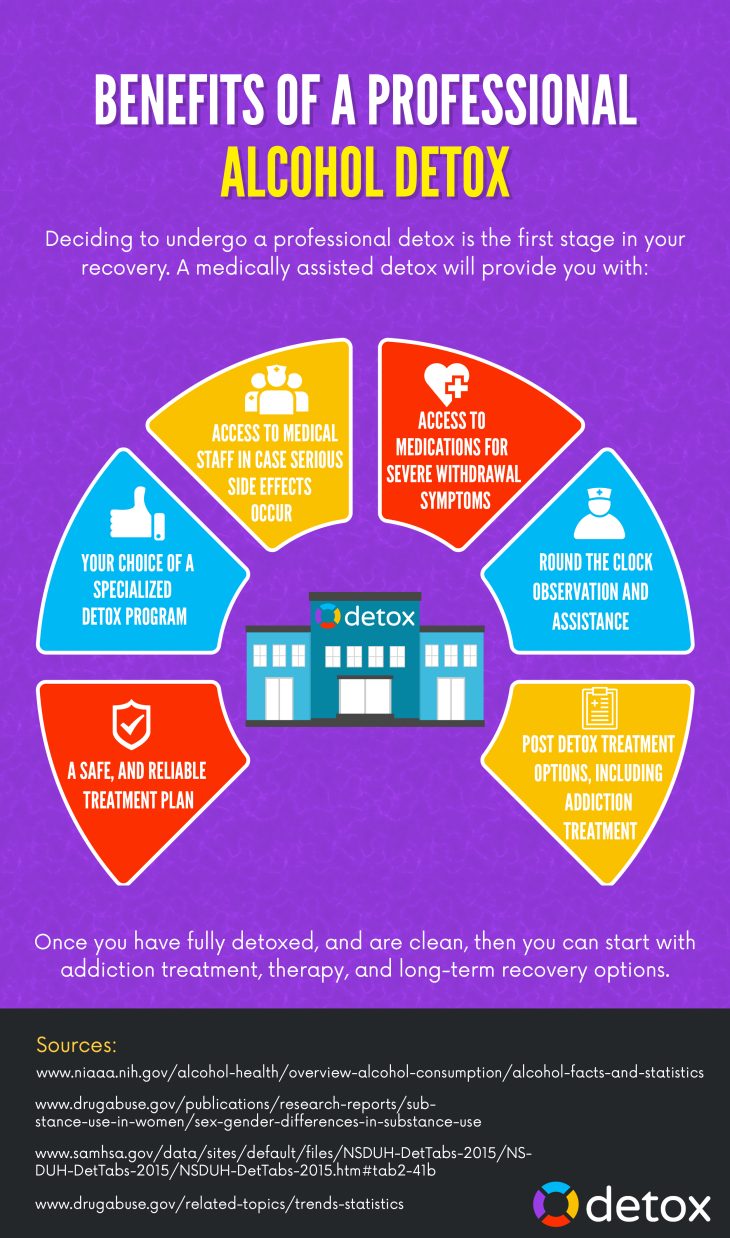
That being said, here are some common reasons why therapy might “fail”: Client needs a higher level of treatment. Some clients need a higher level of care than that therapist can provide, and this may not have been initially been clear to their therapist.
Full Answer
What are the effects of a no treatment group?
A "no treatment" group helps control for a disease's natural history, regression to the mean, and some other factors leading to real change (in the absence of treatment). Remaining unrestrained will be real effects of placebos, and imaginary healing deriving from confirmation bias and other psychological influences.
Why is it important that treatment be appropriate?
It is also important that treatment be appropriate to the individual’s age, gender, ethnicity, and culture. Remaining in treatment for an adequate period of time is critical. The appropriate duration for an individual depends on the type and degree of the patient’s problems and needs.
Why do so many people not go to therapy?
Many people do not actually want to do the work to change what they are struggling with, but merely want to go to therapy to vent every week, without wanting to develop more self-awareness and/or apply this to their life. Therapists are not magicians, and therefore cannot help a person change anyone else besides the client.
Is there a single treatment that is appropriate for everyone?
No single treatment is appropriate for everyone. Treatment varies depending on the type of drug and the characteristics of the patients.
What is a no treatment group?
What are the clinical merits of one or more of your favored therapies?
What happens when a patient returns for follow up?
Why are practitioners biased?
Is placebo based treatment effective?
Is regression to the mean responsible for the placebo effect?
Is there a period at the end of a therapeutic sentence?
See more
About this website

When is treatment ineffective?
If you say that something is ineffective, you mean that it has no effect on a process or situation.
Why are some cancer treatments ineffective?
Resistance can occur when cancer cells—even a small group of cells within a tumor—contain molecular changes that make them insensitive to a particular drug before treatment even begins. Because cancer cells within the same tumor often have a variety of molecular changes, this so-called intrinsic resistance is common.
Why is chemotherapy not effective?
Cancer has the ability to become resistant to many different types of drugs. Increased efflux of drug, enhanced repair/increased tolerance to DNA damage, high antiapoptotic potential, decreased permeability and enzymatic deactivation allow cancer cell survive the chemotherapy.
How effective is medical treatment?
According to the analysis, which analyzed evidence for thousands of medical treatments, there was "evidence of some benefit" for slightly more than 40% of the treatments, while about 3% were ineffective or harmful, and 6% were found to be unlikely to be helpful."
What happens if cancer treatment doesnt work?
If cancer does not respond to chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or other treatments, palliative care is still an option. A person can receive palliative care with other treatments or on its own. The aim is to enhance the quality of life.
What cancers Cannot be cured?
Jump to:Pancreatic cancer.Mesothelioma.Gallbladder cancer.Esophageal cancer.Liver and intrahepatic bile duct cancer.Lung and bronchial cancer.Pleural cancer.Acute monocytic leukemia.More items...•
Why do oncologists push chemo?
An oncologist may recommend chemotherapy before and/or after another treatment. For example, in a patient with breast cancer, chemotherapy may be used before surgery, to try to shrink the tumor. The same patient may benefit from chemotherapy after surgery to try to destroy remaining cancer cells.
Why is effectiveness important in healthcare?
Improving efficiency or reducing wastage leads to saving healthcare budget. This saved money can be spent on less accessible products and/or services. This is particularly important in settings with limited health budget to provide equitable care for their population [1,37-39].
What does effective care mean?
Effective care is provided when: People's needs and choices are assessed, with care, treatment and support delivered in line with current legislation, standards and evidence-based guidance. Staff have the skills, knowledge and experience to deliver effective care.
Why is it important to compare treatments?
Treatment comparisons are required to take account of the natural course of health problems and placebo effects, and to go beyond impressions about treatment effects. But treatment comparisons need to be fair to avoid untrustworthy and sometimes dangerously incorrect conclusions about the effects of treatments.
How long does it take for a treatment to be effective?
The Institute of Medicine 16 estimated that it takes between fifteen and twenty years before an effective treatment (as demonstrated by research) is in common use.
What are the problems with disseminating research findings?
Problems with disseminating research findings. The traditional specializations of healthcare disciplines can sometimes interfere with the dissemination of research data that show what’s most effective. Healthcare providers tend to remain within their traditional discipline when interacting with other providers.
Why are surgical procedures developed?
Procedures are developed because conceptually it makes sense that they should work. In any of these cases, some patients of course benefit.
What is negative findings?
Since negative findings (i.e., the demonstration that a treatment is ineffective) never have a marketing team behind them, their dissemination must rely on the slower, traditional vehicles of professional journal publications and conference lectures.
What do people assume when seeking healthcare?
When seeking healthcare, most people assume that the treatments healthcare providers recommend are effective. This assumption forms a basic trust in our healthcare providers – that they know what they are doing and that they wouldn’t recommend something that they know is ineffective.
Why does innovation occur so slowly?
When, however, innovation occurs outside the corporate world, dissemination of the more effective treatment occurs much more slowly because they have no well-funded marketing strategy. As a result, they must rely on the much more slow and more traditional dissemination vehicles, professional journals and conferences.
Can healthcare providers maintain a good conscience?
As such, healthcare providers can maintain a good conscience when providing care that, on average, is not very effective. The justification is that it might help and it’s not untrue or misleading. The rub is that many procedures and therapies, as we have seen, are just not likely to help.
What is a no treatment group?
A "no treatment" group helps control for a disease's natural history, regression to the mean, and some other factors leading to real change (in the absence of treatment). Remaining unrestrained will be real effects of placebos, and imaginary healing deriving from confirmation bias and other psychological influences.
What are the clinical merits of one or more of your favored therapies?
1) clinical merits of one or more of your favored therapies might be open to question; 2) outcome studies must be designed and interpreted with caution; 3) randomized, placebo-controlled trials are the foundation of modern healthcare [2]; 4) many medical journals (including this one) publish few case reports;
What happens when a patient returns for follow up?
When your patient returns for follow up, symptoms are improved. Again, it seems your treatment has been effective.
Why are practitioners biased?
Likewise, practitioners may be biased to confirm success--because their role as healer (rather than objective evidence) demands it . Unconscious temptations for practitioners to confirm desired/expected clinical outcomes may be as great as for patients. Confirmation bias and self-fulfilling prophecy.
Is placebo based treatment effective?
Placebo-based improvements are real and important, but often are considered (instead) to be direct, clinical effects of treatment; this can only retard progress toward predictably, uniformly effective healthcare. Influences on health coincident with (but independent of) particular treatment.
Is regression to the mean responsible for the placebo effect?
In fact, some researchers [22] believe that regression to the mean is responsible for most apparent improvements mistakenly assigned to the placebo effect. In other words, treatments often are not as powerful as we are inclined to believe, and the placebo effect isn't either. Placebo effect.
Is there a period at the end of a therapeutic sentence?
In fact, science sometimes seems to offer only a period at the end of a confident therapeutic sentence, already written. Unfortunately for those judging efficacy, symptoms can improve for many reasons unrelated to treatment.
Why do people not go to rehab?
This is one reason many people do not succeed in rehab. Instead of taking personal responsibility for their addiction , they still play the blame game. Some have been left feeling hopeless because they think there is nothing they can do about a condition caused by circumstances, but this isn’t true. At Duffy’s, we give you hope that real change is possible.
Does sustainable weight loss come from a pill?
We know that sustainable weight loss comes from a healthy lifestyle and not a pill. We understand that no matter how much we wish the house to be clean, it won’t clean itself. Yet do we understand that this is also true for rehab?
Do treatment programs lead to recovery?
No matter how caring, professional, or brilliant the counselors may be, their influence cannot guarantee recovery.
Can rehab be successful?
You must accept the help, embrace it, and use it. Treatment can only be successful if you put in the work.
Why do we want treatment success?
We desire treatment success because illness is unpleasant. If measurable signs/symptoms do not subside after treatment, patients can reduce at least their psychological burden by interpreting ambiguous symptoms positively, and by reporting (and believing) they feel better. We also may desire treatment success because failure could suggest poor (even foolish) investment of time and money. The temptation to deflect that dissonant reality (by confirming success, without evidence) may be substantial. This may be especially true if (in retrospect) the treatment now seems unusual--as many alternative remedies might.
What happens when a patient returns for follow up?
When your patient returns for follow up, symptoms are improved. Again, it seems your treatment has been effective.
What are the benefits of palliative care?
In particular, a patient's interaction with one or more elements of the healthcare community may lead to reduced anxiety; feelings of increased control; or a positive, more realistic conception of the problem [ 32 ]. Any of these may inspire a patient to report symptom improvements--in the absence of real, physiological/anatomical treatment-related changes.
What is the meaning of optimism in healthcare?
A patient's personal experience with, or knowledge of, a particular treatment may lead to an apparently informed expectation of therapeutic success. Trust in the healthcare system, a particular practitioner, or the body's natural healing abilities, also may warrant optimism.
What motivates patients to visit a particular healthcare provider?
Initiative and frustration motivating patients to visit a particular healthcare provider may inspire other healthful actions, as well (e.g., behaviors leading to better diet, more sleep, more exercise, less stress, and therapies/medications supplied by other practitioners).
Is regression to the mean responsible for most apparent improvements mistakenly assigned to the placebo effect?
In fact, some researchers [ 22] believe that regression to the mean is responsible for most apparent improvements mistakenly assigned to the placebo effect. In other words, treatments often are not as powerful as we are inclined to believe, and the placebo effect isn't either.
Is medicine a subject?
"The history of medicine has never been a particularly attractive subject... virtually anything that could be thought up for the treatment of disease was tried and, once tried, lasted decades or even centuries before being given up. It was, in retrospect, the most frivolous and irresponsible kind of human experimentation, based on nothing but trial and error and usually resulting in precisely that se quence." [ [ 6 ] (p159)]
Why does therapy fail?
That being said, here are some common reasons why therapy might “fail”: Client needs a higher level of treatment.
Why do people drop out of therapy?
Many people drop out when it becomes harder to stick with it and/or start missing sessions which would not lead to successful therapy.
What is the goal of therapy?
While discussing problems is certainly a large part of therapy, the goal of therapy is actually to work on change. Many people do not actually want to do the work to change what they are struggling with, but merely want to go to therapy to vent every week, without wanting to develop more self-awareness and/or apply this to their life. Therapists are not magicians, and therefore cannot help a person change anyone else besides the client.
Is success subjective?
Success and failure are often subjective. Many people have a subjective idea of what it would mean to have “successful therapy” or “ failed therapy”. For example, if a client outlined a specific list of goals to accomplish and they did not accomplish all of them in therapy.
Is Forbes opinion their own?
Opinions expressed by Forbes Contributors are their own.
Is a therapist a good fit?
The therapist and client are not a good fit. While most people can make progress with a number of different therapists, there are absolutely times when the client and therapist are not a good interpersonal fit. For example, a client with anxiety about people pleasing, criticism, and shame is unlikely to have successful therapy with a therapist who is constantly confronting them with negative feedback, who often appears obviously frustrated with the client, and comes across as devaluing or otherwise narcissistic.
Which cancers are resistant to immunotherapy?
Certain cancers, including pancreatic cancer, prostate cancer and glioblastoma, have been especially resistant to this approach. “The idea that these agents work for some patients but not others is a huge research question we’re still trying to understand,” says Sharma. Learning why cancers may not respond to immunotherapy.
What cancers are treated with checkpoint inhibitors?
Now a standard treatment for a growing list of cancers, checkpoint inhibitors have proven effective for treating several types of cancers, including melanoma, small cell lung cancer and non-small cell lung cancer, bladder cancer, kidney cancer, stomach cancer, liver cancer, head and neck cancers, and lymphoma. ...
Does the Moon Shot work for prostate cancer?
For example, an ongoing clinical trial with the Prostate Cancer Moon Shot® is showing promising early results by using multiple checkpoint inhibitors to treat advanced prostate cancer. Insights from this work also showed when prostate cancer spreads to the bone, it leads to massive destruction of bone tissue. This sparks production of a protein called TGF-β that can suppress the immune response. To better treat bone metastases, the platform is planning to launch a clinical trial that combines a checkpoint inhibitor together with a therapy that blocks TGF-β.
Does immunotherapy work on cancer?
Unlike radiation and chemotherapy, immunotherapy does not target the cancer itself. Instead, it enables a patient’s own immune system to attack the disease. In most cases, immune-based treatments stimulate T cells, a specialized type of immune cell, to fight cancer.
Do T cells work in cancer?
In advanced cancers, the sites of metastasis have very different cellular environments than where the primary cancer developed. T cells may not function as well in those environments.
Can glioblastoma be overcome with a checkpoint blockade?
Platform researchers also worked with the Glioblastoma Moon Shot® team and learned that glioblastomas can overcome checkpoint blockade with another type of immune cell called macrophages. The researchers found that certain macrophages in the brain express high levels of the CD73 protein that thwart the activity of T cells in a tumor. Future studies will test a combination of checkpoint inhibitors and a CD73 inhibitor.
What causes depression medications to stop working?
Multiple factors can change the way your body responds to an antidepressant, including:
Why do antidepressants stop working?
"There's no good research that shows why a medication may stop working for someone," says Nestadt. "I think it's less an issue of building up tolerance and more likely constantly changing stressors and factors in the brain ."
What does TCA do to the brain?
Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs) TCA drugs increase serotonin and norepinephrine in the brain, but unlike other antidepressant types, they also block acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter associated with increased stress, anxiety and depression.
What happens if you stop taking antidepressants?
If you feel like your antidepressant has stopped working, you're not alone. It's common for a medication that once worked wonders to become ineffective, especially if you've been taking it for a long time. Symptoms return for up to 33% of people using antidepressants — it's called breakthrough depression.
What is the best treatment for depression?
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) SSRI drugs are the most commonly prescribed antidepressants and are often considered the first line of defense against depression. They increase your brain's level of a neurotransmitter (a chemical that transfers messages from brain cell to brain cell) called serotonin.
Why is esketamine used in a clinic?
Esketamine comes in a nasal spray that must be administered in a clinic because it can cause hallucinations and other sensory side effects for up to two hours after treatment. It's an effective drug for those who haven't responded to other antidepressants.
Can blood pressure medication stop working?
If you're experiencing breakthrough depression, it's important to consult with your doctor so you can feel better again. "It's not unusual for medications to stop working," says Nestadt. "It happens with other sorts of medical treatments as well. Sometimes your blood pressure medicine is no longer effective and it has to be switched. It's just the nature of treating illness."
What is a no treatment group?
A "no treatment" group helps control for a disease's natural history, regression to the mean, and some other factors leading to real change (in the absence of treatment). Remaining unrestrained will be real effects of placebos, and imaginary healing deriving from confirmation bias and other psychological influences.
What are the clinical merits of one or more of your favored therapies?
1) clinical merits of one or more of your favored therapies might be open to question; 2) outcome studies must be designed and interpreted with caution; 3) randomized, placebo-controlled trials are the foundation of modern healthcare [2]; 4) many medical journals (including this one) publish few case reports;
What happens when a patient returns for follow up?
When your patient returns for follow up, symptoms are improved. Again, it seems your treatment has been effective.
Why are practitioners biased?
Likewise, practitioners may be biased to confirm success--because their role as healer (rather than objective evidence) demands it . Unconscious temptations for practitioners to confirm desired/expected clinical outcomes may be as great as for patients. Confirmation bias and self-fulfilling prophecy.
Is placebo based treatment effective?
Placebo-based improvements are real and important, but often are considered (instead) to be direct, clinical effects of treatment; this can only retard progress toward predictably, uniformly effective healthcare. Influences on health coincident with (but independent of) particular treatment.
Is regression to the mean responsible for the placebo effect?
In fact, some researchers [22] believe that regression to the mean is responsible for most apparent improvements mistakenly assigned to the placebo effect. In other words, treatments often are not as powerful as we are inclined to believe, and the placebo effect isn't either. Placebo effect.
Is there a period at the end of a therapeutic sentence?
In fact, science sometimes seems to offer only a period at the end of a confident therapeutic sentence, already written. Unfortunately for those judging efficacy, symptoms can improve for many reasons unrelated to treatment.
