When do you stop anticoagulation for DVT?
The decision to stop anticoagulants at 3 months or to treat indefinitely is more finely balanced after a first unprovoked proximal DVT or pulmonary embolism (PE).
How long should you be on anticoagulation after PE?
The current ACCP guidelines recommend that all patients with unprovoked PE receive three months of treatment with anticoagulation over a shorter duration of treatment and have an assessment of the risk-benefit ratio of extended therapy at the end of three months (grade 1B).Sep 18, 2020
How long does it take for DVT to resolve?
It is important to start treatment right away for DVT. It takes about 3 to 6 months for a blood clot to go away. During this time, there are things you can do to relieve symptoms. Elevate your leg to reduce swelling.Sep 10, 2020
How do you know if a DVT is getting better?
The pain and swelling from a DVT usually start to get better within days of treatment. Symptoms from a pulmonary embolism, like shortness of breath or mild pain or pressure in your chest, can linger 6 weeks or more. You might notice them when you're active or even when you take a deep breath.Mar 16, 2020
How long do you treat a PE for?
The ideal duration of treatment depends on the individual's risk of having another blood clot compared with the individual's risk of bleeding, which the doctor takes into account. Currently, the recommended treatment duration ranges from a minimum of 3 months to a maximum of lifelong treatment.Jul 7, 2015
How long should you take eliquis after a DVT?
How long will I be on ELIQUIS? Your doctor will decide the duration of your treatment. After at least 6 months of treatment for DVT/PE, your doctor may ask you to continue on a lower dose of ELIQUIS to help reduce the risk of them happening again.
Can walking dislodge a DVT?
The authors concluded that walking exercise was safe in acute deep venous thrombosis (DVT) and may improve acute symptoms. Exercise training did not acutely increase leg symptoms of previous DVT and may prevent or improve post-thrombotic syndrome.
Should you walk with a DVT?
For most people, walking or taking care of some housework are fine right after you find out you have DVT. It's also OK right after a pulmonary embolism. Your doctor may prescribe a blood thinner -- they may call it an anticoagulant -- and compression stockings. Those help blood flow in your legs.Apr 18, 2020
Will my leg go back to normal after DVT?
Post-Thrombotic Syndrome is when you have the ongoing symptoms of a blood clot, or deep vein thrombosis (DVT), in the leg. Some people who have had DVT or blood clots in the leg recover completely, but others still experience symptoms, and these symptoms are called PTS.
How do I know if my DVT is moving?
The skin around painful areas or in the arm or leg with the DVT may feel warmer than other skin. Trouble breathing. If this happens, it could mean that the clot has moved from your arm or leg to your lungs. You may also get a bad cough, and might even cough up blood.Jun 17, 2020
What should you not do with a DVT?
DON'T stand or sit in one spot for a long time. DON'T wear clothing that restricts blood flow in your legs. DON'T smoke. DON'T participate in contact sports when taking blood thinners because you're at risk of bleeding from trauma.
Can a blood clot move while on blood thinners?
Yes. Medications that are commonly called blood thinners — such as aspirin, warfarin (Coumadin, Jantoven), dabigatran (Pradaxa), rivaroxaban (Xarelto), apixaban (Eliquis) and heparin — significantly decrease your risk of blood clotting, but will not decrease the risk to zero.
How to treat DVT?
DVT is most commonly treated with anticoagulants, also called blood thinners. These drugs don't break up existing blood clots, but they can prevent clots from getting bigger and reduce your risk of developing more clots. Blood thinners may be taken by mouth or given by IV or an injection under the skin.
How to diagnose DVT?
Diagnosis. To diagnose DVT, your doctor will ask you about your symptoms. You'll also have a physical exam so that your doctor can check for areas of swelling, tenderness or changes in skin color. The tests you have depend on whether your doctor thinks you are at a low or a high risk of DVT. Tests used to diagnose or rule out a blood clot include: ...
What is the purpose of a vena cava filter?
A vena cava filter prevents clots that break loose from lodging in your lungs. Compression stockings. These special knee socks reduce the chances that your blood will pool and clot. To help prevent swelling associated with deep vein thrombosis, wear them on your legs from your feet to about the level of your knees.
What is a D dimer blood test?
D-dimer blood test. D dimer is a type of protein produced by blood clots. Almost all people with severe DVT have increased blood levels of D dimer. A normal result on a D-dimer test often can help rule out PE. Duplex ultrasound.
What is the best test for DVT?
Duplex ultrasound. This noninvasive test uses sound waves to create pictures of how blood flows through your veins. It's the standard test for diagnosing DVT. For the test, a technician gently moves a small hand-held device (transducer) on your skin over the body area being studied.
Can you take kale with warfarin?
Foods high in vitamin K, such as spinach, kale, other leafy greens and Brussels sprouts, can interfere with warfarin. Take your medications as directed. Your doctor will tell you how long you will need treatment. If you're taking certain blood thinners, you'll need a blood test to see how well your blood is clotting.
What blood thinners are used for DVT?
The most commonly used injectable blood thinners for DVT are enoxaparin (Lovenox) and fondaparinux (Arixtra). After taking an injectable blood thinner for a few days, your doctor may switch you to a pill. Examples of blood thinners that you swallow include warfarin (Jantoven) and dabigatran (Pradaxa).
PURPOSE
Major venous thromboembolism (VTE) requires minimum 3 to 6 months of anticoagulation, but when is it time to stop? Uncertainty remains around unprovoked VTE which accounts for approximately 50% of cases. This study by Rodger et al.
RESULTS
2,785 participants with a first unprovoked VTE (DVT and pulmonary embolus) at 44 centers in seven countries were enrolled. All participants completed 5-12 months of short-term anticoagulant treatment.
Learn More – Primary Sources
Validating the HERDOO2 rule to guide treatment duration for women with unprovoked venous thrombosis: multinational prospective cohort management study
How long does it take to treat venous thromboembolism?
It takes about 3 months to complete "active treatment" of venous thromboembolism (VTE), with further treatment serving to prevent new episodes of thrombosis ("pure secondary prevention"). Consequently, VTE should generally be treated for either 3 months or indefinitely (exceptions will be described in the text).
How long does it take to treat pulmonary embolism?
Duration of anticoagulant therapy for deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. It takes about 3 months to complete "active treatment" of venous thromboembolism (VTE), with further treatment serving to prevent new episodes of thrombosis ("pure secondary prevention"). Consequently, VTE should generally be treated for either 3 months ...
How to get around with DVT?
A DVT may make it harder for you to get around at first. You should slowly return to your normal activities. If your legs feel swollen or heavy, lie in bed with your heels propped up about 5 to 6 inches. This helps improve circulation and decreases swelling.
What is a DVT?
What is deep vein thrombosis? Deep vein thrombosis (DVT, also called venous thrombosis) is a blood clot that develops in a vein deep in the body. The clot may partially or completely block blood flow through the vein. Most DVTs occur in the lower leg, thigh or pelvis, although they also can occur in other parts of the body including the arm, brain, ...
Why do my leg veins swell?
The swelling is often because the valves in the leg veins are damaged or the vein is blocked by the DVT.Most compression stockings are worn just below the knee. These stockings are tight at the ankle and become more loose as they go up the leg. This causes gentle pressure (compression) on your leg.
How to treat a blood clot in the leg?
The main goals of treatment are to: Stop the clot from getting bigger. Prevent the clot from breaking off in your vein and moving to your lungs.
Where are blood clots found?
You have a blood clot in an unusual location, such as in a vein from the intestines, liver, kidney or brain. You have a strong family history of blood clots.
What are the causes of DVT?
The following conditions can increase your risk of a DVT: An inherited (genetic) condition that increases your risk of blood clots. Cancer and some of its treatments (chemotherapy) Limited blood flow in a deep vein, due to injury, surgery, or immobilization. Long periods of inactivity that decrease blood flow, such as:
What is the most common test for DVT?
A duplex venous ultrasound. This is the most common test used to diagnose a DVT. It shows the blood flow in the veins and any blood clots that exist. An ultrasound technician will apply pressure while scanning your arm or leg. If the pressure does not cause the vein to compress, it could mean there is a blood clot.
How long does it take to get anticoagulation for VTE?
Guideline recommendations for anticoagulation are divided into phases: initial phase (first week after diagnosis), long-term phase (second week to three months ), and extended phase (beyond three months). 9
Why is thrombolysis recommended?
Because of the high risk of bleeding, thrombolysis is restricted to specific circumstances. Expert consensus guidelines support thrombolytic therapy in patients with persistent hypotension or shock secondary to acute PE. 9 Also, when patients with acute PE who are on anticoagulation deteriorate but are not yet hypotensive, systemic thrombolysis is recommended as long as the risk of bleeding is low. 8 There is better evidence for systemic thrombolysis than for catheter-directed thrombolysis. 8 If systemic thrombolysis fails, catheter-directed thrombolysis is available as a rescue therapy in centers with appropriate expertise. Thrombolysis is not indicated in hemodynamically stable patients with intermediate-risk PE. 23
What is the treatment for VTE?
Anticoagulation is the mainstay of VTE treatment. Most patients with deep venous thrombosis or low-risk pulmonary embolism can be treated in the outpatient setting with low-molecular-weight heparin and a vitamin K antagonist (warfarin) or direct-acting oral anticoagulants.
What is the first direct acting anticoagulant?
In 2012, rivaroxaban became the first direct-acting oral anticoagulant approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for treatment of DVT and PE. Several others followed. These agents belong to two classes: direct thrombin inhibitors (dabigatran) and direct factor Xa inhibitors (apixaban, edoxaban, and rivaroxaban). 14 – 17
What is the risk of recurrence of VTE?
The risk of VTE recurrence is greatest in the first year after the event and remains elevated indefinitely compared with the general population. Lifetime recurrence rates for DVT ranges from 21% to 30%, depending on the population. 10, 28 Risk of VTE is increased by patient factors, such as active cancer and thrombophilia.
How long does Warfarin last?
Warfarin should be started on the same day as heparin, low-molecular-weight heparin, or fondaparinux and continued for = 5 days and until the INR is = 2 for at least 24 hours. 21 to 89 hours. Up to 92% of the orally administered dose is recovered in the urine, primarily as metabolites.
Is warfarin a teratogenic drug?
LMWH is the preferred agent. 39. Warfarin (Coumadin) is teratogenic; avoid in pregnancy. Direct-acting oral anticoagulants are not tested in pregnant patients; therefore, their safety is unknown; avoid in pregnancy. Anticoagulation should be continued for at least 3 months and at least 6 weeks postpartum.
How to keep a DVT from getting bigger?
You probably take medicine that makes your blood slower to clot. These drugs, called anticoagulants or blood thinners, can keep a DVT from getting bigger while your body breaks it down. They also can help keep another clot from forming. Some are given as shots, and some are pills.
How long does it take for a blood clot to heal?
Most people are fully healed from a deep vein thrombosis ( DVT) within a few weeks or months. But if you’re recovering from this type of blood clot (which happens in a large vein, most often in your leg), you might be worried about how it will change your life and whether it will happen again. Learning about the condition and taking charge ...
What does it feel like to have blood in your urine?
Blood in your urine or stool. Unusually heavy vaginal bleeding. Low blood pressure symptoms like weakness, dizziness, and shortness of breath. It may be hard to tell if your symptoms are related to the first clot or if you have a new one.
How to get up after surgery?
Try not to sit for more than a couple of hours at a time at work or in front of the TV. On long trips, get up and walk the aisle of the plane or stop the car to take a walk every hour or two.
Can anticoagulants cause stroke?
Because anticoagulants can cause uncontrolled bleeding, your odds of a stroke or other bleeding problem should be part of your decision. Your treatment plan will be different depending on which medication you take. For decades, warfarin ( Coumadin , Jantoven) has been the go-to drug for treating a DVT.
How long does it take for a DVT to form?
A DVT is a blood clot, or a lump of solidified blood, which has formed in a vein. They can take as little as 3 or 4 hours to form… but can really complicate your patient’s rehab stay. As therapists/nurses, we should be aware of the risks, the signs (when there are signs) and the most effective treatments.
How common is DVT?
Without intervention, as many as 40-80% of surgerical cancer patients will develop DVT in the calf , while 10-20 % will develop DVT in a proximal vein- according to a report published by the Surgeon General regarding DVT and PE.
What is complete decongestant therapy?
Complete Decongestive Therapy (CDT) is the umbrella term for the therapeutic treatment of edema. It includes: 1 Manual Lymphatic Drainage (MLD) – a hands-on, gentle manual therapy approach, which aims to move lymphatic fluid along the pathways in the body, reducing fluid in edematous areas. 2 Compression- a system of short stretch bandages, used with soft foam, to provide localized compression to the edematous region after pathways have been opened with MLD. 3 Exercise- segmental pumping exercises which harness the muscle pumping action of the limbs to move lymphatic fluid back toward proximal regions of the body. 4 Skin care- Hygiene and skin care to ameliorate for specific skin conditions that are associated with chronic swelling. 5 Education- Comprehensive education to the person including management of risk factors, exercises, resources, MLD and compression that can be performed independently.
What are the risk factors for DVT?
Who is at risk for DVT? Risk factors for the development of a Deep vein thrombosis include a blood clotting disorder- a typically inherited condition, such as Factor V Leiden.
What is PTS in medical terms?
Post-thrombotic syndrome (PTS) is a form of chronic venous insufficiency (link to 7 types article), which develops in approximately 20 to 50% those who have had a DVT. PTS presents with leg pain, leg heaviness, vein dilation, skin discoloration, venous ulcers, and edema.
Is compression good for DVT?
Well let’s first ‘bust’ the myth that compression is not a safe modality for use with acute DVT. In fact, strong compression has been shown to have numerous benefits in treating acute DVT- including significantly decreasing pain, swelling, and improving measured quality of life.
What is CDT treatment?
CDT is the gold standard of treatment for chronic, peripheral edema- such as that found by those with DVT or with PTS.

Diagnosis
Treatment
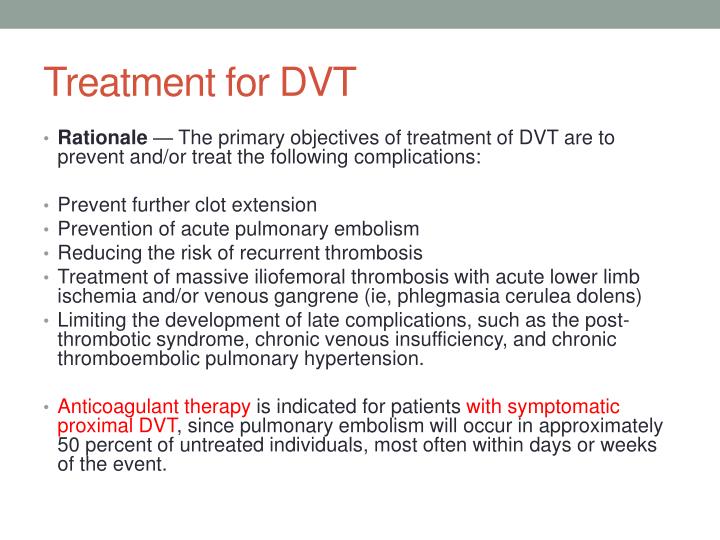
- There are three main goals to DVTtreatment. 1. Prevent the clot from getting bigger. 2. Prevent the clot from breaking loose and traveling to the lungs. 3. Reduce your chances of another DVT. DVTtreatment options include: 1. Blood thinners. DVT is most commonly treated with anticoagulants, also called blood thinners. These drugs don't break up exis...
Clinical Trials
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
- Once you receive treatment for DVT, it's important to follow some lifestyle changes to manage your condition and prevent another blood clot. Lifestyle changes include: 1. Ask your doctor about your diet.Foods high in vitamin K, such as spinach, kale, other leafy greens and Brussels sprouts, can interfere with warfarin. 2. Take your medications as directed.Your doctor will tell you how lo…
Preparing For Your Appointment
- DVTis considered a medical emergency, so it's important to get evaluated quickly. However, if you have time before your appointment, here's some information to help you get ready.