Treatment Medication such as anthelmintics (dewormers) may be used to kill off the parasites, but they may also lead to other complications. Consult your veterinarian for the best course of treatment.
Full Answer
Could My Cat have a brain tumor?
They can even get many of the same types of cancer that humans get – including brain cancer. The most common form of brain cancer in cats is a meningioma or a glioma. Older pets (five or more years old) have a higher risk of getting cancer and both sexes are equally vulnerable.
What are symptoms of brain tumor in cats?
Signs of Brain Tumors in Cats
- Excessive pacing and circling
- Eyesight problems
- Seizures
- Disturbed sleep patterns
- Head tilt
- Balance issues
- Weakness
What are the signs of parasites in cats?
Symptoms of infection with worms in cats include the following manifestations:
- First, vomiting occurs. At first it is rather mild, but soon its attacks become regular and very strong. ...
- Rapid weight loss. ...
- The cat becomes inactive, prefers to sit more often and do not move again.
Does your cat have parasites?
Whether they live exclusively indoors or spend time outside, pet cats may become host to internal parasites such as roundworms, tapeworms, and hookworms. Kittens often pick up worms from the mother in her milk, while adult cats pick up worms by accidentally eating worm eggs or eating vermin infested with worms.

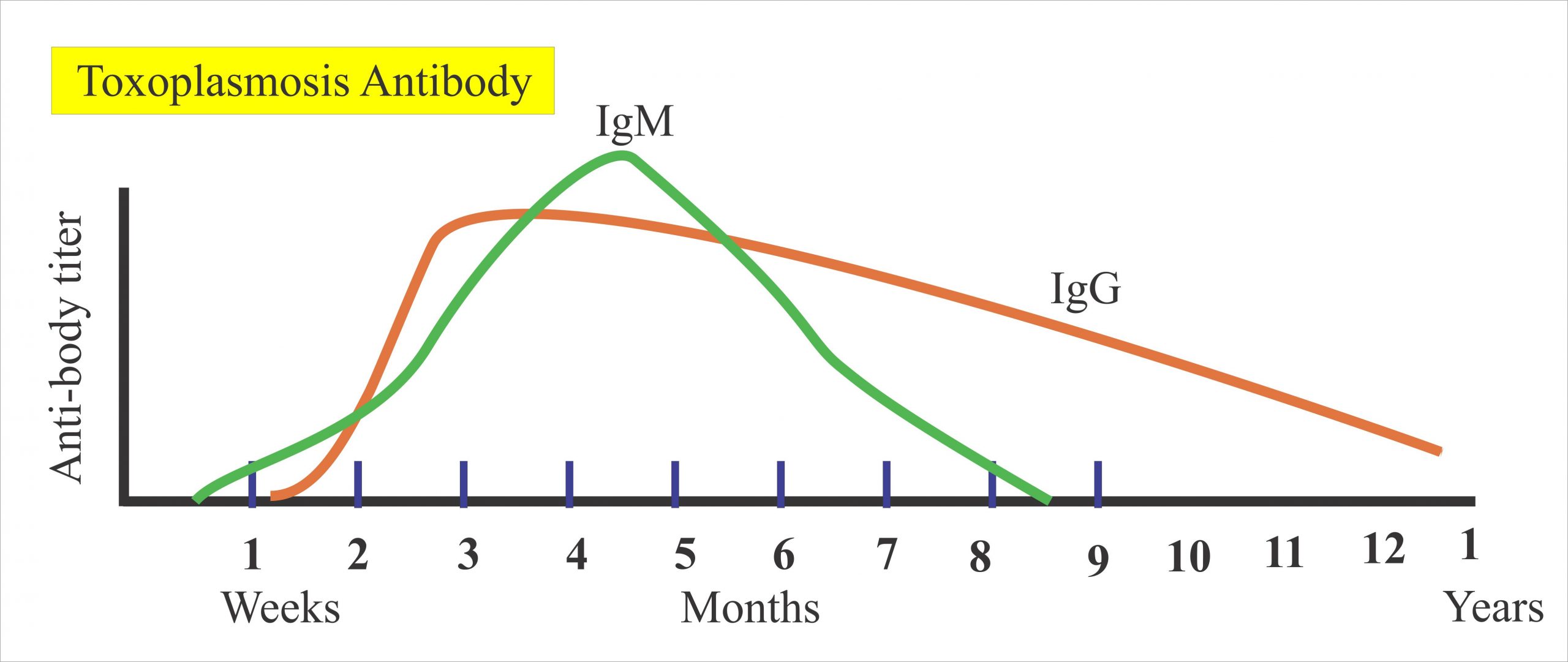
How is toxoplasmosis treated in the brain?
Co-trimoxazole (trimethoprim plus sulfamethoxazole) is the most common drug used in India for the treatment of AIDS-associated cerebral toxoplasmosis. Other alternative drugs used for the treatment of cerebral toxoplasmosis are clindamycin plus pyrimethamine and clarithromycin with pyrimethamine.
How do you get rid of toxoplasmosis in humans?
Most healthy people recover from toxoplasmosis without treatment. Persons who are ill can be treated with a combination of drugs such as pyrimethamine and sulfadiazine, plus folinic acid.
Can you get brain parasites from cats?
No, but they may make you less afraid of risk. There's a single-celled parasite called Toxoplasma gondii, and it can turn a normally risk-averse mouse into a bold, cat-seeking rodent. Cats that devour such mice can then pass the parasite onto humans.
Does toxoplasmosis go away in humans?
For most people, toxoplasmosis will go away without treatment after a few weeks or months. But those people requiring treatment may need to stay on medication for weeks or months for the infection to clear. How is toxoplasmosis transmitted to humans?
What is the best treatment of toxoplasmosis?
Pyrimethamine, considered the most effective drug against toxoplasmosis, is a standard component of therapy. Pyrimethamine is a folic acid antagonist and can cause dose-related suppression of the bone marrow, which is mitigated by concurrent administration of folinic acid (leucovorin).
How long is treatment for toxoplasmosis?
Table 1Clinical entityTreatmentDurationFetal toxoplasmosisCombination 1 + 2 + 3Until delivery1. PYR2. SDZ3. FA5 more rows
How do you test for brain parasites?
Diagnosis may require blood tests and/or imaging studies. Diagnosis of neurocysticercosis is usually made by MRI or CT brain scans. Blood tests are available to help diagnose an infection, but may not always be accurate.
What does cat do to your brain?
Cat is a stimulant, that is the effect it has on the brain which causes a person to feel high. Cat increases the level of dopamine, the neurotransmitter which makes you feel good. It also stimulates the release of the stress hormone norepinephrine, which makes you more alert.
What brain disease can you get from cats?
Untreated, these infections can lead to blindness. But if your immune system is weakened, especially as a result of HIV / AIDS , toxoplasmosis can lead to seizures and life-threatening illnesses such as encephalitis — a serious brain infection. In people with AIDS , untreated encephalitis from toxoplasmosis is fatal.
Will an MRI show parasites?
X-ray, Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) scan, Computerized Axial Tomography scan (CAT)These tests are used to look for some parasitic diseases that may cause lesions in the organs.
Is there a vaccine for toxoplasmosis?
Toxovax, a live-attenuated vaccine based on the tachyzoites of T. gondii S48 strain, is currently the only commercially available toxoplasmosis vaccine [7].
How do they test for toxoplasmosis in humans?
To find out if you have toxoplasmosis, your doctor can do a blood test to see if you have those antibodies. If you've been infected recently, your body may not have had time to make them. So even if your test doesn't show any signs of them, your doctor may want to do another test a few weeks later to be sure.
What is the parasite that can turn a mouse into a cat?
There's a single-celled parasite called Toxoplasma gondii, and it can turn a normally risk-averse mouse into a bold, cat-seeking rodent. Cats that devour such mice can then pass the parasite onto humans.
What is the effect of Toxoplasma gondii on cats?
To aid this transition from vermin to feline host, Toxoplasma gondii has a pretty disturbing technique: brain manipulation. The parasite alters the behavior of rodents, making them less afraid of taking risks. It is also known to make mice attracted to the scent of cat poop.
Why do cats eat rodents?
That's likely because cats prey on rodents, giving the parasite a way to reach the cat gut — the only known place where the parasite can reproduce, as cat guts are rich in linoleic acid, an ingredient necessary for Toxoplasma gondii sex, a 2019 study posted on the preprint database bioRxiv found. To aid this transition from vermin ...
What is the working theory of Toxoplasma gondii?
The working theory is that Toxoplasma gondii is manipulating people's brains into making them less afraid of quitting their jobs and going it alone to start up their own company. "We can't say for sure this is what's happening," said Fitza.
What does a car crash do to the brain?
The researchers behind the car crash studies, however, wrote that the parasite leaves behind life-long cysts in the brain, which is thought to increase the production of dopamine (a chemical messenger in the brain that is known to affect people's risk and reward calculations ), and that may have a role to play.
How many times more likely are business majors to test positive for parasites than biology majors?
The results showed that business majors were 1.4 times more likely to test positive for the parasite than biology majors, and within business majors, those specializing in entrepreneurship were 1.7 times more likely to test positive over students in less risky business studies subspecialties.
Do humans have toxoplasma gondii?
Humans are not immune to Toxoplasma gondii — in fact, at least a third of the world's population is thought to have toxoplasmosis, the infection this parasite causes.
What is the parasite that controls our brains?
Over the past year, a Czech evolutionary biologist named Jaroslav Flegr has made headlines for a radical claim: that a common parasite called Toxoplasma gondii is controlling our brains. "Toxo," which typically infects cats, is famous among scientists for its clever tactic of jumping from one cat to another by infecting rats ...
What cells does toxo destroy?
In order to travel throughout the body and, most importantly, to the brain, toxo hijacks the very cells designed to destroy foreign invaders: the white blood cells .
Can a parasite cause a miscarriage?
For most people, the parasite causes no obvious problems. Pregnant women must be careful, though; the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention warns that women infected during pregnancy face increased risk of miscarriage or birth defects.
Does toxo cause schizophrenia?
discovered that toxo has two genes for making l-DOPA, the precursor molecule to dopamine. Elevated levels of dopamine are associated with schizophrenia. This research told a piece of the story but left many questions.
What is the immune system called when a parasite attacks the brain?
These immune cells are called microglia and they help take down the parasite before it can wage war on the brain. When fighting the parasite, microglia burst, releasing a unique immune molecule called IL-1α that recruits immune cells from the blood to control the parasite in the brain. This keeps people from ever developing symptomatic ...
How many people are infected with brain parasites?
A brain parasite infects millions of people. A new study reveals why most don't get sick. Across the globe, many cat owners pick up a pet-linked parasite without ever knowing. In the United States alone, more than 40 million Americans are infected with Toxoplasma gondii — a brain parasite that's spread by eating undercooked, contaminated meat, ...
What is the role of microglia in the brain?
Brain burst — To unravel microglia's role in defending the brain, researchers infected mice with Toxoplasma gondii. Then the team mapped the mice's brain responses and immune signaling, honing in on microglia. After detailed analysis, the team discovered that the parasite infection caused microglia to die in an inflammatory fashion.
How to reduce exposure to Toxoplasma gondii?
To reduce exposure, cook food well, change the litter box often, and if pregnant, avoid contact with cat poo. Abstract: Microglia, resident immune cells of the CNS, are thought to defend against infections. Toxoplasma gondii is an opportunistic infection that can cause severe neurological disease.
Does parasite affect mental health?
Long-term research debunks these strange claims, showing the parasite does not cause population-wide mental health effects. But, in rare cases, the infection can cause acute, and sometimes devastating health consequences, especially if someone is immunocompromised.
Can microglia help with Alzheimer's?
These findings go far beyond cat lovers. Researchers say understanding microglia's defense capabilities could lead to better ways of treating other brain infections , including neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's, and autoimmune disorders, like multiple sclerosis and strokes.
Can microglia release IL-1?
gondii infection, microglia can release the alarmin IL-1α, promoting neuroinflammation and parasite control.
What diseases can protozoans cause?
While the protozoan invader poses the greatest risk to developing foetuses infected in the womb, new research suggests the parasite could alter and amplify a range of neurological disorders, including epilepsy, Alzheimer's, and Parkinson's, and also cancer.
Is cat litter harmful to humans?
While healthy adults are generally considered not at risk from the parasite – with the exception of pregnant women, who are advised to stay well clear of cat litter – the organism has previously been tied to behaviour-altering disorders, and evidence suggests it can also rewire how our immune system functions.
Is the lodger parasite dangerous?
PETER DOCKRILL. 14 SEPTEMBER 2017. The brain-dwelling parasite Toxoplasma gondii is estimated to be hosted by at least 2 billion people around the world, and new evidence suggests the lodger could be more dangerous than we think. While the protozoan invader poses the greatest risk to developing foetuses infected in the womb, ...
Can T. gondii cause brain disease?
To be clear, the researchers aren't saying the brain parasite is definitively what's behind people developing these debilitating illnesses, but it's possible that T. gondii 's protein-based meddling in the brain environment could possibly influence or enable pre-existing susceptibilities in some people to these kinds of diseases.
How to diagnose brain parasites in cats?
A veterinarian can diagnose brain parasites by confirming the presence of the parasite, its larvae, or its eggs in your pet’s system if clinical signs point to the condition. Other diseases and disorders can cause similar symptoms, so your veterinarian may need to conduct several tests to rule out other ...
Why does my cat have brain parasites?
Brain parasites enter your cat’s system much the same way as any parasite. The most common cause is ingestion, usually through a food source like raw meat or wildlife. Risk factors include spending time outdoors, living in cramped quarters with other animals, and unmonitored eating habits.
What are the different types of parasites?
Various types of parasites can make their way into the brain and related tissues. Parasites that can be found in the central nervous system include: 1 Flukes – two types of these parasitic creatures can make their home in the brain. Schistosomes, or blood flukes, and Paragonimus, or lung flukes, have both been found in the central nervous system. 2 Roundworms – this common type of parasite affects various regions of the body, including the brain and spinal column. Varieties that can infest the brain include, Baylisascaris procyonis which can cause brain and eye damage, Dirofilaria immitis or heartworm, and Gurlita paralysans, which causes paralysis. 3 Myiasis – these are infestations related to insect larvae, and include Cuterebra or botfly larvae, which pets are susceptible to in the summer months in regions where the botfly is found. 4 Toxoplasma gondii – this single-celled parasite can also infest brain tissues, causing issues. It is commonly present throughout the world and can be passed from cat to human and vice versa.
What parasites can cause paralysis?
Varieties that can infest the brain include, Baylisascaris procyonis which can cause brain and eye damage, Dirofilaria immitis or heartworm, and Gurlita paralysans , which causes paralysis.
What are the symptoms of a cat with a parasite infestation?
Symptoms Include: Unsteady gait (ataxia) Loss of muscle control. General weakness.
What happens when a parasite lays its eggs?
Once inside your pet, the parasite takes full advantage of its host, growing to maturity and laying its own eggs, which further the infestation. When the adult parasites, larvae, or eggs find their way through the bloodstream or nasal passages into the central nervous system, they can cause damage to the brain and other related systems. ...
What parasites are found in the brain?
Parasites that can be found in the central nervous system include: Flukes – two types of these parasitic creatures can make their home in the brain. Schistosomes, or blood flukes, and Paragonimus, or lung flukes, have both been found in the central nervous system.
What is the best treatment for toxoplasmosis?
Treatment is recommended for people with serious health problems, such as people with HIV whose CD4 counts are under 200 cells/mm 3. Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole is the drug of choice to prevent toxoplasmosis, but not for treating active disease.
How is toxoplasmosis spread?
Toxoplasmosis is usually spread by eating poorly cooked food that contains cysts, exposure to infected cat feces, and from an infected mother to her baby during pregnancy . Rarely, the disease may be spread by blood transfusion. It is not otherwise spread between people.
What is the disease caused by Toxoplasma gondii?
Toxoplasmosis is a parasitic disease caused by Toxoplasma gondii, an apicomplexan. Infections with toxoplasmosis usually cause no obvious symptoms in adults. Occasionally, people may have a few weeks or months of mild, flu-like illness such as muscle aches and tender lymph nodes.
Can you get T. gondii without knowing?
Due to the absence of obvious symptoms, hosts easily become infected with T. gondii and develop toxoplasmosis without knowing it. Although mild, flu-like symptoms occasionally occur during the first few weeks following exposure, infection with T. gondii produces no readily observable symptoms in healthy human adults. In most immunocompetent people, the infection enters a latent phase, during which only bradyzoites ( in tissue cysts) are present; these tissue cysts and even lesions can occur in the retinas, alveolar lining of the lungs (where an acute infection may mimic a Pneumocystis jirovecii infection), heart, skeletal muscle, and the central nervous system (CNS), including the brain. Cysts form in the CNS ( brain tissue) upon infection with T. gondii and persist for the lifetime of the host. Most infants who are infected while in the womb have no symptoms at birth, but may develop symptoms later in life.
