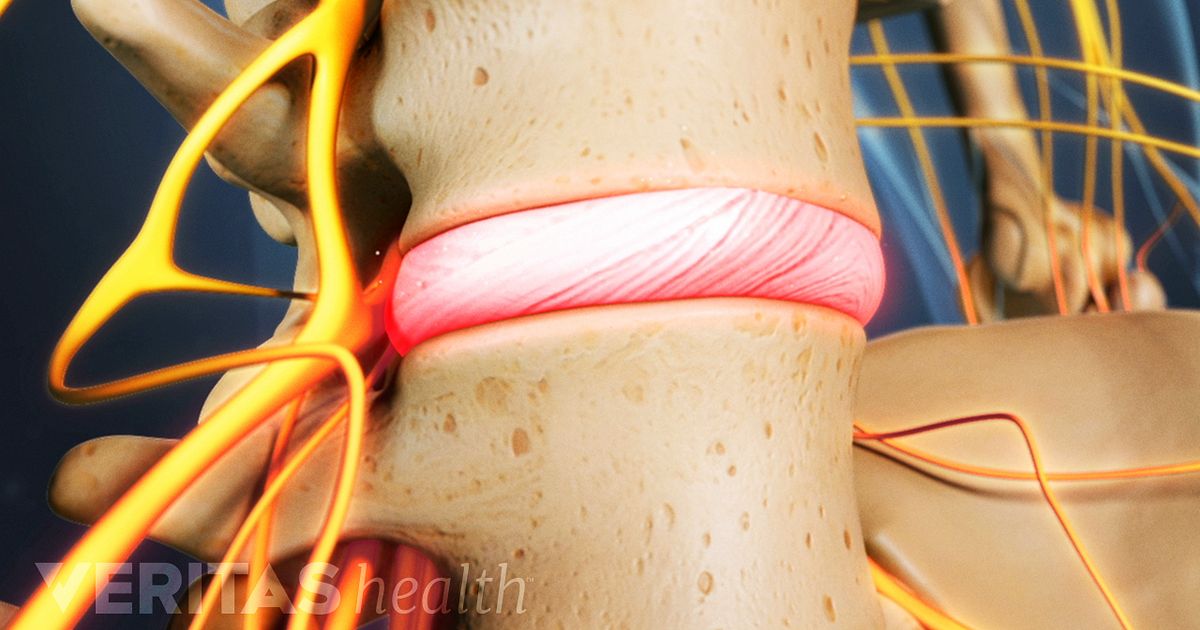
What kind of doctor treats osteoporosis?
Rheumatologists work with teams of other health care providers who treat patients with osteoporosis and can connect patients with gynecologists, endocrinologists, physiatrists, orthopedists, dietitians, and other experts in osteoporosis management. Working with a team can help patients address all aspects of the disease and ensure success.
Why do rheumatologists see osteoporosis?
Because they see lots of patients with osteoporosis, they can add real-world knowledge of the disease to their academic and clinical training . They’re able to assess how well patients respond to certain treatments, have a deeper understanding of how osteoporosis progresses over time, share insight about effectively implementing lifestyle changes, and recognize symptoms that a general practitioner may miss, among other skills.
What is a rheumatologist?
A rheumatologist is a physician who specializes in treating musculoskeletal diseases and autoimmune conditions, collectively known as rheumatic diseases. These can include more than 100 different disorders, so rheumatologists must train extensively to master this area of study. A rheumatologist will have expertise in treating osteoporosis and other conditions like arthritis, gout, lupus, fibromyalgia, and more.
How often do rheumatologists renew their license?
To maintain their board certifications, rheumatologists must keep up with these new developments in their field. They must complete continuing education and renew their licenses every few years, depending on the state in which they practice and other factors. By following these requirements, board-certified rheumatologists stay on top of new treatments and discoveries about the mechanisms involved in osteoporosis, so they can then provide their patients with insightful, informed, and up-to-date treatment plans.
What is the training required for a rheumatologist?
Rheumatologists spend several additional years in a fellowship, during which they train under experienced rheumatologists and focus on patients with osteoporosis and other rheumatic diseases. At the end of this training, specialists can take a qualifying examination to become board-certified rheumatologists.
Is osteoporosis a complex disease?
Osteoporosis is a complex disease that affects everyone differently. That’s why all osteoporosis patients should follow unique treatment plans tailored to their specific needs. But your primary care doctor may not have all the information you need to manage your osteoporosis successfully. That’s where specialists come in: an osteoporosis ...
What is the best treatment for osteoporosis?
If you can't tolerate the more common treatments for osteoporosis — or if they don't work well enough — your doctor might suggest trying: Teriparatide (Forteo). This powerful drug is similar to parathyroid hormone and stimulates new bone growth. It's given by daily injection under the skin.
How to reduce the risk of osteoporosis?
Smoking increases rates of bone loss and the chance of fracture. Avoid excessive alcohol. Consuming more than two alcoholic drinks a day might decrease bone formation.
How long can you take teriparatide for osteoporosis?
After two years of treatment with teriparatide, another osteoporosis drug is taken to maintain the new bone growth. Abaloparatide (Tymlos) is another drug similar to parathyroid hormone. You can take it for only two years, which will be followed by another osteoporosis medication. Romosozumab (Evenity).
What is the newest bone building medication?
Romosozumab (Evenity). This is the newest bone-building medication to treat osteoporosis. It is given as an injection every month at your doctor's office. It is limited to one year of treatment, followed by other osteoporosis medications.
How often is denosumab shot?
Denosumab is delivered via a shot under the skin every six months. If you take denosumab, you might have to continue to do so indefinitely.
How to determine bone density?
Diagnosis. Your bone density can be measured by a machine that uses low levels of X-rays to determine the proportion of mineral in your bones. During this painless test, you lie on a padded table as a scanner passes over your body. In most cases, only a few bones are checked — usually in the hip and spine.
What supplements can help with osteoporosis?
Alternative medicine. There is limited evidence that certain supplements, such as vitamin K-2 and soy, can help lower fracture risk in osteoporosis, but more studies are needed to prove benefits and determine risks.
What kind of doctor treats osteoporosis?
Your primary family doctor can help you choose which one is the best for you: Rheumatologists: They diagnose and treat problems of muscles, joints, and bones, including autoimmune disorders such as lupus.
Who is the first person to diagnose osteoporosis?
A gynecologist or family practitioner is often the first person that diagnoses someone with osteoporosis before providing a recommendation to a specialist. Choosing a doctor to diagnose or treat osteoporosis can be disorienting. With some health problems, the kind of health professional you choose is quite straightforward.
What is the specialty of rheumatology?
In general rheumatology is a sub-specialty of internal medicine and rheumatologists requires board certifications in both rheumatology and internal medicine.
What to do if your doctor doesn't recommend a specialist?
If your doctor doesn’t immediately recommend a specialist, you should ask him why. There is a chance he has a strong interest in osteoporosis and always be updated with the latest developments. If so, that’s a good thing. However, if you think a specialist is better, tell your doctor.
Who can diagnose metabolic bone disease?
Ask your doctor if he has taken such trainings. Some rheumatologists, orthopedic surgeons and endocrinologists often can diagnose and treat patients who have metabolic bone disease accurately, because their works often involves studying bone problems. For unusual or difficult cases, metabolic bone specialist is often a good choice.
Does it hurt to see a family doctor for osteoporosis?
Starting with a family doctor or any medicine specialist won’t hurt. Some family medicine doctors or internists have a special interest or experience in osteoporosis and can be perfectly capable of dealing with your care.
What is the best treatment for osteoporosis?
Bisphosphonates are usually the first choice for osteoporosis treatment. These include: 1 Alendronate (Fosamax), a weekly pill 2 Risedronate (Actonel), a weekly or monthly pill 3 Ibandronate (Boniva), a monthly pill or quarterly intravenous (IV) infusion 4 Zoledronic acid (Reclast), an annual IV infusion
Which osteoporosis medication is usually tried first?
Which osteoporosis medications are usually tried first? Bisphosphonates are usually the first choice for osteoporosis treatment. These include: Alendronate (Fosamax), a weekly pill. Risedronate (Actonel), a weekly or monthly pill. Ibandronate (Boniva), a monthly pill or quarterly intravenous (IV) infusion.
What is the condition of bisphosphonates and denosumab?
A very rare complication of bisphosphonates and denosumab is a break or crack in the middle of the thighbone. This injury, known as atypical femoral fracture, can cause pain in the thigh or groin that begins subtly and may gradually worsen.
How does osteoporosis medication work?
Because bone rebuilding cannot keep pace, bones deteriorate and become weaker. Most osteoporosis medications work by reducing the rate at which your bones break down. Some work by speeding up the bone-building process. Either mechanism strengthens bone and reduces your risk of fractures.
How often is romosozumab given?
Romosozumab is given as a monthly injection at your doctor's office. It is a new drug and less is known about long-term side effects, but it is not given to people who have recently had a stroke or heart attack. Treatment stops after 12 monthly doses.
Does Raloxifene help with bone density?
Current recommendations say to use the lowest dose of hormones for the shortest period of time. Raloxifene (Evista) mimics estrogen's beneficial effects on bone density in post menopausal women, without some of the risks associated with estrogen. Taking this drug can reduce the risk of some types of breast cancer.
Can you take bisphosphonate with water?
Bisphosphonate pills aren't absorbed well by the stomach. It may help to take the medication with a tall glass of water on an empty stomach. Don't put anything else into your stomach for 30 to 60 minutes, after which you can eat, drink other liquids and take other medications.
What is the best treatment for osteoporosis?
Bisphosphonates are commonly prescribed for osteoporosis treatment and prevention. The FDA has approved many bisphosphonates to prevent bone loss and fractures in post-menopausal women: alendronate (brand name Fosamax), etidronate (brand name Didronel), ibandronate (brand name Boniva), risedronate (brand name Actonel), tiludronate (brand name Skelid), pamidronate (brand name Aredia) and zoledronic acid (brand names Reclast and Zometa). Some are taken daily; others are formulated for weekly, monthly or yearly use. Bisphosphonates decrease the rate that bone is destroyed, a process called resorption, by stopping the activity of the cells that cause bone breakdown, called osteoclasts. This slows down the rate of bone loss. The drugs are also incorporated into newly formed bone and can persist in them for years, so the effects last well beyond the final treatment.
What hormones are used to treat osteoporosis?
Two other hormones have been approved to treat osteoporosis: teriparatide and abaloparatide. Teriparatide (brand name Forteo) is a lab-made derivative of human parathyroid hormone (PTH), and abaloparatide (band name Tymlos) is a derivative of human parathyroid hormone-related protein.
How has osteoporosis changed?
Osteoporosis treatment has radically changed in a relatively short period. In the early 1990s, women had few treatment options. Now, there are many different types of treatments available. This has created a dilemma for women trying to decide which, if any, of these medications they need. The NWHN believes that treatment should be focused on women ...
What is the name of the drug that stops bone breakdown?
Denosumab (brand name Prolia) osteoporosis medication (Amgen) Denosumab (brand name Prolia) is an osteoporosis medication that uses human monoclonal antibody. Approved in 2010, this drug works by targeting and inactivating osteoclasts to stop natural bone breakdown, or resorption, processes.
How do bisphosphonates affect bone?
Bisphosphonates decrease the rate that bone is destroyed, a process called resorption, by stopping the activity of the cells that cause bone breakdown, called osteoclasts. This slows down the rate of bone loss.
Do hip fractures prevent osteopenia?
However, they have not been shown to prevent hip fractures in women who have been told that they have osteopenia. They do prevent vertebral fractures, including in women who have not previously fractured. It’s understandable that women may want to prevent vertebral fractures, which can be painful and debilitating.
Is it safe to take a drug for osteoporosis?
Women want to know when it is appropriate to take a drug for osteoporosis, and which treatments are safe and effective. History has shown that preventing loss of bone mineral density in women who are otherwise at low risk of experiencing a fracture is dangerous.
How to contact the National Osteoporosis Foundation?
301-565-2966 (TTY ) [email protected]. www.niams.nih.gov. National Osteoporosis Foundation. 800-231-4222 (toll-free) [email protected]. www.nof.org. This content is provided by the NIH National Institute on Aging (NIA). NIA scientists and other experts review this content to ensure it is accurate and up to date.
How do you know if you have osteoporosis?
For some people, the first sign of osteoporosis is to realize they are getting shorter or to break a bone easily. Don’t wait until that happens to see if you have osteoporosis. You can have a bone density test to find out how strong your bones are.
What is a bone mineral density test?
A bone mineral density test compares your bone density to the bones of an average healthy young adult. The test result, known as a T-score, tells you how strong your bones are, whether you have osteoporosis or osteopenia, and your risk for having a fracture.
Why is osteoporosis considered a silent disease?
Osteoporosis is called a “silent disease” because you may not notice any changes until a bone breaks. All the while, though, your bones had been losing strength for many years. Bone is living tissue. To keep bones strong, your body breaks down old bone and replaces it with new bone tissue.
What happens to the bones in your 40s?
As people enter their 40s and 50s, more bone may be broken down than is replaced. A close look at the inside of bone shows something like a honeycomb. When you have osteoporosis, the spaces in this honeycomb grow larger, and the bone that forms the honeycomb gets smaller. The outer shell of your bones also gets thinner.
How to keep bones strong?
To keep bones strong, your body breaks down old bone and replaces it with new bone tissue. Sometime around age 30, bone mass stops increasing, and the goal for bone health is to keep as much bone as possible for as long as you can. As people enter their 40s and 50s, more bone may be broken down than is replaced.
What are the risk factors for osteoporosis?
Low levels of testosterone, too much alcohol, taking certain drugs, and smoking are other risk factors. Older men who break a bone easily or are at risk for osteoporosis should talk with their doctors about testing and treatment.
Abstract
Approximately 10 million men and women in the U.S. have osteoporosis, 1 a metabolic bone disease characterized by low bone density and deterioration of bone architecture that increase the risk of fractures. 2 Osteoporosis-related fractures can increase pain, disability, nursing home placement, total health care costs, and mortality.
INTRODUCTION
Osteoporosis is a bone disorder that increases a person’s risk of fracture due to low bone mineral density (BMD), impaired bone microarchitecture/mineralization, and/or decreased bone strength.
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
Bones provide structure for the body, protection for the organs, and storage for minerals, such as calcium and phosphorus, that are essential for bone development and stability. Individuals continue to build bone and will reach peak bone mass at about 30 years of age, after which they begin to lose bone mass steadily.
ETIOLOGY
Primary osteoporosis is often associated with age and sex hormone deficiency. Age-related osteoporosis results from the continuous deterioration of the trabeculae in bone. In addition, the reduction of estrogen production in post menopausal women causes a significant increase in bone loss.
SCREENING AND DIAGNOSIS
Published osteoporosis screening guidelines vary greatly. In general, most organizations recommend that all adults older than 50 years of age with a history of fracture receive BMD screening.
SELECT GUIDELINES AND RECOMMENDATIONS
In a systematic review, Solomon et al. looked at 18 osteoporosis guidelines, among them those of the NOF, the ACR, and the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology (AACE/ACE).
NONPHARMACOLOGICAL MANAGEMENT
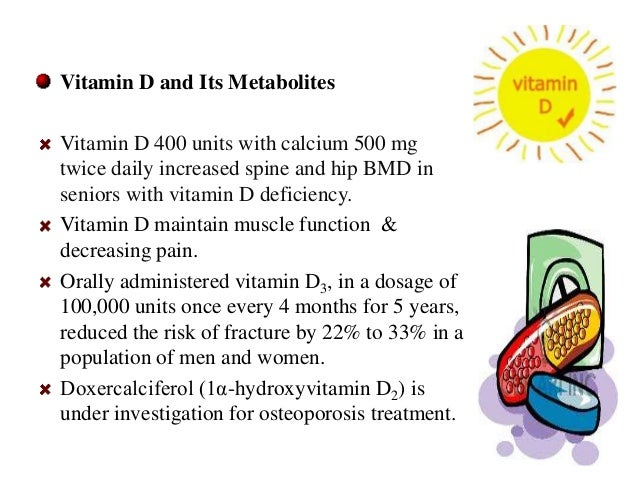
Nonpharmacological management of osteoporosis includes adequate calcium and vitamin D intake, weight-bearing exercise, smoking cessation, limitation of alcohol/caffeine consumption, and fall-prevention techniques. 2 – 6, 9, 18, 34
What is the best treatment for osteoporosis?
Bisphosphonates are the most common osteoporosis drug treatments. They’re typically the first treatments recommended for women who are postmenopausal. Examples of bisphosphonates include: ibandronate (Boniva), available as a monthly oral tablet or as an intravenous injection that you get four times per year.
Why do older people have a higher risk of osteoporosis?
As you age, you lose old bone at a faster rate than your body can replace it. Because of this, older people are at a higher risk of osteoporosis. Women also have a higher risk of developing osteoporosis because they typically have thinner bones than men.
What is the new antibody for bone formation?
The new antibody romosozumab (Evenity) helps to increase bone formation. It was approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in April of 2019. It’s intended for postmenopausal women with a high risk of fracture. This includes women who:
Why do women have brittle bones?
Women who are going through menopause experience a decrease in estrogen levels, which leads to more rapid bone breakdown and can result in brittle bones. Other risks factors include:
How often can you take ibandronate?
ibandronate (Boniva), available as a monthly oral tablet or as an intravenous injection that you get four times per year. risedronate (Actonel), available in daily, weekly, or monthly doses in an oral tablet. zoledronic acid (Reclast), available as an intravenous infusion that you get once every one or two years.
What vitamins are good for bone loss?
Even when you’re taking any of the medications listed above, doctors recommend getting plenty of calcium and vitamin D in your diet. That’s because this mineral and vitamin together can help slow bone loss.
How to prevent bone loss?
The most aggressive way to prevent additional bone loss is to take prescription medications.
Diagnosis
Treatment
- Treatment recommendations are often based on an estimate of your risk of breaking a bone in the next 10 years using information such as the bone density test. If your risk isn't high, treatment might not include medication and might focus instead on modifying risk factors for bone loss and falls.
Clinical Trials
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
- These suggestions might help reduce your risk of developing osteoporosis or breaking bones: 1. Don't smoke.Smoking increases rates of bone loss and the chance of fracture. 2. Limit alcohol.Consuming more than two alcoholic drinks a day may decrease bone formation. Being under the influence of alcohol also can increase your risk of falling. 3. Prevent falls.Wear low-he…
Preparing For Your Appointment
- Your doctor might suggest bone density testing. Screening for osteoporosis is recommended for all women over age 65. Some guidelines also recommend screening men by age 70, especially if they have health issues likely to cause osteoporosis. If you have a broken bone after a minor force injury, such as a simple fall, bone density testing may be impo...