Top10homeremedies.com
1. Manage Stress...
2. Regulate Vitamin D Levels...
3. Follow an Exercise Regimen...
4. Choose Ginger Decoctions...
5. Try Turmeric Tea...
6. Relieve Your Airways with Garlic...
7. Drink a Cup of Coffee to Dilate the Airways...
8. Take Fish Oil to Reduce Inflammation...
Learn More...Allremedies.com
1. Ginger...
2. Coffee...
3. Mustard Oil...
4. Garlic...
5. Figs...
6. Eucalyptus Oil...
7. Onions...
Learn More...Which is worse, asthma or COPD?
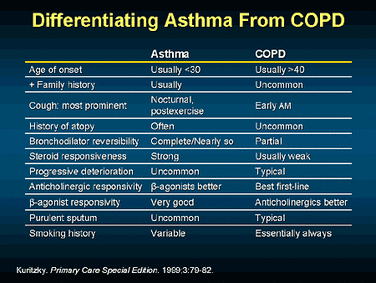
With a prompt diagnosis and treatment, asthma can be well controlled. Some children may even outgrow the condition as they get older. COPD, on the other hand, is considered to be a progressive condition, which means it typically gets worse over time. Even with treatment, lungs damaged by COPD can’t return to normal.
Is COPD different from asthma?
Since asthma and COPD both make your airways swell, they both can cause: One main difference is that asthma typically causes attacks of wheezing and tightness in your chest. COPD symptoms are usually more constant and can include a cough that brings up phlegm.
How does asthma affect COPD?
- Pathology is different in exacerbation of asthma and COPD
- Causes of acute exacerbation of asthma and COPD are different.
- Different role of LABA ( long-acting β-2 agonists) and ICS (inhalatory corticosteroids) in prophylaxis of exacerbation of asthma and COPD.
- Treatment of acute exacerbation is similar in asthma and COPD.
Can you have asthma and COPD together?
The answer to this question is yes. Some people have asthma prior to developing COPD, while others who have COPD may be at risk for developing asthma too. When people have both asthma and COPD, it is called overlap syndrome. It is sometimes referred to as asthma chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or ACOS for short. 2

Is there a difference between asthma and COPD?
COPD is characterized by decreased airflow over time, as well as inflammation of the tissues that line the airway. Asthma is usually considered a separate respiratory disease, but sometimes it's mistaken for COPD. The two have similar symptoms. These symptoms include chronic coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath.
Which is worse COPD or asthma?
COPD is worse than asthma. With a well-designed treatment plan, asthma symptoms can be controlled sufficiently to return lung function to normal, or very close to normal, so the condition is generally considered reversible.
How do you differentiate asthma and COPD based on its pathophysiology and treatment?
Different pathophysiology Although asthma and COPD are both chronic inflammatory lung disorders, perhaps the most important difference between them is the nature of the inflammation that occurs. In asthma, inflammation is mainly caused by eosinophils, whereas in COPD neutrophils are involved.
How is asthma and COPD treated?
Treatment OptionsLow-dose inhaled corticosteroid (ICS) A common long-term control medicine for asthma that treats the ongoing inflammation in the airways.Long-acting bronchodilator (LABA) ... Long-acting muscarinic agonist (LAMA)
What is the best treatment for COPD?
For most people with COPD, short-acting bronchodilator inhalers are the first treatment used. Bronchodilators are medicines that make breathing easier by relaxing and widening your airways. There are 2 types of short-acting bronchodilator inhaler: beta-2 agonist inhalers – such as salbutamol and terbutaline.
Can inhalers make COPD worse?
Aug. 15, 2008 -- For the first time, a major study shows that currently available inhaled medications can slow the deadly loss of lung function in COPD -- chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
How can you tell the difference between asthma and COPD on spirometry?
Also, like asthmatics, patients with COPD will have a reduction in their ability to exhale, and will show reductions in airflow when tested with spirometry. However, unlike asthmatic patients, COPD patients will not be able to completely correct their lung function even with treatment.
Can Ventolin help COPD?
There are several short-acting bronchodilators for COPD. These include: Albuterol (Ventolin®, Proventil®, AccuNeb®) Albuterol sulfate (ProAir® HFA®, ProAir RespiClick)
Can COPD be reversed with exercise?
Exercise can improve the way that you feel, breathe, and function. Although exercise has been shown to improve the lives of people who have COPD, it will not cure or reverse your condition.
Is medication for asthma and COPD the same?
COPD is treated with some of the same medicines as asthma, while others are different. Bronchodilators relax the muscles of your airways. Corticosteroids ease swelling inside your airways. Phosphodiesterase-4 (PDE4) inhibitors bring down swelling in your lungs to prevent COPD flare-ups.
Can you use asthma medication for COPD?
Several twice-daily fixed-dose inhaled corticosteroid (ICS)–LABA combinations are now on the market for asthma and COPD maintenance therapy, including fluticasone propionate–salmeterol, budesonide–formoterol, beclomethasone dipropionate–formoterol, and mometasone–formoterol, with one once-daily combination of ...
Is asthma under the COPD umbrella?
“Emphysema, chronic bronchitis, and refractory (non-reverse) asthma are three conditions that fall under the umbrella of COPD,” says Dr. Pietrantoni, explaining these conditions. Emphysema. Damage to the alveoli (tiny air sacs in the lungs), causes emphysema.
How long does COPD last?
This means that symptoms may appear to some degree all the time. Periods between asthma attacks may last days, weeks, months, or even years. In this way, asthma can seem to go into remission in some people. COPD flare-ups may also be periodic in this way.
What is it called when you have asthma?
When people living with asthma experience symptoms they are generally referred to as asthma attacks. When people living with COPD experience new or worsening symptoms they are generally referred to as COPD flare-ups. Asthma symptoms are completely or almost completely reversible with time or treatment.
Which immune system cells cause inflammation in the airway?
There are two types of immune cells that cause airway inflammation: eosinophils and neutrophils. Both may be present in asthma and COPD. But, asthmatic inflammation is usually associated with eosinophils and COPD inflammation is usually associated with neutro phils. 3,4.
Is asthma reversible?
Asthma symptoms are completely or almost completely reversible with time or treatment. COPD symptoms are only partially reversible or not reversible at all. 1. Asthma symptoms only occur during asthma attacks. COPD symptoms may be present to some degree all the time.
Is COPD a progressive disease?
But, COPD does not go into remission. Asthma usually does not progress over time. COPD is generally considered a progressive disease. But, this progression may be slowed (sometimes significantly) with a proper diagnosis and aggressive treatment.
Is asthma genetic or hereditary?
This is often referred to as genetic COPD. Therefore, most cases of asthma are said to be hereditary or genetic. At the present time, only 5% of people with COPD have genetic COPD.
Is asthma a disease?
Today, asthma is a disease entity on its own. And, as a twist, COPD is now considered an umbrella term. The two most common diseases that fall under the umbrella of COPD are chronic bronchitis and emphysema. COPD is never asthma. But, sometimes asthma can become COPD.
What are the similarities and differences between asthma and COPD?
They are two different diseases with differences in etiology, symptoms, type of airway inflammation, inflammatory cells, mediators, consequences of inflammation, response to therapy , course.
What is COPD characterized by?
COPD is characterized by chronic airflow limitation and a range of pathological changes in the lung, some significant extra-pulmonary effects and important co-morbidities which may contribute to the severity of the disease in individual patient (27, 28).
What is the pulmonary disease that affects millions of people?
Bronchial asthma and COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease) are obstructive pulmonary diseases that affected millions of people all over the world.
What is the goal of asthma treatment?
The GOAL of treatment in ASTHMA is to:reduce inflammation and to achieve¸total control (1). The GOAL of treatment in COPD is to:reduce symptoms, prevent exacerbations and decrease mortality (24). In both asthma and COPD almost the same drugs are used, but not in the same order and the same efficiency in treatment.
What is the name of the chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways?
Different course. 2. ASTHMA . Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways (1).The chronic inflammation is associated with airway hyperresponsiveness that leads to recurrent episodes of wheezing, breathlessness, chest tightness and coughing, particularly at night or in early morning (1, 2).
Which structural cells are involved in the pathogenesis of asthma?
Airway structural cells involved in the pathogenesis of asthma are: airway epithelial cells, airway smooth muscle cells, endothelial cells, fibroblasts and myofibroblasts and airway nerves (13, 14, 22, 23). 3. COPD. COPD is one of the major causes of chronic morbidity and mortality worldwide.
What are the factors that influence asthma?
The first include host factors (which are primarily genetic) and second are usually environmental factors (4, 5, 6).
How does COPD treatment work?
Its aim is to prevent the progression of the disease, relieve the symptoms, improve the patient’s health status, prevent/minimize and treat the exacerbations and complications, improve the tolerance to physical activities, reduce mortality.
What are the medications used for COPD?
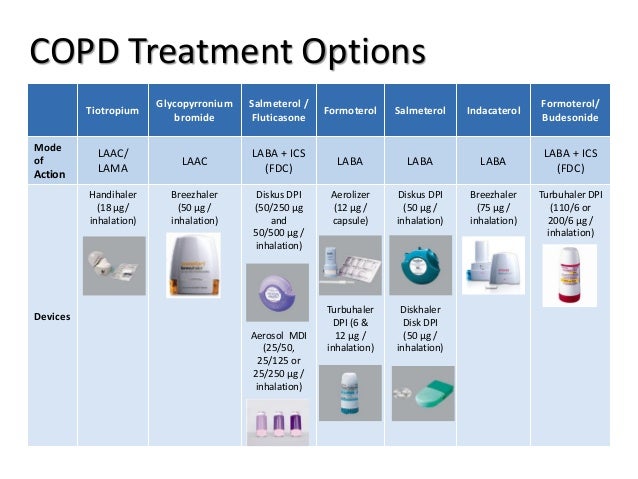
The following medications are used in COPD: Long-acting bronchodilators – preparations of the group of Methylxanthate and long-acting beta2-receptor agonists (Theophylline, Noviline, Formoterol, Salmeterol), providing prolonged dilatation of the bronchial tree.
What are the best medications for asthma?
The medications used in asthma are: 1 Inhaled corticosteroids – the “gold standard” in asthma treatment. They provide relieve of chronic inflammation and suppress the allergic reaction. In severe forms of asthma, as well as during a severe asthma attack, they may be administered orally or intravenously. 2 Long-acting bronchodilators – preparations of the group of Methylxanthate and long-acting beta2-receptor agonists (Theophylline, Noviline, Formoterol, Salmeterol). They provide prolonged dilatation of the bronchial tree and prevent the night attacks. 3 Anti-allergic stabilizers – used in the prophylaxis of asthma attacks – Cromoglycates, Ketotifen. 4 Leukotriene antagonists – a relatively new class of drugs used in the therapy of asthma – Montelukast, etc. 5 Additional treatment– treatment of the prerequisites for the onset of asthma and its complications – antibiotics, mucolytics, secretolytics, treatment of reflux disease, etc.
What is the aim of asthma treatment?
Its aim is to prevent the progression of the disease, relieve the symptoms, improve the patient’s health status, prevent/minimize and treat the exacerbations and complications, improve the tolerance to physical activities, reduce mortality . Asthma’s treatment is driven by the need to avoid/minimize asthma attacks.
What are the factors that trigger asthma attacks?
Factors, triggering asthma attacks, can be different for every patient. The attacks can be triggered by pets, pollen, dust, etc. For patients with asthma it is very important to avoid their personal triggers. The medications used in asthma are: Inhaled corticosteroids – the “gold standard” in asthma treatment.
What is the most important thing to do for COPD?
The most important thing is to quit smoking. Asthma Treatment: For patients with asthma it is important to avoid their personal triggers.
What is the aim of a pulmonary stent?
The aim of the treatment is to: Prevent the progression of the disease; Relieve the symptoms; Improve the patient’s health status; Prevent/minimize and treat the exacerbations; Maintain the function of the lungs as close to normal as possible; Maintain the physical activity levels as close to normal as possible;
What are the symptoms of COPD compared to asthma?
Symptoms felt are similarly, such as shortness of breath, chest tightness, and coughing. Even the medicines used are similar. But, they are two different diseases with different treatment strategies. Here is a list of medications used to treat COPD compared with asthma.
What are some examples of COPD inhalers?
Combining these two long-acting bronchodilators seems to work well for some people with COPD. Examples include umeclidinium and vilanterol (Anoro). Tiotropium bromide and olodaterol (Stiolto), and glycopyrrolate and indacaterol (utibron). These are all inhalers taken once or twice daily.
What is an ICS inhaler?
ICS inhalers are the most basic asthma controller medicines. One of these is usually the first medicine chosen to control asthma. ICS plus Long-Acting Bronchodilator (LABA): These are combination inhalers containing the two medicines. The ICS works to reduce underlying airway inflammation.
What is ICS in asthma?
Controller. These are medicines meant to prevent and control symptoms. These include one of the following types of inhalers. Inhaled corticosteroids (ICS). These help to reduce and control underlying airway inflammation. These work to make airways less twitchy or less sensitive to asthma triggers.
What is the goal of asthma treatment?
The goal of any asthma treatment regimen is to control asthma. Good asthma control means that symptoms are rare and mild and easy to reverse when they do occur. It also means that you are able to maintain your normal activity level between asthma episodes. You should be able to do most of the things you enjoy doing. 1.
Is tiotropium bromide good for COPD?
Again, they are usually only prescribed for COPD. Examples include tiotropium bromide (Spiriva), umeclidinium (Incruse), glycopyrrolate (Seebri), and aclidinium bromide (Tudorza. These are all inhalers. Theophylline. This is a pill taken daily that is also a good bronchodilator.
Do asthmatics need to take medicine?
With good asthma control these should rarely be used. However, it is recommended that all asthmatics have access to reliever medicine at all times to relieve symptoms when they do occur.
What is asthma in the lungs?
Asthma is a condition where the airways of the lungs are hyperresponsive—they overreact— to a specific trigger such as allergens (including to pet dander, dust mites, or pollen), cold air, or exercise.
Why do people get COPD?
COPD usually comes on later in life. It is caused by decades of smoking cigarettes, or exposure to other pollutants. Or it can be caused by an inherited genetic condition called alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency. Asthma can affect children, teenagers, and adults and not the result of long term exposures.
Can you have both asthma and COPD?
Some people can have both asthma and COPD. It’s called asthma-COPD overlap syndrome (ACOS). Symptoms of ACOS include chest tightness, coughing with a mixture of saliva and mucus, and wheezing. It’s important to discuss the right treatment plan for you with your doctor.
How are asthma and COPD similar?
There are a number of ways that asthma and COPD are similar. This is what results in most of the confusion between the two different conditions. For example: 1 1 Both are chronic respiratory conditions with no known cure. 2 Both have airways that are inflamed. leading to swelling, narrowing and blockage of the air passages. 3 In both, the airways can overreact to certain allergens or other environmental conditions/substances. 4 Both diseases can have the symptoms of: cough, shortness of breath, wheezing and chest tightness. 5 Both asthma and COPD are often treated with the same medications.
What is it called when you have asthma and COPD?
When people have both asthma and COPD, it is called overlap syndrome. It is sometimes referred to as asthma chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or ACOS for short. 2. This condition is not well understood because studies tend to address either asthma or COPD, but not both together. Treatment is usually a combination of ...
Why does asthma cause inflammation?
The underlying cause of airway inflammation is different. Asthma inflammation stems from sensitivity to substances called allergens that stimulate the production of a type of white blood cell called eosinophils. This inflammation is relatively short-term. (Allergens include things such as pollen, pet dander, dust mites, and molds.) 1
What are the symptoms of asthma and COPD?
In both, the airways can overreact to certain allergens or other environmental conditions/substances. Both diseases can have the symptoms of: cough, shortness of breath, wheezing and chest tightness. Both asthma and COPD are often treated ...
What is the inflammation associated with COPD?
On the other hand, the inflammation with COPD stems from the production of white blood cell types called macrophages and neutrophils.
When does COPD start?
Asthma is commonly diagnosed during childhood, although it can arise during adulthood as well. COPD typically begins after the fourth decade of life. 1.
Is asthma a coexisting condition?
Because asthma is an allergic disease most often, co-existing conditions tend to be allergic in nature. Things like nasal allergies and eczema are common. In adults with asthma, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD for short) is also common. On the other hand, people who have COPD are more likely to have co-existing conditions more associated ...