Bacterial infection in lung requires long-term antibiotics. Treatment is recommended for people with symptoms and because treatment may reduce ongoing lung damage. The choice of antibiotics depends on the sensitivity of the organism, but one common regimen is clarithromycin, rifampin and ethambutol.
Full Answer
How are chronic lung infections diagnosed and treated?
Since the term “chronic lung infections” is reserved for those that fail to respond to treatment (antibiotics, etc.), the cause of treatment failure is as important as the infectious agent. Diagnosis must include a search for the patient’s underlying host factors, such as age, immunosuppression, and comorbidities.
What is a lung infection?
A lung infection is a condition in which a disease-causing microorganism causes damage and inflammation—due to the gathering of immune cells—in the airways or tissues of the lungs. Lung infections may be caused by viruses, bacteria, fungi, or rarely in the United States, parasites. In some cases, more than one type of microorganism is responsible.
How are chronic lung infections (CLL) prevented?
Prevention of chronic lung infections includes avoiding behaviors that increase risk, immunizations, and societal adjustments. Immunization for influenza and pneumococcus are the most important preventive strategies in prevention of pneumonia, especially for those cloistered in institutionalized settings.
Is a mild lung infection serious?
Lung infections like pneumonia are usually mild, but they can be serious, especially for people with weakened immune systems or chronic conditions, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Read on to learn the most common symptoms of a lung infection and what treatment you can expect if you have one.

What is a long term lung infection?
What Are Chronic Lung Infections? Chronic lung infections are those which do not resolve quickly or at all after antibiotic treatment. The most common causes are from chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), cystic fibrosis, and bronchiectasis, all of which involve inability to clear secretions.
What are some infectious lung diseases?
Lung diseases affecting your alveoli include:Pneumonia. ... Tuberculosis Pneumonia that slowly gets worse, caused by the bacteria Mycobacterium tuberculosis.Emphysema. ... Pulmonary edema. ... Lung cancer. ... Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). ... Pneumoconiosis.
What is emphysema disease?
Emphysema is a lung condition that causes shortness of breath. In people with emphysema, the air sacs in the lungs (alveoli) are damaged. Over time, the inner walls of the air sacs weaken and rupture — creating larger air spaces instead of many small ones.
What are the most serious lung diseases?
The Top 8 Respiratory Illnesses and DiseasesAsthma. ... Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) ... Chronic Bronchitis. ... Emphysema. ... Lung Cancer. ... Cystic Fibrosis/Bronchiectasis. ... Pneumonia. ... Pleural Effusion.More items...
What is the treatment for lungs infection?
Antibiotics are the mainstay of treatment for bacterial lung infections, with different antibiotics recommended depending on the particular type of infection and suspected organism. The choice of using oral antibiotics versus intravenous treatment will depend on the severity of the infection.
What is an infectious disease?
Infectious diseases are disorders caused by organisms — such as bacteria, viruses, fungi or parasites. Many organisms live in and on our bodies. They're normally harmless or even helpful. But under certain conditions, some organisms may cause disease. Some infectious diseases can be passed from person to person.
Is COPD the same as emphysema?
Emphysema is a type of COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease). COPD is a group of lung diseases that make it hard to breathe and get worse over time. The other main type of COPD is chronic bronchitis.
What's the difference between COPD and emphysema?
Emphysema is one type of COPD disease. It damages the air sacs in the lungs, making it progressively harder for the body to get the oxygen it needs. The term COPD also covers chronic bronchitis and asthma. A person with emphysema has COPD, but a person with COPD may not necessarily have emphysema.
What causes COPD?
Smoking. Smoking is the main cause of COPD and is thought to be responsible for around 9 in every 10 cases. The harmful chemicals in smoke can damage the lining of the lungs and airways. Stopping smoking can help prevent COPD from getting worse.
What is a lung disease called?
The term lung disease refers to many disorders affecting the lungs, such as asthma, COPD, infections like influenza, pneumonia and tuberculosis, lung cancer, and many other breathing problems. Some lung diseases can lead to respiratory failure.
What are the 4 main categories of lung diseases?
Lung disease is a general term for several disorders that include airway diseases, lung tissue diseases, and lung circulation diseases, some of which may lead to respiratory failure.
What are 4 types of respiratory infections?
Differences Between the Most Common Respiratory Infections. Four of the most common types of respiratory infections are COVID-19, the flu, pneumococcal disease, and colds.
Preventing Infectious Respiratory Diseases
Get Vaccinated. Talk to your doctor to see if you are up to date on your vaccinations. It’s always better to prevent a disease rather than treat it after it occurs.
Treating Infectious Respiratory Diseases
While each disease has slightly different symptoms, diagnostic tests, and treatment options, these overarching concepts provide a broad overlay for treatment.
Am I at High-Risk?
Depending on the disease, you may be at greater risk for complications if you are an infant, child, adult 50 years of age or older, or have a chronic medical condition.
What is a chronic lung infection?
What Are Chronic Lung Infections? Chronic lung infections are those which do not resolve quickly or at all after antibiotic treatment. The most common causes are from chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), cystic fibrosis, and bronchiectasis, all of which involve inability to clear secretions.
What are the respiratory changes that can begin lengthy (chronic) lung infections?
Depending on specific illnesses or the degree of debilitation, the respiratory changes that can begin lengthy (chronic) lung infections include: Loss of elastic recoil in the chest wall resulting in air trapping and increase in lung capacity and residual volume. Diminished respiratory muscle strength and endurance. Loss of alveoli.
Why are lung infections confusing?
Although different chronic lung infections are caused by different agents, they can be confusing because of similarities in their signs, symptoms, X-ray findings, and pulmonary compromise. The end result is a common syndrome whose cause may be difficult to identify specifically unless further testing is used.
What are the respiratory changes?
Depending on specific illnesses or the degree of debilitation, the respiratory changes that can begin lengthy (chronic) lung infections include: 1 Loss of elastic recoil in the chest wall resulting in air trapping and increase in lung capacity and residual volume 2 Diminished respiratory muscle strength and endurance 3 Loss of alveoli 4 Reduction in oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange 5 Inability to increase rate of respiratory effort 6 Decreased cough or gag reflex (leading to ineffective clearance or aspiration pneumonia 7 Decreased ability of cilia to move mucous and bacterial debris upward
Why are immunocompromised people ineffective?
Those who are immunocompromised (e.g., HIV) are who are pharmacologically immunocompromised (systemic corticosteroid use) may be ineffective in the first lines of defense due to limitations of the innate immune system.
What is the treatment for a fungal infection?
Fungal infections are treated with antifungal agents. Viral infections of the lung which fail to resolve are typically due to immunocompromise, so treatment will involve both antiviral agents and reduction of any immunosuppression.
What test is used to determine the severity of an infection?
Blood tests : helpful in identifying the severity of infection via a white blood count and even an allergic or parasitic component based on eosinophils (WBCs common in allergic reactions and parasites). Pulmonary function testing: to evaluate the degree of lung compromise with functional testing such as spirometry.
What is the best treatment for a fungal lung infection?
A fungal lung infection will require treatment with an antifungal medication, such as ketoconazole or voriconazole. Antibiotics won’t work on viral infections.
What is it called when you have a virus in your lungs?
When the large bronchial tubes that carry air to and from your lungs become infected, it’s referred to as bronchitis. Bronchitis is more likely to be caused by a virus than by bacteria. Viruses can also attack the lungs or the air passages that lead to the lungs. This is called bronchiolitis.
How do you know if you have a lung infection?
If you have a lung infection, here are the most common symptoms to expect: 1. Cough that produces thick mucus. Coughing helps to rid your body of the mucus produced from inflammation of the airways and lungs.
What causes a person to have a lung infection?
A lung infection can be caused by a virus, bacteria, and sometimes even a fungus. One of the most common types of lung infections is called pneumonia. Pneumonia, which affects the smaller air sacs of the lungs, is most often caused by contagious bacteria, but can also be caused by a virus. A person becomes infected by breathing in ...
What are the symptoms of a lung infection?
severe chest pain. a high fever. cough with mucus that is getting worse. People older than 65, children under the age of 2, and people with chronic health conditions or a compromised immune system should seek medical treatment right away if they experience any symptoms of a lung infection.
What causes bronchitis?
They are typically caused by a virus or bacteria. The most common microorganisms responsible for bronchitis include: viruses such as the influenza virus or respiratory syncytial virus (RSV ) bacteria such as Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Chlamydia pneumoniae, and Bordetella pertussis.
Can a viral lung infection last longer?
A lung infection causes symptoms similar to the cold or flu, but may be more severe and typically last longer . Your immune system will typically be able to clear a viral lung infection over time. Antibiotics are used to treat bacterial lung infections. See your doctor right away if you have:
Overview
A group of bacteria called Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC) causes MAC lung disease. Most people who breathe in or swallow these germs don’t get sick. But some pre-existing conditions can make some people more susceptible to developing a slow-growing infection once MAC enters their airway.
Symptoms and Causes
MAC bacteria naturally reside in soil and water. Stirring up soil or dust can make the bacteria airborne, and you may breathe them in. People who garden or work with soil have slightly more MAC than those who don’t. MAC is also in water, including the water in your home.
Diagnosis and Tests
Your healthcare provider will perform a physical exam and ask about symptoms.
Management and Treatment
Because MAC lung disease is difficult to get rid of, you may see an infectious disease or a pulmonary specialist. Both specialties have expertise in diagnosing and treating infections.
Prevention
Avoid hot tubs and saunas that recirculate hot, steamy water if your provider feels they may have been the source of your MAC bacteria.
Frequently Asked Questions
While you can’t catch a MAC infection from someone else, the condition sometimes affects more than one family member. Experts believe certain people have a genetic change (mutation) that makes them more susceptible to MAC infections.
What is lung disease?
Lung disease refers to several types of diseases or disorders that prevent the lungs from functioning properly. Lung disease can affect respiratory function, or the ability to breathe, and pulmonary function, which is how well lungs work.
What are the causes of lung diseases?
There are many different lung diseases, some of which are caused by bacterial, viral, or fungal infections. Other lung diseases are associated with environmental factors, including asthma, mesothelioma, and lung cancer. Chronic lower respiratory diseases is a set of conditions that includes chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), emphysema, ...
How deadly is ARDS?
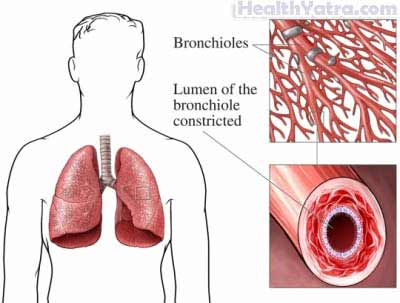
ARDS is deadly in 30-40% of cases, and only a few lung biomarkers have been validated. 11. This diagram compares a healthy (left) to an unhealthy (right) bronchial tube that would cause constricted breathing from asthma.
What is lung cancer?
Lung cancer is a disease caused by the abnormal growth of cells. Though most lung cancer starts in the lungs, some cases start in other parts of the body and spread to the lungs. The two main types of lung cancer—small cell and non-small cell—grow and spread in different ways, and each type may be treated differently.
What is the NHALES study?
NHALES: Asthma Study. RSV Infection and Asthma. Respiratory diseases such as asthma and COPD involve a narrowing or blockage of airways that reduce air flow. In other lung conditions ̶ such as pulmonary fibrosis, a lung tissue scarring that can be caused by different factors, and pneumonia, a bacterial or viral infection in which air sacs fill ...
How does air pollution affect lung development?
Air pollution studies – Long-term exposure to air pollutants can affect lung development and increase the chance of developing asthma, emphysema, and other respiratory diseases.
Does air pollution cause COPD?
Air pollution and COPD – Breathing air pollution can lead to COPD, as shown by a NIEHS-funded study that found diesel exhaust particles, a major source of air pollution, dampened the activity of genes involved stress response in the lung. 7.
What is the most common NTM that causes infections in humans?
M. intracellulare. Mycobacterium abscessus. Mycobacterium kansasii. Mycobacterium xenopi. MAC is the most common species of NTM that causes infections in humans, and the lungs are the most common site for infection.
Can a nontuberculous mycobacteria cause lung damage?
It occurs more frequently in older adults and people with other lung diseases, like bronchiectasis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). If not treated, many NTM infections may cause damage to lung tissue.
Can NTM lung disease be chronic?
NTM lung disease is more common in older adults but can affect any age group. NTM lung infections can become chronic and require ongoing treatment. Severe NTM lung disease can affect a person’s quality of life. Death directly related to NTM lung disease is uncommon. NTM can get into the lungs from the environment.
Can you get surgery for a NTM lung infection?
For severe infections, you may need surgery to remove the most damaged areas of the lung. If you have a severe NTM lung infection, meet with experts in NTM and discuss your need for surgery.
