Angiogenesis
Angiogenesis is the physiological process through which new blood vessels form from pre-existing vessels, formed in the earlier stage of vasculogenesis. Angiogenesis continues the growth of the vasculature by processes of sprouting and splitting. Vasculogenesis is the embryonic formation of endothelial cells from mesoderm cell precursors, and from neovascularization, although discussions are n…
What is antiangiogenic therapy for cancer?
Antiangiogenic therapy for cancer: an update The idea of antiangiogenic therapy was the brainchild of Dr. Judah Folkman in the early 1970s. He proposed that by cutting off the blood supply, cancer cells would be deprived of nutrients and, hence, treated.
What is the goal of antiangiogenesis inhibitors?
The goal of these drugs, also called antiangiogenic agents, is to prevent or slow the growth of cancer by starving it of its needed blood supply. How do angiogenesis inhibitors work?
What are anti angiogenic drugs?
Angiogenesis means the growth of new blood vessels. Anti angiogenic drugs are treatments that stop tumours from growing their own blood vessels. If the drug is able to stop a cancer from growing blood vessels, it might slow the growth of the cancer or sometimes shrink it.
Is anti-angiogenic therapy necessary for metastatic lung cancer?
Since angiogenesis is deemed necessary for the growth of metastases in all sites of the body, it is assumed that anti-angiogenic therapy should be of benefit for patients with metastatic disease.
In which one of the following ways are antiangiogenic drugs used in the treatment of cancer?
Anti angiogenic drugs are treatments that stop tumours from growing their own blood vessels. This might slow the growth of the cancer or sometimes shrink it.
What is angiogenic therapy?
Anti-angiogenic therapy is an old method to fight cancer that aims to abolish the nutrient and oxygen supply to the tumor cells through the decrease of the vascular network and the avoidance of new blood vessels formation.
How does angiogenesis help cancer spread?
The tumor sends signals that stimulate more blood vessels to grow and carry more blood. Angiogenesis inhibitors, also called anti-angiogenics, block blood vessel growth. By blocking nutrients and oxygen from a tumor, the angiogenesis inhibitors "starve" the tumor.
What is the main aim of anti angiogenic therapy?
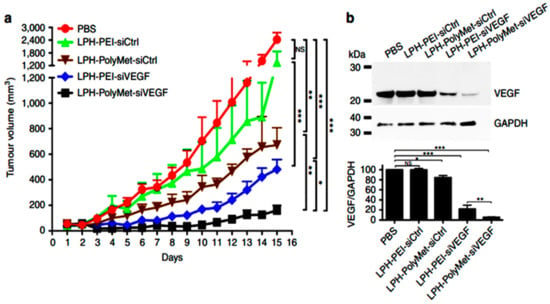
Anti-angiogenic therapies target angiogenesis by two major mechanisms: blocking the receptor tyrosine kinases intracellularly or neutralizing angiogenic factors such as VEGF or its receptors.
How effective is antiangiogenic therapy?
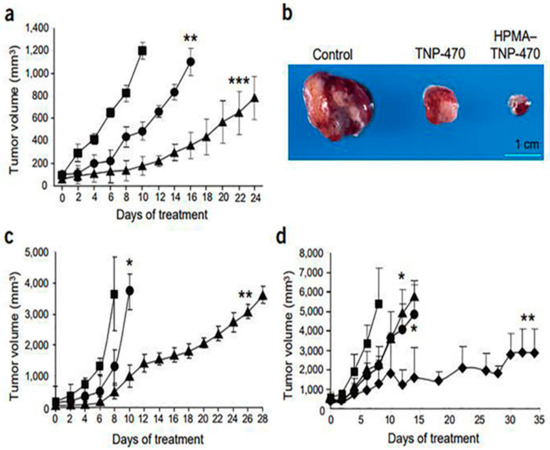
In 1971, Folkman hypothesized that “neovascularization is critical for tumors growth”. Since then, anti-tumor angiogenesis therapy has gained considerable attention, and is currently one of the most effective methods to treat cancer. Tumor blood vessels are fundamental for tumor growth and metastasis.
What is the process of angiogenesis?
Angiogenesis is the formation of new blood vessels. This process involves the migration, growth, and differentiation of endothelial cells, which line the inside wall of blood vessels.
What does angiogenesis mean in cancer?
(AN-jee-oh-JEH-neh-sis) Blood vessel formation. Tumor angiogenesis is the growth of new blood vessels that tumors need to grow. This process is caused by the release of chemicals by the tumor and by host cells near the tumor.
What are antiangiogenic factors?
The primary anti-angiogenic factors include thrombospondins (TSP), angiostatin and endostatin. Now the TSP family includes five members, known as TSP-1, -2, -3, -4 and TSP-5/COMP. They play multiple functions via binding to matrix proteins, plasma proteins and cytokines[90-93].
What are the limitations of antiangiogenic therapy?
Inherent or acquired resistance to anti-VEGF molecules can occur leading to a lack of response and to disease recurrence, although discontinuation of the therapy is the principal factor limiting the effectiveness of anti-angiogenic therapies [9].
What is anti angiogenic agent?
Listen to pronunciation. (AN-tee-AN-jee-oh-JEH-neh-sis AY-jent) A drug or substance that keeps new blood vessels from forming. In cancer treatment, antiangiogenesis agents may prevent the growth of new blood vessels that tumors need to grow.
Which of the following is a potential adverse outcome of an antiangiogenic medication?
The major side effects that are class effects of the blockade of normal angiogenesis are hypertension, bleeding, rare hemorrhage, rare gastrointestinal perforation, diarrhea, hypothyroidism, rare RPLS, teratogenicity, and fetotoxicity.
What is angiogenesis?
Angiogenesis is the formation of new blood vessels. This process involves the migration, growth, and differentiation of endothelial cells , whic...
Why is angiogenesis important in cancer?
Angiogenesis plays a critical role in the growth of cancer because solid tumors need a blood supply if they are to grow beyond a few millimeters...
How do angiogenesis inhibitors work?
Angiogenesis inhibitors are unique cancer-fighting agents because they block the growth of blood vessels that support tumor growth rather than bl...
What angiogenesis inhibitors are being used to treat cancer in humans?
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved a number of angiogenesis inhibitors to treat cancer. Most of these are targeted therapi...
Do angiogenesis inhibitors have side effects?
Side effects of treatment with VEGF-targeting angiogenesis inhibitors can include hemorrhage , clots in the arteries (with resultant stroke or hea...
Why are angiogenesis inhibitors used in cancer treatment?
Angiogenesis inhibitors are unique cancer-fighting agents because they block the growth of blood vessels that support tumor growth rather than blocking the growth of tumor cells themselves. Angiogenesis inhibitors interfere in several ways with various steps in blood vessel growth.
Why is angiogenesis important for cancer?
Angiogenesis plays a critical role in the growth of cancer because solid tumors need a blood supply if they are to grow beyond a few millimeters in size. Tumors can actually cause this blood supply to form by giving off chemical signals that stimulate angiogenesis.
How effective are angiogenesis inhibitors?
Because angiogenesis inhibitors work by slowing or stopping tumor growth without killing cancer cells, they are given over a long period.
Why are there drugs to stop tumors from growing?
Because tumors cannot grow beyond a certain size or spread without a blood supply, scientists have developed drugs called angiogenesis inhibitors, which block tumor angiogenesis. The goal of these drugs, also called antiangiogenic agents, is to prevent or slow the growth of cancer by starving it of its needed blood supply.
How is angiogenesis controlled?
The process of angiogenesis is controlled by chemical signals in the body. Some of these signals, such as vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), bind to receptors on the surface of normal endothelial cells. When VEGF and other endothelial growth factors bind to their receptors on endothelial cells, signals within these cells are initiated ...
What is the process of angiogenesis?
What is angiogenesis? Angiogenesis is the formation of new blood vessels. This process involves the migration, growth, and differentiation of endothelial cells, which line the inside wall of blood vessels. The process of angiogenesis is controlled by chemical signals in the body. Some of these signals, such as vascular endothelial growth factor ...
What is angiogenesis inhibitor?
Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved a number of angiogenesis inhibitors to treat cancer. Most of these are targeted therapies that were developed specifically to target VEGF, its receptor, or other specific molecules involved in angiogenesis. Approved angiogenesis inhibitors include:
What is anti-angiogenic therapy?
Anti-angiogenic therapy is an old method to fight cancer that aims to abolish the nutrient and oxygen supply to the tumor cells through the decrease of the vascular network and the avoidance of new blood vessels formation .
What is the most well studied and targeted in cancer therapy?
While different molecular mediators are important in the control of cancer angiogenesis, the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF-A, also known as simply VEGF) is by far the most well studied and targeted in cancer therapy. Anti-Angiogenic Therapy, Focused on VEGF, for Cancer Treatment. In 1971, Folkman hypothesized ...
What is ANG2 in VEGF?
On the contrary, ANG2 (mostly produced by ECs) acts as an endogenous antagonist of ANG1 function that leads to remodeling processes or vascular sprouting in response to VEGF [68]. The angiogenic pattern activated by ANG2 resembles the cancer angiogenesis, which is characterized by unstable and leakier vessels [69].
What is the standard care for cancer patients with solid tumors?
The standard care of cancer patients with solid tumors is based on surgical resection followed by chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy, in order to prevent cancer recurrence and the progression of occult microscopic tumors [120,121,122].
What happens to tumor cells during vascular co-option?
During vascular co-option, tumor cells migrate along the preexistent blood vessels (specially tumor cells, rich in myofibroblasts), taking over of the existing vasculature to tumor blood supply. This process is essentially reported in highly vascularized tumors, as brain, lung, and liver.
Is therapy resistance a major obstacle to cancer treatment?
However, therapy resistance is still one of the major obstacles for the optimal success of cancer management is [123]. Given the central role of VEGF in the promotion of tumor angiogenesis, its targeting has emerged as the most promising therapeutic strategy for angiogenesis inhibition and cancer treatment.
Is HGF/C-MET a cancer drug?
In cancer models, it was proven that HGF/c-MET is responsible for the resistance to anti-VEGF therapy with sunitinib (VEGFR and PDGFR RTKi), while the concomitant exposure to HGF/c-MET inhibitors and sunitinib abrogated angiogenesis and tumor growth [89].
What is the treatment for cancer that blocks blood vessels?
Drugs that block cancer blood vessel growth (anti angiogenics) Anti angiogenic drugs are treatments that stop tumours from growing their own blood vessels. This might slow the growth of the cancer or sometimes shrink it. There are different types of anti angiogenic drugs. These work in different ways.
What drugs affect the signals between cells?
This can block the formation of blood vessels. Drugs that works in this way include thalidomide and lenalidomide (Revlimid).
What drugs block signalling in blood vessels?
These treatments are also called cancer growth blockers or tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs). Examples of TKIs that block signals inside blood vessels cells include: sunitinib. sorafenib. axitinib. regorafenib.
Why does cancer need blood?
A cancer needs a good blood supply to provide itself with food and oxygen and to remove waste products. When it has reached 1 to 2 mm across, a tumour needs to grow its own blood vessels in order to continue to get bigger. Angiogenesis means the growth of new blood vessels.
What is the protein that attaches to cells that line the walls of blood vessels within the tumour?
Some cancer cells make a protein called vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). The VEGF protein attaches to receptors on cells that line the walls of blood vessels within the tumour. The cells are called endothelial cells. This triggers the blood vessels to grow so the cancer can then grow.
