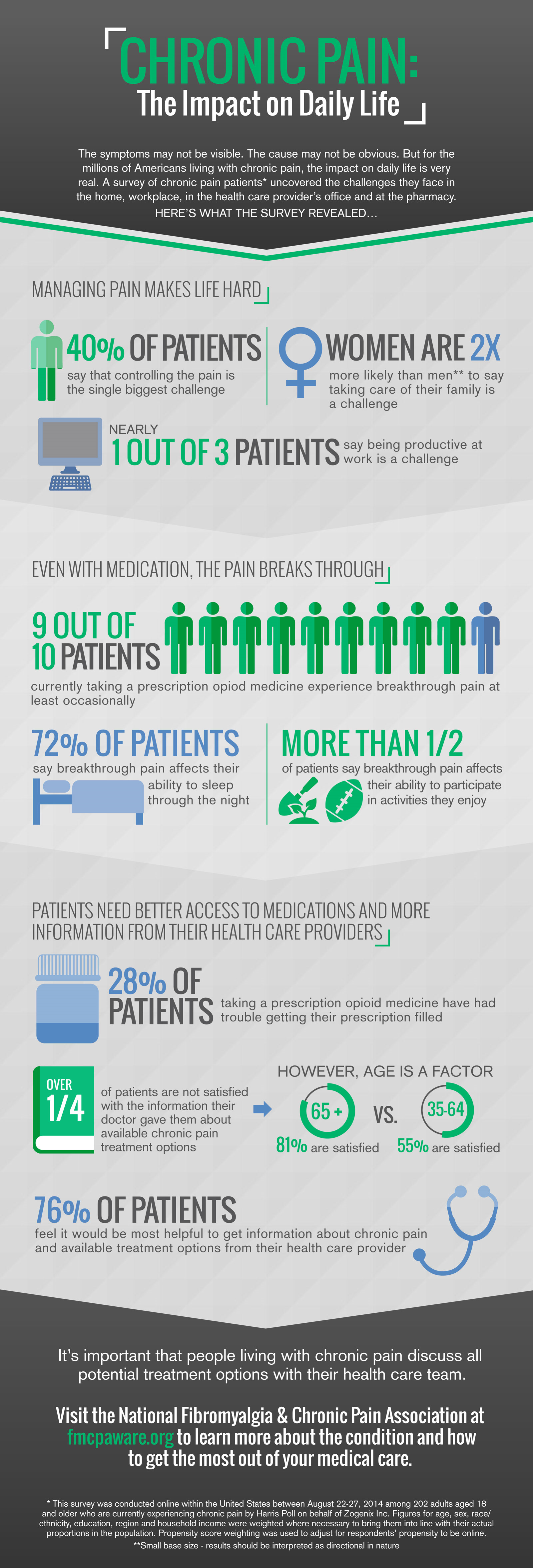
Figure 6.1: Recommended medical care after breast cancer treatment
| Who | Plan for care | |
| Medical history and physical exam | Everyone treated for breast cancer | 1-4 times a year (depending on your situ ... |
| Mammogram (of the remaining breast tissu ... | People treated with lumpectomy plus radi ... | 6-12 months after radiation therapy ends ... |
| Mammogram (of the remaining breast tissu ... | People treated with mastectomy | 1 year after mammogram that led to diagn ... |
| Mammogram (of the remaining breast tissu ... | People treated with mastectomy and breas ... | The reconstructed breast (s) does not ne ... |
When should chemotherapy be given to treat breast cancer?
6 rows · Jun 15, 2021 · 1-4 times a year (depending on your situation) for 5 years, then every year. Mammogram (of the ...
Why is astym after breast cancer treatment?
Mammograms: If you had breast-conserving surgery (lumpectomy or partial mastectomy), you will probably have a mammogram about 6 to 12 months after surgery and radiation are completed, and then at least every year after that. Women who've had a mastectomy (removal of the entire breast) typically no longer need mammograms on that side.
How can you prepare for breast cancer treatment?
Based on your treatment options, you might have different types of doctors on your treatment team. These doctors could include: A breast surgeon or surgical oncologist: a doctor who uses surgery to treat breast cancer; A radiation oncologist: a doctor who uses radiation to treat cancer; A medical oncologist: a doctor who uses chemotherapy, hormone therapy, immunotherapy, …
What is the best treatment for Stage 1 breast cancer?
Typically, you should see your doctors every 3 months for the first 2 years after treatment ends, every 6 months during years 3 through 5, and then annually for the rest of …

What happens after breast cancer treatment?
Breast cancer and its treatments can cause changes to your body and the way you look. For example, after surgery you'll be left with a scar or scars. You may have lost your hair if you had chemotherapy. Many people also put on weight during or after treatment.
What medication do you take after breast cancer?
Tamoxifen (Nolvadex® or Soltamox®) is a drug that treats hormone receptor-positive (hormone-positive) breast cancer. It may also help prevent breast cancer. Since the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved tamoxifen in 1998, it has become one of the most widely used breast cancer treatments.Oct 24, 2020
What treatment do you get after cancer?
Chemotherapy can be used as the primary or sole treatment for cancer. After other treatments, to kill hidden cancer cells. Chemotherapy can be used after other treatments, such as surgery, to kill any cancer cells that might remain in the body. Doctors call this adjuvant therapy.
What happens after breast cancer diagnosis?
Most women with breast cancer have some type of surgery. Common types of breast surgery are lumpectomy, mastectomy, and taking out lymph nodes from the underarm. Women who have breast surgery may also decide to have the breast shape rebuilt, either at the same time or later on. This is called breast reconstruction.Jan 5, 2022
Is tamoxifen a prescription drug?
Female hormones called estrogen, that occur naturally in the body can increase the growth of some breast cancers. Tamoxifen works by blocking the effects of estrogen in the body. This medicine is available only with your doctor's prescription.
What is the 5 year pill for breast cancer?
Tamoxifen. Tamoxifen is usually taken daily in pill form. It's often used to reduce the risk of cancer recurrence in women who have been treated for early-stage breast cancer. In this situation, it's typically taken for five to 10 years.Dec 29, 2020
Will I ever feel normal again after breast cancer?
Many people find they need time to reflect on their cancer experience. With time, they find a new way of living – a "new normal". It's common to have many different feelings after treatment ends. Some of your feelings may be similar to those you experienced when you were first diagnosed with cancer.
How long do cancer patients live after treatment?
A health care provider might say, “People with this type of cancer generally have a 60 percent five-year survival rate.” This means that 60 out of 100 people who were treated for this type of cancer during the research studies were still living after five years.
Can you live a normal life after cancer?
Many people live much longer than 5 years after their cancer diagnosis. The term does not mean a person will only survive for 5 years. For example, 90% of people with breast cancer will be alive 5 years after the diagnosis of cancer.Apr 9, 2021
How soon after diagnosis of breast cancer is surgery?
Overall, the optional time for surgery after diagnosis is less than 90 days. Lumpectomy, mastectomy and lymph node removal are three common surgical procedures to treat breast cancer.Oct 25, 2021
How fast can breast cancer Spread?
According to the Robert W. Franz Cancer Research Center at Providence Portland Medical Center, breast cancer cells need to divide at least 30 times before they are detectable by physical exam. Each division takes about 1 to 2 months, so a detectable tumor has likely been growing in the body for 2 to 5 years.Apr 2, 2021
At what stage of breast cancer the breast is removed?
Surgery for stage three and stage four cancer generally requires removing the entire breast and nearby tissue affected by the cancer.Oct 15, 2020
Which Treatments Are Used For Breast Cancer?
There are several ways to treat breast cancer, depending on its type and stage.Local treatments: Some treatments are local, meaning they treat the...
How Is Breast Cancer Typically Treated?
Most women with breast cancer will have some type of surgery to remove the tumor. Depending on the type of breast cancer and how advanced it is, yo...
Who Treats Breast Cancer?
Doctors on your cancer treatment team might include: 1. A breast surgeon or surgical oncologist: a doctor who uses surgery to treat breast cancer 2...
Making Treatment Decisions
It’s important to discuss all of your treatment options, including their goals and possible side effects, with your doctors to help make the decisi...
Help Getting Through Breast Cancer Treatment
Your cancer care team will be your first source of information and support, but there are many places you can get more help if you need it. Hospita...
How long does breast cancer treatment last?
Almost any cancer treatment can have side effects. Some might only last for a few days or weeks, but others might last a long time.
How to plan for cancer survivorship?
Talk with your doctor about developing a survivorship care plan for you. This plan might include: 1 A suggested schedule for follow-up exams and tests 2 A schedule for other tests you might need in the future, such as early detection (screening) tests for other types of cancer, or tests to look for long-term health effects from your cancer or its treatment 3 A list of possible late- or long-term side effects from your treatment, including what to watch for and when you should contact your doctor 4 Diet, physical activity, and other lifestyle modification suggestions
What is a survivorship plan?
This plan might include: A schedule for other tests you might need in the future, such as early detection (screening) tests for other types of cancer, or tests to look for long-term health effects from your cancer or its treatment.
What happens if cancer comes back?
If cancer does return, your treatment options will depend on where it comes back, what treatments you've had before, and your current health and preferences. For more information on how recurrent cancer is treated, see Treatment of Recurrent Breast Cancer .
Can you call your doctor about cancer?
However, if you have additional concerns about your cancer, you do not have to wait until your next scheduled visit. You can call your doctor immediately.
Do you need a mammogram after a mastectomy?
Women who've had a mastectomy (removal of the entire breast) typically no longer need mammograms on that side. But unless you've had both breasts removed, you still need to have yearly mammograms on the remaining breast. To learn more, see Mammograms After Breast Cancer Surgery.
Can uterine cancer cause spotting?
Although this is usually caused by something that isn’t cancer, it can also be the first sign of uterine cancer.
What type of treatment is used for breast cancer?
Depending on the type of breast cancer, different types of drug treatment might be used, including: Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer. Hormone Therapy for Breast Cancer. Targeted Drug Therapy for Breast Cancer. Immunotherapy for Breast Cancer.
What kind of doctor treats breast cancer?
Based on your treatment options, you might have different types of doctors on your treatment team. These doctors could include: 1 A breast surgeon or surgical oncologist: a doctor who uses surgery to treat breast cancer 2 A radiation oncologist: a doctor who uses radiation to treat cancer 3 A medical oncologist: a doctor who uses chemotherapy and other medicines to treat cancer 4 A plastic surgeon: a doctor who specializes in reconstructing or repairing parts of the body
Why are clinical trials important?
Clinical trials are one way to get state-of-the art cancer treatment. In some cases they may be the only way to get access to newer treatments. They are also the best way for doctors to learn better methods to treat cancer. Still, they're not right for everyone.
What is the difference between a radiation oncologist and a medical oncologist?
A radiation oncologist: a doctor who uses radiation to treat cancer. A medical oncologist: a doctor who uses chemotherapy and other medicines to treat cancer. A plastic surgeon: a doctor who specializes in reconstructing or repairing parts of the body. You might have many other specialists on your treatment team as well, ...
Is treatment information given here official policy of the American Cancer Society?
The treatment information given here is not official policy of the American Cancer Society and is not intended as medical advice to replace the expertise and judgment of your cancer care team. It is intended to help you and your family make informed decisions, together with your doctor.
What is complementary medicine?
Complementary methods refer to treatments that are used along with your regular medical care. Alternative treatments are used instead of a doctor’s medical treatment.
What do people with cancer need?
People with cancer need support and information, no matter what stage of illness they may be in. Knowing all of your options and finding the resources you need will help you make informed decisions about your care.
How long does it take for breast cancer to come back?
Schedule regular appointments with them. Between medical visits, watch for any changes in your body. Most of the time, if cancer comes back, it's within 5 years of when it was first treated.
How long does it take to get a mammogram after breast cancer treatment?
You’ll likely need a mammogram within 6 12 months after finishing your breast cancer treatment and at least annually after that. Routine chest X-rays and blood tests in women who have no symptoms of cancer aren’t always reliable.
What are the risks of breast cancer?
It’s possible to get a second, different breast cancer. And having had breast cancer may put you at higher risk for other types of cancers, including cancers of the: 1 Salivary glands 2 Stomach 3 Esophagus 4 Ovaries 5 Uterus 6 Skin 7 Thyroid 8 Colon
What are the changes in breasts?
Pay attention to any changes in your breast, including: Skin rashes, redness, or swelling. New lumps in your breast or chest. Also pay attention to: Bone pain, back pain, or tenderness that doesn't go away. Shortness of breath or chest pain. Persistent belly pain.
How often should I see a doctor for a syphilis?
Typically, you should see your doctors every 3 months for the first 2 years after treatment ends, every 6 months during years 3 through 5, and then annually for the rest of your life. Your personal schedule will depend on your diagnosis.
What are the causes of bone loss?
Bone density (certain cancer drugs and menopause can weaken your bones) Diabetes. High blood pressure. Heart disease. Weight gain or obesity. Make taking care of your emotional and physical well-being a priority in life. Don't compare your treatment plan and outcome with others. Everyone's cancer is a little different.
Why do we need follow up care for breast cancer?
One goal of follow-up care is to check for a recurrence, which means that the cancer has come back. Treatment for early stage or locally advanced breast cancer is given to eradicate as many cancer cells in the body as possible. However, cancer recurs because small areas of cancer cells that don't respond to treatment may remain undetected in the body. Over time, these cells may increase in number until they show up on test results or cause signs or symptoms.
What is a recurrence of breast cancer?
Generally, a recurrence is found when a person has symptoms or an abnormal finding during a physical examination. Annual mammograms are also recommended after a diagnosis of breast cancer. The symptoms depend on where the cancer has recurred and may include: A lump under the arm or along the chest wall.
How do you know if you have breast cancer?
Breast cancer can come back in the breast or other areas of the body. Generally, a recurrence is found when a person has symptoms or an abnormal finding during a physical examination. Annual mammograms are also recommended after a diagnosis of breast cancer. The symptoms depend on where the cancer has recurred and may include: 1 A lump under the arm or along the chest wall 2 Pain that is constant, worsening, and not relieved by over-the-counter medication such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs) 3 Bone, back, neck, or joint pain, fractures, or swelling, which are possible signs of bone metastases 4 Headaches, seizures, dizziness, confusion, personality changes, loss of balance, nausea, vomiting, or changes in vision, which are possible signs of brain metastases 5 Chronic coughing, shortness of breath, or trouble breathing, which are possible symptoms of lung metastases 6 Abdominal pain, itchy skin or rash, or yellow skin and eyes from a condition called jaundice, which may be associated with liver metastases 7 Changes in energy levels, such as feeling ill or extremely tired 8 Having a low appetite and/or weight loss 9 Nausea or vomiting 10 Rash or skin changes on the breast or chest wall 11 Changes in the shape or size of the breast, or swelling in the breast or arm
Why is follow up care important?
Doctors want to keep track of your recovery in the months and years ahead. Follow-up care is also important for screening for other types of cancer. In some instances, patients may be able to visit a survivorship clinic that specializes in the post-treatment needs of people diagnosed with breast cancer.
What is the goal of cancer rehabilitation?
The goal of rehabilitation is to help people regain control over many aspects of their lives and remain as independent and productive as possible. Learn more about cancer rehabilitation. Learn more about the importance of follow-up care.
Can cancer come back after treatment?
Over time, these cells may increase in number until they show up on test results or cause signs or symptoms. Many survivors feel worried or anxious that the cancer will come back after treatment. While it often does not, it’s important to talk with your doctor about the possibility of the cancer returning.
What is a lump under the arm?
A lump under the arm or along the chest wall. Pain that is constant, worsening, and not relieved by over-the-counter medication such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs) Bone, back, neck, or joint pain, fractures, or swelling, which are possible signs of bone metastases.
What are the treatments for cancer?
Local treatments: These treat cancer at the site and include surgery and radiation therapy. Systemic treatments: These treat cancer throughout the body and include chemotherapy, hormonal therapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy. If a tumor is very small, local treatments 8 are usually all that's required.
What is the purpose of chemo for breast cancer?
13. The purpose of chemotherapy is to treat any cancer cells that may have strayed from your breast before they can grow into metastases. It's often recommended for those with micrometastases in the lymph nodes.
What is stage 1 breast cancer?
Stage 1 breast cancer is the earliest stage of what's considered invasive breast cancer. "Invasive" does not mean that the cancer has invaded other areas of your body. Rather, it simply means that the cells in your tumor have infiltrated the area past what's called the basement membrane. When a tumor first begins, ...
How long does it take for breast cancer to progress?
It is not possible to determine exactly how long it will take for newly diagnosed breast cancer to progress from stage 1 to stage 2. It can happen within months if it is an aggressive high-grade tumor, or it can take longer.
What is the TNM classification?
2. T = Tumor Size: All stage 1 cancer is T-0 or T-1, meaning your tumor is 2 centimeters (cm, roughly an inch) or less in diameter.
Is breast cancer more likely to recur?
A new, unrelated breast cancer is more likely to emerge after stage 1 breast cancer is treated than a recurrence. Your doctor will recommend a surveillance schedule for you so that new breast cancer or a recurrence can be identified and treated as quickly as possible.
What does N mean in cancer?
N = Nodes: All stage 1 cancer is N-0 or N-1mi. N-0 means it has not spread to any lymph nodes. N-1 means that it has spread to lymph nodes nearby. The "mi" means micrometastases, which can only be seen under the microscope. Micrometastases measure between 0.2 millimeters (mm) and 2 mm (0.2 cm) in diameter. 3.
What is breast cancer support?
Breast Cancer Support. Along with a healthcare team, patients should also consider utilizing support networks. Family and friends often serve as an internal network of support, but it can be beneficial to enroll in breast cancer support and advocacy groups to bond with individuals who have faced similar experiences.
Why is it important to understand breast cancer?
When being diagnosed with breast cancer, it's important for patients and their loved ones to take time to process the situation above all else. Although time may be of the essence, it's important that patients enter their treatment journey with a clear head to ensure that every decision is made ...
What is HER2 in cancer?
Coming to terms with a diagnosis is a critical step in the process. HER2 refers to the human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 , a gene that can play a role in breast cancer development. The gene controls how breast cells grow, divide, and repair themselves, making overproduction a potential red flag for breast cancer.
How many women have breast cancer?
Receiving a breast cancer diagnosis can feel crippling and life-altering for both patients and their families. With 1 in 8 women being diagnosed with breast cancer in her lifetime, it's unfortunately a common diagnosis to face. For many women diagnosed with breast cancer, what happens next may be a mystery.
When should women get breast cancer screenings?
Breast Cancer Screening & Early Detection. After the age of 45, women should go for annual mammograms, breast exams, and cancer screenings to be proactive in detecting an abnormality. Catching cancer in its early stages is crucial for increasing a patient's survival rate.
Why should patients form a care team?
Patients should form a care team to ensure complete care is provided upon receiving a breast cancer diagnosis. Whether it is through emotional support or medical procedures, establishing a team that can help a patient's treatment and recovery journey from all angles is essential in the process.
Can cancer be detected in blood?
Yes. Cancerous tumors produce specific proteins that can be found in blood marker tests. Certain markers, such as CA 15.3, TRU-QUANT, and CA 27.29, typically indicate breast cancer may be present or if there is a cancer recurrence. Other markers, like CEA (carcinoembryonic antigen), can indicate that breast cancer is present ...
What is the role of a doctor?
Within this context, the role of your doctor is to provide you full disclosure of your condition and treatment options in a language you understand. The disclosure should be made without prejudice and coercion.
What is patient centered care?
This dictates that people have the right to make decisions about the direction of their health care, even if that decision is to terminate treatment or seek alternative therapies. This applies as much to everyday ailments like the flu as much as it does serious ones like breast cancer .
Why do women choose hospice?
Likewise, some women with advanced cancer will choose hospice care for its emphasis on emotional support and pain control, rather than aggressive therapeutic interventions that cause pain. According to research from Canada, the majority of women who refused breast cancer therapy were over 50 (53%), married (44%), and had metastatic disease (61%).
Is cancer a priority?
Personal priorities: You might assume that cancer would be the number one priority in a person's life, but not everyone agrees. In some cases, a woman may opt to delay treatment for something she considers personally important, such as an upcoming wedding, family trip, or business obligation.
Can a doctor refuse medical treatment?
There are few exceptions to your right to refuse medical treatment, however. In an emergency situation, doctors do have the right to intervene only to control the emergency. Unless there is a legal directive to prevent such treatment, such as a Do-Not-Resuscitate (DNR) order, the doctor has an obligation to step in, albeit in a specific capacity.
What is informed consent?
It involves discussing the potentials risks and benefits of a recommended treatment, as well as the risks and benefits of receiving no treatment.
Is it normal to not seek treatment for breast cancer?
Most people would consider it "normal" to want to seek treatment for breast cancer the moment you are diagnosed, particularly at a time where survival rates are ever-increasing. But this would also infer that not seeking treatment is "abnormal," and that's rarely the case.
What is stage zero breast cancer?
Apar Gupta. Often called “stage zero breast cancer,” DCIS growths are confined to the inside of the breast’s milk ducts, and many never develop into invasive cancers. Several treatment options are available, and opinions about the optimal treatment for DCIS vary widely among doctors.
What is DCIS in mammography?
Before the advent of routine mammography, DCIS (ductal carcinoma in situ) was rarely detected. But today, DCIS accounts for 20% of breast cancer diagnoses and would be the fifth most common cancer in women if classified independently. Apar Gupta. Often called “stage zero breast cancer,” DCIS growths are confined to the inside ...
Does radiation help with survival?
It’s important to understand that radiation and hormone treatments do not change survival—the 10-year survival rate for women diagnosed with DCIS is 98% regardless of whether they receive either treatment. These treatments instead reduce the risk of breast cancer down the road. Since treatment of DCIS after surgery doesn’t improve survival, ...
Is DCIS a pre-invasive cancer?
“DCIS is considered a pre-invasive cancer, but the current standard of care is to treat it like an early-stage invasive breast cancer,” says Apar Gupta, MD, ...