
Radiation therapy is almost always utilized as part of the overall breast-conserving strategy because radiation decreases the risk of local cancer recurrence and improves survival. Standard local treatment for ESBC involves either a mastectomy or a lumpectomy.
What is the goal of radiation therapy for breast cancer?
The goal of radiation therapy is to kill any cancer that might be left in the breast or nearby lymph nodes after surgery. Learn about emerging areas in radiation therapy. Radiation therapy is often given to women who are treated with lumpectomy (also called breast-conserving surgery) for DCIS.
Do all women with breast cancer need radiation therapy?
Not all women with breast cancer need radiation therapy, but it may be used in several situations: After breast-conserving surgery (BCS), to help lower the chance that the cancer will come back in the breast or nearby lymph nodes.
Is radiation necessary after breast-conserving surgery?
Recent clinical trials have shown that 90 percent of early stage breast cancer patients over age 70 do not benefit from radiation after breast-conserving surgery. And yet, use of radiation in this context has dropped only minimally.
How does radiation therapy work to treat cancer?
According to the National Cancer Institute, radiation therapy uses high energy rays or particles to kill cancer cells. Radiation kills or slows the growth of cancer cells. While it also affects nearby healthy cells, the healthy cells typically recover after the course of radiation treatment has ended.

Is radiation therapy necessary for breast cancer?
Radiation therapy can be used to treat all stages of breast cancer. Pregnant women should not have radiation therapy because it can harm the unborn baby. Radiation therapy is recommended for most people who have lumpectomy to remove breast cancer. Lumpectomy is sometimes called breast-conserving surgery.
How many radiation treatments are required for breast cancer?
It's usually recommended after lumpectomy. Radiation therapy for early breast cancer most often involves treatment once a day, 5 days a week, for 1-6 weeks. Getting to and from the treatment center every day for weeks can be hard, especially if you live far away or, if others rely on you for care.
What happens if you don't get radiation after lumpectomy?
A study has found that for women diagnosed with DCIS considered to have a low risk of recurrence treated with lumpectomy without radiation, the risk of DCIS recurrence or developing invasive disease in the same breast increased through 12 years of follow-up and didn't level off.
What happens if you decide not to do radiation?
Missed Radiation Therapy Sessions Increase Risk of Cancer Recurrence. Patients who miss radiation therapy sessions during cancer treatment have an increased risk of their disease returning, even if they eventually complete their course of radiation treatment, according to a new study.
At what stage of cancer is radiotherapy used?
Radiotherapy may be used in the early stages of cancer or after it has started to spread. It can be used to: try to cure the cancer completely (curative radiotherapy) make other treatments more effective – for example, it can be combined with chemotherapy or used before surgery (neo-adjuvant radiotherapy)
Do you lose hair with radiation?
Radiation therapy can also cause hair loss on the part of the body that is being treated. Hair loss is called alopecia. Talk with your health care team to learn if the cancer treatment you will be receiving causes hair loss.
Is radiation worth the risk?
Benefits and Effectiveness. Radiation therapy (also called radiotherapy) is a highly effective cancer treatment with wide-ranging uses. Radiation therapy leads to cancer cure in many patients (either alone or with other treatments) and relieves symptoms or prolongs survival in more advanced cancers.
Do I really need radiation after lumpectomy?
Radiation after lumpectomy If you're having an operation to remove the breast cancer and leave the remaining breast tissue intact (lumpectomy or breast-conserving surgery), your doctor may recommend radiation after your procedure to kill any cancer cells that might remain.
How soon after a lumpectomy does radiation start?
Radiation after Lumpectomy A course of radiation starts between six and 12 weeks after lumpectomy surgery. Most frequently, we target the entire breast (whole-breast radiation). In some cases, we also treat nearby lymph nodes.
How much does radiation therapy reduce risk of recurrence?
“Radiation does not appear to prolong survival. Even though it does significantly decrease the chance of the tumor coming back, after 10 years it was only a 10 percent recurrence rate without radiation. With radiation, it would reduce the recurrence rate to about 2 percent.”
Are lymph nodes always removed during lumpectomy?
Do The Lymph Nodes Always Need To Be Removed? Not always, especially when there is no evidence of any cancer in the lymph system. A mastectomy or lumpectomy operation will most often include either a sentinel node biopsy or an axillary node dissection.
How common is ductal carcinoma in situ?
About 1 in 5 new breast cancers will be ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS). Nearly all women with this early stage of breast cancer can be cured. DCIS is also called intraductal carcinoma or stage 0 breast cancer.
What is radiation therapy for breast cancer?
Radiation for Breast Cancer. Radiation therapy is treatment with high-energy rays (or particles) that destroy cancer cells. Some women with breast cancer will need radiation, in addition to other treatments. Radiation therapy is used in several situations: After breast-conserving surgery (BCS), to help lower the chance that ...
How long does radiation therapy last on breast?
Another option is hypofractionated radiation therapy where the radiation is also given to the whole breast, but in larger daily doses (Monday through Friday) using fewer treatments (typically for only 3 to 4 weeks).
How is brachytherapy done for breast cancer?
Intracavitary brachytherapy: This is the most common type of brachytherapy for women with breast cancer. A device is put into the space left from BCS and is left there until treatment is complete. There are several different devices available, most of which require surgical training for proper placement. They all go into the breast as a small catheter (tube). The end of the device inside the breast is then expanded like a balloon so that it stays securely in place for the entire treatment. The other end of the catheter sticks out of the breast. For each treatment, one or more sources of radiation (often pellets) are placed down through the tube and into the device for a short time and then removed. Treatments are typically given twice a day for 5 days as an outpatient. After the last treatment, the device is deflated and removed.
What is intensity modulated radiotherapy?
Intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT): IMRT is like 3D-CRT, but it also changes the strength of some of the beams in certain areas. This gets stronger doses to certain parts of the tumor bed and helps lessen damage to nearby normal body tissues. Brachytherapy: See brachytherapy below.
What is APBI in breast cancer?
In select women, some doctors are using accelerated partial breast irradiation (APBI) to give larger doses over a shorter time to only one part of the breast compared to the entire breast. Since more research is needed to know if these newer methods will have the same long-term results as standard radiation, not all doctors use them. There are several different types of accelerated partial breast irradiation:
How long does it take for radiation to be done after surgery?
If you will need external radiation therapy after surgery, it is usually not started until your surgery site has healed, which often takes a month or longer . If you are getting chemotherapy as well, radiation treatments are usually delayed until chemotherapy is complete.
What are the side effects of radiation on breast?
The main short-term side effects of external beam radiation therapy to the breast are: Swelling in the breast. Skin changes in the treated area similar to a sunburn (redness, skin peeling, darkening of the skin) Fatigue.
What is the treatment for early stage breast cancer?
Treatment for early stage breast cancer (ESBC) includes surgery, radiation, and/or systemic therapy with chemotherapy, immunotherapy or precision cancer medicines. The specific type and sequence of treatment for each person is individualized and is based on the stage of the cancer and its genomic profile. Radiation therapy uses high energy x-rays ...
How long does radiation therapy last after breast cancer?
Standard radiation therapy is typically delivered to the whole breast from a machine outside the body (external beam radiation therapy) on a daily basis for 5-7 weeks.
What is the treatment for node negative ESBC?
Patients with node-negative ESBC treated with breast-conserving surgery utilizing a lumpectomy are currently recommended to receive additional treatment with radiation therapy to reduce the risk of local cancer recurrence and to prolong survival.
How much radiation is given after lumpectomy?
30. Radiation “boost” therapy: Standard radiation therapy following a lumpectomy consists of a limited dose of radiation (50 Gy) to the entire affected breast.
How many women have stage 1 breast cancer?
The European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer conducted a clinical trial evaluating 5,318 women diagnosed with Stage I or II breast cancer who had undergone a lumpectomy followed by the standard dose of radiation.
What is the best treatment for ESBC?
Standard local treatment for ESBC involves either a mastectomy or a lumpectomy. A mastectomy involves removal of the entire breast, ...
How long does it take to get radiation for breast cancer?
With breast brachytherapy, a site-specific, prescribed dose of radiation is administered during a five-day course of therapy. The procedure involves inserting a deflated balloon into the cavity where the cancer was removed. An applicator shaft, or catheter, connects the balloon to the outside of the breast.
How many radiation oncologists treat breast cancer?
U-M researchers mailed a survey to 879 surgeons and 713 radiation oncologists who regularly treat breast cancer. The survey questions evaluated physician attitudes, knowledge, communication and recommendations regarding the omission of radiation therapy in older women with early stage breast cancer.
What percentage of surgeons are uncomfortable with radiation?
In this large national sample, published in the Annals of Surgical Oncology, researchers found that 40 percent of surgeons and 20 percent of radiation oncologists were uncomfortable with omitting radiation after lumpectomy.
Can breast cancer patients be treated with radiation?
Recent clinical trials have shown that 90 percent of early stage breast cancer patients over age 70 do not benefit from radiation after breast-conserving surgery. And yet, use of radiation in this context has dropped only minimally. A new University of Michigan study examines why.
Can lumpectomy patients avoid radiation?
Researchers, he says, have begun to identify whether patients who undergo lumpectomy can avoid radiation without compromising outcomes. Two recent prospective clinical trials observed a favorable outcome among older women with stage 1, estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer, even with omission of radiotherapy.
What is the goal of radiation therapy?
The goal of radiation therapy is to kill any cancer that might be left in the breast or nearby lymph nodes after surgery. Radiation therapy is an option for many women who have: Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS, non-invasive breast cancer) Early breast cancer. Radiation therapy is standard treatment for most women who have:
Where is radiation used after mastectomy?
However, in some cases, radiation therapy is used after mastectomy to treat the chest wall and lymph nodes. These can include the lymph nodes in the underarm area (axillary nodes), around the collarbone or near the breastbone (internal mammary nodes). Radiation therapy is carefully planned and precisely given.
How long does radiation therapy last after a lumpectomy?
It’s usually recommended after lumpectomy. Radiation therapy for early breast cancer most often involves treatment once a day, 5 days a week, for 3-6 weeks.
What is DCIS radiation?
Radiation therapy and DCIS. Radiation therapy is often given to women who are treated with lumpectomy (also called breast-conserving surgery) for DCIS. In rare cases, radiation therapy is given to women treated with mastectomy for DCIS. Learn more about treatment for DCIS.
What are the side effects of radiation therapy?
Radiation therapy has some short-term side effects (such as skin tenderness) and for some women, long-term side effects (such as lymphedema ). Learn more about possible side effects of radiation therapy.
Can you have radiation on a silicone breast implant?
Women who have breast implants (saline or silicone) can usually have radiation therapy. However, radiation therapy can impact the cosmetic look and the long-term viability of the implant (whether the implant will fail and need to be removed). Side effects of radiation therapy on breast implants.
Can radiation therapy cause breast cancer?
Radiation therapy can cause harm to normal tissue during and after treatment in people who have certain inherited gene mutations. In some women at higher risk of breast cancer recurrence, radiation therapy may still be used. Past radiation therapy to the same breast or to the same side of the chest.
What type of radiation is used for breast cancer?
Two common types of radiation treatment for breast cancer are external beam radiation and internal beam radiation , also known as brachytherapy, which typically has fewer side effects. The type of radiation that’s best suited for you depends on: Talk with your doctor about your treatment options.
How does a breast cancer machine work?
With this method, a large machine sends beams of radiation to the area of your breast that’s been affected by cancer. The beams are aimed directly at the site of your tumor. While the machine moves around you, it can send radiation to your tumor from different directions.
What to expect when you have external beam radiation?
If you have external beam radiation, you’ll meet with your radiation oncologist and a nurse before starting treatment. They will walk you through what to expect with external beam radiation, and the risks and benefits of this treatment. At this time, you’ll likely have a physical exam and go over your medical history.
How long does radiation therapy last?
With breast cancer, radiation therapy usually begins about 3 to 4 weeks after breast-conserving therapy or a mastectomy, according to the National Breast Cancer Foundation. External beam radiation is typically given once a day, 5 days a week, for anywhere from 2 to 10 weeks on an outpatient basis.
What is the most common type of radiation therapy?
The most common type of radiation therapy is external beam radiation, according to the American Cancer Society. With external beam radiation, a machine directs high energy beams of radiation at the area where the cancer cells have been found.
What is the catheter used for breast radiation?
Most internal radiation, or brachytherapy, is given with a catheter. This is a small, flexible tube that’s surgically placed into the space left from breast-conserving surgery. At the end of the catheter is a device that can be inflated inside your breast so that it stays in place for the duration of the treatment.
What is internal radiation?
The National Cancer Institute also shares that internal radiation is when a source of radiation is put into your body. This type of radiation is also known as brachytherapy. In brachytherapy, a device with radioactive seeds or pellets is temporarily put into your breast tissue where the tumor was located.
Does Everybody With Breast Cancer Have Radiotherapy
Not all women with breast cancer will be recommended to have radiotherapy. It is usually recommended, however, for women who have breast-conserving surgery . Radiotherapy is sometimes used following a mastectomy to target any cancer cells that may remain in the chest wall.
Increased Risk Of Leukemia
Very rarely, certain chemo drugs can cause diseases of the bone marrow, such as myelodysplastic syndromes or even acute myeloid leukemia, a cancer of white blood cells. If this happens, it is usually within 10 years after treatment.
How Long Can You Wait For Radiation After Lumpectomy
Radiation therapy usually begins three to eight weeks after surgery unless chemotherapy is planned. When chemotherapy is planned, radiation usually starts three to four weeks after chemotherapy is finished. You will likely get radiation therapy as an outpatient at a hospital or other treatment facility.
Who Is On My Radiation Therapy Team
A highly trained medical team will work together to provide you with the best possible care. This team may include the following health care professionals:
Radiation For Metastatic Breast Cancer
Sometimes breast cancer spreads to other parts of the body. When this happens, the breast cancer is called metastatic or stage IV.
Answers From The Community
You don’t HAVE to do anything in regards to medical treatment. But you need to be informed about what may happen if you don’t. There is a reason why radiation is part of the regimen for treating breast cancer. Your chances of recurrence may increase if you decide to skip it.
Starting With Neoadjuvant Therapy
Most often, these cancers are treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy . For HER2-positive tumors, the targeted drug trastuzumab is given as well, sometimes along with pertuzumab . This may shrink the tumor enough for a woman to have breast-conserving surgery . If the tumor doesnt shrink enough, a mastectomy is done.
What is the best treatment for breast cancer?
External beam radiation is the most common kind of radiation treatment for breast cancer. It’s a painless treatment, like getting an X-ray. A doctor will place a machine on the outside of your body and aim the radiation beams at the area of the cancer.
How long does radiation therapy last in breast cancer?
Outpatient treatment sessions happen twice a day for five days.
What is intraoperative radiation?
Intraoperative radiation (IORT) is a treatment option given after the removal of cancer cells during surgery. A doctor will direct a single, high-dose radiation beam on the part of the exposed breast tissue where the cancer appeared. Doctors will shield normal tissues close to the area from radiation exposure.
What type of radiation is used to treat a tumor?
The rays are directed at the area where the tumor appeared. Two common types of radiation treatment are external beam radiation and internal beam radiation. When radiation treatment starts depends on if you’ve had chemotherapy. It also depends on if you’ve had a mastectomy or breast-conserving surgery.
How long does it take to get rid of breast cancer?
For a short time, internal radiation targets only the area where breast cancer is most likely to return. This causes fewer side effects. The treatment takes a week to complete.
How long does radiation treatment last?
Radiation can start after two weeks, to a month or later. Radiation treatment often lasts more than a month. The number of sessions depends on the type of radiation treatment you have.
How long does it take to get radiation to a cancer patient?
A small device that brings a high dose of radiation to the cancer area. This technique takes up to 10 minutes.
What is a radiation boost for breast cancer?
A radiation boost for breast cancer sounds like what it is—an extra radiation dose given after the regular sessions of radiation are complete. While the bulk of radiation therapy focuses on the whole breast, a boost targets the area where the primary tumor was located. The goal is to reduce the likelihood of breast cancer recurrence.
How long does radiation help with breast cancer?
That said, even though a radiation boost significantly reduces the risk of breast cancer recurrence, it does not appear to have any effect on overall survival up to 20 years out after treatment.
What is the treatment for breast cancer?
Breast cancer is often treated with surgery, either a lumpectomy or mastectomy. 1 In addition to surgery, other treatments may be given, such as chemotherapy and radiation therapy, which is treatment with high-energy rays or particles that kill cancer cells. The most common type of radiation therapy given after a lumpectomy ...
Does radiation therapy affect the heart?
Side Effects of Radiation Therapy. There is some concern with left sided breast cancer that radiation could have negative long-term effects on the heart. A newer technique of breath-holding is used by some cancer centers to reduce this risk.
Does radiation affect breasts?
Side Effects. A radiation boost is generally tolerated quite well, carrying the same side effects as whole breast radiation, including fatigue , swelling of the breast, and skin changes like redness, blistering, peeling, and darkening of the skin.
Can you get radiation after a mastectomy?
Radiation to the chest wall may also be given after a mastectomy, particularly if lymph nodes are positive. If you receive radiation treatment and a radiation boost is planned, it will be administered after your whole breast irradiation treatment sessions are complete.
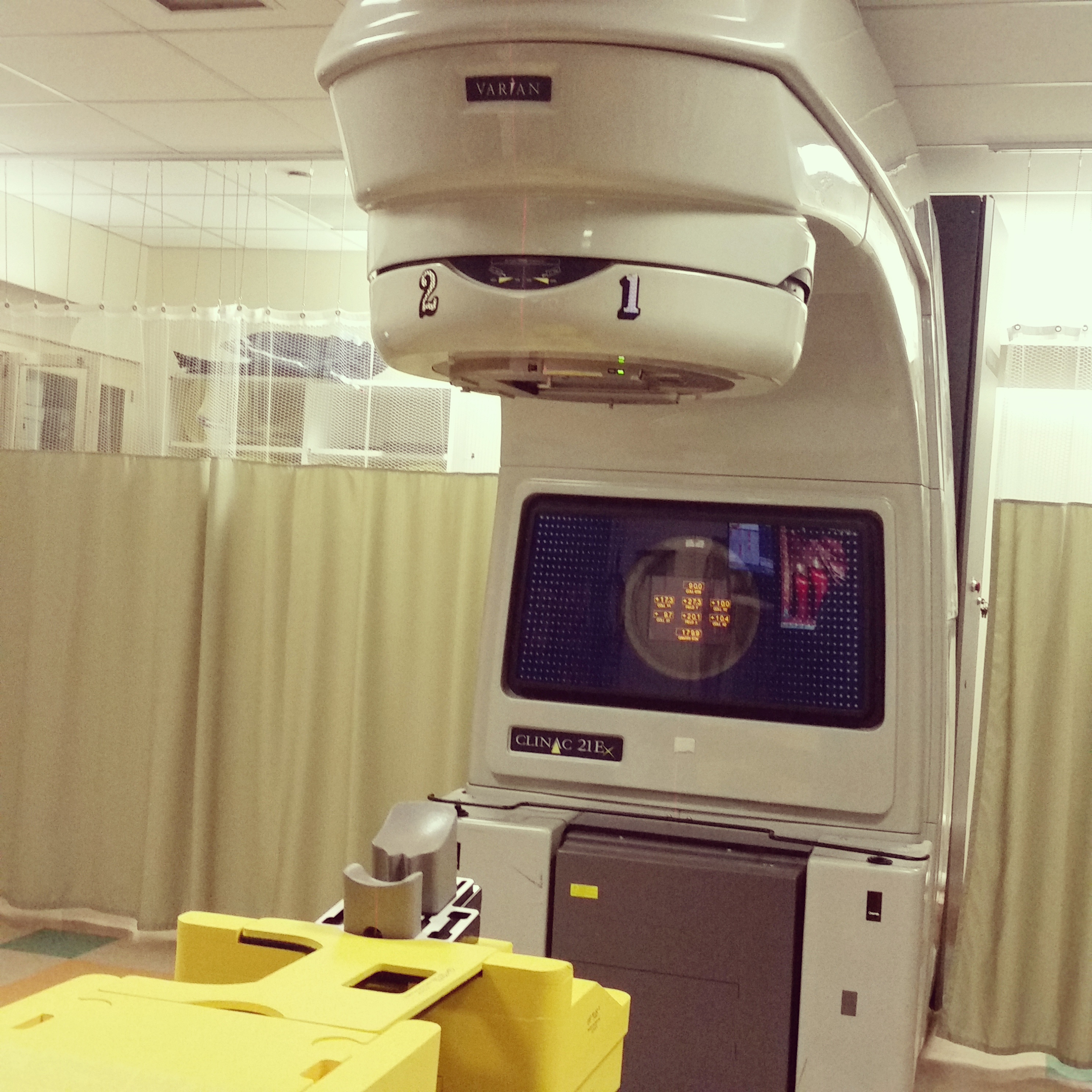
Why It's Done
- Radiation therapy kills cancer cells. It's often used after surgery to reduce the risk that the cancer will come back. It can also be used to provide relief from pain and other symptoms of advanced breast cancer.
Risks
- Side effects from radiation therapy differ significantly depending on the type of treatment and which tissues are treated. Side effects tend to be most significant toward the end of your radiation treatment. After your sessions are complete, it may be several days or weeks before side effects clear up. Common side effects during treatment may include: 1. Mild to moderate fatigu…
How You Prepare
- Before your radiation treatments, you'll meet with your radiation therapy team, which may include: 1. A radiation oncologist,a doctor who specializes in treating cancer with radiation. Your radiation oncologist determines the appropriate therapy for you, follows your progress and adjusts your treatment, if necessary. 2. A radiation oncology medical physicist and a dosimetrist,who make c…
What You Can Expect
- Radiation therapy usually begins three to eight weeks after surgery unless chemotherapy is planned. When chemotherapy is planned, radiation usually starts three to four weeks after chemotherapy is finished. You will likely have radiation therapy as an outpatient at a hospital or other treatment facility. A common treatment schedule (course) historically has included one ra…
Results
- After you complete radiation therapy, your radiation oncologist or other medical professionals will schedule follow-up visits to monitor your progress, look for late side effects and check for signs of cancer recurrence. Make a list of questions you want to ask members of your care team. After your radiation therapy is completed, tell your medical professional if you experience: 1. Persiste…
Clinical Trials
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiesof tests and procedures to help prevent, detect, treat or manage conditions.