Some of the barriers related to mental health care are the stigma [ 6 ], treatment cost, lack of knowledge, and isolation [ 7 ]. Other studies indicated that stigma is an insignificant barrier [ 8 ]. Mental disorders affect the person diagnosed and the family.
Full Answer
What are the barriers to mental health treatment?
Attitudinal barriers to treatment are the ones most commonly reported in these studies (Jagdeo et al., 2009; Sareen et al., 2007), mainly due to negative health beliefs (Prins et al., 2008), misinterpretations about consequences of treatment, and stigma.
How important are attitudinal barriers in the management of serious illness?
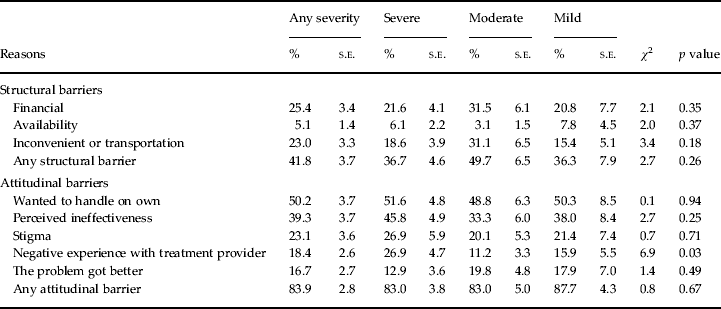
It is striking that attitudinal barriers were more important among serious than moderate or mild cases in most of the countries. This presumably reflects the fact that serious cases are likely to recognize need and would seek care in the absence of attitudinal barriers.
What are the world mental health surveys?
The World Mental Health (WMH) Surveys represent a unique opportunity to do this across countries with different levels of development, health policy, and delivery systems.
What is the prevalence of structural barriers in the US?
Structural barriers were never most commonly-reported, but were second most commonly-reported among respondents with serious disorders in 8 surveys (44.0-0.7%) and among respondents with moderate/mild disorders in 3 surveys (28.0-0.4%). Table 2

What are the barriers to mental health treatment?
We discuss six common barriers below.Desire to Receive Care. ... Lack of Anonymity When Seeking Treatment. ... Shortages of Mental Health Workforce Professionals. ... Lack of Culturally-Competent Care. ... Affordability of Care. ... Transportation to Care. ... Resources to Learn More.
What are the three biggest barriers to treatment for mental illness?
Lack of awareness, social stigma, cost, and limited access are some of the most prominent factors standing in the way of people pursuing mental health treatment.
What are the barriers to improving treatment outcomes for the mentally ill?
(1) Common barriers to mental health care access include limited availability and affordability of mental health care services, insufficient mental health care policies, lack of education about mental illness, and stigma.
What is the greatest barrier to receiving mental health treatment?
Low perceived need and attitudinal/evaluative barriers are the major barriers to treatment seeking and staying in treatment among individuals with common mental disorders.
What are examples of barriers to treatment?
What Are Common Barriers to Treatment ProgressFear.Unclear communication between a therapist and client.Severe symptoms.Substance use.Distractions.
What major challenges are still associated with mental health coverage?
Despite patient interest, access to mental healthcare is left wanting due to limited clinician availability and cultural stigma.Mental health clinician shortage.Limited mental health access parity.Fragmented mental and physical health access.Social stigma and limited mental health awareness.
What are the main sources of and barriers to help-seeking among individuals with mental health problems?
Barriers to help-seeking can include difficulties in accessing support, concerns about confidentiality and trust, a preference for informal sources of help, and stigma.
What are barriers to intervention?
The barriers were conceptualized at three levels: health-care provider (HCP), patient, and unit. Commonly mentioned barriers were time constraints and workload (HCP), patient clinical acuity and their perceived 'sick role' (patient), and lack of proper equipment and human resources (unit level).
Why do people not get treatment for mental illness?
While there are multiple reasons why, one is the fact that people avoid or forego mental health treatment, due to judgment, doubt, pride, fear, misinformation. Individuals fear judgment, change, the unknown, and what they might discover in therapy; additionally, they're too prideful to admit they need help.
Which states have higher barriers to accessing mental health care?
States that are ranked 1-13 have lower prevalence of mental illness and higher rates of access to care for adults. States that are ranked 39-51 indicate that adults have higher prevalence of mental illness and lower rates of access to care....Statistical Data.RankState17Maine18Arizona19Wisconsin20West Virginia47 more rows
What are institutional barriers in counseling?
Institutional barriers (IBs) are policies, procedures, or situations that systematically disadvantage certain groups of people.
What do you believe are some barriers for nonwhites seeking or entering into therapy?
But for members of ethnic and racial minority groups, the road to treatment is often blocked by cultural views of mental illness and therapy, lack of insurance and access to appropriate care, and a critical deficiency of studies pertaining to nonwhite populations.
What are the barriers to mental health?
Barriers to mental health treatment: results from the WHO World Mental Health surveys. Low perceived need and attitudinal barriers are the major barriers to seeking and staying in treatment among individuals with common mental disorders worldwide.
Who is more likely to recognize a need for treatment?
Women and younger people with disorders were more likely to recognize a need for treatment. A desire to handle the problem on one's own was the most common barrier among respondents with a disorder who perceived a need for treatment (63.8%).
Who is the WMH survey?
The WHO WMH Survey Initiative is supported by the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH; R01 MH070884), the John D. and Catherine T. MacArthur Foundation , the Pfizer Foundation, the US Public Health Service (R13-MH066849, R01-MH069864 and R01 DA016558), the Fogarty International Center (FIRCA R03-TW006481), the Pan American Health Organization, Eli Lilly and Company, Ortho-McNeil Pharmaceutical, GlaxoSmithKline and Bristol-Myers Squibb. We thank the staff of the WMH Data Collection and Data Analysis Coordination Centers for assistance with instrumentation, fieldwork and consultation on data analysis. None of the funders had any role in the design, analysis, interpretation of results or preparation of this paper. A complete list of all within-country and cross-national WMH publications can be found at www.hcp.med.harvard.edu /wmh/.
Who is more likely to recognize a need for treatment?
Women and younger people with disorders were more likely to recognize a need for treatment. A desire to handle the problem on one's own was the most common barrier among respondents with a disorder who perceived a need for treatment (63.8%).
How many countries have WMH?
Twenty-five WHO WMH surveys were carried out in 24 countries [two surveys in the People's Republic of China (PRC)]: six low- and lower-middle-income countries (Colombia, India, Iraq, Nigeria, PRC and Ukraine), six upper-middle-income countries (Brazil, Bulgaria, Lebanon, Mexico, Romania and South Africa) and 12 high-income countries (Belgium, France, Germany, Italy, The Netherlands, Spain, Japan, New Zealand, Israel, Northern Ireland, Portugal and the USA) ( Table 1 ). Seventeen surveys were based on nationally representative household samples, two (Colombia and Mexico) on samples representative of urban areas, one of selected states (Nigeria) and the remaining four of selected metropolitan areas (Brazil, India, Japan and PRC). In the latter cases, the surveys represented either only one area (São Paulo in Brazil, Pondicherry in India), three areas (Beijing, Shanghai and Shenzhen in PRC) or 11 different areas (Japan). We refer to these areas as São Paulo, Pondicherry, PRC – Beijing/Shanghai, PRC – Shenzhen and Metropolitan Japan to distinguish them from the more broadly representative nation samples in other countries. Trained lay interviewers conducted face-to-face interviews with respondents aged ⩾18 years in all surveys. Respondents were selected using multistage household probability samples. The total sample size was 121 899. The weighted average response rate across all countries was 72.0%. All surveys were approved by the local human subjects committee.
Abstract
Background. To examine barriers to initiation and continuation of mental health treatment among individuals with common mental disorders.
Fingerprint
Dive into the research topics of 'Barriers to mental health treatment: Results from the WHO World Mental Health surveys'. Together they form a unique fingerprint.
How many countries are there in the WMH survey?
The WMH surveys are representative community surveys that were carried out in 28 countries throughout the world aimed at providing information to mental health policy makers about the prevalence, burden, and unmet need for treatment of common mental disorders.
What is the WMH?
The WMH results regarding impairments are being used to target several such interventions. The World Mental Health (WMH) Survey Initiative is a WHO initiative designed to help countries carry out and analyze epidemiological surveys of the prevalence and correlates of mental disorders.
What is a good argument for expansion of treatment?
A good argument could be made based on the results about treatment effectiveness that an expansion of treatment would be a human capital investment opportunity from the employer perspective. The same argument could be made about human capital consequences of expanded treatment from a societal perspective.
Do mental disorders go untreated?
Despite this burden, the majority of mental disorders go untreated. Although these results suggest that expansion of treatment could be cost-effective from both the employer perspective and the societal perspective, treatment effectiveness trials are needed to confirm this suspicion.