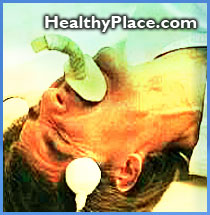
Shock therapy, known medically as electroconvulsive therapy (ECT), is a treatment for major depressive disorder (MDD), bipolar disorder, and other psychiatric conditions. ECT is generally offered when other treatments are ineffective or there is a need for rapid response.
What is shock therapy for depression?
Sep 25, 2020 · For about six in 10, ECT appeared to offer relief from an array of debilitating symptoms -- including delusions, aggressiveness, uncooperativeness, emotional oversensitivity, physical hyperactivity...
Is shock therapy still used today?
Aug 14, 2021 · Shock therapy, known medically as electroconvulsive therapy (ECT), is a treatment for major depressive disorder (MDD), bipolar disorder, and other psychiatric conditions. ECT is generally offered when other treatments are ineffective or there is a need for rapid response.
What is ECT shock therapy for depression?
Mar 06, 2003 · Shock Therapy: Still Here, Still Used ECT Works Better Than Drugs for Some Depression Patients By Salynn Boyles From the WebMD Archives March 6, 2003 -- For most people, the term "shock treatment"...
How does shock therapy affect the brain?
Apr 23, 2022 · Natasha Tracy. "Shock therapy" was so-called, as an electric shock is used to induce a controlled seizure intended as a treatment, primarily for mood disorders, although other conditions may be treated as well. Shock therapy is now known as electroconvulsive therapy or ECT. The brain is still not well understood, nor is the reason for the treatment effects ECT …

What disorder uses shock therapy?
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is a medical treatment most commonly used in patients with severe major depression or bipolar disorder that has not responded to other treatments. ECT involves a brief electrical stimulation of the brain while the patient is under anesthesia.
Is shock treatment still used today?
ECT is much safer today. Although ECT may still cause some side effects, it now uses electric currents given in a controlled setting to achieve the most benefit with the fewest possible risks.Oct 12, 2018
Is shock therapy still used for bipolar?
While the misuse of ECT in the past gave it a bad reputation, it's now considered a safe and effective treatment for bipolar disorder. ECT is mainly used to treat the depressive phase of bipolar disorder, but can also be used during the manic phase.
Is shock therapy still used for schizophrenia?
Abstract. Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) was initially used for the treatment of schizophrenia, but over the years with the advent of antipsychotics, its use in schizophrenia has been limited. Treatment guidelines vary in their recommendations for the use of ECT in schizophrenia.
Is shock therapy still used for depression?
Researchers concluded that ECT remains an important treatment option for the management of severe depression.Mar 6, 2003
Is shock treatment still used in Australia?
ECT treatment varies in different countries. In Australia, ECT is usually given from one to three times a week. A course of ECT involves 8-12 treatments on average. After a successful course of ECT, further treatment is usually given to maintain the improvement and to help prevent relapse.
How does electric shock therapy work for bipolar?
Modern ECT treatment involves stimulating the brain, using a carefully controlled current to induce a seizure while the patient is unconscious, under a short acting general anaesthetic and muscle relaxant.
Why is ECT used for depression?
The electrical stimulation triggers a seizure. Repeated a few times a week for a short period, ECT eliminates depressive symptoms for an extended time in many patients.Jun 19, 2018
For which disorder was electroconvulsive therapy originally developed as a treatment?
Electroconvulsive therapy was born. In 1938, Cerletti and his psychiatrist colleague Lucio Bini developed the first ECT device and treated their first human patient, a diagnosed schizophrenic with delusions, hallucinations, and confusion.Nov 3, 2018
When is ECT used in schizophrenia?
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is a remarkably effective treatment for major depressive disorder, but is less commonly utilized for treatment of psychotic disorders. Recent literature indicates that ECT can be a useful strategy for a wide range of psychotic disorders, including treatment-resistant schizophrenia.Apr 2, 2019
What type of psychotherapy is used for schizophrenia?
Cognitive behavioral therapy, also known as CBT, may be a treatment option for people with schizophrenia. CBT teaches a person to modify beliefs or behaviors that may be leading to negative emotions.
Shock Therapy: Process, Preparation, Outcomes and more
Krystina is a Technical Writer with a background in healthcare. She has spent the last 10 years working for an internationally recognized medical facility where she found her passion for making complicated topics easier to understand.
The Electroconvulsive Therapy Process
An ECT treatment regimen will typically include sessions two to three days a week for a total of six to 12 treatments. The schedule works out to about one month of treatment, although the course may continue for longer.
How to Prepare for Your Treatment
ECT sessions generally do not require much preparation, though you will need to go over the specifics with your doctor. Your doctor may give you orders to follow based on other health conditions you have or medications you take.
Potential Outcomes of Shock Therapy
Most people who undergo ECT will see a noticeable change in their symptoms. Some people will notice an immediate improvement after one session. However, it is more common to not see or feel a significant difference in symptoms for several sessions.
Summary
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) can be used to treat major depressive disorde r, bipolar disorder, and other psychiatric conditions. It is often considered when other treatments have not helped.
A Word From Verywell
If you are wondering if shock therapy might be a treatment option for you, discuss it with your psychiatrist. While ECT can provide lasting relief from the symptoms of MDD, bipolar disorder, and similar conditions, it's not the right choice for everyone.
Frequently Asked Questions
Even though ECT has been around for nearly 90 years, scientists still are not quite sure why or how it benefits some people with depression.
Is ECT more effective than sham?
Findings from 18 studies involving 1,144 patients suggested that ECT was significantly more effective for the short-term treatment of depression than drug therapy. It was also found to be more effective than sham ECT in six studies involving 256 patients.
Is ECT a good treatment for depression?
Researchers concluded that ECT remains an important treatment option for the management of severe depression. "Despite its image, ECT is a sophisticated and complex treatment that can be especially useful in patients who are not helped by drug therapy," researcher John Geddes, MD, of the University of Oxford in England, tells WebMD.
Is electroconvulsive therapy still used?
But electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is still being used -- more in Europe than the United States -- and it may be the most effective short-term treatment for some patients with depressive symptoms, a newly published review in the journal The Lancet suggests.
What is neuromodulation therapy?
It’s one of the most studied mental health treatments available. For some patients with depression, there are also other brain-stimulating treatment options, called transcranial magnetic stimulation and vagus nerve stimulation. Together with ECT, they’re called “neuromodulation” therapies.
What is ECT for mental health?
For people with much rarer mental health conditions, such as schizophrenia, psychosis or a catatonic state caused by a mental health condition, ECT can provide a dramatic and immediate effect.
Does insurance cover ECT?
Most insurance programs cover it with a doctor’s referral. ECT is considered an established therapy option for certain conditions, so many insurance plans cover it — including plans offered by major private insurance companies and Medicare.
How long does an ECT last?
It travels into the brain and causes a seizure that lasts about a minute.
Is ECT done under general anesthesia?
ECT is done under general anesthesia, so patients don’t feel a thing. Modern ECT treatment units, such as the new one that just opened at the University of Michigan, provide comfortable surroundings to prepare for the anesthesia, and to wake up slowly from it.
How long does it take for ECT to go away?
Every person is different, but doctors usually recommend that patients get ECT treatments three times a week for two to four weeks. Many patients find that their symptoms go away, or are much less severe, for months to years after treatment.
Is ECT good for bipolar?
It can help people when other treatments haven’t. Individuals with depression and bipolar disorder should try talk therapy and medicines first. But if someone tries therapy, or three or four medicines over several years, and still fails to improve, ECT might be a good option. The same goes for people with autism who repeatedly show self-injury ...
What is shock therapy?
"Shock therapy" was so-called, as an electric shock is used to induce a controlled seizure intended as a treatment , primarily for mood disorders, although other conditions may be treated as well. Shock therapy is now known as electroconvulsive therapy or ECT.
What is the name of the drug that is used to treat seizures?
A paralyzing agent called succinylcholine is then administered to prevent the seizure from spreading to your body. The electrodes are then applied to your head with conducting jelly and a brief shock (less than 2 seconds) is administered.
Does shock help with depression?
Shock treatment for depression often produces a dramatic improvement in symptoms, especially in elderly individuals, sometimes during the first week of treatment. While it is estimated many of these patients will experience a future return of depression symptoms, the prognosis for each episode of depression is good. Mania also often responds well to shock treatment. The picture is not as bright for schizophrenia, which is more difficult to treat and is characterized by frequent relapses.
Can ECT cause memory loss?
You will likely experience short-term memory loss around the time of the procedure. With multiple treatments, this may increase. Adverse cognitive effects tend to be the most concerning factors around ECT and tend to affect the frequency and duration of treatments and whether ECT is offered at all. Your vital signs will be monitored closely ...
Is electroconvulsive therapy effective?
Electroconvulsive therapy has also shown effectiveness in treating other disorders such as neuroleptic malignant syndrome (a rare, severe, adverse reaction to antipsychotic medication). Shock treatment for depression and other disorders is indicated when the patient needs rapid improvement because the patient is:
What is ECT therapy?
Therefore, ECT therapy is most commonly used in severe major depression or bipolar disorder that have failed to respond to traditional methods of cognitive-behavioral therapy, medication, or talk therapy. The most common side effects of electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) are:
Why do doctors use ECT?
Doctors these days are much more hesitant to use ECT than passed, if for no other reason than because people are typically opposed. In addition, ECT is required by law to be used only by your consent or under the most severe conditions, such as: 1 To save your life 2 If urgently needed to prevent a rapid worsening of your condition
What is the hippocampus?
As a result, the size of certain brain structures can be changed as well. The hippocampus is the center of emotion, memory, and the autonomic nervous system. People with a smaller hippocampus volume tend to benefit the most from ECT because the treatment increases the size of this structure.
How many people die from ECT?
Only about 1 in 10,000 (or 10 per 100,000) people who have ECT die from it. The U.S. suicide rate, at 12 per 100,000 people, is higher. At least 133 in 100,000 people die of a heart attack. Surgery always carries a risk; even liposuction has a mortality rate of 20 in every 100,000 people.
Can a blood pressure cuff cause a seizure?
Because of the muscle relaxant, you might show few or no signs of seizure activity in your body. The blood pressure cuff on your ankle keeps the muscle relaxant from entering your foot. The doctor watches this foot to know when you're seizing.
What do doctors do before giving you ECT?
Before making the final decision to give you ECT, your doctor will take your medical history, give you a physical exam, do a psychiatric assessment, take basic blood tests, and do an ECG to check your heart.
How effective is ECT?
It's very effective for many people, too. For example, about 78% of people who receive ECT for depression improve , and of all the people who receive ECT, 70% to 90% go into remission from their condition. Unfortunately, with medications, the remission rate is only 20% to 30%!
