Medication
Intravenous administration of diltiazem or verapamil can be effective for acute treatment in patients with hemodynamically stable SVT (class IIa recommendation, level B-R evidence) Intravenous use of β-blockers is reasonable for acute treatment in patients with hemodynamically stable SVT (class IIa recommendation, level C-LD evidence)
Procedures
Synchronized cardioversion is recommended for acute treatment in patients with hemodynamically stable SVT when pharmacologic treatment is ineffective or contraindicated (class I recommendation, level B-NR evidence)
Therapy
If the arrhythmia does not stop and symptoms are severe, you may need a procedure called electrical cardioversion to reset your heart rhythm. Ongoing treatment of recurring SVT If you have recurring episodes of SVT, you may need to take medicines, either on an as-needed basis or daily.
Nutrition
Delays were secondary to lack of recognition of "unstable" SVT, due to failure to assess perfusion and mental status. Errors encountered during simulatio … Recognition and treatment of unstable supraventricular tachycardia by pediatric residents in a simulation scenario Simul Healthc.
See more
How is SVT treated in patients with hemodynamically stable SVT?
When is synchronized cardioversion indicated in the treatment of SVT?
What to do if SVT does not go away?
Why do delays occur in SVT treatment?

How do you treat unstable SVT?
The treatment for all unstable tachycardic rhythms is synchronized cardioversion. Like defibrillation, synchronized cardioversion delivers a shock across the chest, either by placing a pair of manual paddles on the chest or through the application of adhesive “hands-free” pads.
How do you treat a patient with SVT?
Most people with supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) don't need treatment....However, if you have long or frequent episodes, your health care provider may recommend the following:Carotid sinus massage. ... Vagal maneuvers. ... Medications. ... Cardioversion. ... Catheter ablation. ... Pacemaker.
What is the first-line treatment for stable SVT?
The first-line treatment in hemodynamically stable patients, vagal maneuvers, such as breath-holding and the Valsalva maneuver (ie, having the patient bear down as though having a bowel movement), slow conduction in the AV node and can potentially interrupt the reentrant circuit.
What is the best medication to treat SVT?
You might get a shot of a fast-acting medicine to block the electrical impulses that are causing your heart to race. Examples include adenosine (Adenocard or Adenoscan) and verapamil (Calan, Verelan). Adenosine has milder side effects, such as dizziness or nausea.
Do you give adenosine for SVT?
Adenosine is administered intravenously in specific clinical cases. For the management of SVT, adenosine is ideally given through a peripheral intravenous (IV) access initially as a 6 mg dose followed by a 20 mL saline flush for rapid infusion.
Which of the following is the drug of choice for a patient with stable ventricular tachycardia?
Amiodarone is the drug of choice for acute VT refractory to cardioversion shock. After recovery, oral medications are used for long-term suppression of recurrent VT. Current evidence favors class III antiarrhythmic drugs over class I drugs.
What medications are used to treat SVT?
Commonly prescribed medications are beta-blockers, verapamil, and digoxin. Occasionally, other medications called antiarrhythmic drugs (such as amiodarone or sotalol) may be given to prevent SVT episodes from occurring.
What is unstable SVT?
Ventricular tachycardia is unstable any time a patient is in dysrhythmia and hemodynamic compromise. This is most often associated with mental status changes or a loss of consciousness.
What is the preferred treatment for recurrent SVT?
Ongoing treatment of recurring SVT Medicine treatment may include beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, or other antiarrhythmic medicines. In people who have frequent episodes, treatment with medicines can decrease how often these occur. But these medicines may have side effects.
How do you slow down SVT?
Healthcare providers often use these:Valsalva maneuver (bearing down like you're having a bowel movement (pooping). See below).Diving reflex.Carotid sinus massage.Gag reflex.Coughing.Handstand for 30 seconds. ... Applied abdominal pressure.
Introduction: What Is Supraventricular Tachycardia?
Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) is an arrhythmia initiated above the ventricles, at or above the atrioventricular (AV) node. This cardiac rhythm occurs due to improper electrical conduction within the heart that disrupts the coordination of heartbeats.
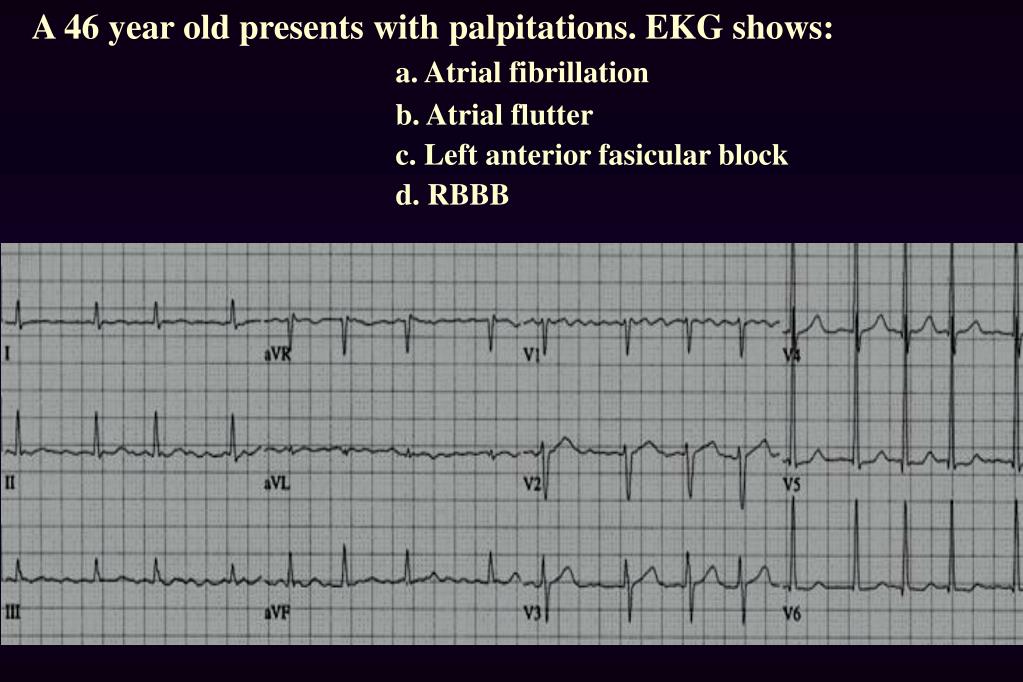
What Are ECG Characteristics of Supraventricular Tachycardia?
Typically characterized by having a narrow QRS complex that is less than or equal to 0.12 seconds. A wide QRS (greater than or equal to 0.12 seconds) can occur, but is less common.
What Signs or Symptoms May Be Present?
Symptom severity tends to be associated with the duration of time that supraventricular tachycardia takes place. Signs or symptoms that may present with SVT include:
Treatment of Supraventricular Tachycardia
Care of the conscious patient should be initiated using the Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support (ACLS) Primary Assessment. Components of this assessment include evaluating the patient’s airway, breathing, circulation, disability, and potential exposure.
How To Prepare for Your ACLS Exam
Are you ready to test your knowledge and skills to identify and treat supraventricular tachycardia? Numerous quizzes are available to help you evaluate and reinforce your understanding of cardiac rhythms. You may access quizzes here and here.
What is the treatment for recurring SVT?
Ongoing treatment of recurring SVT. If you have recurring episodes of SVT, you may need to take medicines, either on an as-needed basis or daily. Medicine treatment may include beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, or other antiarrhythmic medicines.
How to treat sudden onset SVT?
Your doctor will teach you how to do these safely. These are things such as bearing down or putting an ice-cold wet towel on your face.
How to tell if you have SVT?
SVT is usually treated if: 1 You have symptoms such as dizziness, chest pain, or fainting that are caused by your fast heart rate. 2 Your episodes of fast heart rate are occurring more often or do not return to normal on their own.
How is supraventricular tachycardia treated?
How is supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) treated? Your treatment for SVT depends on a few things. They include what type of SVT, how often you have episodes, and how severe your symptoms are. The goals of treatment are to prevent episodes, relieve symptoms, and prevent problems.
What are the symptoms of SVT?
SVT is usually treated if: You have symptoms such as dizziness, chest pain, or fainting that are caused by your fast heart rate. Your episodes of fast heart rate are occurring more often or do not return to normal on their own.
What is an electric shock to the heart called?
Other treatment. An electric shock to the heart is called electrical cardioversion. It may be needed if you are having severe symptoms of SVT and your heart rate doesn't go back to normal using vagal maneuvers or fast-acting medicines. Types.
What is a supraventricular tachycardia?
Supraventricular tachycardias are usually narrow-complex tachycardias with a QRS interval of 100 ms or less on an electrocardiogram (ECG). Occasionally, they may show a wide QRS complex in the case of a pre-existing conduction delay, an aberrancy due to rate-related conduction delay or a bundle branch block.
Should a patient with SVT be referred to a cardiologist?
All patients with symptomatic SVT should be referred to a cardiologist for assessment and management. Depending on patient preferences, curative radiofrequency ablation should be considered because of its high success rate, which will subsequently improve quality of life and reduce associated costs. Key points.
Does adenosine slow the ventricular rate?
In patients whose tachycardia does not involve the AV node (e. g., atrial flutter and atrial tachycardia), vagal manoeuvres or intravenous use of adenosine may slow the ventricular rate briefly and thu s unmask the underlying atrial rhythm.
Is AVNRT a sinus rhythm?
A narrow-complex tachycardia with a regular rhythm is likely to be sinus tachycardia, AVRT, AVNRT, atrial flutter or atrial tachycardia.
What is supraventricular tachycardia?
Supraventricular Tachycardia, Initial Diagnosis and Treatment. When supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) causes symptoms, it requires immediate medical attention. Although many physicians believe that the precise type of SVT must be identified before providing treatment, this is not true: treatment can often be started safely ...
Is a wide QRS complex tachycardia dangerous?
The origin of wide QRS tachycardias can be either atrial (if a bundle branch block or accessory pathway is present) or ventricular (V-tach, V-fib), so they are trickier, and often more dangerous.
What is the primary factor to consider when considering hemodynamic stability?
Outside of a hospital, the primary factor to consider is hemodynamic stability —that is, the stability of blood flow from the heart to the brain. When there is hemodynamically unstable tachycardia, the chambers of the heart do not have enough time to fill with blood between contractions. A patient with no obvious signs of hemodynamic instability ( ...
What is tachycardia in 2021?
Updated on May 16, 2021. Tachycardia (rapid heart rate ) is one of the more complicated dysrhythmias to treat because it has so many presentations and so many causes. This article focuses on the treatment of cardiac-related unstable tachycardia in the emergency setting by prehospital professionals.
Why isn't a 12-lead ECG available?
One reason not to treat tachycardia unless it's hemodynamically unstable is because of the possibility of treating a wide-complex tachycardia as ventricular tachycardia when it is not. Taking that chance when the patient is in significant danger of cardiac arrest is acceptable. ...
What are the signs of unstable tachycardia?
Identifying clinical stability depends on the cause of the tachycardia. Some say that cardiac-related symptoms (chest pain, shortness of breath, etc.) are significant indicators of unstable tachycardia. That is more true in the hospital setting than in the field, as more treatment options are available to hospitalized patients.
Is tachycardia more complicated than wide complex?
Narrow-complex tachycardias are more complicated than wide-complex arrhythmias. In this case, the regularity of the arrhythmia becomes important. For narrow-complex arrhythmias that are hemodynamically unstable (systolic blood pressure below 90 mm/Hg, loss of consciousness, confusion, or only able to find a carotid pulse), synchronized cardioversion is indicated.
Can a patient with no obvious signs of hemodynamic instability be transported to the hospital?
A patient with no obvious signs of hemodynamic instability ( low blood pressure, thready or weak pulse, postural changes, etc.) can probably be safely transported to the hospital without attempting to treat the tachycardia first.
Does adenosine help with tachycardia?
Adenosine works very similarly to electrical cardioversion, leading to depolarization of the heart muscle and allowing the sinus node to reset. If adenosine doesn't work, which is very likely if the tachycardia is irregular, two other classes of medication can be tried.
What is SVT in ventricular?
SVT is a broad term for a number of tachyarrhythmias that originate above the ventricular electrical conduction system (Purkinje fibers). Classic Paroxysmal SVT has a narrow QRS complex & has a very regular rhythm. Inverted P waves are sometimes seen after the QRS complex. These are called retrograde p waves.
What is a vagal maneuver?
A: A vagal maneuver is a technique by which you attempt to increase intrathoracic pressure which stimulates the vagus nerve. This can result in slowed conduction of electrical impulses through the AV node of the heart. The following methods can be used. Cough Method: Have a patient cough forcefully.
What is the inverted wave of the heart called?
Inverted P waves are sometimes seen after the QRS complex. These are called retrograde p waves. The heart fills during diastole, and diastole is normally 2/3 the cardiac cycle. A rapid heart rate will significantly reduce the time which the ventricles have to fill.

Diagnosis
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Alternative Medicine
Preparing For Your Appointment