If the DCIS is hormone receptor-positive (estrogen or progesterone), treatment with tamoxifen (for any woman) or an aromatase inhibitor, such as exemestane or anastrozole, (for women past menopause) for 5 years after surgery can lower the risk of another DCIS or invasive cancer developing in either breast.
Full Answer
What is the best treatment for DCIS?
The Bottom Line. In women diagnosed with DCIS, hormonal therapy can help prevent DCIS from recurring. If a woman doesn’t undergo radiation therapy, hormonal therapy can reduce her chances of invasive cancer in the opposite breast, but not invasive cancer in the same breast.
Is radiation or hormone therapy better for DCIS?
In addition, radiation is only beneficial for preventing cancer in the one breast, while hormone therapy helps prevent cancer in both breasts. A study of more than 1,700 women with DCIS who underwent a lumpectomy evaluated radiation and/or tamoxifen.
What is DCIS (DCIS breast cancer)?
DCIS is considered non-invasive or pre-invasive breast cancer. DCIS can’t spread outside the breast, but it still needs to be treated because it can sometimes go on to become invasive breast cancer (which can spread).
How does DCIS affect a woman's risk of dying?
Overall, women treated for DCIS had a 10% lower risk of dying from any cause compared to women with no history of the disease. The women who had been diagnosed with DCIS did have a higher risk of dying from breast cancer, but a lower risk of dying from most other conditions and other cancers.
Can you live 20 years after DCIS?
Using statistical formulas, the researchers estimated how many women would die from breast cancer 20 years after being diagnosed with DCIS. They calculated that 3.3% of the women would die from breast cancer. Looking at it another way, 96.7% of the women would be alive 20 years after being diagnosed with DCIS.
Is DCIS 100 curable?
Many women — perhaps assuming all breast cancers are dangerous — may believe that removing the healthy breast after a diagnosis of DCIS improves their chances of survival. But DCIS is nearly 100 percent curable.
How long does it take for DCIS to turn into invasive cancer?
It assumes that all breast carcinomas begin as DCIS and take 9 years to go from a single cell to an invasive lesion for the slowest growing lesions, 6 years for intermediate growing DCIS lesions, and 3 years for fast-growing DCIS lesions.
What percentage of women with DCIS have mastectomy?
Presently in the United States, 97% of patients with DCIS undergo surgical excision, of which one-third will involve mastectomy (1,2). The most recent NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (v. 2.2010) recommend total mastectomy as one treatment option for DCIS (3).
Why did I get DCIS?
DCIS forms when genetic mutations occur in the DNA of breast duct cells. The genetic mutations cause the cells to appear abnormal, but the cells don't yet have the ability to break out of the breast duct. Researchers don't know exactly what triggers the abnormal cell growth that leads to DCIS.
Can DCIS come back after lumpectomy?
A study found that radiation therapy given after DCIS is removed by lumpectomy reduces the risk that the DCIS will come back (recurrence).
Can I survive DCIS?
It's important to understand that radiation and hormone treatments do not change survival—the 10-year survival rate for women diagnosed with DCIS is 98% regardless of whether they receive either treatment.
How do you know if DCIS has spread?
The doctor will remove a bit of tissue to look at under a microscope. They can make a diagnosis from the biopsy results. If the biopsy confirms you have cancer, you'll likely have more tests to see how large the tumor is and if it has spread: CT scan.
Should I have a mastectomy for DCIS?
In most cases, a woman with DCIS can choose between breast-conserving surgery (BCS) and simple mastectomy. But sometimes, if DCIS is throughout the breast, a mastectomy might be a better option. There are clinical studies being done to see if observation instead of surgery might be an option for some women.
How do you stop DCIS from coming back?
Radiation Greatly Reduces Risk of Recurrence for Women with DCIS, a Type of Noninvasive Breast Cancer. Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) is a low-risk form of early-stage breast cancer. Women with DCIS can have radiation after the tumor is removed to lower the risk that the cancer could come back.
Is Tamoxifen necessary after DCIS?
Research shows that radiation therapy and hormonal therapy after surgery for DCIS reduces the risk of being diagnosed with either another DCIS or invasive breast cancer in the future.
How long can you wait for DCIS surgery?
In women with a clinical diagnosis of DCIS, greater delay to surgery is associated with lower OS. Although most women with DCIS undergo surgical extirpation within 2 months of diagnosis, longer time to surgery is associated with greater risk of finding invasion and should be limited.
Who performed a biopsy on Brenda's mammogram?
The MRI revealed two more masses. Deanna Lane, M.D., performed a biopsy that confirmed there was more breast cancer than originally thought.
What stage of cancer did Brenda have?
Brenda then had a breast biopsy. Her medical team in Dallas diagnosed her with ductal carcinoma in situ, or DCIS, often called stage 0 breast cancer. They recommended a lumpectomy and radiation therapy.
Where did Brenda Scherer get her second opinion?
Before starting breast cancer treatment near her home in Dallas, Brenda Scherer decided to get a second opinion at MD Anderson. Looking back, she’s glad she did. If she’d stuck with the treatment plan her local medical team had recommended, she would have had the wrong treatment and surgery.
Did Brenda have a mammogram?
A kindergarten teacher at the time, Brenda had her annual mammogram during spring break 2017. The technician noticed something unusual immediately, but Brenda wasn’t concerned. “I have dense breasts and knew I had lumps, so I wasn’t worried,” she says.
How is DCIS diagnosed?
If a doctor sees the calcifications on your mammogram, he or she will recommend more tests, which could include a breast biopsy. During the biopsy, a doctor or other health care provider takes samples of cells or tissues from your body. The cells are examined by a pathologist — a doctor who checks for signs of disease in body tissues.
What is the treatment for DCIS?
Lumpectomy with radiation. The standard treatment is breast-preserving surgery (a lumpectomy) with radiation therapy, which results in successful outcomes for most patients. Cancers can be larger than expected, so about 20% of the time, patients need a re-excision lumpectomy — another surgery — to remove all of the cancer.
What should I expect after a DCIS diagnosis?
The outlook after DCIS diagnosis, Sun says, is encouraging. “With continued, rigorous monitoring, the prognosis for DCIS is excellent,” she explains. “Your doctor will recommend a regular screening schedule to guard against recurrence in the original breast, and to monitor the other breast for any signs of malignancy.
What happens after a woman is diagnosed with DCIS?
After a woman is diagnosed with DCIS and has the abnormal growth removed via surgery, the next step is to assess her risk of a recurrence or a more invasive cancer.
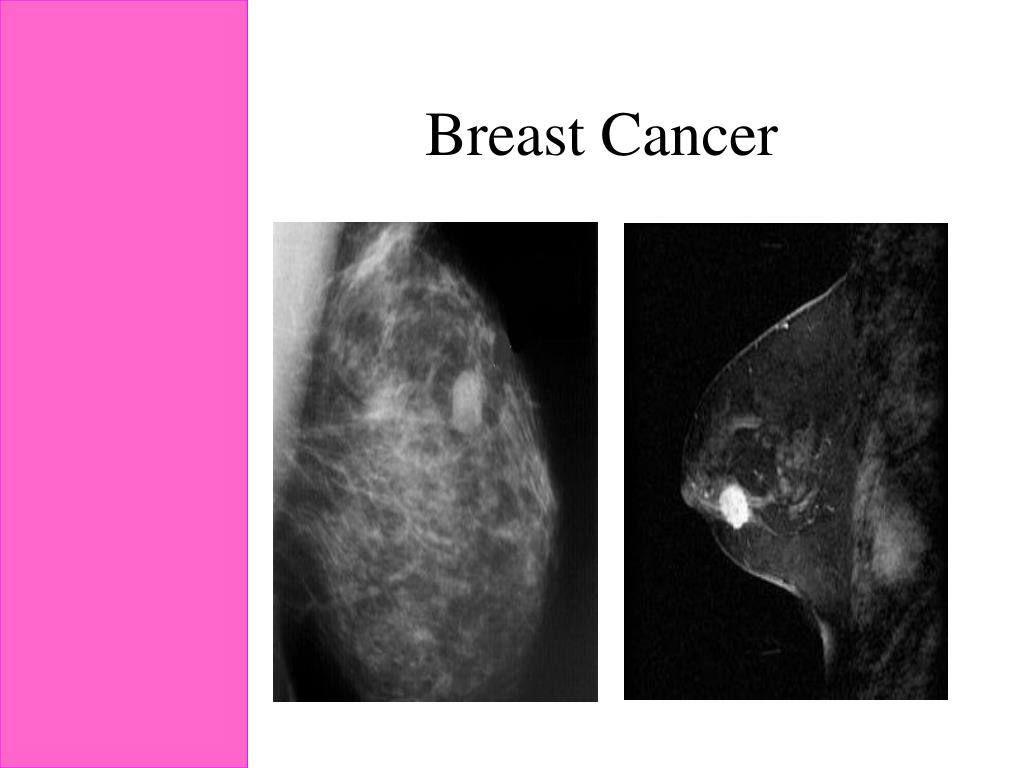
What is DCIS in breast cancer?
DCIS occurs when cells in one of those milk ducts have mutated and multiplied to look like cancer cells. About one in five newly diagnosed breast cancers is DCIS. Because those cells usually stay confined to the duct and do not spread to surrounding tissue, DCIS is also known as stage 0 breast cancer or sometimes pre-cancer. ...
What is a DCIS score?
“You get back what’s called a DCIS score, from zero to 100, that tells you the likelihood of a DCIS recurrence or of an invasive cancer in the next 10 years,” says Dr. White.
How does DCIS affect breasts?
DCIS occurs when cells in one of those milk ducts have mutated and multiplied to look like cancer cells. About one in five newly diagnosed breast cancers is DCIS.
How many DCIS cases were diagnosed in the 1990s?
In the 1990s, only about 15,000 to 18,000 DCIS cases were diagnosed per year, she says; now, that number has grown to more than 60,000, according to the American Cancer Society. “That’s because so many women are now getting mammograms, and the technology is so good, that we pick up very small lesions,” says Dr. White.
What is a high grade DCIS?
High-grade DCIS is sometimes described as “comedo” or “comedo necrosis,” which means that dead cells have built up inside the fast-growing tumor. The higher the grade, the greater chance a person has of also having invasive breast cancer, either with the DCIS or at some point in the future. 10 of 22. View All.
How to remove DCIS?
DCIS can often be removed via a lumpectomy— a surgery that spares the surrounding breast tissue. (In some cases, if DCIS has infiltrated multiple ducts or a tumor has grown large enough, removing the entire breast via mastectomy may be recommended.)
How is DCIS treated?
DCIS usually is treated with surgery to remove the cancer -- in most cases a lumpectomy, even though DCIS doesn’t usually form a lump. After lumpectomy, many women have radiation therapy to the rest of the breast. Radiation reduces the risk of an invasive cancer and also helps reduce the risk of DCIS coming back (recurrence).
What is the goal of DCIS?
If you’ve been diagnosed with DCIS, the goal is to provide you with the best treatment for your unique situation. This takes into account: your family history of breast cancer and other diseases. your personal health history. any other breast cancer risk factors you may have.
Do women who have DCIS live longer?
The results suggest that women treated for DCIS actually live longer than women who haven’t been diagnosed with DCIS. The study, “Low cause-specific mortality in women treated for ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast,” was presented at the European Cancer Congress on Jan. 27, 2017.
Does radiation reduce DCIS?
Experts agree radiation does reduce the risk of DCIS recurrence. Still, some earlier studies have found a link between whole breast radiation and a higher risk of heart and lung problems, especially if the DCIS is in the left breast.
Can you feel DCIS on a mammogram?
The mammogram will show the cancer cells inside the ducts as a cluster of these microcalcifications, which appear either as white specks or as a shadow. Most of the time, you don’t feel DCIS as a lump. If the biopsy results find DCIS, doctors want to remove the whole area of concern to make sure the DCIS has been removed completely.
Is DCIS a higher risk than breast cancer?
Overall, women treated for DCIS had a 10% lower risk of dying from any cause compared to women with no history of the disease. The women who had been diagnosed with DCIS did have a higher risk of dying from breast cancer, but a lower risk of dying from most other conditions and other cancers. "Being diagnosed with DCIS can be extremely distressing, ...
What is the best treatment for DCIS?
Most DCIS patients will choose a lumpectomy (which removes the DCIS but does not remove the entire breast), and radiation therapy is usually recommended for those women to destroy any stray abnormal cells in the same breast. [1] Some women also try hormone therapy such as tamoxifen or aromatase inhibitors.
What is stage zero breast cancer?
In recent years, ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) has become one of the most commonly diagnosed breast conditions. It is often referred to as “stage zero breast cancer” or a “pre-cancer.”. It is a non-invasive breast condition that is usually diagnosed on a mammogram when it is so small that it has not formed a lump.
How many women develop a blood clot?
blood clots- for every 1,000 women, 20 more will develop a blood clot. strokes- for every 100 women, 2 more will develop a stroke. Joint pain for every 1000 women, 20 to 100 more will develop joint pains. hot flashes.
Does tamoxifen reduce the chances of breast cancer?
For women who did not have radiation therapy, tamoxifen reduced the chances of developing DCIS within 10 years in the same breast by about 3% and the chances of developing DCIS in the other breast by about 1%. Interestingly, tamoxifen did not significantly decrease the chances of developing invasive breast cancer in the same breast, ...
Does tamoxifen stop breast cancer?
Tamoxifen blocks the effects of estrogen on breast cells, which can stop the growth of cancer cells that are sensitive to estrogen. A study of more than 1,800 pre-menopausal and post-menopausal women with DCIS evaluated the benefits of tamoxifen for women who had lumpectomy and radiation treatment.
Can a DCIS woman develop cancer?
Most women with DCIS will never develop invasive cancer whether they are treated or not, but it is impossible to predict which women with DCIS will develop cancer and which ones won’t. That’s why treatment is recommended.
Is DCIS invasive or invasive?
If it develops into breast cancer, it can spread, at which point it is called invasive. The goal of treating invasive cancer is to prevent it from spreading to the lungs, bones, brain, or other parts of the body, where it can be fatal. Since DCIS is not an invasive cancer, it is even less of a threat than Stage 1 or Stage 2 breast cancer, ...
What type of cancer is Donna?
Donna was diagnosed with stage 0 ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), the most common type of non-invasive breast cancer, according to BreastCancer.org. Only about 40 to 50 percent of DCIS cases progress to invasive breast cancer, research shows.
Did Donna Pinto have a mastectomy?
Donna Pinto. You get diagnosed with breast cancer, and then you get a mastectomy. That’s just the way it goes, right? But when Donna Pinto was told she had the disease, she opted not to have the surgery—and she may be on to something. Among women diagnosed with breast cancer, about 20 percent will have a slow-growing tumor ...
Is cancer a death sentence?
“Everyone has the association that cancer is a death sentence,” says Donna. “You go to that place. You wonder, ‘Is this my silent killer?’ Doctors are treating DCIS the same way they treat someone with invasive breast cancer.”