase the risk of developing heart disease and metabolic syndrome, which is also a risk factor for heart disease, diabetes, and stroke. Non-HDL cholesterol below 160 mg/dL.
Where does cholesterol come from?
About 75% of the cholesterol in the body is naturally produced in the liver, and the remaining 25% of cholesterol comes from foods we eat .
Is LDL bad for you?
Low density lipoproteins (LDL) “Bad” cholesterol. Too much LDL can build up in the artery walls and form plaque that narrows arteries and restricts blood flow, which lead to coronary artery disease. High levels of LDL cholesterol mean a person has an increased risk of stroke and heart attack. High density lipoproteins ( HDL ) “Good” cholesterol.
Understanding Cholesterol
Cholesterol is a type of lipid, a fatty, waxy substance in your blood. High amounts of cholesterol can build up inside your arteries. This can clog and narrow your arteries so blood can’t flow easily. Blood clots can form, break away, and cause a stroke or heart attack.
Types of High Cholesterol
There are different types of high cholesterol, based on what’s causing it:
How to Know if You Need Treatment
Everyone with high cholesterol should start with heart-healthy lifestyle changes like diet, exercise, quitting smoking, and weight loss. But if your cardiac risk is high, you may need treatment with medications, too.
How High Is Too High?
Very high HDL cholesterol levels not only don't protect you more, but they might be harmful. In one study, people who had HDL cholesterol levels above 60 mg/dL were nearly 50% more likely to have a heart attack or die from heart disease than people whose HDL levels were between 41 and 60 mg/dL.
What Causes High HDL Levels?
A few things can push your HDL level above 60 mg/dL. You can control some of these factors. Others you can’t.
Treating High HDL Cholesterol
If you don't have any symptoms or other heart disease risks, you might not need any treatment for high HDL cholesterol. You may be able to lower your HDL by drinking less alcohol and eating a low-fat diet. It might also help to change your medication if you take a statin or another drug that raises HDL levels.

What Is High LDL?
Lifestyle
Weight
Age and Sex
Specialist to consult
Genetics
- Cholesterol itself is a necessary substance in the body. It’s manufactured in your liver and it can be present in certain foods, especially meats, eggs, and dairy. LDL is a lipoprotein—a substance that conveys cholesterol to cells, aiding in maintaining cell structure, and serving as a precurso…
Race and Ethnicity
- If your LDL levels are high or borderline, your doctor will`tell you about what you can do to lower your numbers. Among the most significant means of taking on this condition are making meaningful lifestyle changes.
Medications
- Another major risk factor for high LDL is excessive weight. Being overweight or clinically obese limits your body’s ability to remove this type of cholesterol from the bloodstream and is directly related to higher levels.8 How are these weight statuses defined? The standard measure is the body mass index (BMI), which compares your height and weight to estimate your level of body f…
Other Health Conditions
- Your age and sex can also have a significant influence on LDL levels. As both men and women age, they usually rise. Men tend to have higher LDL levels than women during younger years (ages 20 to 59). In contrast, women consistently had higher values of LDL after midlife (age 60).13 For women, going through menopause can also influence LDL. The risk of having high cholesterol pr…
A Word from Verywell
- As with a great deal of health conditions, a family history of high cholesterol increases the risk of your developing it. High LDL levels due to genetics, a condition called familial hypercholesterolemia (FH), occurs in one out of every 500 people.14This condition is especially concerning because it‘s often undetected and is associated with early heart attack, stroke, and p…
Diagnosis
- According to a growing body of research, race and ethnicity is also a factor in high cholesterol levels. While all races and ethnicities can develop high LDL, there are differences based on status. Here’s a quick breakdown:15 1. African Americans: High cholesterol is seen in nearly even amounts among African American men and women, occurring in 10.6% of the former, and 10.3…
Treatment
- Medications you’ve been prescribedcan also cause LDL levels to be elevated. This can be especially challenging as drugs for heart conditions and high blood pressure, among other related conditions, are on the list. Prior to any prescription, your doctor will have to carefully outline the risks and benefits. So what types of drugs raise LDL levels? There are quite a few:16 1. Cardiova…
Clinical Trials
- Finally, high cholesterol can also be caused by a range of other health conditions, disorders, or diseases you may have. These include:2 1. Type 2 diabetes: One of the main effects of diabetes is insufficient production of insulin, which breaks down sugars. This limits the body’s ability to process LDL. 2. Liver disease: Liver problems like liver cirrhosis can also have an immediate imp…
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
- Given how fundamental cholesterol is to the processes of the body and the function of the circulatory system, it’s little wonder that many factors can cause high LDL. Since there are so many dangers associated with it, however, figuring out what specific behaviors, medications, or other issues are causing the problem can be key in solving it. Ultimately, there is no singular met…
Preparing For Your Appointment