AEDs – The only effective intervention for sudden cardiac arrest. If an AED recognizes either of these rhythms, it will charge and indicate that a shock is advised, usually with a voice command. The benefit of the shock is to correct the abnormal electrical disturbance that is causing the irregular heart rhythm,...
What are the benefits of using an AED to treat cardiac arrest?
An AED is a portable lifesaving device that can help a person suffering from sudden cardiac arrest. When a person’s heart stops beating unexpectedly, rescuers can place the AED the person’s chest to deliver an electric shock to the heart to restart it, according to the American Heart Association (AMA).
What is an AED?
Automated External Defibrillator (AED): An AED is a small, portable device that analyzes the heart’s rhythm and prompts the user to deliver a defibrillation shock if it determines one is needed. Once turned on, the AED guides the user through each step of the defibrillation process by providing voice and/or visual prompts.
Should you use an AED to perform CPR?
An AED, or automated external defibrillator, is used to help those experiencing sudden cardiac arrest. It's a sophisticated, yet easy-to-use, medical device that can analyze the heart's rhythm and, if necessary, deliver an electrical shock, or defibrillation, to help the heart re-establish an effective rhythm.
How effective is AED for ventricular fibrillation in the home?
In these cases, an electric shock from an AED within a few minutes of onset can significantly improve a patient's chance of survival by restoring the heart to its normal rhythm. CPR has also been shown to be effective in increasing survival from sudden cardiac arrest.

Why the the AED helpful is patients with sudden cardiac arrest?
Should you use an AED for cardiac arrest?
What is an AED and why is it important?
How do AEDs work?
How does AED affect the rhythm of the heart?
Why is an AED effective?
How do AEDs save lives?
Why is AED needed quizlet?
What is an AED?
An AED is a small, portable device that analyzes the heart’s rhythm and prompts the user to deliver a defibrillation shock if it determines one is needed. Once turned on, the AED guides the user through each step of the defibrillation process by providing voice and/or visual prompts. AEDs are specially designed for easy use by any “first responder” who arrives on the scene of a medical emergency. A “first responder” can be an emergency medical services worker, a firefighter or police officer, or it can be a layperson with minimal AED training.
Who can use an AED?
AEDs are specially designed for easy use by any “first responder” who arrives on the scene of a medical emergency. A “first responder” can be an emergency medical services worker, a firefighter or police officer, or it can be a layperson with minimal AED training.
How long does it take to defibrillate a person?
Statistics and Advisory Statements: 1 The American Heart Association (AHA) states that 350,000 Americans die each year from sudden cardiac arrest (SCA), of those approximately 7,000 are children. 2 When SCA occurs, the AHA recommends defibrillation within 3-5 minutes, or sooner. On average, EMS teams take 6-12 minutes to arrive. 3 Survival rates drop 10% as each minute passes without defibrillation. While the national SCA survival rate is 5-10%, studies have shown that defibrillation within 3 minutes raises the survival rate to 74%. Timing is everything. 4 An Advisory Statement from the Pediatric Advanced Life Support Task Force (PALS), International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation (ILCOR) states: Automated external defibrillators (AEDs) may be used for children 0 to 8 years of age who have no signs of circulation.
What is sudden cardiac arrest?
Sudden cardiac arrest (SCA) is a condition in which suddenly and unexpectedly the heart stops beating due to a malfunction in the heart’s electrical system. The malfunction that causes SCA is a life-threatening abnormal rhythm, or arrhythmia. The most common arrhythmia is ventricular fibrillation (VF). When in VF, the heart’s rhythm is so chaotic (called “fibrillating”) that the heart merely quivers, and is unable to pump blood to the body and brain. Once a heart has entered VF, sudden cardiac arrest occurs. A victim in SCA first loses his or her pulse, then consciousness, and finally the ability to breathe. But all of this happens quickly – in a matter of seconds. Without immediate treatment from a defibrillator, 90-95 percent of SCA victims will die.
How long does it take for an EMS to arrive?
When SCA occurs, the AHA recommends defibrillation within 3-5 minutes, or sooner. On average, EMS teams take 6-12 minutes to arrive.
What do electrodes do in AED?
The electrodes (pads) placed on the victim’s body send the heart rhythm information (ECGs) to the AED.
What happens when the blood supply to part of the heart muscle is severely reduced or stopped?
Heart attack , on the other hand, occurs when the blood supply to part of the heart muscle itself is severely reduced or stopped because of an obstruction in an artery. A heart attack can trigger sudden cardiac arrest, but they are not the same. Cardiac Arrest.
What is an AED?
An AED, or automated external defibrillator, is used to help those experiencing sudden cardiac arrest. It's a sophisticated, yet easy-to-use, medical device that can analyze the heart's rhythm and, if necessary, deliver an electrical shock, or defibrillation, to help the heart re-establish an effective rhythm.
Why is shipping delayed for Red Cross?
Due to current natural disasters and the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, please expect shipping delays when purchasing product from the Red Cross Store.
How long does it take to respond to 911?
However, because the average response time for first responders once 911 is called is 8-12 minutes, and for each minute defibrillation is delayed, the odds of survival are reduced by approximately 10%, having access to and AED and knowing how to use one, is critical. CPR/AED Classes.
Can you get AED certification with a passing score?
Additionally, because this option allows you to demonstrate your skills to a certified instructor, you can receive full certification with a passing score. Why Train With the Red Cross. Red Cross CPR/AED Training Saves Lives.
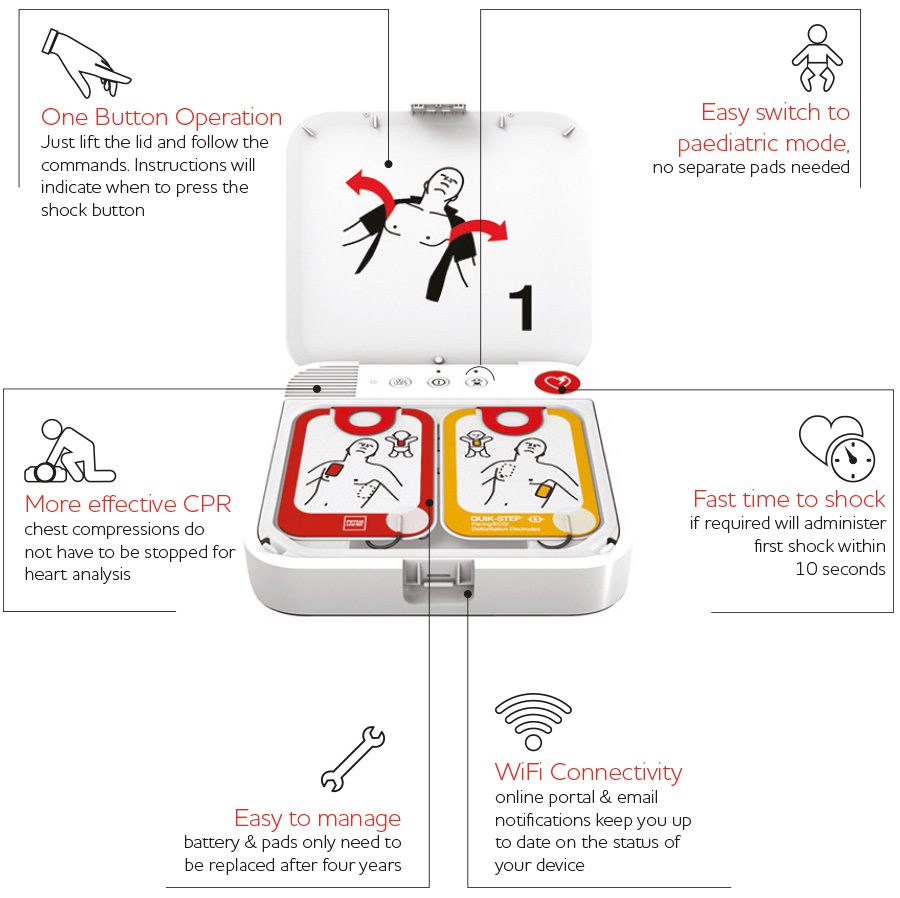
How does an AED work?
If the AED determines that the problem is caused by ventricular fibrillation, the AED instructs the user to hit a button to deliver an electric shock. The AED transmits the shock through the electrodes, then rereads the heart rhythm to determine if another shock is needed .
Where are AEDs used?
The AEDs used in the study are the same types of devices that are now available in many airports, fitness centers, and other public places , which have been shown to be safely and easily used by bystanders with little training to perform life-saving treatment on individuals in cardiac arrest.
How many people died in the AED study?
Overall, 450 participants died during the study, with nearly equal numbers of participants in the control group (228 or 6.5 percent) and the AED treatment group (222 or 6.4 percent). Participants were equally likely to die from sudden cardiac arrest (35.6 percent) as from other causes not related to cardiovascular disease (37.8 percent), and 160 deaths during the study were due to sudden cardiac arrest.
How often does a person die from cardiac arrest?
Every two to three minutes, someone in the United States goes into cardiac arrest, and at least 95 percent of cases end in death within a few minutes. Three out of four sudden cardiac arrests take place when the patient is at home. During sudden cardiac arrest, the heart suddenly and unexpectedly stops beating effectively;
What happens when you have a sudden cardiac arrest?
During sudden cardiac arrest, the heart suddenly and unexpectedly stops beating effectively; blood stops flowing to the brain and other vital organs, and the individual collapses into unconsciousness and stops breathing. Although sudden cardiac arrest is not the same as a heart attack, which is the result of a loss of blood supply to ...
Where was the AED study conducted?
The study was conducted in 178 clinical sites in the United States, Canada, Britain, New Zealand, Australia, Germany, and the Netherlands. "Cardiac arrest is a top killer of Americans, and this study shows that the strategies of placing an AED in the home and of being prepared to give CPR are equally effective at saving lives in a population ...
Who donated HeartStart?
Philips Medical Systems and Laerdal Medical donated HeartStart Home Defibrillators for use by participants in the AED group. The HeartStart is the only FDA-approved home defibrillator available without a prescription.
What does an AED do?
We’ve all seen the TV commercials that show people being saved by an AED, but what does it actually do? An AED is a device that can be used in conjunction with CPR to save someone who has experienced SCA. It sends electric shocks through the chest muscles and helps restore heart rhythm. The key takeaway from this blog post is not just how important an AED is for saving the lives of victims of SCA, but also how they are only effective when combined with quick-acting CPR. When you think about your workplace or school environment where there may not always be immediate access to emergency medical services, this knowledge becomes more crucial than ever before. If you want help understanding how the use of the lifesaving AED machine along with the quick use of CPR, contact AED USA today to learn more about training for SCA events in your home or organization today.
What does AED stand for in CPR?
AED stands for Automated External Defibrillator, this device can detect SCA by using an electric shock should it occur. AEDs are not used independently from CPR but rather in conjunction with the technique to save the victim’s life. More access to AED’s in public places for all first responders has a direct correlation to increased survival rates.
What is the difference between CPR and AED?
The difference between CPR with AED intervention and just CPR without is that an automated external defibrillator can detect SCA and provide the necessary electric shock needed to terminate it. A person who has AED intervention with CPR will have greater chances of survival than someone without AED intervention with or without a bystander performing chest compressions. The reason being is that if the victim is indeed suffering from SCA and the AED recognizes and shocks the heart into a normal rhythm, thereby establishing oxygenated blood pumping throughout the body, the victim would have a higher probability of making a full recovery. For this reason, AED training, CPR training along with the American Heart Association recommends the use of CPR in conjunction with an AED in case defibrillation is needed before trained medical professionals can arrive on the scene.
What is the purpose of CPR?
CPR stands for cardiopulmonary resuscitation which is a lifesaving technique to help keep someone’s heart beating and therefore circulating oxygen throughout the body during a sudden cardiac event. The early compressions to a person’s chest are often done by pushing on the chest at a rate of 100 times per minute, with depth that is enough to break up the obstruction in their airway.
What is the name of the device that is used when a person's heart stops beating?
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation, or CPR, is used when a person’s heart stops beating. An Automated External Defibrillator (AED) is a device that can be used on people who are experiencing SCA and it’s often used in conjunction with CPR to save them.
Where do AEDs make contact with the body?
The electrodes pads must make contact with skin, usually around the victim’s torso near the anterior chest area. AEDs are not designed to be used for a complete shock, only as a backup in conjunction with CPR which consists of continued compression on the victim’s chest and breathing air into their lungs.
Can AEDs replace lifesaving care?
AEDs should never replace actual life-saving care by professionals but it does offer many benefits such as decreased time to defibrillation and increased survival rates from SCA when in public places where AED access is well distributed among first responders
What is an AED?
An AED is a type of computerized defibrillator that automatically analyzes the heart rhythm in people who are experiencing cardiac arrest. When appropriate, it delivers an electrical shock to the heart to restore its normal rhythm.
How does an AED work?
How AEDs Work. An AED system includes an AED device and accessories, such as a battery, pad electrodes, and if applicable, an adapter. The devices give verbal instructions to users. The user turns on the AED and follows the voice prompts . Some devices turn on automatically when the user opens the lid.
How does an AED shock work?
If a defibrillation shock is needed, the AED uses the voice prompts to instruct when to press a button to deliver the shock. In some devices, the voice prompts announce that a shock is going to be delivered and the AED delivers the shock without intervention by the user.
What is the name of the device that is used to treat cardiac arrest?
If cardiac arrest does occur, rapid treatment with a medical device called an automated external defibrillator (AED) can be life-saving.
What do you call someone who has a cardiac arrest?
But as always, in an emergency, call 911 immediately. If you’re somewhere that has an emergency response system that includes a clearly visible number, call that number for assistance. In either case, an operator can give instructions on how you can help someone who has sudden cardiac arrest.
What can you learn from a cardiac class?
Classes can teach you how to recognize the signs of a sudden cardiac arrest, when to call emergency medical services, how to do CPR, and how to use an AED.
What is sudden cardiac arrest?
Sudden cardiac arrest occurs when the heart suddenly and unexpectedly stops pumping blood. It can happen to anyone, at any time, and signs include sudden collapse and immediate loss of consciousness. Unlike heart attacks, which are caused by a blockage in an artery to the heart, sudden cardiac arrest is caused when the heart’s electrical system ...
What is the treatment for cardiac arrest?
Treatments might include: Drugs. Doctors use various anti-arrhythmic drugs for emergency or long-term treatment of arrhythmias or potential arrhythmia complications.
What is the best medication for sudden cardiac arrest?
A class of medications called beta blockers is commonly used in people at risk of sudden cardiac arrest. Other possible drugs that can be used to treat the condition that led to the arrhythmia include angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and calcium channel blockers. Implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD).
What is the best way to help someone who is at risk of cardiac arrest?
The American Red Cross and other organizations offer courses in CPR and defibrillator use. Being trained will help not only your loved one, but your training might help others.
What is the importance of CPR?
Immediate CPR is crucial for treating sudden cardiac arrest. By maintaining a flow of oxygen-rich blood to the body's vital organs, CPR can provide a vital link until more-advanced emergency care is available. If you don't know CPR and someone collapses unconscious near you, call 911 or emergency medical help.
What is the procedure called when you have ventricular fibrillation?
The procedure, called defibrillation, momentarily stops the heart and the chaotic rhythm.
What to do if you survive sudden cardiac arrest?
If you survive sudden cardiac arrest, your doctor will try to learn what caused it to help prevent future episodes. Tests your doctor may recommend include:
What is the ejection fraction of a heart?
Ejection fraction refers to the percentage of blood that's pumped out of a filled ventricle with each heartbeat. A normal ejection fraction is 50% to 70%. An ejection fraction of less than 40% increases your risk of sudden cardiac arrest. Nuclear scan.
