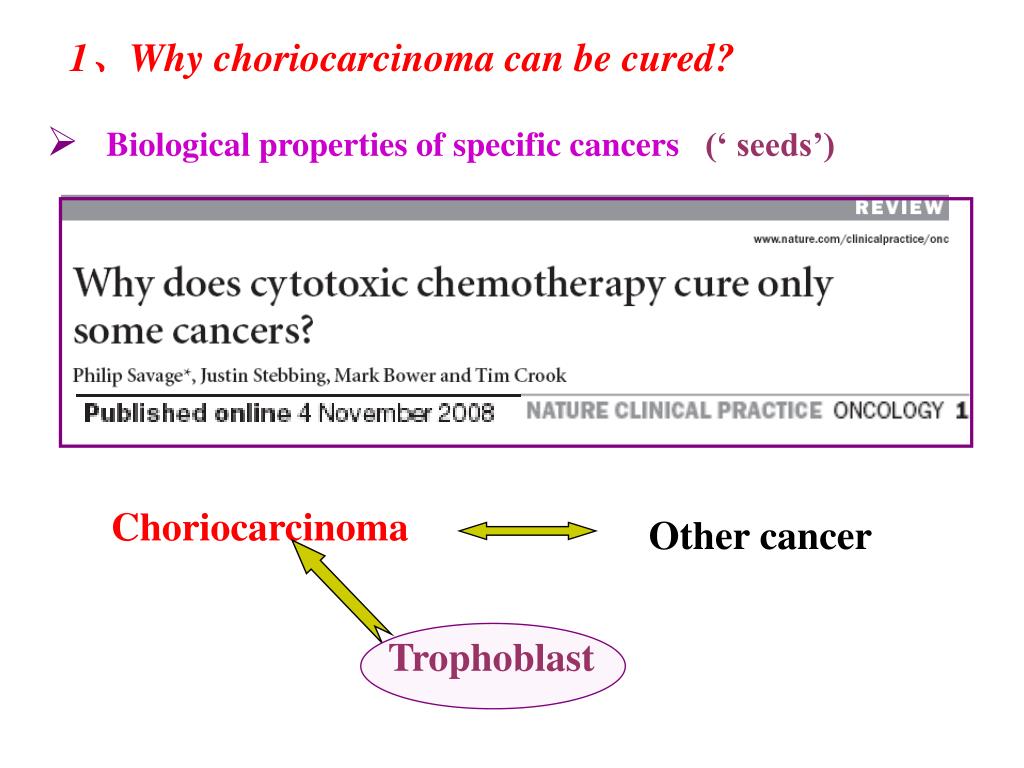
Treatment Since gestational choriocarcinoma (which arises from a hydatidiform mole) contains paternal DNA (and thus paternal antigens), it is exquisitely sensitive to chemotherapy. The cure rates, even for metastatic gestational choriocarcinoma, more than 90% when using chemotherapy for invasive mole and choriocarcinoma.
Full Answer
Is there a cure for choriocarcinoma?
Without treatment, choriocarcinoma can result in death. With the advent of chemotherapy, many patients can achieve remission and cure of their disease.
What is choriocarcinoma and what causes it?
It is a type of gestational trophoblastic disease (GTD). The cancer usually starts in your uterus but can spread to other parts of the body. What Causes It? Choriocarcinoma forms when cells that were part of the placenta in a normal pregnancy become cancerous.
What is the clinical evaluation of choriocarcinoma?
Choriocarcinoma predominantly occurs in women but can also occur in men, usually as part of a mixed germ cell tumor. This activity reviews the clinical evaluation of choriocarcinoma and the role of the interprofessional team in caring for patients with this disease.
What are the symptoms of choriocarcinoma metastases?
Individuals with metastases to the lungs possibly will have a dry cough with blood, chest pain and shortness of breath. Spreading of Choriocarcinoma to the intestinal tract may also be related with chronic blood loss and anemia or hemorrhage. And brain metastases are allied with brain tumor or stroke.

Are choriocarcinoma responsive to treatment?
The most common treatment is chemotherapy. Some people with the cancer will also need radiation therapy, surgery, or both. The majority of people who have had gestational choriocarcinoma will still be able to conceive and have a normal, healthy pregnancy after treatment.
How is choriocarcinoma treated?
If your tumor is low-risk, meaning it's small and hasn't spread, chemotherapy is the main treatment. You'll get it until there are no signs of cancer in your body based on hCG levels. If your cancer is high-risk, you may need surgery and chemo, or surgery, chemo, and radiation.
Can Stage 4 choriocarcinoma be cured?
Fortunately, most women who are found to have choriocarcinoma can be cured; treatment with a combination of chemotherapy agents such as etoposide, methotrexate, actinomycin D, cyclophosphamide and vincristine (EMA-CO) is found to be very effective at achieving remission.
What is the survival rate of choriocarcinoma?
The complete remission rate and 5-year overall survival rate of postterm choriocarcinoma patients in our cohorts were 87.9 and 86.7 %, respectively. A history of resistance to multiagent chemotherapy, liver metastasis and a FIGO score greater than 12 were shown to be independent risk factors of prognosis.
What is the drug of choice for choriocarcinoma?
If you have high risk PTD or choriocarcinoma, you might have the drug methotrexate by drip into a vein (intravenous infusion). This is followed a week later by the drugs actinomycin and etoposide. Or you may have a combination of chemotherapy drugs called EMA-CO.
Is choriocarcinoma benign or malignant?
Unlike a hydatidiform mole, a choriocarcinoma is a malignant and more aggressive form of GTD that spreads into the muscle wall of the uterus. A choriocarcinoma can also spread more widely to other parts of the body such as the lungs, liver, and/or brain.
How long is the treatment for choriocarcinoma?
Treatment for choriocarcinoma usually takes 4-5 months to complete and the cure rate is over 95%.
How long can you live with choriocarcinoma?
While 5-year overall survival and cure for this population is greater than 95%, choriocarcinoma is an aggressive subtype of this disease with far worse prognosis--5-year survival for choriocarcinoma is less than 80%.
How quickly does choriocarcinoma spread?
Choriocarcinoma can develop some months or even years after pregnancy and can be difficult to diagnose, because it is so unexpected. They can grow quickly and might cause symptoms within a short period of time. They can spread to other parts of the body but are very likely to be cured by chemotherapy treatment.
What are the stages of choriocarcinoma?
Stage I: Disease is only in the uterus. Stage II: GTD extends outside the uterus but is limited to the genital structures. Stage III: GTD extends to the lungs and may or may not involve the genital tract. Stage IV: GTD has extended to other distant sites, called metastasis.
Can choriocarcinoma come back?
A choriocarcinoma may come back within a few months to 3 years after treatment. The condition is harder to cure if the cancer has spread and one or more of the following happens: Disease spreads to the liver or brain. Pregnancy hormone (HCG) level is higher than 40,000 mIU/mL when treatment begins.
What is metastatic choriocarcinoma?
Choriocarcinoma is a malignant proliferation of trophoblasts that complicates a normal or abnormal pregnancy. Intraparenchymal brain metastases from choriocarcinoma occur in 10-20 % of the cases and are often haemorrhagic.
How to diagnose choriocarcinoma?
If your doctor thinks you have choriocarcinoma, they’ll do some tests: 1 A pelvic exam to feel for lumps or unusual changes 2 A test to look for levels of a hormone called hCG. They’ll be high if you have a GTD. 3 Blood and urine tests 4 An exam to see if the cancer has spread to other parts of your body 5 Imaging tests such as CT, MRI, ultrasound, or X-ray
What tests can you do if you have choriocarcinoma?
If your doctor thinks you have choriocarcinoma, they’ll do some tests: A pelvic exam to feel for lumps or unusual changes. A test to look for levels of a hormone called hCG. They’ll be high if you have a GTD. Blood and urine tests. An exam to see if the cancer has spread to other parts of your body.
What is the treatment for a tumor that hasn't spread?
If your tumor is low-risk, meaning it’s small and hasn’t spread, chemotherapy is the main treatment. You’ll get it until there are no signs of cancer in your body based on hCG levels. If your cancer is high-risk, you may need surgery and chemo, or surgery, chemo, and radiation.
How long does it take for a period to go back to normal after chemo?
They may go back to normal, and then stop again if you have chemo. They should restart again and go back to normal 3 to 6 months after chemo stops.
Can choriocarcinoma cause bleeding?
If the choriocarcinoma is in your vagina, it could cause bleeding. If it has spread to your abdomen, you might also have pain or pressure there. If it has spread to other parts of your body like your lungs or brain, you may notice: Cough. Trouble breathing.
What is choriocarcinoma?
Choriocarcinoma is an invasive condition seemingly involving reactivation of pregnancy implantation. In choriocarcinoma, placental tissue can invade through the myometrium and into the lymphatic system, metastasizing possibly to the pelvis, to the liver, then to the lungs, and finally to the brain.
How aggressive is choriocarcinoma?
Choriocarcinoma is a malignant germ cell tumor that is very aggressive because of early hematogenous dissemination. Choriocarcinoma has been reported to occur in 1 in 20,000 to 50,000 pregnancies.63 Half of these cases occur in patients with previous complete hydatidiform moles, and the other cases occur after nonmolar pregnancies (normal gestation, ectopic pregnancy, or abortion). About 3% to 5% of molar pregnancies are complicated by choriocarcinoma. 9 Clinically, women present with vaginal bleeding and weight loss, generally within 1 year of pregnancy. Choriocarcinoma may be confined to the uterus, but in most cases it is widely metastatic to the pelvis, liver, lung, and brain. There may be symptoms of cough, hemoptysis, dyspnea, or pleuritic chest pain associated with lung metastases. Focal neurologic signs or convulsions may be present in the setting of brain metastases. Epigastric and right upper quadrant pain may indicate hepatic metastases.
What is the name of the rare malignancy that arises from placental trophoblastic tissue?
Gestational trophoblastic disease (Choriocarcinoma) Choriocarcinoma is a rare malignancy that arises from placental trophoblastic tissue. It has a high rate of metastasis, including to the brain in 20% of cases (Shaaban et al., 2017 ). These metastases are highly vascularized and thereby prone to hemorrhage.
How many pregnancies are there with choriocarcinoma?
Choriocarcinoma occurs after pregnancy in 1 in 30,000 pregnancies in the United States [33]. Choriocarcinoma also occurs after complete hydatidiform mole. Complete hydatidiform mole occurs in 1 in 900 pregnancies in the United States. It affects approximately 1 in 50 complete hydatidiform mole cases [33].
Where does choriocarcinoma occur?
Choriocarcinoma is a gestational trophoblastic tumor in most cases arising in the uterus, although ectopic pregnancies provide extra-uterine sites of origin. Histologically, it is differentiated from other gestational trophoblastic tumors by the absence of chorionic villi, although it is composed of sheets of both anaplastic cyto- and syncytiotrophoblasts, which are cells types of the early embryo and gestational sac. Choriocarcinoma may also rarely occur in primary locations other than the placenta; very rarely, it occurs in testicles. Pure choriocarcinoma of the testis represents the most aggressive pathologic variant of germ cell tumors in adults, characteristically with early hematogenous and lymphatic metastatic spread. Because of early spread and inherent resistance to anticancer drugs, patients have poor prognosis. Choriocarcinomas can also occur in the ovaries.
What is the trophoblast positive for?
Intermediate trophoblasts are positive for human placental lactogen and hLA-G (human leukocyte antigen G). All cell types stain positive for cytokeratin. PLAP and Epithelial Membrane Antigen (EMA) are positive in about 50% of the choriocarcinoma. Glypican 3 is positive for syncytiotrophoblasts and cytotrophoblasts.
Is choriocarcinoma invasive?
Again, the invasive cytotrophoblast cells of pregnancy implantation are rapidly growing and highly invasive. However, nobody has demonstrated that choriocarcinoma cytotrophoblast cells differ in any way from normal pregnancy cytotrophoblast cells, which are naturally extremely invasive cells.
How often does choriocarcinoma occur?
Choriocarcinoma happens in about 1 in every 40,000 pregnancies. In rare cases, it can develop in males as a rare type of testicular cancer. The outlook for someone with choriocarcinoma who receives treatment is very positive. The most common treatment is chemotherapy.
How does gestational choriocarcinoma work?
gestational choriocarcinoma with chemotherapy. It works by either killing the cancerous cells or stopping the tumor from growing. Some people might need more than one type of chemotherapy. If the tumor has spread, the person might also need radiation therapy and surgery. In many cases, surgeons will be able to remove.
Is choriocarcinoma a rare disease?
Gesta tional choriocarcinoma, which develops in the uterus, accounts for the majority of choriocarcinoma cases. It is a rare form. Trusted Source. of gestational trophoblastic disease (GTD). GTDs are tumors that grow from abnormal cells inside the uterus.
Is choriocarcinoma curable?
It usually develops from cells that remain inside the body after a pregnancy. In the vast majority of cases, choriocarcinoma is curable. The outlook for people with this condition is generally very good, although it can sometimes cause complications. In this article, we discuss choriocarcinoma in more ...
Can choriocarcinoma cause vaginal discharge?
infections that cause vaginal discharge, pelvic cramps, and fever. Choriocarcinoma tumors can spread to other parts of the body, especially the lungs. Signs that this may have happened include: According to the American Cancer Society, choriocarcinoma does not always cause symptoms.
What Is Choriocarcinoma?
Choriocarcinoma is a malignant tumour. It mostly occurs in the placenta of pregnant women. The cancerous cells first develop in the tissue of a developing placenta. However, in some rare cases, it forms in men’s testicles and in the uterus of the affected post-menopausal woman.
How Common Is It During Pregnancy?
Choriocarcinoma is relatively rare with an incidence of one case per 40,000 pregnancies and for it to occur during pregnancy is even rarer. Studies suggest that about one in every 40,000 pregnant women and one in 40 patients with hydatidiform moles are likely to develop the disease in America and Europe.
Stages of Choriocarcinoma
Choriocarcinoma, also referred to as uterine choriocarcinoma, had the FIGO staging system, which is as follows:
How Is the Diagnosis Made?
Choriocarcinoma can be diagnosed and detected firstly through lumps in the uterus. However, lumps or oedema may not be detected in all cases. The HCG level is tested, and in this disease, it is noticed that it becomes very high. Apart from this, the doctor may recommend a kidney test, a liver test and a complete blood count test.
Treatment for Choriocarcinoma
Treatment for choriocarcinoma is according to the stage of cancer. If a tumour is small and has not spread to other parts of the body, it is low-risk. Such tumours can be cured by chemotherapy alone.
Can You Get Pregnant?
The high levels of HCG may stop your periods. It may again start after a while, and the cycle may become normal; however, after chemotherapy, it will again stop. Your cycle will again get back to normal after 3-6 months after your chemo stops.
What is the best treatment for choriocarcinoma?
Methotrexate is the drug of choice for treating Choriocarcinoma. The need of hysterectomy is rare in such cases as the disease gets treated with chemotherapy. Radiation therapy is required only when the cancer has spread to the brain.
What is choriocarcinoma?
Choriocarcinoma is a category of gestational trophoblastic disease which is quick-growing form of cancer that occurs in a woman’s uterus (womb). It is a malignancy of placental origin in which the trophoblastic cells of the uterus undergo malignant alteration that causes improper progress of the villous. The chorionic villi are small hair like structures that attaches the placenta to the uterus during pregnancy. When the trophoblastic cells of the uterus undergo malignant transformation the tissues then form bunch-like watery structures which are unable to sustain the developing fetus.
Why should grapes be removed?
The grape-like structures grow and should be removed because it does not cause feasible pregnancy and may form malignant cells. In tetsicles it is a rare form of Choriocarcinoma. But testicular Choriocarcinoma is not responsive to anticancer drugs and has a poor prognosis.
How many pregnancies are there with choriocarcinoma?
According to revealed statistics Choriocarcinoma occurs in 1 out of every 40,000 pregnancies. The development of Choriocarcinoma leads by other pregnancy related conditions like hydatidiform mole, which constitutes 50% of all cases. Spontaneous abortion and ectopic pregnancy also results to 20% and 2% of the cases respectively.
What is the chorionic villi?
The chorionic villi are small hair like structures that attaches the placenta to the uterus during pregnancy. When the trophoblastic cells of the uterus undergo malignant transformation the tissues then form bunch-like watery structures which are unable to sustain the developing fetus. A woman who suffers from a molar pregnancy is ...
Is choriocarcinoma a tumor?
Choriocarcinoma hardly grows outside the reproductive organs and are usually found in males. Choriocarcinoma if detected in early stages it is a highly curable tumor related to pregnancy.
Can cancer be cured?
Women whose cancer has not spread can be cured and will still be able to have children. On the other hand if the cancer metastasized and spreads to the liver or brain, HCG level is higher than 40,000 mIU/mL or Cancer returns after having chemotherapy, may reduce the cure rate.