Key messages from the 2015 WHO ARV guidelines •Treat all (at any CD4) - PLHIV across all ages, but the sickest remain a priority (symptomatic disease and CD4 < 350). •Phased introduction of optimized regimens (new drug class; optimized dosing and formulations)
Full Answer
Who is at risk for getting HIV?
disseminated in December 2015. iii FOREWORD With this update of the consolidated guidelines on the use of antiretroviral drugs for treating and preventing HIV infection, WHO, for the first time, recommends that all people living with HIV be provided with antiretroviral therapy (ART). This will bring us one step closer
What you should know about HIV treatment?
WHO to update guidelines on antiretrovirals in 2015 December 2014. WHO Department of HIV/AIDS is planning to release updated recommendations on the use of antiretroviral (ARV) drugs to treat and prevent HIV along the continuum of care, following the successful first publication of the consolidated guidelines in 2013.
Who recommends dolutegravir for HIV?
1 Consolidated guidelines on the use of antiretroviral drugs for treating and preventing HIV infection: recommendations for a public health approach. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2013. These guidelines will be updated in 2015. SECOND-LINE ANTIVIRAL THERAPIES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF TREATMENT FAILURE
Who is at greatest risk for HIV transmission?
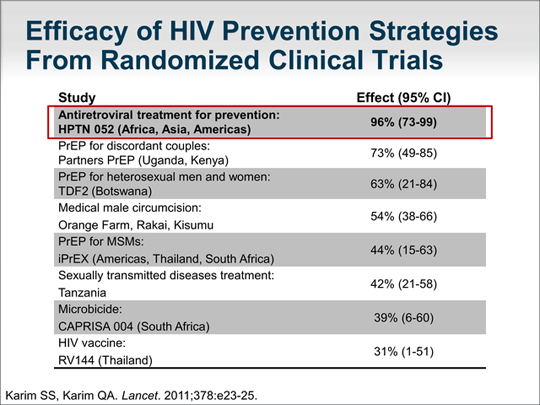
(WHO 2013 guidelines) Eligible but not receiving treatment Eligible and receiving treatment 850,000 Total eligible: 28,287,000 2012 9,724,000 *2012 ART/WHO 2013 guidelines estimate for 2013 . Children have inequitable access to treatment—two ...
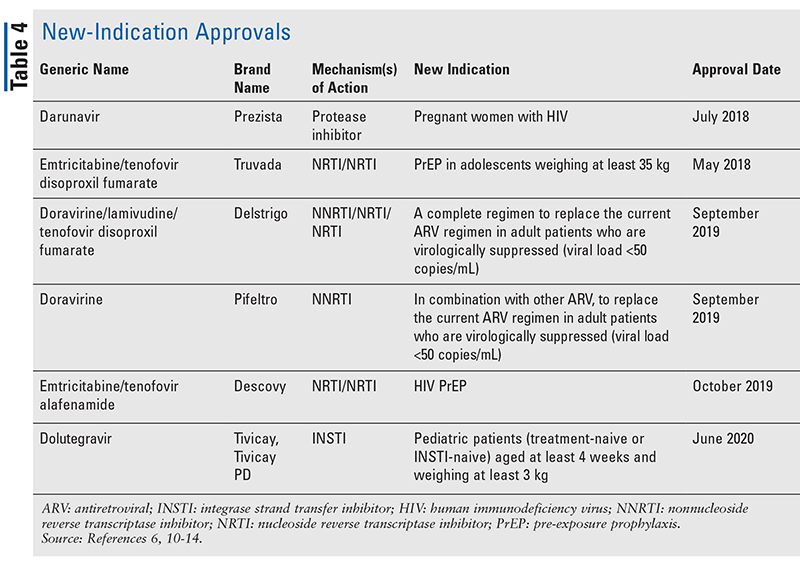
WHO recommended drugs for HIV prophylaxis?
PEP RegimenDrug nameDrug classEmtricitabine (Emtriva; FTC)NRTIEtravirine (Intelence; ETR)NNRTILamivudine (Epivir; 3TC)NRTILopinavir/ritonavir (Kaletra; LPV/RTV)PI9 more rows•Sep 22, 2021
What is the treatment protocol for HIV?
The treatment for HIV is called antiretroviral therapy (ART). ART involves taking a combination of HIV medicines (called an HIV treatment regimen) every day. ART is recommended for everyone who has HIV. People with HIV should start taking HIV medicines as soon as possible.Aug 16, 2021
What is first-line treatment for HIV?
The recommended first-line HIV treatment regimens include antiretroviral (ARV) drugs that are safe, effective, and convenient for most people with HIV who have never taken ARVs before.
What is the gold standard for HIV treatment?
An international team of AIDS researchers at Johns Hopkins and other institutions has found that a once-daily combination of three antiretroviral drugs works better as an initial treatment for HIV infection than another three-drug combination long considered the gold standard.Jan 19, 2006
WHO recommended antiretroviral therapy?
The 2013 WHO ARV guidelines recommended initiating ART for all adults with HIV and a CD4 count at or below 500 cells/mm3, regardless of WHO clinical stage, giving priority to those with severe or advanced HIV disease (WHO clinical stage 3 or 4) or a CD4 cell count at or below 350 cells/mm3 (9).
What is 2nd line treatment?
Second-line treatment is treatment for a disease or condition after the initial treatment (first-line treatment) has failed, stopped working, or has side effects that aren't tolerated. It's important to understand "lines of treatment" and how they differ from first line treatment and can play a role in clinical trials.Jun 9, 2020
What does third line treatment mean?
Treatment that is given when both initial treatment (first-line therapy) and subsequent treatment (second-line therapy) don't work, or stop working.
What are the 3 active antiretrovirals comprised of?
Most HAART regimens include drugs from at least two of the three classes of antiretroviral therapy (nucleoside analog reverse transcriptase (RT) inhibitors, non-nucleoside analog RT inhibitors, and protease inhibitors).
How long do Arvs take to work?
Most people living with HIV who start taking antiretroviral therapy daily as prescribed achieve an undetectable viral load within one to six months after beginning treatment.Jun 12, 2020
Is T cell same as CD4?
A CD4 count is a test that measures the number of CD4 cells in your blood. CD4 cells, also known as T cells, are white blood cells that fight infection and play an important role in your immune system.Nov 30, 2020
How long after tinidazole can you drink alcohol?
To reduce the possibility of a disulfiram-like reaction, abstinence from alcohol use should continue for 72 hours after completion of tinidazole. Alternative regimens include several tinidazole regimens ( 601) or clindamycin (oral or intravaginal) ( 602 ).
Where is HBV found?
The highest concentrations of HBV are found in blood, with lower concentrations found in other body fluids including wound exudates, semen, vaginal secretions, and saliva ( 829,830 ). HBV is more infectious and more stable in the environment than other bloodborne pathogens (e.g., HCV and HIV).
What is pelvic inflammatory disease?
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) comprises a spectrum of inflammatory disorders of the upper female genital tract, including any combination of endometritis, salpingitis, tubo-ovarian abscess, and pelvic peritonitis ( 728 ).
How long does ceftriaxone last?
Although limited clinical studies, along with biologic and pharmacologic evidence, suggest that ceftriaxone (1–2 g daily either IM or IV for 10–14 days) is effective for treating primary and secondary syphilis, the optimal dose and duration of ceftriaxone therapy have not been defined ( 413 ).
Can a point of care test show urethral inflammation?
Clinicians should attempt to obtain objective evidence of urethral inflammation. However, if point-of-care diagnostic tests (e.g., Gram, MB or GV, or Gram stain microscopy) are not available, all men should be tested by NAAT and treated with drug regimens effective against both gonorrhea and chlamydia.
Is fluconazole good for HIV?
albicans colonization and symptomatic VVC (727), this regimen is not recommended for women with HIV infection in the absence of complicated VVC ( 247 ).
Is HPV 16 or 18?
HPV testing for 16 and 18 is also used to triage discordant test results (i.e., in the case of a negative Pap test and positive HPV test). In the future, oncogenic (high-risk) HPV tests might be considered for primary cervical cancer screening, but no such recommendation has been made by any medical organization.
What is the window period for HIV?
During this time, people experience the so-called “window” period – when HIV antibodies haven’t been produced in high enough levels to be detected by standard tests and when they may have had no signs of HIV infection, but also when they may transmit HIV to others.
How does HIV treatment work?
HIV disease can be managed by treatment regimens composed of a combination of three or more antiretroviral (ARV) drugs. Current antiretroviral therapy (ART) does not cure HIV infection but highly suppresses viral replication within a person's body and allows an individual's immune system recovery to strengthen and regain the capacity to fight off opportunistic infections and some cancers.
What is the most advanced stage of HIV?
The most advanced stage of HIV infection is acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), which can take many years to develop if not treated, depending on the individual. AIDS is defined by the development of certain cancers, infections or other severe long-term clinical manifestations.
How long does it take for HIV to show symptoms?
In the first few weeks after initial infection people may experience no symptoms or an influenza-like illness including fever, headache, rash or sore throat.
When can a child get tested for HIV?
For children less than 18 months of age, serological testing is not sufficient to identify HIV infection – virological testing must be provided as early as birth or at 6 weeks of age.
What is STI in medical terms?
having unprotected anal or vaginal sex; having another sexually transmitted infection (STI) such as syphilis, herpes, chlamydia, gonorrhoea and bacterial vaginosis; sharing contaminated needles, syringes and other injecting equipment and drug solutions when injecting drugs;
How long does it take for a person to develop antibodies to HIV?
In most cases, people develop antibodies to HIV within 28 days of infection.
