
The accurate quantity of flow is a essential for future planning and management. Knowing the rate of flow of industrial effluents or wastewater and concentration of substances in it is necessary to find a solution of many problems in Industrial process, water supply, utilization and ultimate disposal.
Why is wastewater treatment necessary?
It may also be necessary to remove nitrates and phosphates (plant nutrients) and to neutralize or remove industrial wastes and toxic chemicals. The degree to which wastewater must be treated varies, depending on local environmental conditions and governmental standards. Two pertinent types of standards are stream standards and effluent standards.
What is flow in wastewater?
Flow is a very fluid term in wastewater and can be defined a number of ways based on what is being measured. Flow is typically measured using a p arshall flume (see image to the right). Average Daily Flow (ADF): Average Daily Flow is the average of 24-hour volumes to be received by the wastewater system for a continuous 12-month period.
How does a wastewater treatment plant work?
Effectively, wastewater treatment plants do as described; they treat the water that goes down our drains before discharging it back into the environment. Regardless of the efforts that are being made to install these plants worldwide, more is required. Water is one of our most important resources and it’s being squandered.
What is the role of oxygen in wastewater treatment?
The supplied oxygen is utilised by bacteria in the wastewater to break down the organic matter containing carbon to form carbon dioxide and water. Without the presence of sufficient oxygen, bacteria are not able to biodegrade the incoming organic matter in a reasonable time.
Why flow rate is important in wastewater treatment?
Flow measurement is a basic and important control parameter for ensuring that clean, high-quality water is available. Applications ranging from water storage and transmission to wastewater treatment, leak detection and pump management cannot be done without flow meter technology.
What is flow in water treatment?
Flow equalization is the process of controlling hydraulic velocity, or flow rate, through a wastewater treatment system. The equalization of flow prevents short term, high volumes of incoming flow, called surges, from forcing solids and organic material out of the treatment process.
How does the wastewater flow to the treatment plant?
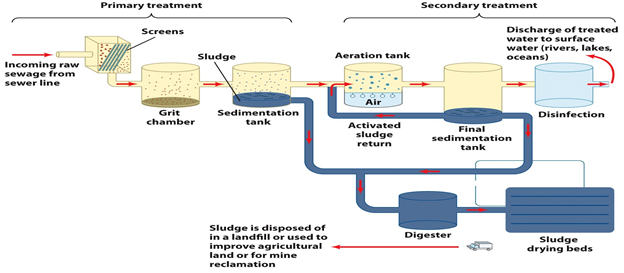
Primary Treatment As sewage enters a plant for treatment, it flows through a screen, which removes large floating objects such as rags and sticks that might clog pipes or damage equipment. After sewage has been screened, it passes into a grit chamber, where cinders, sand, and small stones settle to the bottom.
What is wastewater flow rate?
The USEPA estimates average daily wastewater flows of approximately 50 to 70 gallons per person per day being typical of residential dwellings built before 1994 (USEPA, 2002). This average is based on a number of recent studies summarized in Table 1.
What does water flow mean?
Definition of water flow : a flow or flowing of water also : the amount of water flowing (as past a valve) per unit of time.
What is the difference between flow and capacity?
Summary. Flow is the actual amount of water being treated, moved or reused. Flow frequently is expressed in MGD. Capacity represents the ability to treat, move or reuse water.
What is sewage flow?
The average sewage flow rate is usually about the same as the average water use in the community. In a lateral sewer, short-term peak flow rates can be roughly four times the average flow rate. In a trunk sewer, peak flow rates may be two-and-a-half times the average.
What is the process of wastewater treatment?
Treatment StepsStep 1: Screening and Pumping. ... Step 2: Grit Removal. ... Step 3: Primary Settling. ... Step 4: Aeration / Activated Sludge. ... Step 5: Secondary Settling. ... Step 6: Filtration. ... Step 7: Disinfection. ... Step 8: Oxygen Uptake.
What are the 3 stages of wastewater treatment?
There are three main stages of the wastewater treatment process, aptly known as primary, secondary and tertiary water treatment. In some applications, more advanced treatment is required, known as quaternary water treatment.
How is wastewater flow measured?
The traditional method of measuring wastewater flows is through the use of a flume and an ultrasonic flow meter in a flow manhole (concrete vault / manhole or fiberglass packaged metering manhole). The combination is reliable and usually requires low maintenance.
What are the components of wastewater flows?
Components of Waste WaterBiochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD) ... Total Suspended Solids (TSS) ... Pathogens. ... Nutrients. ... Contaminants of Emerging Concern (CEC)
What is maximum flow in sewage?
(a)maximum to the average flow of sewage is between 1.5 to 1.0 and average to the minimum is between 1.2 to 1.0.
What is wastewater and what does the treatment of it entail?
To put it simply, wastewater is any form of water that has been contaminated by a commercial or domestic process. This includes water that was used for sewerage and water that’s a by-product of large-scale industries such as mining and manufacturing. While wastewater is still a huge problem in Ireland and all around the world, the most affected areas are developing nations – mainly Asia and South America.
Why is wastewater considered a water use?
We consider wastewater treatment as a water use because it is so interconnected with the other uses of water. Much of the water used by homes, industries, and businesses must be treated before it is released back to the environment.
Why is wastewater reuse important?
The reuse of treated wastewater has become a viable option to minimising water scarcity problems. The world has a growing and developing population and as things stand right now, we’re on a downward slope in terms of water conservation. Having said this, with some smart thinking, wastewater treatment and some generous open mindedness (something previously almost unheard of from corporations) we can turn this around and make much needed changes all around the globe.
Is water a resource?
Water is one of our most important resources and it’s being squandered. There are multiple ways to treat wastewater, and the better the process, the higher the percentage that it can be reused before it gets dumped into the ocean.
Is wastewater bad for the environment?
All around the world, it’s common practice to pump enormous volumes of wastewater into rivers, oceans and streams. This has extremely negative effects on the environment, fisheries, animals, and that’s not to mention it’s an aptly named ‘waste’ of water too.
Why is wastewater treated?
In either case, wastewater must be purified or treated to some degree in order to protect both public health and water quality. Suspended particulates and biodegradable organics must be removed to varying extents. Pathogenic bacteria must be destroyed.
Why is sewage flow higher?
Although sewage flows depend upon residential, commercial, and industrial connections, sewage flow rates potentially can become higher as a result of inflows and infiltration (I&I) into the sanitary sewer system. Inflows correspond to storm water entering sewers from inappropriate connections, such as roof drains, storm drains, ...
How is wastewater capacity determined?
The size and capacity of wastewater treatment systems are determined by the estimated volume of sewage generated from residences, businesses, and industries connected to sewer systems as well as the anticipated inflows and infiltration (I&I). The selection of specific on-lot, clustered, or centralized treatment plant configurations depends upon factors such as the number of customers being served, the geographical scenario, site constraints, sewer connections, average and peak flows, influent wastewater characteristics, regulatory effluent limits, technological feasibility, energy consumption, and the operations and maintenance costs involved.
What is inflow in sewer system?
Inflows correspond to storm water entering sewers from inappropriate connections, such as roof drains, storm drains, downspouts and sump pumps. High amounts of rainwater runoff can reach the sewer system during precipitation and stormflow events or during seasonal spring flooding of rivers inundated with melting ice.
What are the three levels of wastewater treatment?
There are three levels of wastewater treatment: primary, secondary, and tertiary (or advanced). Primary treatment removes about 60 percent of total suspended solids and about 35 percent of BOD; dissolved impurities are not removed. It is usually used as a first step before secondary treatment. Secondary treatment removes more than 85 percent of both suspended solids and BOD. A minimum level of secondary treatment is usually required in the United States and other developed countries. When more than 85 percent of total solids and BOD must be removed, or when dissolved nitrate and phosphate levels must be reduced, tertiary treatment methods are used. Tertiary processes can remove more than 99 percent of all the impurities from sewage, producing an effluent of almost drinking-water quality. Tertiary treatment can be very expensive, often doubling the cost of secondary treatment. It is used only under special circumstances.
What are the factors that determine the effluent standards?
The factors controlled under these standards usually include biochemical oxygen demand (BOD), suspended solids, acidity, and coliforms.
How long does it take to disinfect a water tank?
Disinfection is usually accomplished by mixing the effluent with chlorine gas or with liquid solutions of hypochlorite chemicals in a contact tank for at least 15 minutes. Because chlorine residuals in the effluent may have adverse effects on aquatic life, an additional chemical may be added to dechlorinate the effluent.
Drinking Water Production & Distribution Systems
There are a number of safety demands that drinking water production and distribution systems need to meet. Flow meters can help municipalities make a difference at every phase of the water production process, from acquiring and clarifying to delivering to consumers.
Collection & Recovery Systems
Municipal and industrial wastewater treatment plants perform many critical tasks during the collection and recovery process. Whether it’s purifying water for reuse or discharging it back into the world for reuse, flow meters can be installed at each step of the process to ensure the quality and condition of the water before it leaves a facility.
Implementing Flow Meters in Water & Wastewater Treatments
Whether water and wastewater facilities are currently using flow meters in their processes or are looking to improve accuracy within a specific step of the process, there are several factors that should be addressed to ensure the right meter is installed and meets the safety and variable demands of your system.
What is the purpose of wastewater treatment facilities?
Summary. The main goal of wastewater treatment facilities is to protect humans and the ecosystem from harmful and toxic elements found in wastewater. Water treatment facilities were designed to speed up the natural process of purifying water because the natural process is overloaded.
Why is wastewater important for the ecosystem?
Wastewater treatment also protects the ecosystem. Fish and aquatic life require fresh water. When their water environment is laden with wastewater, they cannot survive. If chemicals, such as nitrogen and phosphates, enter streams, rivers or large bodies of water in excessive amounts, it causes excessive plant growth which release toxins into ...
Why do we need water treatment facilities?
Water treatment facilities are designed to speed up the natural process of purifying water. With billions of people and even more wastewater, the natural process is overloaded. Without wastewater treatment, the amount of wastewater would cause devastation, as it still does today in developing countries. Globally, over 80 percent of all wastewater is discharged without treatment. 1 In the countries that do have water treatment facilities, they use various methods to treat water with one common goal: purify water as much as possible and send it back into the environment to keep humans and the Earth safe and thriving.
What are the health risks of wastewater treatment?
Unclean water poses significant health risks, accounting for 1.7 million deaths annually, of which over 90 percent are in developing countries. 2 Several water-related diseases, including cholera and schistosomiasis, remain widespread across many developing countries, where only a very small fraction (in some cases less than 5 percent) of domestic and urban wastewater is treated prior to its release into the environment 3.
Why is natural water treatment overloaded?
While Mother Nature does her best to naturally process wastewater, there is too much for her to handle. Because the global population is so large and growing, so is wastewater. Nature can’t keep up with naturally processing the excessive amounts of wastewater.
How much of the world's wastewater is discharged without treatment?
Globally, over 80 percent of all wastewater is discharged without treatment. 1 In the countries that do have water treatment facilities, they use various methods to treat water with one common goal: purify water as much as possible and send it back into the environment to keep humans and the Earth safe and thriving.
What is the cause of flow measurement failure?
The quick answer can be everywhere from the design of flow measurement structures, choosing the wrong technology or the wrong place, to poor operation; or, in some cases, accidental (through poor knowledge) or deliberate tampering to misguidedly make the treatment works “pass.”
What is the problem with flow meters?
Lack of meter cleaning. This is prevalent with all types of flow meters and can be a major problem.
Why is my flow meter scaling so bad?
Poor scaling on telemetry that can be caused by raising the maximum flow rate on-site and at the meter, but not in the telemetry system. As a result, the flow meter is incorrect by a variable factor.
Where are flow meters placed?
The electromagnetic flow meters have been placed downstream of 45-degree bends and upstream of non-return valves, gate valves, and other bends (flow is right to left) for sludge measurement. To minimize pipe lengths, the flow meters that control the chemicals being dosed to the sludge aren’t given a chance to measure correctly, which potentially causes more chemical to be used than needed. Simple advice from the manufacturer, which is usually available as part of product support, would have prevented this situation entirely.
Is flow meter technology valid?
All of the technologies available are valid, and all of them have their strengths and their weaknesses. It’s up to the engineer to select the most appropriate technology and to ensure that it is designed and installed correctly, which can be a difficult process. Thankfully, flow meter suppliers are usually available to help get a technology working as well as it should.
Can you see debris in an electromagnetic flow meter?
This risk is hidden when it comes to electromagnetic flow meters as they are a closed-piped system. Therefore, it’s not possible to see the debris that accumulates within the flow measurement tube. Figures 5 and 6 show the debris that can accumulate within an electromagnetic flow meter, which is why a regular cleaning regimen is important.
What is aeration in wastewater treatment?
Aeration is the most critical component of a treatment system using the activated sludge process. A well designed aeration system has a direct impact on the level of wastewater treatment it achieves. An ample and evenly distributed oxygen supply in an aeration system is the key to rapid, economically-viable, and effective wastewater treatment.
What is the process of adding air into wastewater to allow aerobic bio-degradation of the pollutant components?
Wastewater aeration is the process of adding air into wastewater to allow aerobic bio-degradation of the pollutant components. It is an integral part of most biological wastewater treatment systems.
How does Aeration Work?
Aeration provides oxygen to bacteria for treating and stabilizing the wastewater. Oxygen is needed by the bacteria to allow biodegradation to occur. The supplied oxygen is utilised by bacteria in the wastewater to break down the organic matter containing carbon to form carbon dioxide and water. Without the presence of sufficient oxygen, bacteria are not able to biodegrade the incoming organic matter in a reasonable time. In the absence of dissolved oxygen, degradation must occur under septic conditions which are slow, odorous, and yield incomplete conversions of pollutants. Under septic conditions, some of the biological process convert hydrogen and sulphur to form hydrogen sulphide and transform carbon into methane. Other carbon will be converted to organic acids that create low pH conditions in the basin and make the water more difficult to treat and promote odour formation. Bio-degradation of organic matter in the absence of oxygen is a very slow biological process.
When is Aeration Used?
In municipal and industrial wastewater treatment, aeration is part of the stage known as the secondary treatment process. The activated sludge process is the most common option in secondary treatment. Aeration in an activated sludge process is based on pumping air into a tank, which promotes the microbial growth in the wastewater. The microbes feed on the organic material, forming flocks which can easily settle out. After settling in a separate settling tank, bacteria forming the "activated sludge" flocks are continually recirculated back to the aeration basin to increase the rate of decomposition.
Why is water and wastewater important?
Water and wastewater processes are important to cities and towns of all sizes. These operations are complex and involve a wide range of flow measurement applications. They demand high flow meter accuracy and reliability as well as long-term stability and a low cost of ownership.
Why is it important to monitor and control wastewater?
As sewage networks and wastewater treatment plants strive for greater efficiency and cost reduction, it is imperative that they monitor and control operations more precisely. When heavy rainfall or other abnormal events occur, wastewater levels in the collection system and wet wells can rapidly reach critical levels and accurate information from flow metering equipment is needed to take appropriate actions.
What is a noninvasive flow meter?
Noninvasive flow measurement instruments, such as ultrasonic clamp-on flow meters, are a good solution when users cannot shut down water and wastewater operations to install a traditional inline meter. As ultrasonic meters measure from the pipe wall outside, there is no wear on the device.
Why is flow measurement important?
Flow measurement is a basic and important control parameter for ensuring that clean, high-quality water is available to commercial, residential and industrial users. Applications ranging from water storage and transmission to wastewater treatment, leak detection and pump management require flow meter technology.
What is ultrasonic transit time flow?
A growing number of municipal wastewater departments are finding that ultrasonic transit time flow meters are a good solution for lift stations. The meters enable improved diagnostics to measure flow, help identify potential pump failures and initiate appropriate preventative maintenance programs on equipment at the stations—which extends asset life.
Why do municipalities need lift stations?
Municipalities have a significant financial stake in the performance of lift stations. When groundwater and stormwater enter city collection systems , treatment processes become less efficient and sanitary sewer systems become strained. Lift station pumps run for a longer duration after a rain event and have a larger number of starts and stops—indicating stormwater has entered the sanitary sewer system and is on its way to be treated. This additional stormwater costs municipalities money by increasing pump operation and wastewater treatment.
What is flow meter?
Flow meters measure, monitor and control many water-related processes. The question is which technology to use, since a wide variety of meter designs are available. Each type of meter has pros and cons and must be properly deployed to achieve optimal performance.
Why is alkalinity important in wastewater treatment?
This ability to maintain the proper pH in the wastewater as it undergoes treatment is the reason why alkalinity is so important to the wastewater process. If all alkalinity in the wastewater process is consumed , an alkaline solution such as caustic soda or magnesium hydroxide can be added to maintain the system pH between 7-8 as ...
What pH is needed for wastewater treatment?
The bacteria and other organisms which play an active role in wastewater treatment are most effective at a neutral to slightly alkaline pH of 7 to 8. To maintain these optimal pH conditions for biological activity there must be sufficient alkalinity present in the wastewater to neutralize acids generated by the active biomass during waste treatment especially nitrification. This ability to maintain the proper pH in the wastewater as it undergoes treatment is the reason why alkalinity is so important to the wastewater process. If all alkalinity in the wastewater process is consumed, an alkaline solution such as caustic soda or magnesium hydroxide can be added to maintain the system pH between 7-8 as the denitrifying bacteria generate acid but this adds cost and complexity to the system.

Drinking Water Production & Distribution Systems
- There are a number of safety demands that drinking water production and distribution systems need to meet. Flow meters can help municipalities make a difference at every phase of the water production process, from acquiring and clarifying to delivering to consumers. 1. Acquire:Water acquisition is the first step in successful water production and distribution. It involves managin…
Collection & Recovery Systems
- Municipal and industrial wastewater treatment plants perform many critical tasks during the collection and recovery process. Whether it’s purifying water for reuse or discharging it back into the world for reuse, flow meters can be installed at each step of the process to ensure the quality and condition of the water before it leaves a facility. 1. Collect:Collection is the first step of the r…
Implementing Flow Meters in Water & Wastewater Treatments
- Whether water and wastewater facilities are currently using flow meters in their processes or are looking to improve accuracy within a specific step of the process, there are several factors that should be addressed to ensure the right meter is installed and meets the safety and variable demands of your system.