
Antibiotics alone won’t treat sepsis; you also need fluids. The body needs extra fluids to help keep the blood pressure from dropping dangerously low, causing shock. Giving IV fluids allows the health care staff to track the amount of fluid and to control the type of fluid.
Full Answer
How is sepsis treated with fluids?
People who have sepsis often receive intravenous fluids right away, usually within three hours. Vasopressors. If your blood pressure remains too low even after receiving intravenous fluids, you may be given a vasopressor medication, which constricts blood vessels and helps to increase blood pressure.
What is sepsis and why is it important?
Like strokes or heart attacks, sepsis is a medical emergency that requires rapid diagnosis and treatment. Sepsis kills and disables millions and requires early suspicion and rapid treatment for survival. Septic shock disproportionately affects certain communities, increasing their disability and mortality rates.
How can we improve survival in patients with sepsis?
Early diagnosis and timely and appropriate clinical management of sepsis, such as optimal antimicrobial use and fluid resuscitation, are crucial to increase the likelihood of survival.
Does fluid administration in early sepsis affect clinical outcomes?
Alternatively, the effects of fluid administration in early sepsis on clinical outcomes may be similar in high- and low-resource settings, but the effects have only been observed in low-resource settings in which current usual care does not involve early fluid bolus administration.
What is the best treatment for sepsis?
Doctors and nurses should treat sepsis with antibiotics as soon as possible. Antibiotics are critical tools for treating life-threatening infections, like those that can lead to sepsis.
What are the 3 treatments for sepsis?
TreatmentAntibiotics. Treatment with antibiotics begins as soon as possible. ... Intravenous fluids. The use of intravenous fluids begins as soon as possible.Vasopressors. If your blood pressure remains too low even after receiving intravenous fluids, you may be given a vasopressor medication.
Why do we give oxygen in sepsis?
Patients with septic shock require higher levels of oxygen delivery (Do 2) to maintain aerobic metabolism. When Do 2 is inadequate, peripheral tissues switch to anaerobic metabolism and oxygen consumption decreases.
How do hospitals treat sepsis?
The main treatment for sepsis, severe sepsis or septic shock is antibiotics. If you have severe sepsis and septic shock, antibiotics will be given directly into a vein (intravenously). Ideally, antibiotic treatment should start within an hour of diagnosis to reduce the risk of serious complications or death.
How does an endotracheal tube work?
When the tube comes out, they are extubated. Patients with ET tubes cannot speak as the tube passes through the vocal cords. If there is damage in the mouth but a patient needs intubation, the doctor can insert a nasotracheal tube through the nose. Patients who are intubated may be restrained, their hands fastened down, if there is a danger of them unknowingly pulling the tube out. The physicians may opt to perform a tracheostomy if a patient must be on a ventilator for an extended time or there is too much damage to the mouth or throat. The doctor makes an opening in the throat for direct access to the trachea. A tube is inserted through the opening, fastened down, and connected to the ventilator.
How do vasopressors help with blood pressure?
The vasopressors act constrict or tighten up the blood vessels, forcing the blood pressure to go up . Oxygen – Patients usually get oxygen, by mechanical ventilator, mask or nasal cannula. This ensures the body has enough oxygen in its system.
How to treat sepsis?
It needs to be treated as such. In other words, sepsis should be treated as quickly and efficiently as possible as soon as it has been identified. Treatment includes rapid administration of antibiotics and fluids.
What is the best fluid for sepsis?
Several types of fluid. While there are several types of IV fluids, some are standard in treating sepsis. Normal saline is one commonly given fluid. It is a crystalloid fluid. These are fluids that contain minerals, such as sodium, and are water-soluble, or dissolve in water. These add fluid to the blood system.
Why do we give IV fluids?
Giving IV fluids allows the health care staff to track the amount of fluid and to control the type of fluid. Ensuring the body has enough fluids helps the organs to function and may reduce damage from sepsis.
What is the first line of antibiotics?
Physicians prescribe antibiotics (usually more than one type) based on the type of infection. Broad-spectrum antibiotics are the first-line medications. These antibiotics work against several of the more common bacteria. These are intravenous antibiotics so they can get into the blood system quickly and efficiently.
What is an intracranial pressure monitor?
Intracranial Pressure Monitor – An intracranial pressure (ICP) monitor measures the fluid pressure in the brain. A sensor placed directly below the skull is attached to the monitor. Kidney dialysis (renal replacement therapy) – Patients may need dialysis if their kidneys cannot filter the blood as they should.
How to treat septic shock?
A number of medications are used in treating sepsis and septic shock. They include: 1 Antibiotics. Treatment with antibiotics begins as soon as possible. Broad-spectrum antibiotics, which are effective against a variety of bacteria, are usually used first. After learning the results of blood tests, your doctor may switch to a different antibiotic that's targeted to fight the particular bacteria causing the infection. 2 Intravenous fluids. The use of intravenous fluids begins as soon as possible. 3 Vasopressors. If your blood pressure remains too low even after receiving intravenous fluids, you may be given a vasopressor medication. This drug constricts blood vessels and helps increase blood pressure.
What is the best treatment for sepsis?
Supportive care. People who have sepsis often receive supportive care that includes oxygen. Depending on your condition, you may need to have a machine help you breathe. If your kidneys have been affected, you may need to have dialysis.
What antibiotics are effective against a variety of bacteria?
Broad-spectrum antibiotics, which are effective against a variety of bacteria, are usually used first. After learning the results of blood tests, your doctor may switch to a different antibiotic that's targeted to fight the particular bacteria causing the infection. Intravenous fluids.
What organs can be seen on a CT scan?
Infections in your liver, pancreas or other abdominal organs are easier to see on CT scans. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). This technology uses radio waves and a strong magnet to produce cross-sectional or 3D images of the internal structures of your body.
What is the best way to check for gallbladder infections?
Ultrasound may be particularly useful to check for infections in your gallbladder and kidneys. Computerized tomography (CT). This technology takes X-rays from a variety of angles and combines them to depict cross-sectional slices of your body's internal structures.
What tests can be done to determine if you have an infection in your lungs?
If the site of infection is not readily found, your doctor may order one or more of the following imaging tests: X-ray. X-rays can identify infections in your lungs. Ultrasound. This technology uses sound waves to produce real-time images on a video monitor.
Why does the immune system go into overdrive?
Your immune system protects you from many illnesses and infections, but it’s also possible for it to go into overdrive in response to an infection. Sepsis develops when the chemicals the immune system releases into the bloodstream to fight an infection cause inflammation throughout the entire body instead. Severe cases of sepsis can lead ...
Why is sepsis increasing?
Possible reasons for the increase include: an aging population, because sepsis is more common in seniors.
What are the most common causes of sepsis in seniors?
The most common types of infections to cause sepsis in seniors are respiratory like pneumonia or genitourinary like a urinary tract infection.
What happens if you have septic shock?
These clots block the flow of blood and oxygen to vital organs and other parts of your body. This increases the risk of organ failure and tissue death ( gangrene ).
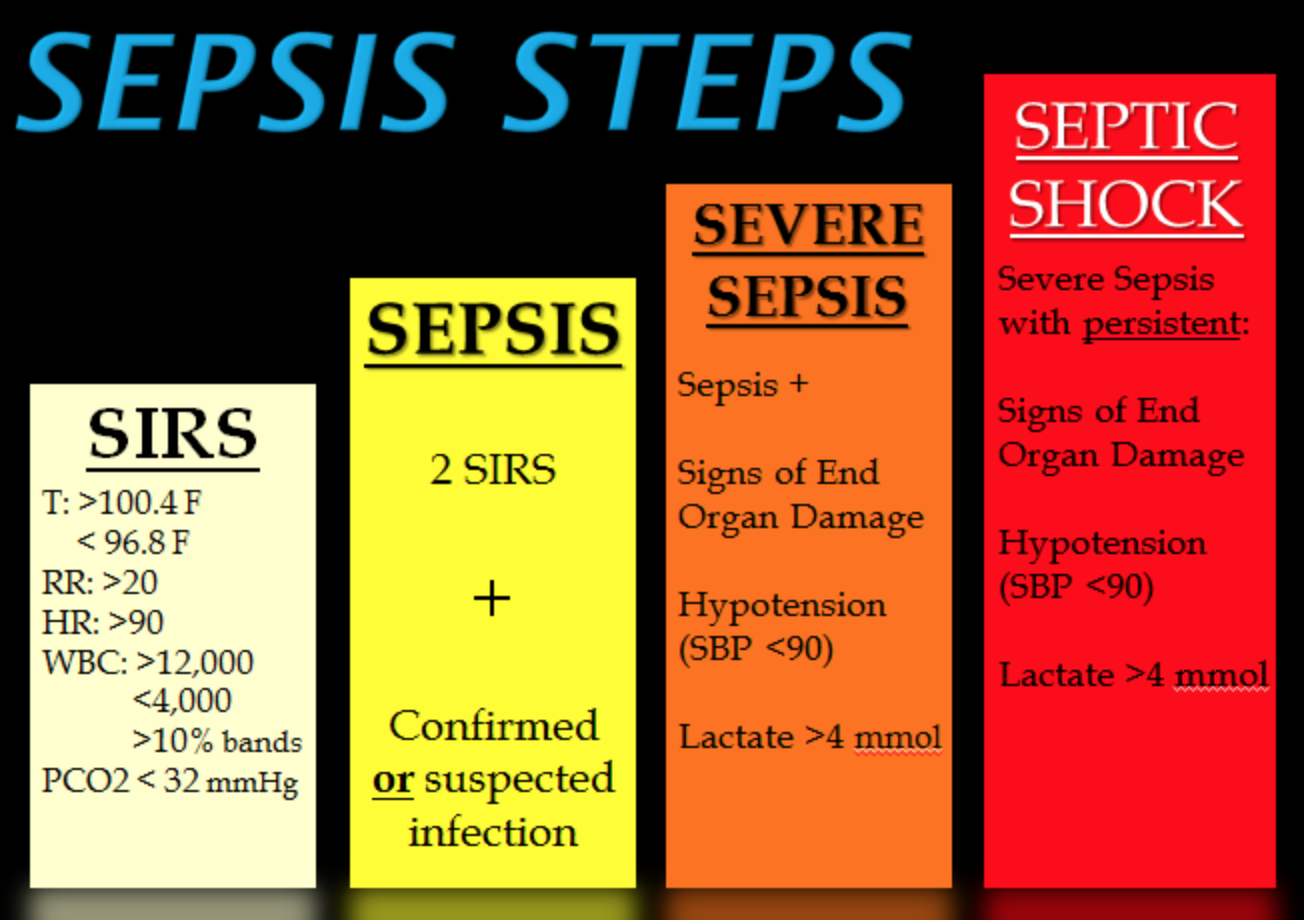
How many stages of sepsis are there?
There are three stages of sepsis: sepsis, severe sepsis, and septic shock. Sepsis can happen while you’re still in the hospital recovering from a procedure, but this isn’t always the case. It’s important to seek immediate medical attention if you have any of the below symptoms.
What are the criteria for sepsis?
There are two tools, or sets of criteria, doctors use to determine the severity of your condition. One is the systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS). SIRS is defined when you meet two or more of the following criteria:
What is the temperature of a person with sepsis?
Sepsis. Symptoms of sepsis include: a fever above 101ºF (38ºC) or a temperature below 96.8ºF (36ºC) heart rate higher than 90 beats per minute. breathing rate higher than 20 breaths per minute. probable or confirmed infection. You must have two of these symptoms before a doctor can diagnose sepsis.
When Sepsis Becomes Septic Shock
Sepsis treatment usually requires intravenous (IV) fluids and antibiotics. It is essential that the treatment begin as early as possible. The chance of sepsis progressing to severe sepsis and septic shock, causing death, rises by 4% to 9% for every hour treatment is delayed.
Why Septic Shock Is Dangerous
As your heart pumps blood throughout your body, it produces a certain amount of pressure to help push the blood through the blood vessels. The blood then delivers oxygen and nutrients to the organs and other body tissues. It also removes toxins. The average blood pressure for a healthy adult is less than or around 120/80 mmHg.
Septic Shock Complications
One of the most serious septic shock complications is organ damage. In some cases, the damage may only be temporary. For example, a person in septic shock may develop acute kidney injury. The kidneys are not able to filter out the toxins from the blood.
Septic Shock Treatment
Treating septic shock focuses on increasing the blood pressure, eliminating the infection that triggered the sepsis, and providing support for the organs that are failing. Some treatments could include:
After Septic Shock
Most often, you can be discharged from the ICU once your blood pressure is stable and supportive treatment, like a ventilator or dialysis, are no longer required. You will still be monitored and cared for, but in a lower-acuity ward or unit.
Is Volume Responsiveness a Meaningful Term?
Many methods exist and have been evaluated in attempts to identify patients who are “fluid responsive.” However, this term is ultimately ambiguous and may not be clinically meaningful. We may be able to identify patients in whom IVFs will increase stroke volume and/or cardiac output in the short term.
What About Guidelines for Resuscitation?
It is important to note that FRESH was conducted in a common scenario where patients who presented to an ED had initial resuscitation, as suggested by current guidelines.
Linked Article
Physiologically informed fluid and vasopressor resuscitation with the use of the passive leg raise-induced stroke volume change to guide management of septic shock is safe and demonstrated lower net fluid balance and reductions in the risk of renal and respiratory failure.
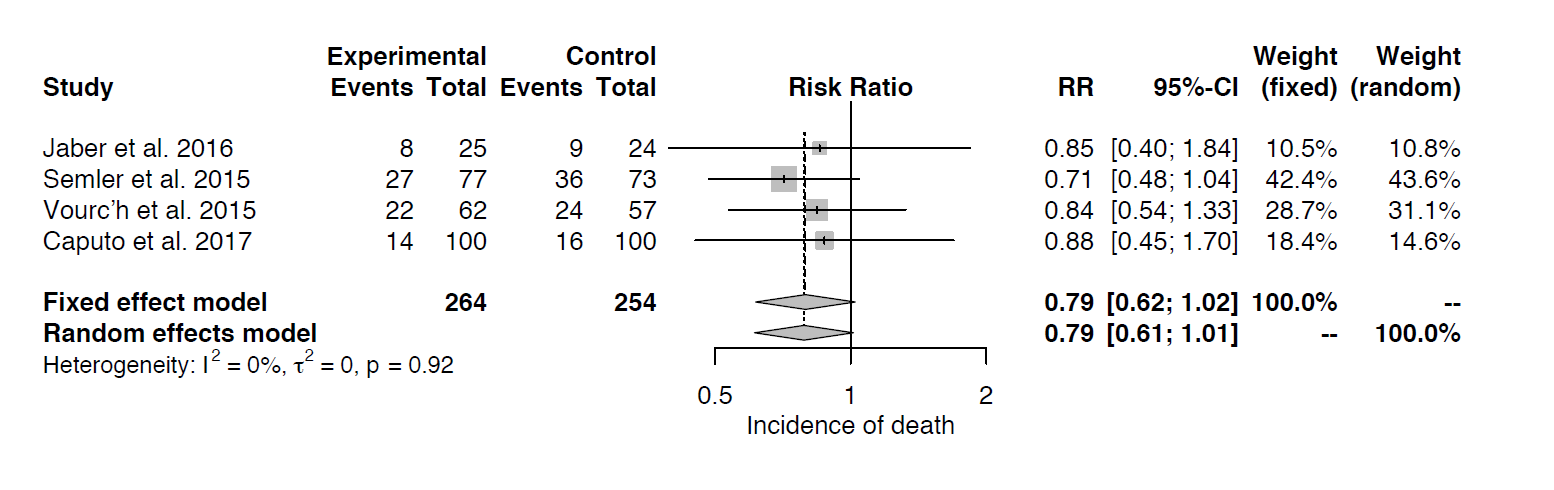
Is fluid resuscitation effective for sepsis?
Among critically ill adults, sepsis remains both common and lethal. In addition to antibiotics and source control, fluid resuscitation is a fundamental sepsis therapy. The physiology of fluid resuscitation for sepsis, however, is complex. A landmark trial found early goal-directed sepsis resuscitation reduced mortality, but 3 recent multicenter trials did not confirm this benefit. Multiple trials in resource-limited settings have found increased mortality with early fluid bolus administration in sepsis, and the optimal approach to early sepsis resuscitation across settings remains unknown. After initial resuscitation, excessive fluid administration may contribute to edema and organ dysfunction. Using dynamic variables such as passive leg raise testing can predict a patient's hemodynamic response to fluid administration better than static variables such as central venous pressure. Whether using measures of "fluid responsiveness" to guide fluid administration improves patient outcomes, however, remains unknown. New evidence suggests improved patient outcomes with the use of balanced crystalloids compared to saline in sepsis. Albumin may be beneficial in septic shock, but other colloids such as starches, dextrans, and gelatins appear to increase the risk of death and acute kidney injury. For the clinician caring for patients with sepsis today, the initial administration of 20 mL/kg of intravenous balanced crystalloid, followed by consideration of the risks and benefits of subsequent fluid administration represents a reasonable approach. Additional research is urgently needed to define the optimal dose, rate, and composition of intravenous fluid during the management of patients with sepsis and septic shock.
Is albumin good for septic shock?
Albumin may be beneficial in septic shock, but other colloids such as starches, dextrans, and gelatins appear to increase the risk of death and acute kidney injury. For the clinician caring for patients with sepsis today, the initial administration of 20 mL/kg of intravenous balanced crystalloid, followed by consideration ...
How many people died from sepsis in 2017?
The global burden of sepsis is difficult to ascertain, although a recent scientific publication estimated that in 2017 there were 48.9 million cases and 11 million sepsis-related deaths worldwide, which accounted for almost 20% of all global deaths (1)
What are the causes of sepsis in children?
Among children, the most common causes of sepsis-related deaths were neonatal disorders, lower respiratory infections, and diarrhoeal diseases (1). Group B streptococcus is the leading cause of both neonatal and maternal sepsis, though Escherichia coli is an emerging threat (8,9). Both of these pathogens have displayed considerable resistance ...
What is the role of antimicrobial resistance in sepsis?
Antimicrobial resistance is a major factor determining clinical unresponsiveness to treatment and rapid evolution to sepsis and septic shock. Sepsis patients with resistant pathogens have been found to have a higher risk of hospital mortality.
What is the clinical manifestation of infections acquired in the community setting?
Sepsis can be the clinical manifestation of infections acquired both in the community setting or in health care facilities. Health care-associated infections are one of, if not the most frequent type of adverse event to occur during care delivery and affect hundreds of millions of patients worldwide every year (2).
Why is AMR important in sepsis?
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) can jeopardize clinical management of sepsis because empirical antibiotic treatment is often required .
What are the symptoms of sepsis?
Warning signs and symptoms include: fever or low temperature and shivering, altered mental status, difficulty breathing/rapid breathing, increased heart rate, weak pulse/low blood pressure,
What is the cause of septic shock?
Sepsis is a life-threatening organ dysfunction caused by a dysregulated host response to infection (3). If not recognized early and managed promptly, it can lead to septic shock, multiple organ failure and death. It is most frequently a serious complication of infection, particularly in low- and middle-income countries where it represents ...
Antibiotics
IV Fluids
- Antibiotics alone won’t treat sepsis; you also need fluids. The body needs extra fluids to help keep the blood pressure from dropping dangerously low, causing shock. Giving IV fluids allows the health care staff to track the amount of fluid and to control the type of fluid. Ensuring the body has enough fluids helps the organs to function and may re...
Several Types of Fluid
- While there are several types of IV fluids, some are standard in treating sepsis. Normal saline is one commonly given fluid. It is a crystalloidfluid. These are fluids that contain minerals, such as sodium, and are water-soluble, or dissolve in water. These add fluid to the blood system. Colloids, another type of fluid, are thicker fluids. For example, blood is a colloid. Colloids given by IV inclu…
Additional Possible Treatments and Equipment
- Since all patients are different and there are many causes of sepsis, not every available treatment is right for each patient. To find out what treatment is being you or your loved one need and why, speak with your health care provider. Here are treatments, medications, and types of equipment that may be used on a patient with sepsis or septic shock.
Extracorporeal Therapies
- Extracorporeal therapiesare treatments done using machines and techniques such as continuous renal replacement therapy (a type of dialysis) or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, or ECMO (life support).
Special Types of Ivs
- Arterial lines– Arterial lines look like IV lines but they go directly into an artery, usually the wrist or groin. Nurses can monitor blood pressure and take frequent blood samples without inserting a needle in a vein each time one is needed. A special cap protects the line. It allows blood draws directly from the line. The line and cap must be monitored closely because the pressure caused …
Medications
- Corticosteroids– Although doctors don’t know why corticosteroids work for some patients who have sepsis and not others, they can be helpful. Corticosteroids can help reduce inflammation in the body and depress the immune system, making it less active. Vasopressors– Physicians prescribe vasopressors to patients who are in shock and whose blood pressures have dropped …
Equipment
- Endotracheal Tube– An endotracheal tube, or ET tube, goes through the mouth into the trachea (windpipe) and is attached to a ventilator. A patient who has an ET tube is intubated. When the tube comes out, they are extubated. Patients with ET tubes cannot speak as the tube passes through the vocal cords. If there is damage in the mouth but a patient needs intubation, the doct…