
What is the difference between coagulation and flocculation?
The Differences Between Coagulation and Flocculation in Water Treatment
- Coagulation. Coagulation in water treatment uses specialized chemicals to encourage fine particles to clump together.
- Flocculation. ...
- Expert Water Treatment by Reynolds Culligan. ...
What is the goal of flocculation in water treatment?
Thus, flocculation can be used to eliminate visible sediments and materials from impure water, or to treat water turbidity by removing colloids such as milk, glues or inks. There are various chemical and natural substances that are used in removing unwanted particles through flocculation.
What is the process of flocculation?
Stages Involved in Flocculation Process
- First Stage. The goal of the first stage in this process is to negatively charge the suspended solid materials in the water.
- Second Stage. Once the particles have been neutralized, the second stage begins in which the water has to be agitated through mixers.
- Third Stage. ...
- Fourth Stage. ...
What is added to water to cause flocculation?
Which coagulant is best?
- Aluminum Sulfate (Alum) – One of the most commonly used water treatment chemicals in the world.
- Aluminum Chloride – A second choice to Alum as it is more expensive, hazardous and corrosive.
- Polyaluminum Chloride (PAC) & Aluminum Chlorohydrate (ACH)
What is the difference between coagulation and flocculation?
What is the process of coagulation?
Why is coagulation important?
How to achieve coagulation?
What happens when coagulants are added to a coagulant?
Why is water treatment important?
What are some examples of coagulants?
See more
About this website
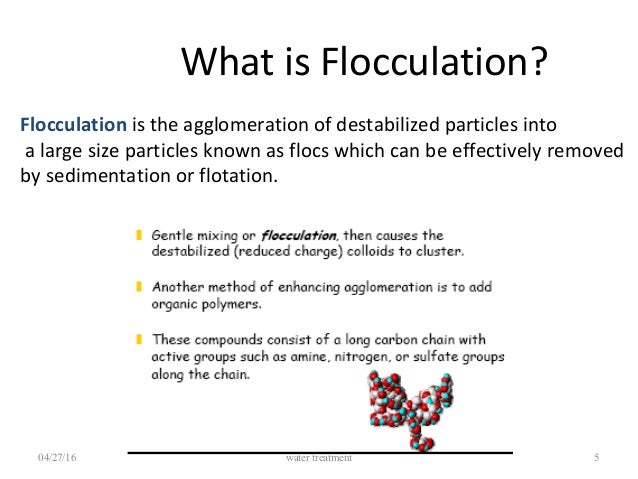
What type of process is flocculation?
4 Flocculation. Flocculation is a process by which a chemical coagulant added to the water acts to facilitate bonding between particles, creating larger aggregates which are easier to separate. The method is widely used in water treatment plants and can also be applied to sample processing for monitoring applications.
What is coagulation and flocculation process in water treatment?
Coagulation and flocculation are two separate processes, used in succession, to overcome the forces stabilising the suspended particles. While coagulation neutralises the charges on the particles, flocculation enables them to bind together, making them bigger, so that they can be more easily separated from the liquid.
What is coagulation process in water treatment?
Coagulation is the chemical water treatment process used to remove solids from water, by manipulating electrostatic charges of particles suspended in water. This process introduces small, highly charged molecules into water to destabilize the charges on particles, colloids, or oily materials in suspension.
What kind of process is coagulation filtration?
precipitative processCoagulation/filtration is a precipitative process. The most widely used coagulants for water treatment are aluminum and ferric salts, which hydrolyze to form aluminum and iron hydroxide particulates, respectively.
What are the types of water treatment process?
Water treatment stepsCoagulation. Coagulation is often the first step in water treatment. ... Flocculation. Flocculation follows the coagulation step. ... Sedimentation. Sedimentation is one of the steps water treatment plants use to separate out solids from the water. ... Filtration. ... Disinfection.
What is conventional water treatment?
Conventional filtration treatment means a series of processes including coagulation, flocculation, sedimentation, and filtration resulting in substantial particulate removal. Wastewater treatment plant means a facility designed and constructed to receive, treat, or store waterborne or liquid wastes.
What is flocculation coagulation?
Coagulation is the destabilization of colloidal particles brought about by the addition of a chemical reagent called as coagulant. Flocculation is the agglomeration of destabilized particles into microfloc and after into bulky floccules which can be settled called floc.
What methods are used in primary treatment of wastewater?
There are three basic biological treatment methods: the trickling filter, the activated sludge process, and the oxidation pond.
How does tertiary treatment of wastewater work?
Tertiary water treatment is the final stage of the multi-stage wastewater cleaning process. This third stage of treatment removes inorganic compounds, bacteria, viruses, and parasites. Removing these harmful substances makes the treated water safe to reuse, recycle, or release into the environment.
Is coagulation a filtration?
Coagulation and filtration is one of the most common water treatment techniques used by larger water systems, used for removing particulates and turbidity from surface water. A coagulant (typically either iron or aluminum salts with polymeric materials) is added and mixed with the influent water.
What is activated sludge treatment process?
The activated sludge process is a means of treating both municipal and industrial wastewater. The activated sludge process is a multi-chamber reactor unit that uses highly concentrated microorganisms to degrade organics and remove nutrients from wastewater, producing quality effluent.
What are the coagulation process?
Coagulation, also known as clotting, is the process by which blood changes from a liquid to a gel, forming a blood clot. It potentially results in hemostasis, the cessation of blood loss from a damaged vessel, followed by repair.
What is coagulation in water treatment?
Coagulation water treatment is the first step in chemical wastewater treatment. Instead of passing over particles that would otherwise slip through the filter and fall too slowly to be trapped as sediment, coagulation clumps them together so they are more easily removed. Most of us know coagulation from anatomy class.
Why is flocculation so popular?
Coagulation and flocculation processes have become more and more popular due to the increasingly stringent filtration requirements for industrial and municipal water treatment and wastewater treatment facilities levied by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA.)
What is a flocculant?
Flocculants are lightweight, medium weight and heavy polymers that cause the destabilized clumps of particles to agglomerate and drop out of the solution, removing them from the filtered water. The weight used depends on the type of particle.
When was coagulation water used?
Yet coagulation water treatment is far from being a new process. In fact, it was in use by the Egyptians as early as 2,000 B.C. Later the Romans used the coagulation process in water treatment, as did the English in the 18th century.
Is alum a good coagulant?
It’s the same principle with wastewater treatment. In coagulation treatment, a harmless chemical such as alum causes all of the particles to give off a positive charge and thus clump together, making them easier to filter. Coagulation is especially useful in removing the chemical phosphorus from water. Yet coagulation water treatment is far ...
What are some examples of coagulation operations?
Coagulation operations can be useful in some cases for the removal of inorganics. Examples of successful applications are copper and mercury reductions from wastewaterplant effluents. Two applications discussed in more detail below are arsenic and fluoride removals in potable water treatment:
Why is coagulation important?
Coagulation is also important in several wastewater treatment operations. A common example is chemical phosphorus removal and another, in overloaded wastewatertreatment plants, is the practice of chemically enhancing primary treatment to reduce suspended solids and organic loads from primary clarifiers.
What is the best coagulant for organics removal?
Organics removal and enhanced coagulation are effective with traditional coagulants like aluminum sulfate, ferric chloride and ferric sulfate, as well as formulations like polyaluminum chloride (PACl) and acid alum. Acid alum formulations are aluminum sulfate with 1 to 15-percent free sulfuric acid.
What are the variables in coagulation?
The efficiency of the coagulation-flocculation process is dependent on many variables. For a particular water these may include: 1 Type of coagulant used 2 Coagulant dosage 3 Final pH 4 Coagulant feed concentration 5 Type and dosage of chemical additives other than primary coagulant (e.g. polymers) 6 Sequence of chemical addition and time lag between dosing points 7 Intensity and duration of mixing at rapid mix stage 8 Type of rapid mix device 9 Velocity gradients applied during flocculation stage 10 Flocculator retention time 11 Type of stirring device used 12 Flocculator geometry.
How does orthokinetic flocculation work?
Orthokinetic flocculation arises from induced velocity gradients in the liquid. It is here that primary particles are induced to approach close enough together, make contact and progressively form larger agglomerates, or flocs. The principal parameter governing the rate of orthokinetic flocculation is the velocity gradient applied. The degree or extent of flocculation is governed by both applied velocity gradients and time of flocculation. These two parameters influence the rate and extent of particle aggregation and the rate and extent of breakup of these aggregates.
What happens when you add coagulants to water?
When metal coagulants are added to water the metal ions (Al and Fe) hydrolyze rapidly but in a somewhat uncontrolled manner, forming a series of metal hydrolysis species. The efficiency of rapid mixing, the pH, and the coagulant dosage determine which hydrolysis species is effective for treatment.
Why are synthetic polymers more effective than flocculants?
They are, in general, more effective as flocculants because of the level of control made possible during manufacture. Important mechanisms relating to polymers during treatment include electrostatic and bridging effects.
Coagulation And Flocculation Definition
Coagulation and flocculation in water treatment is essential in water and wastewater treatment. Coagulation refers to the addition of coagulation agents with positive ions in wastewater.
Mechanism of coagulation and flocculation in Water Treatment
The action mechanism of the coagulant used in water treatment is to compress the electric double layer and neutralize the electricity. According to the nature of the turbidity substance formed in the raw water, the appropriate pH value should be controlled.
What is coagulation and how is it used in water treatment?
Coagulation is the process of adding specific chemicals to untreated water in order to destabilize the particles within the water. In most cases, aluminum sulfate or ferric chloride is added to achieve this. These particles have positive charges that are opposite to the negative charges of suspended particles within the water.
What is flocculation and how is it used in water treatment?
Flocculation is the process of encouraging the formation of flocs, or small clumps, from solids in the water. The water is mixed and activated slowly, allowing movement of particles and micro solid throughout the waste water treatment chamber.
Deploying coagulation and flocculation together in sequence
Where coagulation is found to be lacking — i.e., in creating large macro flocs that can be easily filtered and removed — flocculation can help. In areas where flocculation is inadequate by itself — for example, in targeting the particles that are suspended within the untreated water — coagulation is useful.
What is the difference between coagulation and flocculation?
The key difference between coagulation and flocculation in water treatment is that the coagulation is a chemical process while flocculation is a physical process.
What is the process of coagulation?
What is Coagulation? Coagulation, in simple terms, is referred to as curdling or clotting. In the chemical aspect, it could be explained as a process by which destabilizes the charges of particles which are not settling down. This is an important step in many different biochemical processes.
Why is coagulation important?
Coagulation and flocculation steps are important aspects in the context of drinking and wastewater treatment since it allows the separation of suspended particles present in water effectively. Coagulation is a chemical process and flocculation is a physical process, In coagulation, the process involves the utilization of a coagulant ...
How to achieve coagulation?
Coagulation could be achieved simply by adding a coagulant to the medium. This causes the clumping of particles. In respects to the chemistry of this procedure, adding a coagulant destabilizes the particle’s charges. This is achieved by adding a coagulant that possesses an opposite charge to that of the suspended solids.
What happens when coagulants are added to a coagulant?
Once the coagulants are added and the charges of the particles are neutralized, it allows the particles to interact with each other and stick together. These joined particles are referred to as microflocs. But these particles are not visible to the naked eye. This step is followed by flocculation.
Why is water treatment important?
Water treatment is an important aspect which involves many different steps. Since water treatment is a very sensitive and important process it requires the presence of both physical and chemical processes. Restoration of water quality is assured during water treatment. Coagulation and flocculation steps are important aspects in the context ...
What are some examples of coagulants?
Coagulants include inorganic salts of aluminum or iron . Examples are aluminum sulfate, aluminum chloride, alum and ferric sulfate.
How does flocculation work?
Flocculation follows coagulation in the conventional water treatment process. Flocculation causes the agglomeration or collection of small particles into larger, more readily settleable floc particles. It is usually a tapered process with two or more units in series. The first unit has a higher mix speed and the mixing speed decreases in subsequent basins to promote the growth of floc particles. The total detention time in the flocculation basin is normally 30 to 60 minutes. Through experience, we see that effective mixing reduces the required amount of chemicals and greatly improves the sedimentation process, which results in longer filter runs and higher quality finished water. The goal of flocculation is to form a uniform, feather-like material similar to snowflakes - a dense, clingy floc that traps the fine, suspended, and colloidal particles and carries them down rapidly in the settling basin. To increase the speed of floc formation and the strength and weight of the floc, polymers are often added.
Why is coagulation important in water treatment?
It is, however, an important primary step in the water treatment process, because coagulation removes many of the particles, such as dissolved organic carbon, that make water difficult to disinfect. Because coagulation removes some of the dissolved substances, less chlorine must be added to disinfect the water.
What is coagulation reaction?
cationic, anionic, and nonionic) and molecular weight. Coagulation is a reaction caused by adding salts of iron or aluminum to the water.
What is the purpose of coagulation?
The primary purpose of the coagulation/flocculation process is the removal of turbidity from the water. Turbidity is a cloudy appearance of water caused by small particles suspended therein. Water with little or no turbidity will be clear.
Why are adjustments necessary in water treatment plants?
In a well-run water treatment plant, adjustments are often necessary in order to maximize the coagulation/flocculation process. These adjustments are a reaction to changes in the raw water entering the plant. Coagulation will be affected by changes in the water's pH, alkalinity, temperature, time, velocity and zeta potential.
When operators determine the best coagulant dosage for the current raw water quality conditions based on jar tests and other
When operators determine the best coagulant dosage for the current raw water quality conditions based on jar tests and other lab data, they must be able to set the chemical feeders to apply the proper quantity of coagulant. As part of the routine, an operator must deal with preparing solutions from dry chemicals and for jar tests.
Does temperature affect coagulation?
The higher the temperature, the faster the reaction, and the more effective is the coagulation. Winter temperature will slow down the reaction rate, which can be helped by an extended detention time. Mostly, it is naturally provided due to lower water demand in winter. Time is an important factor as well.
Why is coagulation important in water treatment?
It is, however, an important primary step in the water treatment process, because coagulation removes many of the particles, such as dissolved organic carbon, that make water difficult to disinfect. Because coagulation removes some of the dissolved substances, less chlorine must be added to disinfect the water.
What is added to ferric chloride?
If ferric chloride is used, iron and chloride are added. And if aluminum sulphate is used, aluminum and sulphate are added. The majority of municipal water treatment plants use aluminum sulphate as the coagulation chemical. Generally, water treatment facilities have the coagulation process set up so that the coagulant chemicals are removed with ...
What is the most widely used water treatment technology?
Many water treatment plants use a combination of coagulation, sedimentation, filtration and disinfection to provide clean, safe drinking water to the public. Worldwide, a combination of coagulation, sedimentation and filtration is the most widely applied water treatment technology, and has been used since the early 20th century.
What is slow sand filtration?
that are used. Slow sand filtration removes bacteria, protozoa and viruses, and produces. essentially clean water, though it is still advisable to use a disinfectant as a precautionary. measure.
What is the difference between coagulation and flocculation?
The key difference between coagulation and flocculation in water treatment is that the coagulation is a chemical process while flocculation is a physical process.
What is the process of coagulation?
What is Coagulation? Coagulation, in simple terms, is referred to as curdling or clotting. In the chemical aspect, it could be explained as a process by which destabilizes the charges of particles which are not settling down. This is an important step in many different biochemical processes.
Why is coagulation important?
Coagulation and flocculation steps are important aspects in the context of drinking and wastewater treatment since it allows the separation of suspended particles present in water effectively. Coagulation is a chemical process and flocculation is a physical process, In coagulation, the process involves the utilization of a coagulant ...
How to achieve coagulation?
Coagulation could be achieved simply by adding a coagulant to the medium. This causes the clumping of particles. In respects to the chemistry of this procedure, adding a coagulant destabilizes the particle’s charges. This is achieved by adding a coagulant that possesses an opposite charge to that of the suspended solids.
What happens when coagulants are added to a coagulant?
Once the coagulants are added and the charges of the particles are neutralized, it allows the particles to interact with each other and stick together. These joined particles are referred to as microflocs. But these particles are not visible to the naked eye. This step is followed by flocculation.
Why is water treatment important?
Water treatment is an important aspect which involves many different steps. Since water treatment is a very sensitive and important process it requires the presence of both physical and chemical processes. Restoration of water quality is assured during water treatment. Coagulation and flocculation steps are important aspects in the context ...
What are some examples of coagulants?
Coagulants include inorganic salts of aluminum or iron . Examples are aluminum sulfate, aluminum chloride, alum and ferric sulfate.

Coagulation and Flocculation in Water and Wastewater Treatment
The Coagulants
- The commonly used metal coagulants fall into two general categories: those based on aluminum and those based on iron. The aluminum coagulants include aluminum sulfate, aluminum chloride and sodium aluminate. The iron coagulants include ferric sulfate, ferrous sulfate, ferric chloride and ferric chloride sulfate. Other chemicals used as coagulants include hydrated lime and magn…
Removal of Natural Organic Matter
- Natural organic material (NOM) is usually associated with humic substances arising from the aqueous extraction of living woody substances, the solution of degradation products in decaying wood and the solution of soil organic matter. These substances are objectionable for a number of reasons: they tend to impart color to waters; they act as a vehicle for transporting toxic substan…
Pathogen Removal
- The U.S. EPA surface water treatment rule requires 99.9-percent (3-log) Giardia removal or inactivation, and at least 99-percent (2-log) removal of Cryptosporidium. Adequately designed and operated water treatment plants, with coagulation, flocculation, sedimentation and filtration are assigned a 2.5-log removal credit for Giardia, leaving only 0.5-log inactivation to be achieved by …
Removal of Inorganics
- Coagulation operations can be useful in some cases for the removal of inorganics. Examples of successful applications are copper and mercury reductions from wastewaterplant effluents. Two applications discussed in more detail below are arsenic and fluoride removals in potable water treatment:
Wastewater Treatment
- Physical-chemical treatment of wastewater was widely practiced until the late 19th century, until the advent of the trickling filter for biological treatment. The early 1970s saw a partial revival of interest that has continued to the present day, particularly for treatment plants that are overloaded during peak flow events. The addition of coagulant chemicals to primary clarifiers, or to other de…
Factors Affecting Coagulation Operations
- Temperature
Temperature significantly affects coagulation operations, particularly for low turbidity waters, by shifting the optimum pH. This can be mitigated by operating at an optimum pOH as given by: pH + pOH = pKW; where pKW = 0.01706xT + 4470.99/T – 6.0875 and T = temperature in °K = 273.15 … - Sequence of chemical addition
Traditionally, the sequence of chemical addition for coagulation operations is to first add chemicals for pH correction, then add the metal coagulant, then add the flocculant aid. Not all these chemicals are necessarily added, but the sequence logic is often as described. However, t…
Rapid Mixing
- The rapid mixing stage is possibly the most important component of coagulation-flocculation processes, since it is here that destabilization reactions occur and where primary floc particles are formed, whose characteristics markedly influence subsequent flocculation kinetics. In general it is likely that the metal coagulant hydrolysis products that are formed within the tim…
Flocculation
- Orthokinetic flocculation arises from induced velocity gradients in the liquid. It is here that primary particles are induced to approach close enough together, make contact and progressively form larger agglomerates, or flocs. The principal parameter governing the rate of orthokinetic flocculation is the velocity gradient applied. The degree or extent of flocculation is g…
Testing and Control
- The efficiency of the coagulation-flocculation process is dependent on many variables. For a particular water these may include: 1. Type of coagulant used 2. Coagulant dosage 3. Final pH 4. Coagulant feed concentration 5. Type and dosage of chemical additives other than primary coagulant (e.g. polymers) 6. Sequence of chemical addition and time lag between dosing points …