Disinfection is the final stage in drinking water treatment before its distribution. Disinfection is used to remove pathogenic micro-organisms from the water.
Full Answer
What is the purpose of water disinfection?
Water disinfection. The agents also remove organic contaminants from water, which serve as nutrients or shelters for microorganisms. Disinfectants should not only kill microorganisms. Disinfectants must also have a residual effect, which means that they remain active in the water after disinfection.
Do disinfectants kill microorganisms in water?
Disinfectants should not only kill microorganisms. Disinfectants must also have a residual effect, which means that they remain active in the water after disinfection. A disinfectant should prevent pathogenic microorganisms from growing in the plumbing after disinfection, causing the water te be recontaminated.
How to disinfect water adequately?
To disinfect water adequately, the water must have been pretreated, when necessary, to reduce the concentration of solid materials to an acceptably low level.
What determines disinfectant efficacy?
Model Systems and Indicator Organisms A major factor that influences the evaluation of the efficacy of a particular disinfectant is the test microorganism. There is a wide variation in susceptibility, not only among bacteria, viruses, and protozoa (cyst stage), but also among genera, species, and strains of the microorganism.
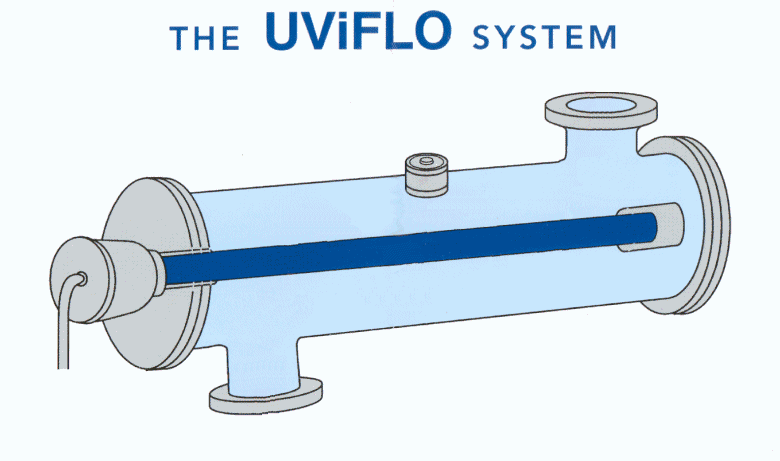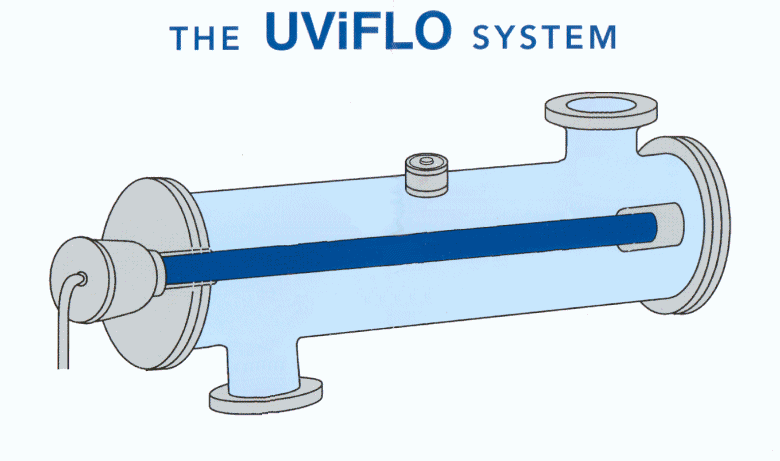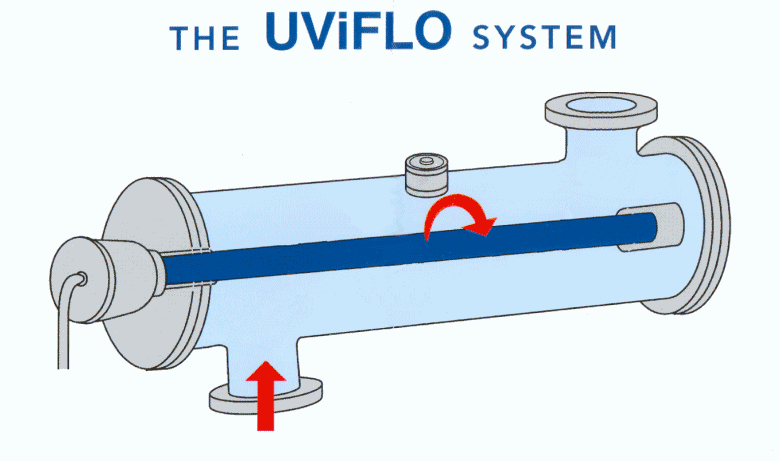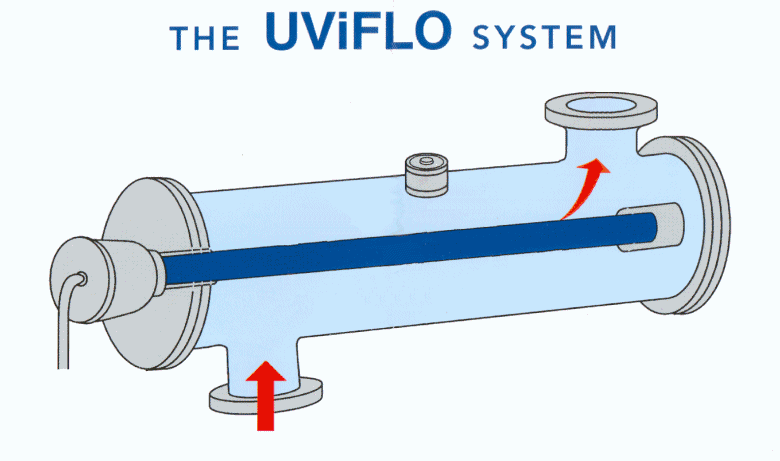
What is the last process of water treatment?
Disinfection. The final stage in the community water treatment process involves adding a disinfectant such as chlorine or chloramine to the water supply. Chlorine has been used since the late 1800s. The type of chlorine used in water treatment is monochloramine.
Which disinfectant has the longest lasting residual in water?
ChloraminesChloramines provide longer-lasting disinfection as the water moves through pipes to consumers. This type of disinfection is known as secondary disinfection.
What is the purpose of disinfection in water treatment?
To prevent contamination with germs, water companies add a disinfectant—usually either chlorine or chloramine—that kills disease-causing germs such as Salmonella, Campylobacter, and norovirus.
What is the disinfection stage of the water treatment process?
Disinfection is the final stage in drinking water treatment before its distribution. Disinfection is used to remove pathogenic micro-organisms from the water.
How long does chlorine last in water?
2 ppm of Chlorine will take up to 4 and a half days or around 110 hours to evaporate from 10 gallons of standing water. Ultraviolet light, water circulation, and aeration will speed up the evaporation process dramatically. Chlorine will last between 6 and 8 minutes in 10 gallons of boiling tap water.
What is the primary purpose of a residual disinfectant in the water distribution system?
Following disinfection of a water supply at a treatment plant, the water is distributed to the consumers. A persistent residual is important for continued protection of the water supply against subsequent contamination in the distribution system.
What is the purpose of disinfection?
Disinfection describes a process that eliminates many or all pathogenic microorganisms, except bacterial spores, on inanimate objects (Tables 1 and 2). In health-care settings, objects usually are disinfected by liquid chemicals or wet pasteurization.
What is the mechanism of disinfection?
In general, disinfectants have three mechanisms of action or ways that they affect or kill an organism: Cross-linking, coagulating, clumping; structure and function disruption; and oxidizing. Mechanism of action: Cross-linking, coagulating, clumping.
What are the 5 stages of water treatment?
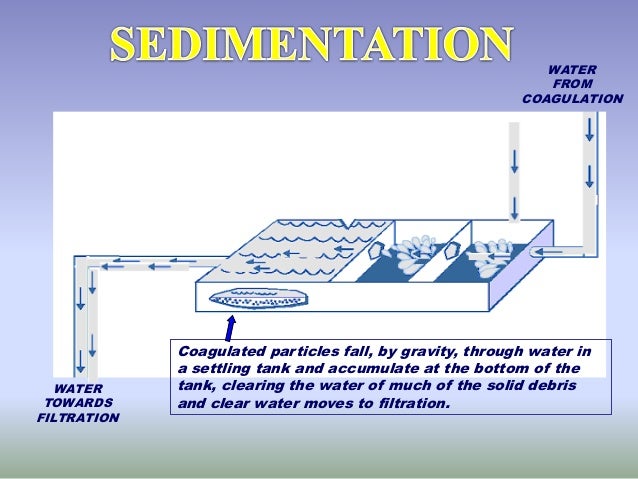
The 5 major unit processes include chemical coagulation, flocculation, sedimentation, filtration, and disinfection (described below). There are chemicals added to the water as it enters the various treatment processes.
Why is contact time so important in the disinfection process?
Products that require long contact times can evaporate before achieving disinfection, such as in environments with high temperatures and low humidity. This means that disinfection will not be achieved with one application. You would have to reapply the disinfectant—wasting product, time and money.
What is chlorine dioxide used for?
In England, Italy, and Switzerland, it is used for disinfection of water supplies. The Chemistry of Chlorine Dioxide in Water. Chlorine dioxide reacts with a wide variety of organic and inorganic chemicals under conditions that are usually found in water treatment systems (Stevens et al., 1978).
What is the most significant member of the coliform group?
The most significant member of this group (currently called the coliform group) is Escherichia coli. Since the late nineteenth century, this coliform group has served as an indicator of the degree of fecal contamination of water, and E. colihas been used routinely as a disinfection model for enteric pathogens.
What is the goal of disinfecting public water?
The goal of disinfection of public water supplies is the elimination of the pathogens that are responsible ...
Does chlorine oxidize sulfites?
Hypochlorous acid and other chlorine compounds having disinfecting ability by virtue of their being oxidizing agents will oxidize sulfites (SO32-), sulfides (S-), and ferrous (Fe2+) or manganous (Mn2+) ions. The disinfecting species are reduced, and the products have no disinfecting activity.
What is the bulk of nonparticulate organic material in raw water?
The bulk of the nonparticulate organic material in raw water occurs as naturally derived humic substances, i.e., humic, fulvic, and hymatomelanic acids, which contribute to color in water. The structure of these molecules is not yet fully understood.
How is ozone produced?
Ozone is produced on site from a stream of clean dry air or oxygen by passing an electrical discharge between electrodes that are separated by a dielectric. Approximately twice the percent of ozone by weight is obtained if oxygen, rather than air, is used as the feed stream.
What diseases can be controlled with treatment?
The transmission of diseases such as typhoid and paratyphoid fevers, cholera, salmonellosis, and shigellosis can be controlled with treatments that substantially reduce the total number of viable microorganisms in the water.
What is the process of removing pathogenic microorganisms from water?
Water disinfection means the removal, deactivation or killing of pathogenic microorganisms. Microorganisms are destroyed or deactivated, resulting in termination of growth and reproduction. When microorganisms are not removed from drinking water, drinking water usage will cause people to fall ill. Sterilization is a process related to disinfection.
Why does disinfection occur?
Disinfection commonly takes place because of cell wall corrosion in the cells of microorganisms, or changes in cell permeability, protoplasm or enzyme activity (because of a structural change in enzymes). These disturbances in cell activity cause microorganisms to no longer be able to multiply.
What happens during sterilization?
However, during the sterilization process all present microorganisms are killed, both harmful and harmless microorganisms. Media. Disinfection can be attained by means of physical or chemical disinfectants. The agents also remove organic contaminantsfrom water, which serve as nutrients or shelters for microorganisms.
What happens when you oxidize disinfectant?
This will cause the microorganisms to die out. Oxidizing disinfectants also demolish organic matter in the water, causing a lack of nutrients. More information about the effects of detergent pollution in freshwaterecosystems.
What is the final step to reduce pathogenic microorganisms in drinking water?
Chemical inactivation of microbiological contamination in natural or untreated water is usually one of the final stepsto reduce pathogenic microorganisms in drinking water. Combinations of water purification steps (oxidation, coagulation, settling, disinfection, filtration) cause (drinking) water to be safe after production.
Do disinfectants kill bacteria?
Disinfectants should not only kill microorganisms. Disinfectants must also have a residual effect, which means that they remain active in the water after disinfection. A disinfectant should prevent pathogenic microorganisms from growing in the plumbing after disinfection, causing the water te be recontaminated.
Can bacteria be in water?
Bacteria can remain in the water after the first disinfection step or can end up in the water during backflushing of contaminated water (which can contain groundwater bacteria as a result of cracks in the plumbing). Disinfection mechanism.
Why are chloramines used in water?
Chloramines are virtually no longer used for their bactericidal effect (far too weak) but more as a “bacteriostatic” measure in the distribution network because of their strongly persistant residual effect, especially when distributing relatively hot water (25°C or higher) because chloramines are more stable than free chlorine at these temperatures. In countries where a high level of residual disinfectant is acceptable at the consumer tap, a greater use is being made of chloramines after disinfection using ozone or chlorine (bactericidal effect).
What is the remanent effect of disinfectant?
bactericidal effect – remanent effect. The disinfection of water comprises two important steps that refer to two different properties of a given disinfectant: bactericidal effect : this is the disinfectant’s capacity for destroying microorganisms during a specific stage of the treatment; remanent effect : this is the disinfectant’s capacity ...
How long to keep a poliovirus serum?
For the purpose of eliminating pathogenic bacteria and polioviruses, maintaining a 0. 4 mg · L –1 residual for 4 minutes (C·T = 1.6) is recommended. At 5°C, a C·T equal to 2 will be required in order to ensure that Giardia cysts are eliminated; this value must be higher than 15 in the case of Cryptosporidium oocysts. Under these conditions, it is essential to ensure that the use of this type of treatment does not create unwanted oxidation by-products, particularly bromates (BrO 3–) that are regarded as dangerous at levels lower than < 10 µg · L –1. In effect, this type of observation rise to the "multiple barrier" treatment concept already mentioned: chemical disinfection against bacteria and viruses by applying customary criteria, whereas cyst removal efficiency will mainly rely on filtration effectiveness (through fine granular material or, better still, through clarification membranes) or even UV irradiation.
What is UV disinfection?
UV disinfection has been described in the section ultraviolet disinfection along with the recommended target dosage based on the treated water transmittance, target microorganisms and the elimination performance sought.
What is the final stage of drinking water treatment?
Disinfection is the final stage in drinking water treatment before its distribution. Disinfection is used to remove pathogenic micro-organisms from the water. However, it should be noted that disinfection is not the same as sterilisation (sterilisation = destruction of all germs present in a medium) and therefore a few common germs may remain in ...
How much suspended solids should be kept in water?
In order to be effective, disinfection must be carried out on good quality water. The suspended solids content must be kept as low as possible and equal to no more than 1 mg·L –1. In effect, bacteria and especially viruses collect on suspended solids which can protect them from the effect of disinfectants.
How does a water treatment unit work?
Even though EPA regulates and sets standards for public drinking water, many Americans use a home water treatment unit to: 1 Remove specific contaminants 2 Take extra precautions because a household member has a compromised immune system 3 Improve the taste of drinking water
What is the process of boiled water?
Distillation is a process in which impure water is boiled and the steam is collected and condensed in a separate container, leaving many of the solid contaminants behind. Disinfection. Disinfection is a physical or chemical process in which pathogenic microorganisms are deactivated or killed.
What are the steps of water treatment?
Today, the most common steps in water treatment used by community water systems (mainly surface water treatment) include: Coagulation and flocculation are often the first steps in water treatment. Chemicals with a positive charge are added to the water.
What is a CCR report?
Every community water supplier must provide an annual report, sometimes called a Consumer Confidence Report, or “CCR,” to its customers. The report provides information on your local drinking water quality, including the water’s source, contaminants found in the water, and how consumers can get involved in protecting drinking water.
Why is surface water more contaminated than ground water?
Typically, surface water requires more treatment and filtration than ground water because lakes, rivers, and streams contain more sediment and pollutants and are more likely to be contaminated than ground water. Some water supplies may also contain disinfections by-products, inorganic chemicals, organic chemicals, and radionuclides.
What is a water softener?
Water Softeners. A water softener is a device that reduces the hardness of the water. A water softener typically uses sodium or potassium ions to replace calcium and magnesium ions, the ions that create “hardness.”. Distillation Systems.
What is the most common type of water treatment system?
The most common types of household water treatment systems consist of: Filtration Systems. A water filter is a device which removes impurities from water by means of a physical barrier, chemical, and/or biological process. Water Softeners. A water softener is a device that reduces the hardness of the water.
