Explore
Oct 13, 2014 · 2-3 weeks on ECMO is generally speaking the maximum time As a rule of thumb, 2-3 weeks is probably the longest I have seen for a critically ill Patient to be on either VV-ECMO(for lung failure) or VA- ECMO(for heart failure).
How long does it take to get off ECMO?
Jun 02, 2021 · In general, doctors aim to take patients off ECMO therapy as quickly as possible. Because it is used for patients with a range of conditions, each with its own recovery timetable, the length of time someone is on ECMO therapy can vary greatly. Some patients need it for only a few hours while others may require days or weeks of ECMO support.
When is ECMO therapy recommended?
How long can I stay on ECMO? People can stay on ECMO anywhere from days to weeks. The length of time that a person will spend on ECMO depends on why they need this treatment.
What is an ECMO weaning trial?
The ECMO machine replaces the function of the heart and lungs. People who need support from an ECMO machine are cared for in a hospital’s intensive care unit (ICU). Typically, people are supported by an ECMO machine for only a few hours to days, but may require it for a few weeks, depending on how their condition progresses.
What is the ECMO process?
Oct 21, 2020 · "We tend to think of weaning being appropriate once the underlying illness that put them on ECMO in the first place is getting better," Agerstrand says. "Typically, patients who need ECMO support...

What is the ECMO respiratory machine for in COVID-19?
Essentially, ECMO helps these patients by acting as their heart and lungs. The machine is used when all other medical options have been exhausted for patients whose lungs can't provide enough oxygen to their body or rid themselves of carbon dioxide.
What does a ventilator do during COVID-19?
A ventilator doesn't cure COVID-19 or other illnesses that caused your breathing problem. It helps you survive until you get better and your lungs can work on their own. When your doctor thinks you are well enough, they will test your breathing.Aug 9, 2021
Why do some people with COVID-19 need ventilators to breath?
When your lungs inhale and exhale air normally, they take in oxygen your cells need to survive and expel carbon dioxide. COVID-19 can inflame your airways and essentially drown your lungs in fluids. A ventilator mechanically helps pump oxygen into your body.Aug 9, 2021
When do patients need ventilators to help treat COVID-19?
For the most serious COVID-19 cases in which patients are not getting enough oxygen, doctors may use ventilators to help a person breathe. Patients are sedated, and a tube inserted into their trachea is then connected to a machine that pumps oxygen into their lungs.Jun 18, 2020
Does ventilation help reduce the spread of COVID-19?
Bringing fresh, outdoor air into your home helps keep virus particles from accumulating inside.• If it’s safe to do so, open doors and windows as much as you can to bring in fresh, outdoor air. While it’s better to open them wide, even having a window cracked open slightly can help.
Do all patients with COVID-19 get pneumonia?
Most people who get COVID-19 have mild or moderate symptoms like coughing, a fever, and shortness of breath. But some who catch the new coronavirus get severe pneumonia in both lungs. COVID-19 pneumonia is a serious illness that can be deadly.Jan 25, 2022
When does COVID-19 affect breathing?
For most people, the symptoms end with a cough and a fever. More than 8 in 10 cases are mild. But for some, the infection gets more severe.About 5 to 8 days after symptoms begin, they have shortness of breath (known as dyspnea). Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) begins a few days later.Jan 21, 2022
Can COVID-19 damage organs?
COVID-19 can cause lasting damage to multiple organs, including the lungs, heart, kidneys, liver and brain. SARS CoV-2 first affects the lungs through the nasal passages. When the lungs are severely affected, it can affect the heart.
How long does it take to recover from ECMO?
Some patients need it for only a few hours while others may require days or weeks of ECMO support.
What is ECMO therapy?
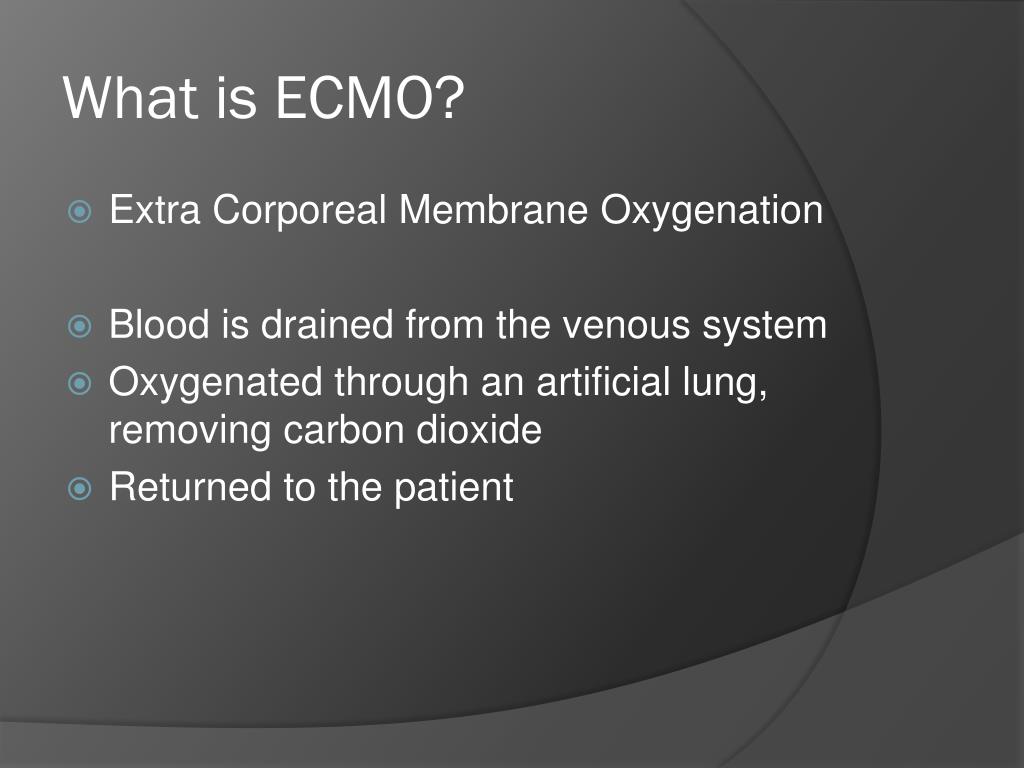
ECMO is a therapy used to treat people with life-threatening heart and lung failure. ECMO involves the use a machine to replace some of the functions of a patient’s lungs or heart, or both simultaneously. While ECMO therapy can be life-saving, it is not itself a treatment. Instead, it provides a kind of bridge, ...
How does an ECMO machine work?
The ECMO machine connects to a patient through plastic tubes called cannulas. After giving the patient an anticoagulant, a medication that prevents blood from clotting, the doctor inserts cannulas into large arteries and veins located in the chest, neck, or legs.
What are the conditions for ECMO?
While there is no fixed list of conditions for which ECMO is used, doctors may recommend its use in the following situations: 1 Respiratory failure (when the lungs fail to maintain adequate oxygen levels or remove enough carbon dioxide from the blood) 2 Heart transplantation 3 Lung transplantation 4 Cardiac arrest (when the heart fails to pump blood effectively) 5 Cardiogenic shock (when the ventricles of the heart do not function properly, resulting in insufficient blood flow) 6 Pulmonary embolism (when an artery in the lungs is blocked) 7 Birth defects of the heart 8 Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome, ARDS (a type of respiratory failure that prevents adequate oxygen from getting to the lungs and blood)
What is an ECMO machine?
It is effectively a modified heart-lung bypass machine—a machine that takes over heart and lung function (meaning it adds oxygen to and removes carbon dioxide from a patient’s blood supply). But unlike a heart-lung bypass machine, which is designed for short-term use (during heart surgery, for instance), ECMO machines provide long-term heart ...
What are the risks of ECMO?
Stroke: In rare cases, ECMO patients develop small blood clots that can reduce the flow of blood to the brain. This raises risk for stroke.
What is the purpose of an ECMO machine?
The ECMO machine then warms this treated blood to body temperature and pumps it back into the patient. In cases where a patient’s heart cannot circulate blood on its own, a mechanical pump takes over the heart’s role and pumps blood through the patient’s circulatory system.
Overview
Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation is a type of artificial life support that can help a person whose lungs and heart aren't functioning correctly. Also called ECMO, this setup continuously pumps blood out of your body and then sends it through a series of devices that add oxygen and remove carbon dioxide.
Frequently Asked Questions
People can stay on ECMO anywhere from days to weeks. The length of time that a person will spend on ECMO depends on why they need this treatment.
How long can you take ECMO?
Depending on your condition, ECMO can be used for a few days to a few weeks. The amount of time you receive ECMO depends on your condition.
What are the conditions that ECMO is used for?
Some heart conditions in which ECMO may be used include: Shock caused by the heart not pumping enough blood (cardiogenic shock) Some lung (pulmonary) conditions in which ECMO may be used include: Defect in the diaphragm (congenital diaphragmatic hernia) High blood pressure in the lungs (pulmonary hypertension)
What are the risks of ECMO?
The most common risks that may occur with ECMO include: 1 Bleeding 2 Blood clot (thromboembolism) 3 Blood clotting disorder (coagulopathy) 4 Infection 5 Loss of blood in hands, feet or legs (limb ischemia) 6 Seizures 7 Stroke (part of the brain is damaged by loss of blood or by a blood vessel that bursts)
When is ECMO used?
ECMO is used when life support is needed after surgery, or when you are very ill and your heart or lungs need help so that you can heal. Your doctor will decide when it may be helpful. If you need ECMO, your doctor and trained respiratory therapists will prepare you.
Where does extracorporeal membrane oxygenation take place?
In extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), blood is pumped outside of your body to a heart-lung machine that removes carbon dioxide and sends oxygen-filled blood back to tissues in the body. Blood flows from the right side of the heart to the membrane oxygenator in the heart-lung machine, and then is rewarmed and sent back to the body.
How long does it take to recover from ECMO?
It usually takes several days to wean patients, she says. However, she adds, some patients recover quickly and are weaned within 24 hours or so.
When to use ECMO?
ECMO is generally used in patients who are younger than 65 and who were previously healthy , Hodgson says: "People who are older, frail or have other medical conditions do not respond as well.". The decision to put a patient on ECMO is painstaking, with assistance from the ELSO COVID-19 Guidelines.
What is ECMO in medical terms?
Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation , or ECMO, replaces the function of the heart and lungs. ECMO is helping some COVID-19 patients for whom standard treatments have failed and a mechanical ventilator alone is not enough to safely support their breathing.
What is ECMO in dialysis?
ECMO removes carbon dioxide waste from the blood and returns oxygen-rich blood back to the body. "ECMO is akin to dialysis for the lungs – in that the same way that dialysis cleans the blood of toxins when the kidneys have failed, ECMO removes the carbon dioxide from the blood to support the body when the lungs have failed," says Dr.
What is the extracorporeal membrane?
The extracorporeal in ECMO means "outside the body.". The membrane is the gas-exchange device that takes over the work of the patient's lungs. Oxygenation is treatment to increase oxygen supply to the lungs and to blood circulation. ECMO removes carbon dioxide waste from the blood and returns oxygen-rich blood back to the body.
When is ECMO added to a ventilator?
Most COVID-19 patients placed on ECMO are already on a ventilator. ECMO is added when the ventilator alone is not meeting the patient's needs. "Normally, the lung takes on oxygen and removes CO2," Barbaro explains.
What happens if you go into ECMO?
Patients who go on ECMO are often placed in a medically induced coma and kept immobilized, says Hodgson, who is also deputy director of the Australian and New Zealand Intensive Care-Research Center and a specialist ICU physiotherapist at the Alfred Hospital in Melbourne.
How long did Lloyd stay on ECMO?
He primarily needed it for his lungs, badly damaged by the coronavirus. He would remain on the system for 95 days , far exceeding the time most patients spend on it. In a rare move, Lloyd was on not one, but two ECMO circuits, a maze of tubes carrying blood back and forth, keeping him alive. And then, a miracle.
How old was Zach Lloyd when he was on ECMO?
COVID recovery included long stay on ECMO, double-lung transplant. Zach Lloyd was only 37 years old with no pre-existing health conditions, but COVID-19 was bringing him within an inch of his life. Beginning in October 2020, he lay immobile in a bed at Vanderbilt University Medical Center, hooked up to a life-sustaining mechanical system called ...
When did Bacchetta get his lungs transplanted?
He was placed on the transplant list on Christmas Eve, and Bacchetta transplanted his two new lungs on Jan. 28. The cardiothoracic anesthesia team included Bantayehu Sileshi, MD, associate professor of Anesthesiology, and fellow Karl Hillenbrand, MD.

Overview
- In extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), blood is pumped outside of your body to a heart-lung machine that removes carbon dioxide and sends oxygen-filled blood back to tissues in the body. Blood flows from the right side of the heart to the membrane oxygenator in the heart-lung machine, and then is rewarmed and sent back to the body. This met...
Why It's Done
- ECMO may be used to help people who are very ill with conditions of the heart and lungs, or who are waiting for or recovering from a heart transplant. It may be an option when other life support measures haven't worked. ECMOdoes not treat or cure a disease, but can help you when your body temporarily can't provide your tissues with enough oxygen. Some heart conditions in whic…
Risks
- The most common risks that may occur with ECMOinclude: 1. Bleeding 2. Blood clot (thromboembolism) 3. Blood clotting disorder (coagulopathy) 4. Infection 5. Loss of blood in hands, feet or legs (limb ischemia) 6. Seizures 7. Stroke (part of the brain is damaged by loss of blood or by a blood vessel that bursts)
How You Prepare
- ECMO is used when life support is needed after surgery, or when you are very ill and your heart or lungs need help so that you can heal. Your doctor will decide when it may be helpful. If you need ECMO, your doctor and trained respiratory therapists will prepare you.
What You Can Expect
- Your doctor will insert a thin, flexible tube (cannula) into a vein to draw out blood and a second tube into a vein or artery to return warmed blood with oxygen to your body. You will receive other medications, including sedation, to make you comfortable while receiving ECMO, and may not be able to talk during this time. Depending on your condition, ECMO can be used for a few days to …
Results
- The outcomes associated with ECMO depend upon the severity of the health condition that led to use of ECMO. Your doctor can explain how helpful ECMOmay be in your situation.
Clinical Trials
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiesof tests and procedures to help prevent, detect, treat or manage conditions.