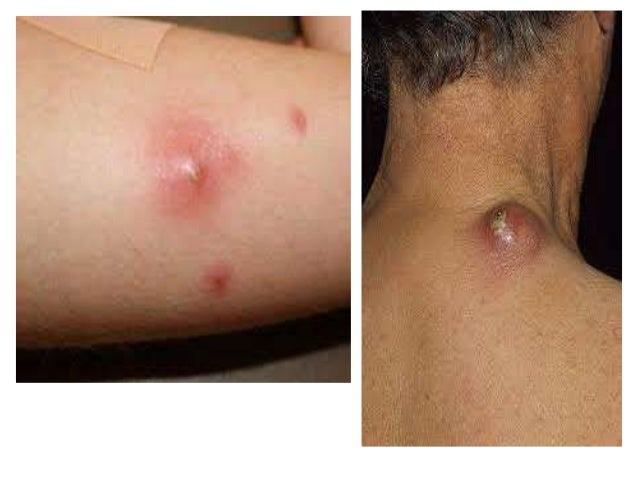
Medication
Prevention & Treatment of Cellulitis
- Often, a prescription medication like an oral antibiotic will be prescribed by a doctor.
- Topical ointments or creams may also be of use for the patient.
- In some cases, if cellulitis doesn’t go away quickly or you develop a high fever, you may need to take a stronger antibiotic medication.
Procedures
Cellulitis is a treatable condition, but antibiotic treatment is necessary to eradicate the infection and avoid complications and spread of the infection. Most cellulitis can be effectively treated with oral antibiotics at home. Sometimes hospitalization and intravenous antibiotics are required if oral antibiotics are not effective.
Self-care
- are severely unwell or
- have infection near the eyes or nose (including periorbital cellulitis) or
- could have uncommon pathogens, for example, after a penetrating injury, exposure to water-borne organisms, or an infection acquired outside the UK or
- have spreading infection that is not responding to oral antibiotics or
- lymphangitis or
Nutrition
- Assess for potential necrotizing infection. Emergent surgical consultation, consideration for debridement.
- Empiric: Vancomycin 15 mg IV q 12h IV PLUS piperacillin/tazobacatam 3.375 g IV q 4-6h.
- Microbiology/special associations--pathogen-specific: see specific modules for details. ...
What is the best drug for cellulitis?
What are the best treatments for cellulitis?
How are antibiotics used to treat cellulitis?
What medications are used for cellulitis?

How long does it take for facial cellulitis to go away with antibiotics?
Treatment for cellulitis It's important to keep taking antibiotics until they're finished, even when you feel better. Most people make a full recovery after 7 to 10 days.
Is 5 days of antibiotics enough for cellulitis?
In general, five to six days of therapy is appropriate for patients with uncomplicated cellulitis whose infection has improved within this time period [2,11,12]. Extension of antibiotic therapy (up to 14 days) may be warranted in the setting of severe infection, slow response to therapy, or immunosuppression.
How long after starting antibiotics should cellulitis improve?
Cellulitis symptoms should gradually get better. Symptoms usually begin to improve within 1 to 3 days of starting antibiotics. Pain and firmness will begin to subside. You should see the area become less red and swollen.
Should cellulitis be completely gone after antibiotics?
Your cellulitis symptoms will likely resolve before you finish taking the prescribed antibiotics. However, you must finish your prescription to ensure complete treatment of the infection.
Is 5 days of antibiotics enough for skin infection?
The trend is to try to limit antibiotic exposure, even for more serious infections like pneumonia. For cellulitis, the IDSA guidelines recommend 5 days treatment; many physicians would extend that to 7 days, but few treat for longer.
How do you treat cellulitis on the face?
Cellulitis treatment usually includes a prescription oral antibiotic. Within three days of starting an antibiotic, let your health care provider know whether the infection is responding to treatment. You'll need to take the antibiotic for the full course, usually 5 to 10 days, even if you start to feel better.
How do you know if cellulitis is healing?
In most cases, you should feel better within seven to 10 days after you start taking antibiotics. You'll notice signs that your cellulitis infection is healing a few days after starting antibiotics. Your pain will decrease, swelling will go down and any discoloration will begin to fade.
How long does it take for antibiotics to work for skin infection?
With antibiotic treatment, signs and symptoms of skin infections begin to improve after approximately 2 to 3 days. If your skin infection does not improve or gets worse (especially if you develop a fever or the infection spreads), notify your doctor right away.
How long does it take an infection to heal with antibiotics?
How quickly you get better after antibiotic treatment varies. It also depends on the type of infection you're treating. Most antibiotics should be taken for 7 to 14 days . In some cases, shorter treatments work just as well.
What is the strongest antibiotic for cellulitis?
The best antibiotic to treat cellulitis include dicloxacillin, cephalexin, trimethoprim with sulfamethoxazole, clindamycin, or doxycycline antibiotics.
Why do I keep getting cellulitis on my face?
Cellulitis is caused when bacteria, most commonly streptococcus and staphylococcus, enter through a crack or break in the skin. The incidence of a more serious staphylococcus infection called methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is increasing.
What happens if antibiotics don't work on cellulitis?
Without antibiotic treatment, cellulitis can spread beyond the skin. It can enter your lymph nodes and spread into your bloodstream. Once it reaches your bloodstream, bacteria can cause quickly cause a life-threatening infection known as blood poisoning.
Facial Cellulitis Common Causes
Facial cellultis is caused when bug bites transmit the bacteria. Rarely, the infection is also transmitted by anaerobic bacteria. Other traumas tha...
Symptoms of Facial Cellulitis
Facial cellulitis typically begins with swelling and redness in the face, particularly in the cheeks. The condition is also accompanied by burning...
How to Cure Facial Cellulitis?
Facial cellulitis is commonly treated with antibiotics for a period of 10 to 14 days. If the infection is accompanied by high fever, hospitalizatio...
How to cure facial cellulitis?
Facial cellulitis is commonly treated with antibiotics for a period of 10 to 14 days. If the infection is accompanied by high fever, hospitalization may be suggested by the doctor. Severe cases may require intravenous administration of antibiotics. Most patients who present with a condition of facial cellulitis have a recurrence of the infection.
How does facial cellulitis occur?
Certain types of bacteria (streptococcus and staphylococcus) enter the soft tissues of the skin through cuts and bruises. Facial cellulitis most commonly occurs in infants aged between 3 months and 2 years or adults older than 50 years of age. This type of infection is not contagious.
What is the most common cause of cellulitis?
Facial cellulitis is typically an infection of the subcutaneous tissue and the dermis of the facial skin. Though bacteria are the most common cause for the infection, occasionally the infection can also be caused by a fungus. Certain types of bacteria (streptococcus and staphylococcus) enter the soft tissues of the skin through cuts and bruises.
What causes cellulitis in infants?
In infants, cellulitis is caused by spread of group B streptococci bacteria.
What are the symptoms of cellulitis?
Symptoms of facial cellulitis. Facial cellulitis typically begins with swelling and redness in the face , particularly in the cheeks. The condition is also accompanied by burning and itchiness of the skin. Facial cellulitis causes the tongue to swell up and become very sensitive to touch.
Why do you need surgery for an abscess?
Surgery may be required in extreme cases to drain the pus when the patient develops an abscess on the face. Dead infected tissue is sometimes derided surgically to ease the healing of the surrounding skin. The accompanying pain and fever are treated with over-the-counter drugs.
Can cellulitis be detected on the face?
Symptoms of facial cellulitis appearing on the face can be promptly detected. However, it is a good idea to seek medical attention immediately. The medical specialist is likely to conduct a physical exam after checking the medical history of the patient. Certain laboratory tests that are conducted can confirm the presence of facial cellulitis. Treatment is decided by culturing the bacteria that is causing the infection.
What antibiotics are prescribed for cellulitis?
Depending on how advanced the infection is, these may include: Your doctor may prescribe dicloxacillin, cephalexin, trimethoprim with sulfamethoxazole, clindamycin, or doxycycline antibiotic s.
What is the best medicine for cellulitis?
Yarrow. Calendula flower. Tea tree oil. You should not only use herbal supplements or plant oils to treat cellulitis. Although they can help kill bacteria on the skin and be useful if your cellulitis is resistant to treatment, they may also interact negatively with your medications.
What is cellulitis?
The best antibiotic to treat cellulitis include dicloxacillin, cephalexin, trimethoprim with sulfamethoxazole, clindamycin, or doxycycline antibiotics.
What is cellulitis caused by?
All About Cellulitis: Causes, Symptoms, Treatments. Cellulitis is a type of skin infection caused by bacteria. It is a common but serious skin condition that needs urgent medical attention. In the United States, cellulitis affects around 14.5 million cases each year. Cellulitis can occur anywhere on the skin.
What is the most common cause of cellulitis?
The most common cause of cellulitis is the bacteria staph ( Staphylococcus aureus ).
How to treat cellulitis at home?
These can include: Elevating the affected part of your body to reduce swelling. Regularly moving the joint near the affected area, such as your ankle, to prevent stiffness. Drinking plenty of fluids.
How to diagnose cellulitis?
Your doctor will usually diagnose cellulitis based on its appearance and your symptoms. They will need to examine your skin, look at your personal and medical history, and create a record of your symptoms.
How to treat cellulitis?
It can help you avoid serious medical problems like blood poisoning and severe pain. To treat cellulitis, doctors prescribe: Antibiotics: An oral (you take by swallowing) antibiotic can effectively clear cellulitis. The type of antibiotic you need and how long you’ll need to take it will vary.
How long do you stay in hospital for cellulitis?
Most people are hospitalized for just over one week. Wound care: This is an important part of treating cellulitis. Covering your skin will help it heal. If you need special wound coverings or dressings, you’ll be shown how to apply and change them.
How is cellulitis diagnosed?
We don’t have a medical test that can diagnose cellulitis. Doctors diagnose it by examining the infected skin and asking questions.
What is the outcome for someone who gets cellulitis?
With treatment, you should quickly start to see less redness, swelling, pain, and warmth.
How to prevent cellulitis from getting worse?
Rest: This can help prevent cellulitis from becoming serious and help your body heal.
What doctor do you see for cellulitis?
A referral to a dermatologist: If you are seeing a doctor other than a dermatologist, you may be sent to a dermatologist. Cellulitis can look like other skin conditions and infections.
What happens if you stop taking antibiotics?
If you stop taking the antibiotic early, there is a risk the antibiotic won’t kill all the bacteria that made you sick. Taking all of the antibiotic exactly as prescribed helps clear cellulitis.
How long can cellulitis be treated?
Comment: Randomized trial for 5 vs 10 days of treatment showed uncomplicated cellulitis could be treated for 5 days.
How many cases of cellulitis fail?
Comment: Cellulitis failure rates according to literature review vary widely (6-37%). The author speculates that this reflects many cases that simply mimic cellulitis.
How many cases of dermatologic surgery were antibiotics used?
Comment: Clean dermatologic surgery database was reviewed for use of topical antibiotics. Topical antibiotics were used in 8 million of 212 million cases (5%), which the authors considered inappropriate use. Note that this reiew was selected because of the useless but sometimes common practice of using topical antibiotics on clean wounds.
What is the most common form of cellulitis?
Most common form of cellulitis: leg (tibial area) with breach in skin usually due to intertrigo.
Is orbital cellulitis serious?
Orbital cellulitis is potentially serious and merits an ophthalmology consultation and a CT scan to exclude preseptal infection.
Who wrote the systematic review of bacteremias in cellulitis and erysipelas?
Gunderson CG, Martinello RA. A systematic review of bacteremias in cellulitis and erysipelas. J Infect. 2011. [PMID:22101078]
Is cellulitis a subcutaneous disease?
Cellulitis: deeper (subcutaneous) than erysipelas. Also usually group A Streptococcus, but other streptococci occasionally implicated, e.g., group G.
How long does it take for cellulitis to heal?
You should start to see improvement in 3 days. If cellulitis is not treated, the infection can spread through your body and become life-threatening. You may need any of the following medicines: Antibiotics help treat the bacterial infection. Acetaminophen decreases pain and fever.
How long does it take for a fever to go away after antibiotics?
The red, warm, swollen area gets larger. Your fever or pain does not go away or gets worse. The area does not get smaller after 3 days of antibiotics. You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
What to do if you have a swollen ear?
Apply cream or ointment as directed. These help protect the area. Most over-the-counter products, such as petroleum jelly, are good to use. Ask your healthcare provider about specific creams or ointments you should use.
How to take medicine if you are allergic to it?
Contact your healthcare provider if you think your medicine is not helping or if you have side effects. Tell him or her if you are allergic to any medicine. Keep a list of the medicines, vitamins, and herbs you take. Include the amounts, and when and why you take them.
What is the cause of cellulitis?
WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW: Cellulitis is a skin infection caused by bacteria. Cellulitis is common and can become severe. Cellulitis usually appears on the lower legs. It can also appear on the arms, face, and other areas. Cellulitis develops when bacteria enter a crack or break in your skin, such as a scratch, bite, or cut.
Does acetaminophen help with fever?
Acetaminophen decreases pain and fever. It is available without a doctor's order. Ask how much to take and how often to take it. Follow directions. Read the labels of all other medicines you are using to see if they also contain acetaminophen, or ask your doctor or pharmacist.
How is cellulitis treated?
Cellulitis is treated with antibiotics. Most cellulitis infections can be treated with antibiotics that are taken by mouth (oral antibiotics). More serious infections may need to be treated in the hospital with intravenous (IV) antibiotics, which are given directly into a vein.
How to prevent cellulitis?
Common sense and good wound care are the best ways to prevent bacterial skin infections, including cellulitis. Clean all minor injuries that break the skin with soap and water. Clean all minor cuts and injuries that break the skin (like blisters and scrapes) with soap and water.
What is the condition that causes redness, swelling, and pain in the infected area of the skin?
Cellulitis is a common bacterial skin infection that causes redness, swelling, and pain in the infected area of the skin. If untreated, it can spread and cause serious health problems. Good wound care and hygiene are important for preventing cellulitis.
How do you get cellulitis?
How People Get Cellulitis. Experts do not know how the bacteria get into the body for many people who get cellulitis. Sometimes the bacteria get into the body through openings in the skin, like an injury or surgical wound. In general, people cannot catch cellulitis from someone else.
What are the factors that increase the risk of cellulitis?
Other factors that increase someone’s risk for cellulitis include: Problems with the lymphatic system so it does not drain the way it should (lymphedema); the lymphatic system is a part of the body’s immune system that helps move fluid that contains infection-fighting cells throughout the body.
How do doctors diagnose cellulitis?
Doctors Diagnose Cellulitis by How It Looks. Doctors typically diagnose cellulitis by doing a physical examination and looking at the affected skin. Blood or other lab tests are usually not needed.
What are the causes of cellulitis?
This page focuses on one of the most common causes of cellulitis: group A Streptococcus or group A strep.