Is water treatment aerobic or anaerobic?
Since anaerobic treatment is preferred when the dissolved organic concentrations of untreated wastewater are high, aerobic treatment is often used as a secondary treatment process and follows an anaerobic stage. Aerobic treatment consists of activated sludge processes or oxidation lagoons.
What is anaerobic method?
Anaerobic digestion is a process through which bacteria break down organic matter—such as animal manure, wastewater biosolids, and food wastes—in the absence of oxygen.
How does an anaerobic filter work?
An anaerobic filter is a fixed-bed biological reactor with one or more filtration chambers in series. As wastewater flows through the filter, particles are trapped and organic matter is degraded by the active biomass that is attached to the surface of the filter material.
What is aerobic and anaerobic process in wastewater treatment?
Aerobic wastewater treatment is a biological wastewater treatment process which uses an oxygen rich environment. Anaerobic wastewater treatment is a process where anaerobic organisms break down organic material in an oxygen absent environment. Bacteria involved the aerobic wastewater treatment are aerobes.
How does anaerobic wastewater treatment work?
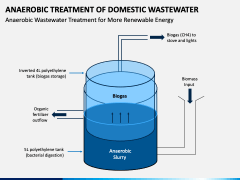
Basically, an anaerobic treatment cycle involves wastewater entering a bioreactor receptacle containing a thick semi-solid substance called sludge, full of anaerobic bacteria and other microorganisms which break down the organic contaminants present in the wastewater.
What is anaerobic digestion wastewater treatment?
Anaerobic digestion is the biological degradation of organic matters in the absence of oxygen and converts the chemical energy in organic carbon to biogas. Typically, anaerobic digestion has been used for wastewater sludge treatment and reduction, agricultural manure management, and food waste management.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of anaerobic treatment of wastewater?
Up-flow or down-flow anaerobic filters: suited to treating wastes containing organic matter in soluble form, which excludes many forms of municipal waste. It is more widely applied to treating industrial wastes. The main disadvantage of the anaerobic filter reactor is the high cost of the filter material.
What are the steps of wastewater treatment?
The Wastewater Treatment ProcessStage One — Bar Screening. ... Stage Two — Screening. ... Stage Three — Primary Clarifier. ... Stage Four — Aeration. ... Stage Five — Secondary Clarifier. ... Stage Six — Chlorination (Disinfection) ... Stage Seven — Water Analysis & Testing. ... Stage Eight — Effluent Disposal.
What is biological treatment of water?
The principle of biological water treatment methods is on the degradation of organic compounds present in the effluent by microorganisms (aerobic and/or anaerobic). On one hand, to develop them, they will consume the dissolved organic pollution.
What is difference between aerobic and anaerobic?
In aerobic, or “with oxygen” exercise, your muscles have enough oxygen to produce the energy needed to perform. Anaerobic “without oxygen” exercise means oxygen demand is greater than oxygen supply and you can't keep up with the energy your body is demanding.
What is the difference between anaerobic and aerobic processes?
There are two types of Respiration: Aerobic Respiration — Takes place in the presence of oxygen. Anaerobic Respiration –Takes place in the absence of oxygen.
What is aerobic wastewater treatment used for?
Aerobic treatment of wastewater is a biological process that uses oxygen to break down organic contaminants and other pollutants like nitrogen and phosphorous. Oxygen is continuously mixed into the wastewater or sewage by a mechanical aeration device, such as an air blower or compressor.
What are the advantages of anaerobic treatment?
3.5.4.6.1 Advantages of anaerobic treatment processes. Anaerobic treatment processes have several advantages over the aerobic treatment processes. Anaerobic treatment processes require less energy for its operation than the aerobic treatment process. The biomass generation in anaerobic process is six- to eightfolds lower than ...
Why is anaerobic process smaller?
Anaerobic process requires smaller reactor volume as it can handle higher volumetric loading rates.
What is the first step in the process of hydrolysis?
Stage 1: Hydrolysis —The organic waste material mainly consists of carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. Complex and large substances are broken down into simpler compounds by the activity of the microbes and the extracellular enzymes released by these microbes. The hydrolysis or solubilization is mainly done by hydrolytic microbes such as Bacteroides, Bifidobacterium, Clostridium, and Lactobacillus. These organisms hydrolyze complex organic molecules (cellulose, lignin, proteins, lipids) into soluble monomers such as amino acids, sugars, fatty acids, and glycerol. These hydrolysis products are used by the fermentative acidogenic bacteria in the next stage.
What is biodigestor sludge used for?
In most of the industrial countries, the biodigestor sludge is used as fertilizer, and when used for food production hygienic safety is especially important. The gas is used as an energy source, for example, as household gas, which also has raised concerns about the risk of spreading pathogens.
What is anaerobic digestion?
Anaerobic digestion as a unit process in municipal wastewater treatment has been in use for many years now. It is employed for stabilization of sludge solids from primary and secondary sedimentation tanks either in closed digesters or open lagoons. Anaerobic lagoons are also used for treatment of industrial wastes.
What are the chemicals in industrial waste?
Industrial wastes might contain inhibitory concentrations of various salts containing sodium, potassium, magnesium, calcium, ammonium, and sulfide. Heavy metals might also be a problem. In general, monovalent cations such as sodium and potassium are less toxic than divalent cations such as magnesium and calcium.
What pH is toxic to anaerobic?
3.4.5.7 pH and Toxicity. Anaerobic treatment is very sensitive to pH. The process thrives well in the pH range 6.5–7.8, with an optimum pH near neutral. At pH values below 6.0, the reaction rate drops off rapidly, and the resulting acidity can become quite toxic to the methanogens.
Is anaerobic treatment good for water?
Ask anyone in the water treatment industry about anaerobic wastewater treatment and they’ll reel off its many benefits: it’s efficient, doesn’t create nasty smells, and can treat water with high levels of organic contamination.
What is anaerobic wastewater treatment?
Anaerobic wastewater treatment is often the default choice for wastewater with high concentrations of organic material, and is often used as the first step before the water flows through any aerobic treatment systems.
What is anaerobic treatment?
The anaerobic treatment of water is a basic biological process. Bacteria and other microorganisms process organic contaminants, without using oxygen to do so. In the most basic type of treatment system, wastewater flows into a bioreactor container. This bioreactor holds a thick substance called sludge which is made from microorganisms ...
What are the phases of anaerobic digestion?
The two phases of anaerobic digestion. There are two phases to any anaerobic digestion process. The first is the acidification phase and the second is the methane production phase.
How deep are anaerobic lagoons?
Anaerobic lagoons. Anaerobic or waste lagoons are large artificial ponds, usually up to 20 feet deep and as large as 2 acres. This method is most commonly used to treat agricultural wastewater, as well as waste water from the meat production and processing industries. These artificial lagoons or pools often also form the first step in drinking ...
How long does it take for water to break down?
Although the process can be completed in just a few weeks, it can take as long as six months to get the contaminants in the water down to acceptable levels.
What is anaerobic sludge blanket reactor?
Anaerobic sludge blanket reactors are a different sort of anaerobic treatment where the wastewater flows through suspended sludge particles known as a “blanket”. The anaerobes in the sludge digest the organic components in the water which then collect as granules at the base of the reactor tank.
Where are wastewater treatment facilities located?
Located in Urban Areas – Wastewater treatment facilities are often located in dense, urban areas, where compost facilities are not. It makes logical sense for a highly populated area to ship organic waste to a nearby anaerobic digester where the energy content is recovered and the volume reduced.
What is anaerobic digestion?
There are two distinct uses of Anaerobic Digestion in Wastewater Treatment: 1 As a treatment process in its own right for primary sewage treatment/ organic industrial effluent, as known as a “UASB” 2 As a method of treating the sludge produced by Wastewater Treatment Plants.
What is sludge digested?
The digested sludge is de-watered, dried up and used as sewage sludge fertilizer while the gases produced are used as fuel or for driving gas engines. The supernatant liquor is re-treated at the treatment plant along with the raw sewage. The tanks in which sludge digestion is carried out are called sludge digestion tanks.
What are the products of decomposition of sewage sludge?
The products of decomposition are acid carbonates, organic acids with gases as carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulfide.
Is sludge disposal expensive?
Sludge disposal can be expensive in other anaerobic digestion processes, especially where the material contains pollutants. 2. Treating the Sludge Produced by Wastewater Treatment Plants. Download our free book!
What is anaerobic treatment of waste water?
In this article you will learn about the anaerobic treatment of waste water. Waste water containing biodegradable organics (dissolved and / or suspended ) when subjected to anaerobic treatment, the organics undergo various biochemical reactions. The reactions are broadly classified as hydrolysis, acidogenesis and methanogenesis.
What is the advantage of anaerobic treatment?
The major advantage of the anaerobic treatment process over that of the aerobic process is that no energy is to be spent for supplying air (oxygen). Moreover, methane, which is produced as a by-product of the anaerobic process, has an economic value as a fuel.
What would happen if the lagoon was only a shallow layer?
Hence only a shallow layer close to the surface would contain facultative organisms, whereas the remaining portion of the lagoon would have anaerobes only. The zone close to the bottom would contain a sludge made up of unrelated solid particles (if any in the influent) and bacterial mass synthesized during the process.
What is anaerobic lagoon?
Anaerobic lagoons are similar to the facultative lagoons in construction but are much deeper. During operation grease and some solid particles may float up to the surface and form a scum layer. This layer prevents re-oxygenation of the surface zone.
Where does sludge accumulate in a tank?
Sludge (biomass) produced accumulates on floor of the basin/tank. Influent waste water free from suspended matter is introduced close to the bottom and the treated effluent flows out through an outlet located at one of the sides of the tank close to the surface.
What happens when anaerobic treatment is carried out in anyone of the units (a) to (d)
When anaerobic treatment is carried out in anyone of the units (a) to (d) listed earlier, the methane produced is not collected, but vented to the atmosphere along with some obnoxious gases which cause atmospheric pollution and local nuisance.
Is an acidogene an anaerobic process inhibitor?
Some acidogenes are facultative while the others are obligate (strict) anaerobes. The acidogenes are not too sensitive to pH and inhibitors like heavy metals and sulfides. For the methanogenes the optimum pH ranges from 6.6 to 7.6. Below a pH of 6.2 the methanogenes become inactive (dormant). Some of the inorganic anaerobic process inhibitors are listed in Table 9.12.
What is the process of removing organics from wastewater?
As organics are removed from the wastewater during the anaerobic digestion process , methane-rich biogas is produced. Anaerobic digestion produces very little excess sludge & with treatment the agriculturally-beneficial sludge can safely be applied to land as fertilizer.
What is anaerobic digestion?
Anaerobic digestion is a process in which microorganisms convert organic matter into biogas in the absence of oxygen. Anaerobic treatment is typically utilized to treat warm, high-strength industrial wastewater containing high concentrations of biodegradable organic matter. This energy-efficient process reliably removes biochemical oxygen demand ...
Is biogas a renewable resource?
In addition, the biogas produced in the anaerobic process is a source of renewable energy that can be used to displace fossil fuels such as oil or natural gas, or to generate electricity. Re newable Energy from Biogas. As organics are removed from the wastewater during the anaerobic digestion process, methane-rich biogas is produced.
What is anaerobic wastewater treatment?
The anaerobic wastewater treatment uses anaerobic bacteria that change organic matter into organisms that contain large quantities of methane gas and carbon dioxide. In some systems, this process is used as a pre-treatment to aerobic wastewater treatment. The professionals at AOS can discuss various municipal wastewater treatment options ...
What is anaerobic treatment?
Anaerobic treatment of wastewater may be used to treat industrial wastewater. This type of wastewater often contains high levels of organic matter in warmer temperatures. Anaerobic treatment systems may be used in areas where a central treatment plant is not possible.
Why is anaerobic treatment better than aerobic treatment?
In comparison, the anaerobic wastewater treatment process is typically more economically friendly for the following reasons: 1 The anaerobic treatment of wastewater generates much less sludge than the aerobic treatment does. 2 The sludge produced in anaerobic wastewater treatment can be used for soil enrichment. 3 There are lower costs required to handle sludge compared to those incurred in aerobic treatment. 4 Fewer chemicals are used in the process when compared to aerobic wastewater treatment. 5 The biogas can be used to produce electricity and heat and serve as a renewable energy source that effectively replaces fossil fuels.
What is the difference between aerobic and anaerobic wastewater treatment?
One key difference between aerobic and anaerobic wastewater treatment is the process by which the treatment mechanisms work.
Why is air circulated throughout wastewater treatment?
In the aerobic process, air is circulated throughout a treatment in order to cause bacteria that break down waste within the wastewater. Electricity is used throughout the process. Some systems may use a pre-treatment process that reduces solids that aerobic bacteria may have difficulty compressing.
Is wastewater treated anaerobic or aerobic?
The anaerobic treatment of wastewater generates much less sludge than the aerobic treatment does. The sludge produced in anaerobic wastewater treatment can be used for soil enrichment. There are lower costs required to handle sludge compared to those incurred in aerobic treatment. Fewer chemicals are used in the process when compared ...
What is aerobic bacteria?
The aerobic bacteria in sewage treatment feed on the water, which is mixed with air. The bacteria reproduce and continue to attack the waste, with some waste settling on the bottom of water as sludge. This sludge may be pumped out of the system so that the system is not clogged.
What is the difference between aerobic and anaerobic treatment?
While both rely on a process of microbial decomposition to treat wastewater, the key difference between anaerobic and aerobic treatment is that aerobic systems require oxygen, ...
What is anaerobic system?
On the other hand, anaerobic systems are typically used for treatment of waste streams with high concentrations of organic contaminants, and for warm wastewater streams.
What is the secondary aerobic treatment step?
In some cases, the secondary aerobic treatment step is used to oxidize ammonia to form nitrate. In general, using both technologies together results in more efficient treatment than if an aerobic system were used alone, as well as more complete contaminant removal than if anaerobic treatment were used alone.
How does aerobic system work?
System design. Aerobic systems require some means of supplying oxygen to the biomass, which may be accomplished by wastewater treatment ponds (which work by creating a large surface area for introducing air to the wastewater), and/or by incorporating some type of mechanical aeration device to introduce oxygen into the biomass.
Can aerobic and anaerobic wastewater treatment be used together?
Indeed, anaerobic and aerobic wastewater treatment technologies can be used independently or in combination with one another. In this post, we’ll take a look at how anaerobic and aerobic wastewater treatment technologies differ from one another, as well as their respective advantages and drawbacks that lend to their ability to complement one another on a wastewater treatment train.
Is anaerobic or aerobic better?
As a result of these system design differences, anaerobic systems tend to offer a few benefits over aerobic systems, including lower operational costs and energy demands, though they also tend to be slower, and usually require more upfront capital.
