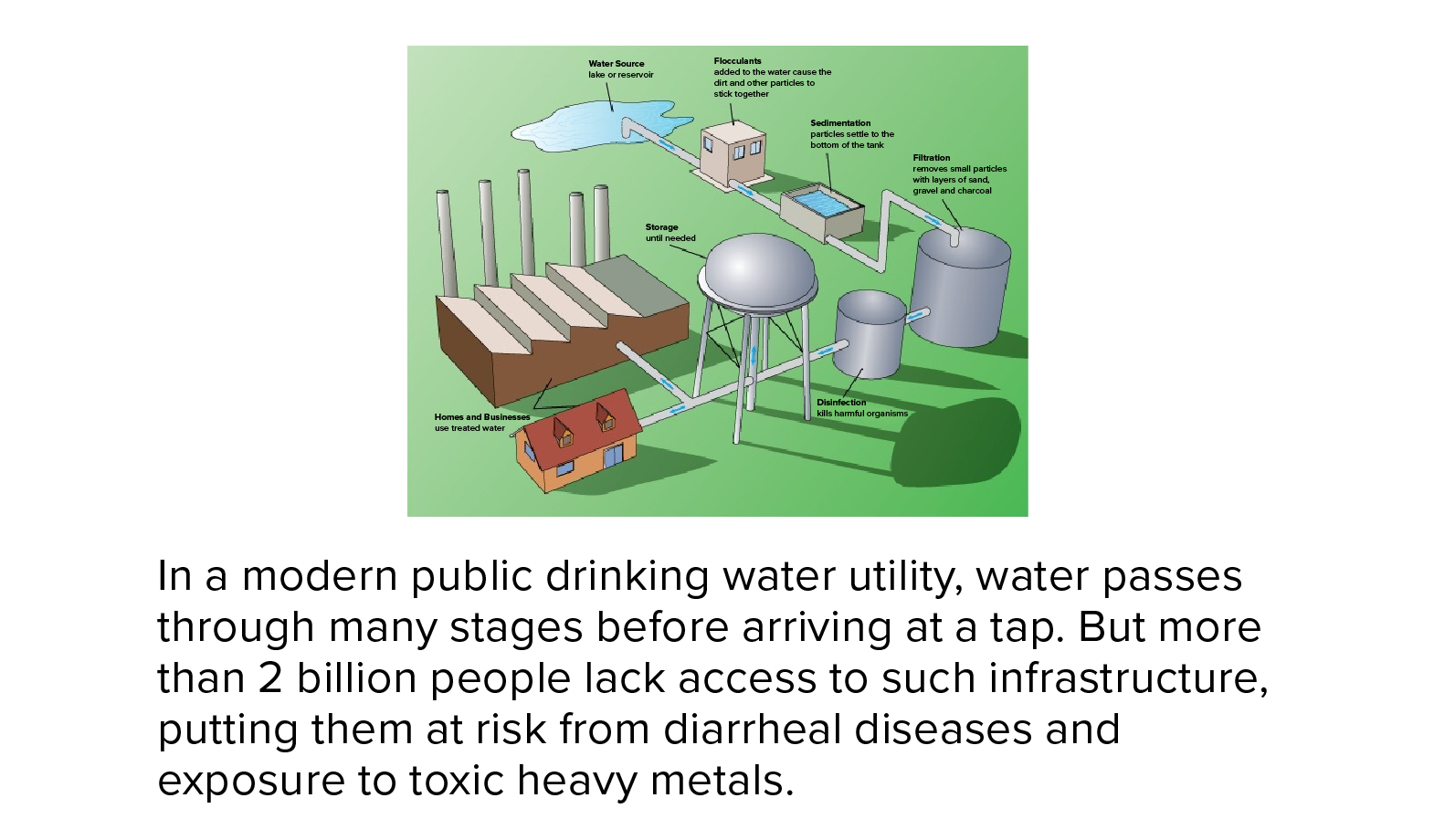
Drinking water treatment stages Public water networks use different methods to treat drinking water. To rid them of contaminants and make them safer to use.
Full Answer
Do you know the 5 stages of water treatment?
So, knowing the 5 stages of water treatment is of the utmost importance. As water enters a water treatment plant, either from lakes, rivers, or the ground, it passes through a screening. This screening keeps large natural contaminants out of the water.
What is involved in the water treatment process?
The first step in the treatment process is to screen the water to remove larger items of suspended materials, such as rubbish, plants, trees, animals and other debris. As the name suggests, these are captured and removed via the use of a large metal screen.
What happens during the coagulation phase of a water treatment plant?
During the coagulation phase, workers at the treatment plant add chemicals to the water that cause particles to form in the water. The most common coagulants are aluminum sulphate and ferric sulphate. They are added to the water at a point of high turbulence. The particles formed by these chemicals are sticky and called floc.
What happens to materials in the wastewater treatment process?
Once settled, these materials are held back while the remaining liquid is discharged or moved through to the more rigorous secondary phase of wastewater treatment.

What are the two stages of water treatment?
The Two Main Steps of the Wastewater Treatment ProcessPrimary Treatment. During primary treatment, 40-50% of solids are removed from wastewater. ... Secondary Treatment. ... Tertiary Treatment. ... Ensuring Safety During The Treatment Process.
What is the purpose of primary and secondary treatment of wastewater?
While secondary treatment may use similar items, this method uses biological treatment through microbes. The initial and primary water treatment process removes large matter from wastewater while the secondary treatment will remove smaller particles already dissolved or suspended.
What is the purpose of the secondary treatment step?
Secondary treatment is the removal of biodegradable organic matter (in solution or suspension) from sewage or similar kinds of wastewater. The aim is to achieve a certain degree of effluent quality in a sewage treatment plant suitable for the intended disposal or reuse option.
What are the stages of water treatment?
Public water systems often use a series of water treatment steps that include coagulation, flocculation, sedimentation, filtration, and disinfection.
What is the key difference between primary treatment and secondary treatment?
The main difference is the way each respective treatment is processed. Primary treatment works on sedimentation, where solids separate from the water through several different tanks. In contrast, secondary treatment uses aeration, biofiltration and the interaction of waste throughout its process.
What does primary secondary and tertiary water treatment achieve?
Wastewater is treated in 3 phases: primary (solid removal), secondary (bacterial decomposition), and tertiary (extra filtration).
Why is secondary wastewater treatment important?
The secondary stage of treatment removes about 85 percent of the organic matter in sewage by making use of the bacteria in it. The principal secondary treatment techniques used in secondary treatment are the trickling filter and the activated sludge process.
What is done during second stage of primary treatment?
Answer: Secondary Wastewater treatment is the second stage of wastewater treatment. In primary treatment, suspended solids, colloidal particles, oil, and grease are removed. In secondary treatment, biological treatment is done on the wastewater to remove the organic matter present.
What is meant by secondary treatment?
Secondary treatment is the second step in most waste treatment systems during which bacteria consume the organic parts of the wastes. This is accomplished by bringing the sewage, bacteria and oxygen together in trickling filters or within an activated sludge process.
What are stages of water?
There are four main stages in the water cycle. They are evaporation, condensation, precipitation and collection. Let's look at each of these stages.
What is the first stage of water treatment?
Primary treatment (stage 1) This is when wastewater is temporarily held in large sedimentation tanks to remove settleable solids. With gravity, heavier solids sink to the bottom while lighter solids rise to the top. Chemicals can also be added as coagulants to remove more solids.
What is the most important step in water treatment?
It is, however, an important primary step in the water treatment process, because coagulation removes many of the particles, such as dissolved organic carbon, that make water difficult to disinfect. Because coagulation removes some of the dissolved substances, less chlorine must be added to disinfect the water.
What is water treatment?
Water treatment is the process of removing all those substances, whether biological, chemical, or physical, that are potentially harmful to the water supply for human and domestic use. This treatment helps to produce water that is safe, palatable, clear, colorless, and odorless. Water also needs to be non-corrosive, meaning it will not cause damage to pipework.
How does aerated water work?
After screening, the water is aerated (supplied with air) by passing it over a series of steps to take in oxygen from the air. This process helps in expelling soluble gases such as carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulfide (both of which are acidic, so this process makes the water less corrosive) and expels any gas eous organic compounds an undesirable taste to the water. Aeration also removes iron or manganese by oxidation of these substances to their insoluble form. Iron and manganese can cause peculiar tastes and can stain clothing. Once in their insoluble forms, these substances can be removed by filtration.
What is the process of separating solids from liquids?
Filtration is the process where solids are separated from a liquid. In water treatment, the solids that are not separated in the sedimentation tank are removed by passing the water through sand and gravel beds. With a flow rate of 4–8 cubic meters per square meter of filter surface per hour, rapid gravity filters are often used.
What happens after aeration?
After aeration, coagulation occurs to remove the fine particles (less than 1 µm in size) suspended in the water . In this process, a chemical called a coagulant (with a positive electrical charge) is added to the water, which neutralizes the fine particles' negative electrical charge. The coagulant's addition takes place in a rapid mix tank where a high-speed impeller rapidly disperses the coagulant.
What are the steps of water purification?
There are 5 Steps of Water Purification treatment. Water shortage is the main problem, with billions of individuals around the globe lacking access to clean and safe water. Water cleansing assumes a significant job in guaranteeing access to safe drinking water and, in this way, can improve instruction, wellbeing, nourishment security, and destitution in creating nations.
What is sedimentation in a water tank?
Sedimentation In the sedimentation bowl, the water sits still, and the floc aggregates soil, which in the end gets sufficiently substantial to sink to the base of the tank, thus permitting it to be expelled from the water before it moves through to filtration.
What is screening in water?
Screening expels the greatest hindrances from water originating from lakes or streams, similar to wood, plants, fish, and waste. It guarantees that the system can run at its best without large items meddling or blocking passages.
What is wastewater treatment
Treatment of wastewater is a major step in preventing the pollution of our freshwater resources. The process uses specialized machines to remove pollutants such as metals, debris, microorganisms, and biowaste from the water before it is returned to its source, be it surface water or groundwater.
There are four types of wastewater treatments
This treatment method involves the following steps: infiltration, grit removal, primary sedimentation tank, secondary sedimentation tank, and secondary clarification. This process is used to treat domestic wastewater and commercial waste.
Stages of wastewater treatment
Wastewater treatment is the process of cleaning wastewater before it is discharged back into waterways or utilized as a reclaimed water source. Here are the three stages that help us achieve that.
What are the stages of wastewater treatment?
What Are the Three Stages of Wastewater Treatment? There are three main stages of the wastewater treatment process, aptly known as primary, secondary and tertiary water treatment. In some applications, more advanced treatment is required, known as quaternary water treatment.
What is the process of removing sediment from a wastewater system?
1. Biofiltration. Bio filtration uses sand filters, contact filters or trickling filters to ensure that any additional sediment is removed from the wastewater. 2. Aeration. Aeration is a lengthy process which increases oxygen saturation by introducing air to wastewater.
What is tertiary treatment?
In the case of water treated by municipalities, tertiary treatment also involves the removal of pathogens, which ensures that water is safe for drinking purposes.
Where is wastewater held?
During primary treatment, wastewater is temporarily held in a settling tank where heavier solids sink to the bottom while lighter solids float to the surface. Once settled, these materials are held back while the remaining liquid is discharged or moved through to the more rigorous secondary phase of wastewater treatment.
How is water treated?
Water is treated to remove any harmful components before being fed into the public supply. This is done in several ways. Sedimentation – the water is stored in a large tank or a reservoir. This slows down the flow of the water and allows large, insoluble particles to settle to the bottom.
What are the processes used to make water safe to drink?
Different methods are used to do this, such as sedimentation, filtration and chlorination. Learn also about the processes of fluoridation, desalination and distillation.