Why don't all HIV medications work?
Sometimes the HIV medications don't work. This may occur because the drugs don't completely stop the virus from reproducing. As the virus makes copies of itself, changes (or mutations) sometimes occur. These changes may result in a new strain of the virus that is resistant to the action of the drugs.
What happens when HIV treatment fails?
When an HIV treatment regimen fails, the virus begins to multiply and mutate, or change, which can lead to disease progression and eventually AIDS. For this reason, routine blood testing is extremely important.
Why is it important to start HIV treatment right away?
Similarly, if you are pregnant or intend to become pregnant, it is important to start HIV treatment right away both to protect your own health and to reduce the risk of passing HIV to the baby during pregnancy or at the time of birth. Your provider will talk with you and together you will come up with a personal treatment plan.
How do I know if my HIV treatment is working?
How do you really know if your HIV treatment is working? There are three key things to keep track of: How much your viral load is dropping. How much your immune system is recovering. How you're actually feeling. Recently diagnosed with HIV?

Why does HIV medication not work?
People living with HIV may have one or more drug-resistant mutations that make them less sensitive to one or more antiretrovirals. For example, if people have protease mutations, their HIV is resistant to protease inhibitors, meaning that a drug like darunavir (Prezista), a protease inhibitor, may not work for them.
How do I know if my HIV medication is not working?
Ask your doctor about testing for HIV drug resistance. This type of testing looks for drug-resistant mutations in your specific strain of HIV and is usually done when you're first diagnosed. This helps determine the medication that will be most effective for you.
Do Arvs always work?
Yes, Everyone can get an undetectable viral load on ART. If you do not get a full response it can be for one (or more) of the reasons below.
Can your body reject ARVs?
If you do find out that your virus has developed resistance, you and your doctor should be aware of the risk of cross resistance when choosing a new medication. If your virus is resistant to a drug from a certain class of antiretrovirals, there's a chance it will be resistant to other drugs within the same class.
Can stress increase viral load?
Further, findings related to the link between stress and clinical outcomes are mixed; however, stress was shown to be related to lower CD4 cell counts, higher viral load, and disease progression. Several studies also showed a link between stress and poorer treatment adherence.
Why is my body drug-resistant?
Resistance appears because of the mutations that take place spontaneously in any group of growing cells, whether exposed to drugs or not. Most such mutations change the cell's structure or biochemical pathways in a harmful way.
What is HIV treatment?
HIV treatment (antiretroviral therapy or ART) involves taking medicine as prescribed by a health care provider. HIV treatment reduces the amount of...
When should I start HIV treatment?
Start HIV treatment as soon as possible after diagnosis. All people with HIV should take HIV treatment, no matter how long they’ve had HIV or how h...
What if I delay HIV treatment?
If you delay treatment, HIV will continue to harm your immune system. Delaying treatment will put you at higher risk for transmitting HIV to your p...
Are there different types of HIV treatment?
There are two types of HIV treatment: pills and shots. Pills are recommended for people who are just starting HIV treatment. There are many FDA-app...
What are HIV treatment shots?
HIV treatment shots are long-acting injections used to treat people with HIV. The shots are given by your health care provider and require routine...
Can I switch my HIV treatment from pills to shots?
Talk to your health care provider about changing your HIV treatment plan. Shots may be right for you if you are an adult with HIV who has an undete...
What are the benefits of taking my HIV treatment as prescribed?
HIV treatment reduces the amount of HIV in the blood (viral load). Taking your HIV medicine as prescribed will help keep your viral load low. HIV t...
Does HIV treatment cause side effects?
HIV treatment can cause side effects in some people. However, not everyone experiences side effects. The most common side effects are Nausea and vo...
What should I do if I’m thinking about having a baby?
Let your health care provider know if you or your partner is pregnant or thinking about getting pregnant. They will determine the right type of HIV...
Can I take birth control while on HIV treatment?
You can use any method of birth control to prevent pregnancy. However, some HIV treatment may make hormone-based birth control less effective. Talk...
Why don't people get HIV medication?
In some instances, people don’t get the full dose of medication because their bodies aren’t able to absorb the HIV medication properly.
How to prevent HIV treatment failure?
You can help avoid HIV drug resistance by taking these steps to prevent it from occurring: Take your medication every day. This helps block HIV replication, says Guderian.
What is it called when you have a drug resistance to HIV?
HIV Drug Resistance. It’s also possible that your type of HIV has developed a resistance to one or more of the HIV drugs in your regimen. This is called drug resistance , and it occurs when the virus mutates in your body and the new form of the virus doesn’t respond to the medication anymore.
What is the goal of antiretroviral therapy?
A goal of antiretroviral therapy as treatment for HIV is to keep your immune system healthy. A low CD4 count alerts your doctor that your medication isn’t working as it should.
How to keep HIV treatment on track?
The answers you need to keep your HIV treatment on track come from the results of a blood test that measures your viral load. Your treatment regimen is considered effective if it’s able to control HIV to the point that the virus is virtually undetectable in your body. The virus is still present, but the viral load level is low enough ...
What is CD4 in HIV?
The higher the viral load level, the more active the virus is in your system. CD4 cells are the cells in your body that help fight infection. HIV destroys these cells when it attacks your immune system. A goal of antiretroviral therapy as treatment for HIV is to keep your immune system healthy. A low CD4 count alerts your doctor ...
How to prevent HIV?
You can help avoid HIV drug resistance by taking these steps to prevent it from occurring: 1 Take your medication every day. This helps block HIV replication, says Guderian. Use an alarm on your phone, watch, or another device to make sure you follow your prescribed dosing schedule. Fill prescriptions early, so you don’t risk running out of medication. 2 Take your medication as directed. Some HIV medications must be taken with food to ensure that the drug is properly absorbed into the body. Be sure you know how your medication should be taken. 3 Let your doctor know about side effects or other treatment challenges. It’s essential that you tell your doctor if any side effects — such as nausea, diarrhea, depressed mood, or poor appetite — are making it difficult for you to stick to your HIV treatment regimen. These side effects can usually be managed, and if not, your doctor may prescribe different combinations of medicines for you. 4 Ask your doctor about testing for HIV drug resistance. This type of testing looks for drug-resistant mutations in your specific strain of HIV and is usually done when you’re first diagnosed. This helps determine the medication that will be most effective for you. Testing for drug resistance should be performed again anytime your HIV viral load increases to make sure new drug-resistant mutations haven’t developed.
Why is it important to take HIV medication?
Taking HIV medication consistently, as prescribed, helps prevent drug resistance. Drug resistance develops when people with HIV are inconsistent with taking their HIV medication as prescribed. The virus can change (mutate) and will no longer respond to certain HIV medication. If you develop drug resistance, it will limit your options ...
What does it mean when your HIV is suppressed?
Viral suppression is defined as having less than 200 copies of HIV per milliliter of blood. HIV medicine can make the viral load so low that a test can’t detect it (called an undetectable viral load ). If your viral load goes down after starting HIV treatment, that means treatment is working.
What is the amount of HIV in the blood called?
The amount of HIV in the blood is called viral load . Taking your HIV medicine as prescribed will help keep your viral load low and your CD4 cell count high. HIV medicine can make the viral load very low (called viral suppression ). Viral suppression is defined as having less than 200 copies of HIV per milliliter of blood.
What happens if you skip your medication?
If you skip your medications, even now and then, you are giving HIV the chance to multiply rapidly. This could weaken your immune system, and you could become sick. Getting and keeping an undetectable viral load (or staying virally suppressed) is the best way to stay healthy and protect others.
How long does it take for a mother to give her baby HIV?
If a mother with HIV takes HIV medicine as prescribed throughout pregnancy, labor, and delivery and gives HIV medicine to her baby for 4 to 6 weeks after birth, the risk of transmitting HIV to her baby can be 1% or less.
How long does it take to get rid of HIV?
There is no effective cure for HIV. But with proper medical care, you can control HIV. Most people can get the virus under control within six months. Taking HIV medicine does not prevent transmission ...
What are the factors that affect your willingness to stick to your treatment plan?
Being sick or depressed. How you feel mentally and physically can affect your willingness to stick to your treatment plan. Your health care provider, social worker, or case manager can refer you to a mental health provider or local support groups. Alcohol or drug use.
What are the problems with HIV?
Poor drug absorption, which can happen to people with chronic HIV-associated diarrhea or other malabsorption issues. Not following food requirements, which can also affect drug absorption and metabolism. Cost and affordability, including the lack of adequate health insurance.
What happens when antiretroviral drugs fail?
HIV treatment failure occurs when your antiretroviral drugs are no longer able to suppress the virus or prevent the deterioration of your immune system, leaving you vulnerable to opportunistic infections . Katarzyna Bialasiewic / Getty Images.
How many T cells can you get from low pretreatment CD4?
3 Similarly, those with mild to moderate immune suppression will sometimes see an improvement of several hundred T-cells, while others will see their numbers shoot well above 1,000 or 1,500.
What happens if you have virologic failure?
Changing Therapy. If virologic failure is declared, your doctor will order one or more tests to evaluate your "viral pool.". When you have HIV, you do not have just one virus but rather a multitude of variants, some of which are drug-resistant.
What is the normal blood count for HIV?
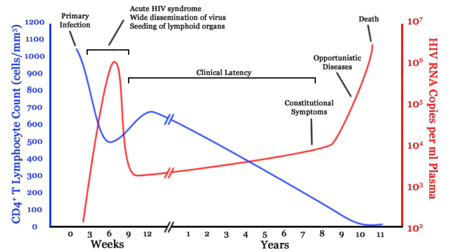
The immune status of people with HIV is measured by a blood test called the CD4 count. "Normal" values are typically defined as being 500 cells/mL or above, while those below 200 are classified as AIDS . In the past, the CD4 count (and other values such as the CD4/CD8 ratio) factored greatly into how HIV was treated.
How many copies of a viral load can be detected?
When antiretroviral therapy is working, the viral load should be fully undetectable, meaning that it is below the level of detection (under 20 to 75 copies/mL, depending on the test). 1 If failure is allowed to continue, the viral load will continue to rise, in some cases into the millions.
What is acquired drug resistance?
Acquired drug resistance, in which you "pick up" a drug-resistant variant through sex, shared needles, or other modes of transmission. Previous treatment failure, during which you will likely have developed levels of resistance to antiretrovirals of the same class. High baseline viral load, as some drug regimens are less effective ...
Why do you prescribe HIV?
Your health care provider may prescribe medicines to prevent certain infections. HIV treatment is most likely to be successful when you know what to expect and are committed to taking your medicines exactly as prescribed.
How long do HIV side effects last?
Some side effects can occur once you start a medicine and may only last a few days or weeks.
What is the treatment for HIV?
HIV treatment involves taking medicines that slow the progression of the virus in your body. HIV is a type of virus called a retrovirus, and the combination of drugs used to treat it is called antiretroviral therapy (ART). ART is recommended for all people living with HIV, regardless of how long they’ve had the virus or how healthy they are.
What happens if your CD4 is low?
If your CD4 cell count falls below a certain level, you are at risk of getting an opportunistic infection. These are infections that don’t normally affect people with healthy immune systems but that can infect people with immune systems weakened by HIV infection.
What is drug resistance in HIV?
What Is HIV Drug Resistance? Drug resistance can be a cause of treatment failure for people living with HIV. As HIV multiplies in the body, it sometimes mutates (changes form) and produces variations of itself. Variations of HIV that develop while a person is taking ART can lead to drug-resistant strains of HIV.
How soon can you start ART for HIV?
Treatment guidelines from the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services recommend that a person living with HIV begin ART as soon as possible after diagnosis. Starting ART slows the progression of HIV and can keep you healthy for many years.
Is HIV treatment a prevention?
There is also a major prevention benefit. People living with HIV who take HIV medication daily as prescribed and get and keep an undetectable viral load have effectively no risk of sexually transmitting HIV to their HIV-negative partners. This is called treatment as prevention.
What Causes Drugs to Become Less Effective
Knowing what causes HIV medicines to fail can help prevent it from happening to you. There’s no guarantee, because every human body is different, and every virus affects it in a slightly different way.
Come join our private, stigma-free, supportive community
Health management tools with medication & appointment reminders. Social networking in a community conversation & private chats.
Side Effects and Drug Effectiveness
Some HIV meds have side effects. They’re usually mild, and they often go away after you’ve been taking the meds for a few weeks.
What happens if you take HIV meds for a while?
For instance, maybe you started HIV meds and discovered over the course of several months that your sleep isn't that great, or your mood has slipped.
Why do people feel better about HIV?
And they feel better emotionally, for a whole host of potential reasons—possibly including better physical health, knowing their HIV is under control, feeling confident they can’t transmit HIV to others, and generally beating a lot of their fears and anxieties about HIV treatment.
How long does it take for a virus to be undetectable?
While more virus for HIV medications to attack often means more time to become undetectable, if you're adherent to your meds, your viral load should be undetectable within six months of starting treatment, and often much sooner.
What drugs cause rapid decline in viral load?
This can also depend on the types of HIV drugs you’ve been prescribed: For instance, treatment regimens that include a family of HIV drugs called integrase inhibitors tend to cause more rapid declines in viral load than other families of medicines.
What is the goal of HIV treatment?
The goal of HIV treatment is to disrupt the replication of the virus so much that the amount circulating in your blood is extremely low. So low, in fact, that the blood test you'll take to keep track of your HIV—your HIV viral load—will report it as "undetectable.". No matter how high your viral load is when you start treatment, ...
How long does it take for HIV to dissipate?
Others have a minor side effect or two (like headaches, nausea, or diarrhea) that will dissipate over the first few weeks.
Can you tell if you have HIV?
There are few certainties in HIV treatment, but one is that you can't tell what your viral load or CD4 count is by how you feel. Only those blood tests you take can tell you for sure. However, focusing on how you feel can give you a lot of important information about how your HIV medications are working for you.
Why don't HIV drugs work?
Sometimes the HIV medications don't work. This may occur because the drugs don't completely stop the virus from reproducing. As the virus makes copies of itself, changes (or mutations) sometimes occur. These changes may result in a new strain of the virus that is resistant to the action of the drugs.
How does HIV work after taking drugs?
If the drugs are working, your viral load goes down. You will have less of the virus in your bloodstream.
What is the drug that blocks HIV from binding to the coreceptor?
To infect a cell, HIV must bind to two types of molecules on the cell's surface. One of these is called a chemokine coreceptor. Drugs known as chemokine coreceptor antagonists block the virus from binding to the coreceptor.
What is the role of CD4 in HIV?
CD4 cells play a major role in helping your immune system work properly. HIV causes disease by killing off CD4 cells.
How does HIV make copies of itself?
When the HIV virus enters a healthy cell , it attempts to make copies of itself. It does this by using an enzyme called reverse transcriptase. The NRTIs work because they block that enzyme. Without reverse transcriptase, HIV can't make new virus copies of itself.
Why is HIV treatment important?
Starting therapy. HIV drugs are essential in keeping people healthy over the years. Effective treatment stops or slows the progression of HIV and has important benefits, even for persons whose immune systems appear to be functioning well. HIV drugs are recommended for ALL people with HIV infection.
How does HIV work?
These medicines work by blocking protease.
Who is the co-author of the study on HIV?
In a related article, Christy Newman , one of the co-authors of the study, comments that with the increasing focus on the benefits of HIV treatment, there are fewer opportunities for people with HIV to express their fears or concerns.
Do people with HIV feel under pressure?
People not taking HIV treatment feel under pressure to ‘do the right thing’. Australian people living with HIV who have chosen not to take antiretrovirals and who have doubts about HIV medicine report feeling excluded and silenced within HIV organisations and communities, according to a qualitative study published online ahead ...
Does HIV treatment reduce infectiousness?
Almost all interviewees were aware of the evidence that HIV treatment reduces the infectiousness of people living with HIV and of the increasing policy emphasis on increasing the uptake of HIV treatment for this reason.
Is pharmaceutical citizenship related to HIV?
To give an example of pharmaceutical citizenship related to HIV, a previous study showed how an awareness of the impact of HIV treatment on prevention was helpful for couples in which one person has HIV and the other does not.
Do interviewees deny the benefits of antiretrovirals?
In general, the interviewees did not deny the benefits of antiretrovirals, but did not yet feel ready to make a commitment to start a lifelong regimen of medication. They were aware that good adherence is vital but may be challenging, and also of the potential of all prescribed medications to do harm as well as good.

Causes
Virologic Failure
- Virologic failure is defined as the inability to maintain a viral load of fewer than 200 copies per milliliter (mL) despite adherence to antiretroviral therapy.1 When antiretroviral therapy is working, the viral load should be fully undetectable, meaning that it is below the level of detection (under 20 to 75 copies/mL, depending on the test).1 If failure is allowed to continue, the viral l…
Immunologic Failure
- Immunologic failure occurs when defensive immune cells, called CD4 T-cells, fail to recover despite fully suppressive antiretroviral therapy. These are the cells that HIV preferentially attacks, and their depletion is a reliable marker for your immune status. The immune status of people with HIV is measured by a blood test called the CD4 count. "No...
Changing Therapy
- If virologic failure is declared, your healthcare provider will order one or more tests to evaluate your "viral pool." When you have HIV, you do not have just one virus but rather a multitude of variants, some of which are drug-resistant. Under the pressure of antiretroviral therapy, the viral pool can change with drug-resistant variants becoming more and more predominant. In some c…
A Word from Verywell
- Treatment failure can also occur in people who are fully adherent, typically after many years of treatment. This is particularly true for those who take some of the older antiretroviral drugs, some of which are more durable (longer-lasting) than others. However, if treatment failure occurs within a relatively short period of time, poor adherence almost invariably plays a part. If this is the case…