
How can you tell if you have dissociative identity disorder?
· What are the Treatment Options? Psychotherapy. The most popular and successful treatment for dissociative identity disorder is psychotherapy. ... The... Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR). EMDR is another effective treatment option. This method focuses on... Medications. While ...
Can You Live a normal life with dissociative identity disorder?
· Dissociative Identity Disorder Treatment Medications Used for Treating Dissociative Identity Disorder. Medications for dissociative identity disorder are usually... Therapy Options for Dissociative Identity Disorder. Therapy for dissociative identity disorder focuses on processing... Treating ...
How to live with someone with dissociative identity disorder?
· Treatment for dissociative identity disorder aims to: 3. Relieve symptoms. Keep the person and other people around them safe. Integrate the different identities into one well-functioning identity. A therapist helps the person process memories related to their trauma, develop coping skills, improve functioning, and have better relationships. 3
How to act toward someone with dissociative identity disorder?
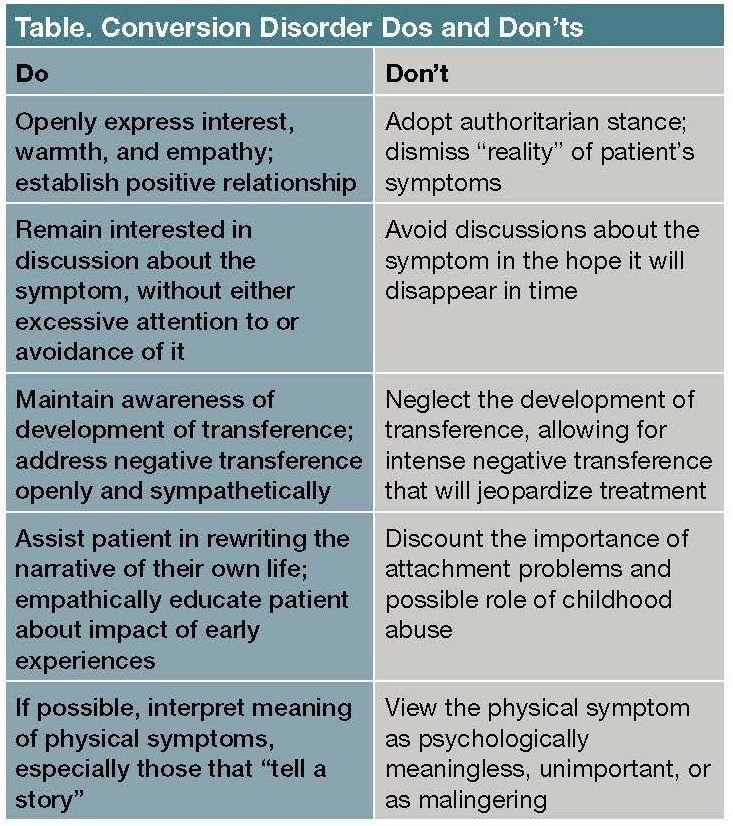
· The treatment of choice for dissociative identity disorder is long- term, one- to- one, relationally- based psychotherapy. In most cases, therapy will be at minimum once weekly, but this would be dependent on a number of factors such as level of functioning, support and motivation. Longer sessions (of 75 to 90 minutes, or in some cases longer) are often required, …
Psychotherapy for DID
Psychotherapy, or talk therapy, is the most effective treatment for dissociative identity disorder. 1 This condition frequently develops from childhood abuse or other traumatic events.
Medications for DID
There's no specific medication for treatment of dissociative identity disorder. 8 However, medications can be effective for treating depression and anxiety that often occur with this condition.
Coping Strategies for DID
A variety of coping strategies can be helpful for managing life with dissociative identity disorder. These include:
Summary
Dissociative identity disorder is a mental health condition that is commonly treated with psychotherapy, including cognitive behavioral therapy, dialectical behavioral therapy, psychodynamic psychotherapy, eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR) therapy, and schema therapy.
A Word From Verywell
Dissociative identity disorder can affect every area of your life. In some cases, it can prevent a person from working or having meaningful relationships. However, seeking treatment through therapy and other support networks can decrease dissociative episodes, or possibly eliminate them altogether. You're not alone.
What is dissociative identity disorder?
Here is more on dissociative identity disorder: who gets it, what causes it, what its symptoms are, and how it’s treated.
What percentage of people with dissociative identity disorder have a past history of childhood neglect and abuse?
While there is no specific roadmap of who gets this disorder, statistics show that around 90 percent of people with dissociative identity disorder have a past history of childhood neglect and abuse. And these numbers are not just from the United States but Canada and Europe too.
How effective is EMDR?
The client thinks of a disturbing event. The client is then led through eye-tracking movement or bilateral stimulation. It has proven to be effective according to a study published in the Journal of Psychoactive Drugs.
What are the causes of DID?
There are a few things that cause DID. These include long-term sexual abuse, child abuse, emotional abuse, physical abuse, and traumas like those from combat or natural disasters.
What is the goal of therapy?
The goal of therapy is to help integrate the different elements of identity. Therapy may be intense and difficult as it involves remembering and coping with past traumatic experiences. Cognitive behavioral therapy and dialectical behavioral therapy are two commonly used types of therapy. Hypnosis has also been found to be helpful in ...
Is being possessed a dissociative disorder?
Yet, this does not count. The disturbance must not be a normal part of a broadly accepted cultural or religious practice. As noted in the DSM-51, in many cultures around the world, experiences of being possessed are a normal part of spiritual practice and are not dissociative disorders.
Does cultural background count as dissociative disorder?
For example, a person from another country who is exposed to another culture may seem to exhibit an alternative personality. Yet, this does not count.
How to treat dissociative disorder?
Dissociative disorders treatment may vary based on the type of disorder you have, but generally include psychotherapy and medication.
What is dissociative identity disorder?
For dissociative identity disorder: You display, or others observe, two or more distinct identities or personalities, which may be described in some cultures as possession that is unwanted and involuntary. Each identity has its own pattern of perceiving, relating to and thinking about yourself and the world.
How does a therapist help you?
Your therapist will work to help you understand the cause of your condition and to form new ways of coping with stressful circumstances. Over time, your therapist may help you talk more about the trauma you experienced, but generally only when you have the coping skills and relationship with your therapist to safely have these conversations.
What is the diagnosis of a mental illness?
Diagnosis usually involves assessment of symptoms and ruling out any medical condition that could cause the symptoms. Testing and diagnosis often involves a referral to a mental health professional to determine your diagnosis.
What is the best medication for dissociative disorder?
Although there are no medications that specifically treat dissociative disorders, your doctor may prescribe antidepressants, anti-anxiety medications or antipsychotic drugs to help control the mental health symptoms associated with dissociative disorders.
What is dissociative fugue?
You may also experience dissociative fugue, where you purposefully travel or experience confused wandering that involves amnesia — inability to remember your identity or other important personal information.
What is it called when you can't remember your identity?
Dissociative amnesia. For dissociative amnesia: You've had one or more episodes in which you couldn't remember important personal information — usually something traumatic or stressful — or you can't remember your identity or life history. This memory loss is too extensive to be explained by ordinary forgetfulness.
What is a dissociative identity disorder?
Dissociative Identity Disorder (Multiple Personality Disorder) A mental health condition, people with dissociative identity disorder (DID) have two or more separate personalities. These identities control a person’s behavior at different times. DID can cause gaps in memory and other problems.
What is the best treatment for DID?
Some medications may help with certain symptoms of DID, such as depression or anxiety. But the most effective treatment is psychotherapy. A healthcare provider with specialized training in mental health disorders, such as a psychologist or psychiatrist, can guide you toward the right treatment.
How to make living with DID more manageable?
A strong support system can make living with DID more manageable. Make sure you have healthcare providers, family members and friends who know about and understand your condition. Communicate openly and honestly with the people in your support system, and don’t be afraid to ask for help.
How to prevent DID?
There’s no way to prevent DID. But identifying the signs as early in life as possible and seeking treatment can help you manage symptoms. Parents, caregivers and teachers should watch for signs in young children. Treatment soon after episodes of abuse or trauma may prevent DID from progressing.
What does "did" mean in therapy?
The condition can cause memory loss, delusions or depression. DID is usually caused by past trauma. Therapy can help people manage their behaviors and reduce the frequency of identity “switches.”. It’s important for anyone with DID to have a strong support system.
What is core identity?
The “core” identity is the person’s usual personality. “Alters” are the person’s alternate personalities. Some people with DID have up to 100 alters. Alters tend to be very different from one another. The identities might have different genders, ethnicities, interests and ways of interacting with their environments.
What is depersonalization disorder?
Depersonalized or derealization disorder, which causes a feeling of detachment from your actions.
What are the best medications for dissociative identity disorder?
Antidepressant medication has little effect on dissociative identity disorder. However, these medications are commonly used to treat depression, a mental health condition that commonly co-occurs with DID. Whether depression reaches a level requiring clinical diagnosis, treatment with antidepressants may help elevate mood. Some antidepressants that may be prescribed to someone with DID include: 1 Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) 2 Tricyclic antidepressants like Doxepin 3 Clonidine 4 Anticonvulsants 5 Benzodiazepines
What is the treatment for DID?
Treatment for DID will likely consist of therapy and in some cases, medication management. While there are several approaches to treat DID, most treatment methods have the goal of reconnecting the patient’s multiple personalities into one identity.
What is cognitive behavioral therapy?
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT). This kind of therapy is the most common type of therapy used by treatment providers. Developed originally to treat depression, CBT is used to treat several types of mental health disorders. During therapy, patients will learn healthy ways to manage stressful situations and difficult emotions by changing the way they think and correcting their behaviors.
What are the effects of antipsychotics on the personality?
These medications may reduce dissociations and other symptoms caused by the transition between realities. Levels of dopamine, noradrenaline and serotonin are regulated with antipsychotic medications which can help alleviate some symptoms of DID. Some antipsychotic medications that may be prescribed to someone with DID include:
Is substance use common in people with a dissociative identity disorder?
Substance use is common in people with a dissociative identity disorder. The difficulties caused by living with DID can be challenging and some people may turn to substance misuse to numb their symptoms.
Can dissociative identity disorder cause anxiety?
People living with dissociative identity disorder can also develop anxiety. Once someone is diagnosed and becomes aware of their alternate personalities and dissociations, further anxiety may be experienced about behaviors that can occur when they are not in conscious control.
Can antidepressants help with dissociative identity disorder?
Antidepressant medication has little effect on dissociative identity disorder. However, these medications are commonly used to treat depression, a mental health condition that commonly co-occurs with DID. Whether depression reaches a level requiring clinical diagnosis, treatment with antidepressants may help elevate mood. Some antidepressants that may be prescribed to someone with DID include:
What is the treatment for DID?
Treatment for DID includes psychotherapy and may include the use of medications. Treatment for co-occurring disorders such as DID and addiction requires an integrated approach that can treat both conditions at the same time.
What is dual diagnosis?
When someone has a mental health disorder and a substance use disorder, it’s called a dual diagnosis. Both conditions need to be treated simultaneously for the best chance of a complete recovery. Integrated treatment—treating a substance use disorder and mental health issues at the same time—is the optimal method to deal with co-occurring disorders. Increasingly, rehab programs offer dual diagnosis treatment.
Can multiple identities affect children?
The differing styles of a parent with multiple identities can also compromise the safety of the children . The parent’s different identities may have different values, disciplinary codes, and memories of daily routines. Some may even have abusive identities or put themselves in situations that can cause trauma to the child. 4
Can mental health and substance abuse occur together?
In many instances, mental health conditions and substance abuse occur together in the same person because: 6
What is it called when you have a mental health disorder and a substance use disorder?
When someone has a mental health disorder and a substance use disorder, it’s called a dual diagnosis.
Can a person's identity affect their work?
For example, a person who has an angry identity may lash out at a co-worker or boss. 2
Who said that therapy is the first order of treatment regardless of diagnosis?
James Chu quotes Dr David Caul who once observed: Therapists should always remember that good basic psychotherapy is the first order of treatment regardless of any specific diagnosis. (Chu, 2011, p.227).
What is phase 1 therapy?
Phase 1 focuses on establishing safety and stabilisation and reducing symptoms. People with dissociative disorders often enter therapy in a very dysregulated, chaotic state and it is important to bring some balance and safety back to their lives before working on traumatic material. The focus during Phase 1 work is on: 1 establishing a therapeutic alliance 2 educating patients about their diagnosis and symptoms 3 explaining the process of treatment. 4 The goals of Phase 1 work include: 5 maintaining personal safety 6 controlling symptoms 7 modulating affect (managing emotions) 8 building stress tolerance 9 enhancing basic life functioning 10 building or improving relational capacities.
Is there a linear progression in dissociative identity disorder?
In reality, there is unlikely to be a linear progression through these three stages: more commonly the work will spiral through each phase, with a frequent need to return to stabilisation work during the middle and later stages. As well as addressing dissociative symptoms, and working through and integrating the underlying trauma, a third area of treatment is that of ‘attachment’, with the vast majority of dissociative identity disorder clients presenting with disorganised attachment patterns.
What is the treatment for dissociative identity disorder?
Psychotherapy, which is a form of psychology, uses psychological methods that are based on the regular interaction between a mental healthcare professional and their patient. Psychotherapy is the main form of treatment for those suffering from dissociative disorders. It is also known as counselling, talk therapy and psychosocial therapy. This form of treatment will involve the patient talking about their condition and the issues related to it with a trained professional who will have had experience in working with individuals with mental health conditions as severe as dissociative identity disorder.
What does a therapist need to treat a case of DID?
The therapist treating a case of DID will need to have a thorough understanding of the condition in order to adequately deal with the different alters or personalities of the patient and be able to identify whom they are working with at any given session. The psychology behind these alters will be explained further in the section that follows.
Why is it important to take caution when administering medication to a DID patient?
Caution should be taken when administering medication to DID individuals as a number of these can often make the patient feel ‘numb’ and in a sense, ‘controlled’. This can cause the patient to experience a form of trauma and provoke emotions of distress.
Why is hypnosis used in psychology?
Hypnosis is also used to aid in increasing the information the patient has on their alters and increase the control they may have over these personalities.
What is the therapy called for a person who has DID?
A form of therapy that is used in a number of cases of DID is known as dialectical behaviour therapy (DBT). This kind of psychotherapy is a type of cognitive behavioural therapy that focuses on mindfulness and aids the patient through decreasing their negative reactions to specific stressors or triggers. Dialectical behaviour therapy focuses on the following factors:
How does a therapist help a patient?
The therapist will attempt to lead the patient to an understanding of the underlying cause of their condition and form ways that suit them in coping with these traumatic circumstances. Eventually, the therapist will try to form a relationship of trust with their patient in order for the individual to feel comfortable in expressing their emotions.
Can dissociative identity disorder be treated?
There has been research that shows that those suffering from dissociative identity disorder will have the best chance of living a healthy and productive life if they are able to undergo comprehensive treatment for their disorder. Granted, there are often a number of variables present in how different practitioners conduct their diagnostic procedure and treatment plans. These differences make it rather difficult to predict the outcomes for patients.
What is the cornerstone of treatment for dissociative disorders?
Psychotherapy is the cornerstone of treatment for dissociative disorders and hence choosing the right therapist is of paramount importance. The following section enumerates the characteristics of a therapist ideally suited to engage in therapy for dissociative disorders.
What training is needed for a dissociative disorder?
A formal training in psychotherapy is desirable before the therapist attempts to undertake therapy for dissociative disorders. Patients with dissociative disorders may need to be approached from a psychodynamic perspective to gain a better understanding of the role of past trauma in the manifestation of their current symptoms and unless the therapist is well versed in the nuances of psychodynamic approach and trained formally in psychotherapy, only crisis intervention and supportive therapy will be done, which will partially ameliorate the patient's symptoms. Ideally, an experienced therapist should be able to incorporate eclectic therapeutic techniques, psychoeducation and skills development flexibly within an overall psychodynamic framework and undertake therapy.
What is the process of desensitization?
The process of desensitization involves: Therapist guided lateral eye movements and substitute activities in the patient, in order to process the target picture, emotion, physical symptoms, and cognitions. Once the process of desensitization is achieved a positive/healthier cognition is paired with eye movement.
What happens when a therapist explores unconscious conflicts?
As therapy progresses, the therapist explores the patient's unconscious conflicts which may be a cause of maladaptive functioning. Also, resistance emerges and the therapist may experience counter transference. The therapist should be experienced enough to recognize counter transference which can provide valuable information about the original trauma by its re-enactment within the therapeutic context and to manage it sensitively so that trust in the therapeutic alliance is maintained
What are the principles of dissociation?
Three principles for treatment of dissociation in a contextual approach. Psychoanalytical symptoms have a relation with the unconscious conflict. Psychological (learning) Symptoms are learnt in childhood as a means of coping with unpleasant events. Role of trauma and altered information processing.
What is dissociation in psychology?
Dissociation is a mechanism that allows the mind to compartmentalize certain memories or thoughts from normal consciousness. These split-off mental contents are available and may return to consciousness either by an event or spontaneously. Broadly, dissociative disorders may be viewed as shown in Table 1. Table 1.
What is dissociative disorder?
Dissociative disorders as described by ICD 10 include a range of disorders and combine what are conversion disorders (assumed under somatoform disorders in Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fourth Edition) and the cluster of dissociative disorders. The mutual idea shared by these disorders is a partial or complete loss of usual integration between memories, cognizance of identity, and immediate sensations and voluntary control of body movements. Conversion occurs when there are clinical symptoms representing alteration of functioning of motor or sensory systems and which do not follow a pattern of a known neurological or medical disease. Dissociation is a mechanism that allows the mind to compartmentalize certain memories or thoughts from normal consciousness. These split-off mental contents are available and may return to consciousness either by an event or spontaneously.

Definition
Symptoms
- Dissociative disorders treatment may vary based on the type of disorder you have, but generally include psychotherapy and medication.
Epidemiology
Cause
Purpose
Benefits
- Instances of true DID are very rare. When they occur, they can occur at any age. Females are more likely than males to get DID.
Examples
- A history of trauma is a key feature of dissociative identity disorder. About 90% of the cases of DID involve some history of abuse. The trauma often involves severe emotional, physical, and/or sexual abuse. It might also be linked to accidents, natural disasters, and war. An important early loss, such as the loss of a parent or prolonged periods of isolation due to illness, may be a facto…
Characteristics
- Dissociation is often thought of as a coping mechanism that a person uses to disconnect from a stressful or traumatic situation, or to separate traumatic memories from normal awareness. It is a way for a person to break the connection with the outside world, and create distance from an awareness of what is occurring.