What is the purpose of aeration in wastewater treatment?
Aeration is the process by which air is circulated through, mixed with or dissolved in a liquid or substance. Aeration brings water and air in close contact in order to remove dissolved gases and to oxidize dissolved metals, including iron, hydrogen sulfide, and volatile organic chemicals (VOCs).Sep 9, 2020
Why is aeration of water important?
With proper aeration, high levels of carbon dioxide are removed from the water. CO2 is only dangerous when it's allowed to convert into carbonic acid, which brings down the pH levels of the water making it nearly toxic. Aeration also reduces phosphorus concentrations in ponds.
How does aeration improve water quality?
An aerator improves water quality by circulating the water. This improve stabilizes pH balances. It also reduces alkalinity and removes excess carbon dioxide. If your pond is deprived of oxygen, sediments at the bottom release gases and metals that compromise the water quality.Jun 5, 2018
How does aeration work?
Aeration involves perforating the soil with small holes to allow air, water and nutrients to penetrate the grass roots. This helps the roots grow deeply and produce a stronger, more vigorous lawn. The main reason for aerating is to alleviate soil compaction.
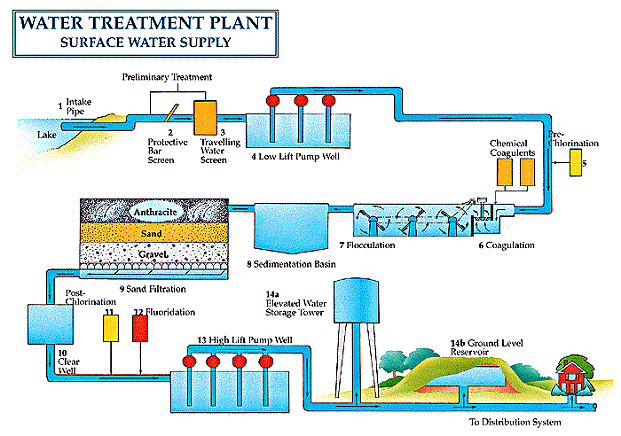
What is Aeration in Water Treatment?
There are three major parts of water treatment. The first is sort of a screening process. This is where they basically remove all the big stuff out of the water. This may be branches, tires, last year’s taxes, Jimmy Hoffa… (What a find that would be!)
Types of Aerators Used in Water Treatment
Some aeration devices are simple schematics where open holding tanks allow dissolved gases to escape into the open surrounding air. Other aeration devices have a more complex design featuring a column or tower filled with packing material. When the water passes through the packing material, the gases are released.
Aerating Raises pH During Wastewater Treatments
Because aeration can raise the pH during wastewater treatment, it is a good idea to monitor it carefully. Microorganism colonies tend to thrive best in pH ranges between 6.5 and 8.5. Monitoring and adjusting pH is considered a best practice and serves to keep healthy levels of microorganisms needed during wastewater treatment.
Aeration Plays a Role in the Nutrient Tests for Wastewater Treatment
There are many contributors to what is known as wastewater contaminants. Agriculture, animal feeding, and stormwater runoff are some of the many contributors to excessive algae bloom. This occurs because of too many nutrients in the wastewater.
Atlas Scientific for Wastewater Testing Tools and Resources
We know that wastewater isn’t something most people want to visualize. However, all communities want to be able to view clean and safe waterways. Water is something most people probably take for granted and don’t pay attention to the processes that make it possible for both humans and aquatic life to have viable, pure water sources.
More To Explore
In this article, we will show you how to connect an Atlas Scientific EZO-RGB™ Embedded Color Sensor to a Raspberry Pi. There are multiple ways to connect Atlas Scientific sensors to your device of choice. In previous posts we have shown how to wire our EZO™ sensors directly into an Arduino and/or a Raspberry Pi.
Why is aeration important?
The advantage of aeration is that there is no disposal or regeneration of treatment media necessary. This is especially important when the contaminant being treated would constitute a hazardous waste disposal problem , such as radon. Re-pressurizing the treated water is usually necessary.
How does aeration work?
How aeration works. Aeration treatment consists of passing large amounts of air through water and then venting the air outside. The air causes the dissolved gases or volatile compounds to release from the water. The air and the contaminants released from the water are vented. In the case of iron and manganese, the air causes these minerals ...
How does a spray aerator work?
In a spray aeration system, water enters through the top of the unit and emerges through spray heads in a fine mist. Treated water collects in a vented tank below the spray heads. Radon and other volatile contaminants are released and vented to the outside.
What is aeration in chemistry?
Aeration is an in-line point-of-entry process that reduces the concentration of volatile organic compounds. Aeration also removes dissolved gases such as hydrogen sulfide, methane, and radon. Aeration oxidizes dissolved iron, although the resulting iron particles can foul the packing material in some aeration devices.
What to know before buying a water treatment system?
Before purchasing a water treatment device, have your water tested at a state certified laboratory to determine the contaminants present. This will help determine if aeration is an effective treatment method for the situation. See Questions to Ask Before You Buy A Water Treatment System for more information.
What causes rust in water?
If there are elevated levels of dissolved iron or manganese in the water, the aeration process can cause rust and other solids to form, staining plumbing fixtures and clothing unless a post treatment filter is installed to trap the solid forms of iron and manganese.
What is maintenance of aeration system?
Maintenance of aeration systems. Regardless of the quality of the equipment purchased, it will not perform satisfactorily unless maintained in accordance with the manufacturer’s recommendations for maintenance, cleaning, and part replacement.
What is water treatment?
The most common water treatment technique is aeration that can be achieved using anything from small pond pumps to much larger aeration pumps.
Is aeration good for fresh water?
No-one wants to add lots of chemicals to fresh water bodies, whether this is their backyard fish pond, a beautiful lake or a dam on their property. Reducing our environmental impact is important for everyone and water treatments using aeration comes out tops for being the cleanest type of treatment available.
What is Aeration Wastewater Treatment?
Aeration is an important step in the process of treating wastewater, including sewage effluent. Microorganisms in aeration wastewater treatment tanks break down organic compounds and nutrients. The removal of nutrients is critical, because wastewater that is overly rich in nutrients can cause ecosystem imbalances if released into the environment.
How is Aeration Wastewater Treatment Used?
Due to the ecological impact of nutrient enriched wastewater, governments enforce regulation to control the amount of nutrients allowed in wastewater discharge. To comply with regulations, industrial, agricultural, and other wastewater producers must carry out treatment.
Monitoring Dissolved Oxygen for Aeration Wastewater Treatment
Aeration wastewater treatment tanks are subject to careful monitoring to ensure that nutrient removal is achieved safely and efficiently. Dissolved oxygen is a critical parameter in the aeration process, because oxygen levels in the tank impact the health of the biomass (microorganisms) breaking down the nutrients.
Monitoring pH for Aeration Wastewater Treatment
Another parameter that is monitored during wastewater aeration treatment is pH. Microbial communities involved in nutrient removal survive and thrive in certain pH ranges, usually between 6.5 and 8.5. Monitoring and adjusting pH helps maintain healthy communities of the microbes needed during wastewater treatment.
Why is aeration important?
Aeration is used in liquids, soils and foods to improve quality and reduce contamination. The process is used to oxidize soluble iron and manganese to insoluble precipitates. Aeration can also reduce ammonia and hydrogen sulfide and is ideal for bacteria control.
How does aeration work?
Aeration brings water and air in close contact by exposing drops or thin sheets of water to the air or by introducing small bubbles of air and letting them rise through the water. Dissolved gases are then removed from the solution and allowed to escape into the surrounding air.
What is aeration in science?
What is Aeration? Aeration is the process by which air is circulated through, mixed with or dissolved in a liquid or substance. Aeration brings water and air in close contact in order to remove dissolved gases and to oxidize dissolved metals, including iron, hydrogen sulfide, and volatile organic chemicals (VOCs).
Why is oxygen important in wastewater treatment?
An evenly distributed oxygen supply in an aeration system is essential to effective wastewater treatment for fostering microbial growth. According to the Missouri Rural Water Association, the efficiency of aeration depends on the amount of surface contact between air and water.
What is surface aeration?
Surface Aeration. Surface aeration is best in shallow water applications or when large amounts of oxygen are needed immediately. According to Kasco Marine, splashing style surface aerators create more surface area for the gas exchange, which can add large amounts of oxygen to the water.
What is the most common method of aeration?
In industrial use, the most common method of aeration is water-fall aeration, through the use of spray nozzles. There is also the air diffusion method of aeration, in which air is diffused into a receiving vessel containing counter-current flowing water. Aeration is used in liquids, soils and foods to improve quality and reduce contamination.
Is aeration a secondary treatment?
In municipal and industrial wastewater treatment, aeration is part of the secondary treatment process. The activated sludge process is the most common option in secondary treatment, according to Oxymem .
