The 2001 World Health Organization (WHO) classification of hepatic hydatid cysts is used to assess the stage of hepatic hydatid cysts on ultrasound and is useful in deciding the appropriate management for it depending on the stage of the cyst. This classification was proposed by the WHO in 2001 and, at the time of writing (July 2016), remains the most widely used classification for hepatic hydatid cysts.
Full Answer
How is hydatid cyst treated?
Many people with echinococcosis or hydatid disease can be treated with anti-worm medicines. A procedure that involves inserting a needle through the skin into the hydatid cyst may be tried. The contents of the cyst is removed (aspirated) through the needle. Then medicine is sent through the needle to kill the Echinococcus tapeworm.
Is a large transparent cannula suitable for laparoscopic management of hydatid cysts?
The use of a large transparent cannula, with a beveled tip, for safe laparoscopic management of hydatid cysts of liver. Surg Endosc. 1995;9:1304–1305.
What is the who classification of hepatic hydatid cysts?
The 2001 World Health Organization (WHO) classification of hepatic hydatid cysts is used to assess the stage of hepatic hydatid cyst on ultrasound and is useful in deciding the appropriate management for it depending on the stage of the cyst 8).
What is the most common site of occurrence of hydatid cysts?
The most common site of occurrence of hydatid cysts in humans is the liver (50%–93%).1,2Liver hydatid cysts (LHCs), left untreated grow and follow one of several courses: develop fistulae with adjacent organs or the biliary system, rupture into the peritoneal cavity seeding daughter cysts, and develop daughter cysts within or rarely die.3
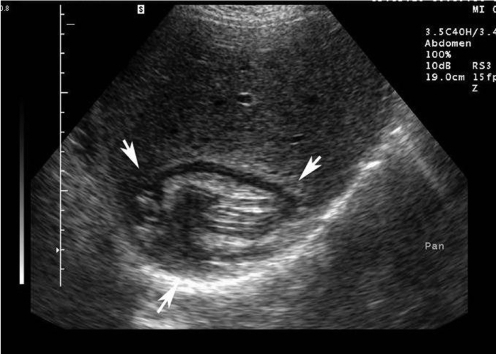
Who Gharbi classification of hydatid cyst?
The Gharbi ultrasound classification consists of five stages 4: stage 1: homogeneously hypoechogenic cystic thin-walled lesion. stage 2: septated cystic lesion. stage 3: cystic lesion with daughter lesions.
Who hydatid cyst treatment?
Percutaneous drainage with albendazole therapy is a safe and effective alternative treatment for hydatid cysts of the liver. Radical surgery with pre- and post-operative administration of albendazole is the best treatment option for liver hydatid cysts due to low recurrence and complication rates.
What is the first line treatment in hydatid disease?
Although mebendazole, the first benzoimidazole used, has some beneficial effects on the disease in selected patients, it has also been associated with treatment failure in some cases, perhaps because of its poor absorption. Albendazole, a more recently developed benzoimidazole, is more effective than mebendazole.
Who echinococcosis treatment?
Chemotherapy, cyst puncture, and PAIR (percutaneous aspiration, injection of chemicals and reaspiration) have been used to replace surgery as effective treatments for cystic echinococcosis. However, surgery remains the most effective treatment to remove the cyst and can lead to a complete cure.
How is hydatid disease treated?
Surgery is the main form of treatment for hydatid disease. A risk of surgery is that a hydatid cyst may rupture and spread tapeworm heads throughout the patient's body. To reduce this risk, the doctor may prescribe high doses of the drug albendazole in conjunction with surgery.
What is the only treatment for hydatid cysts in humans?
Medical Care Two benzimidazolic drugs, mebendazole and albendazole, are the only anthelmintics effective against cystic echinococcosis. Albendazole and mebendazole are well tolerated but show different efficacy. Albendazole is significantly more effective than mebendazole in the treatment of liver cysts.
What is Scolicidal agent?
To date, many scolicidal agents including some plant extracts, mannitol, ABZ, chlorhexidine gluconate (Chx-Glu), honey, hypertonic saline, silver nitrate, cetrimide, ethyl alcohol, H2O2, and povidone-iodine have been used for inactivation of the hydatid cyst content.
How do you test for hydatid?
Computed tomography (CT) scanning CT scanning has an accuracy of 98% and the sensitivity to demonstrate the daughter cysts. It is the best test for the differentiation of hydatid from amebic and pyogenic cysts in the liver.
How is hydatid cyst diagnosis?
The diagnosis is most easily set by ultrasound or other imaging techniques such as CT-scan or MRI, combined with case history. Serology tests such as ELISA or immunoblotting can be used in addition, being 80-100% sensitive for liver cysts but only 50-56% for lungs and other organs [21].
Which anti parasitic drug is used for hydatid cyst?
Drug therapy for echinococcosis is limited. The anthelmintic benzimidazoles, namely albendazole and mebendazole, are used for treatment and prophylaxis. Praziquantel, an isoquinoline derivative, is used as an adjunct for therapy.
How is neurocysticercosis treated?
Corticosteroids are frequently used in patients with neurocysticercosis. The most frequent regimen is dexamethasone at doses of between 4.5 and 12 mg/day. Prednisone at 1 mg/kg/day may replace dexamethasone when long-term steroid therapy is required.
How is alveolar echinococcosis treated?
Alveolar echinococcosis requires chemotherapy with or without surgery; radical surgery is the preferred approach in suitable cases. Effective treatment involves benzimidazoles administered continuously for at least 2 years and patient monitoring for 10 years or more since recurrence is possible.
What is hydatid disease?
Hydatid disease also known as hydatidosis, is a zoonotic disease (a disease that is transmitted to humans from animals) caused by a parasitic infestation by a tapeworm of the genus Echinococcus 1). Human echinococcosis or hydatid disease is caused by the larval stages of cestodes (tapeworms) of the genus Echinococcus.
Is polycystic echinococcosis rare?
The serologic diagnosis of polycystic echinococcosis has not been extensively studied as infections with Echinococcus vogeli are very rare. One antigen has been described (Ev2) that distinguishes Echinococcus vogeli from Echinococcus granulosus but not Echinococcus multilocularis.
Is cystic echinococcosis expensive?
Both cystic echinococcosis and alveolar echinococcosis are often expensive and complicated to treat, sometimes requiring extensive surgery and/or prolonged drug therapy; the choice depends on a variety of factors including the patient’s clinical picture and the size of the cyst (ultrasound-guided staging system is the method used in liver cysts).
What is the procedure for a hepatic hydatid cyst?
The classical surgery procedures used for the treatment of the hepatic hydatid cyst are divided, according to their attitude towards the pericyst, into procedures that do not involve pericyst resection (cystectomy) and procedures involving pericyst resection (partial pericystectomy, pericystoresection, hepatectomy). They are associated with procedures that should treat the remaining cavity: external drainage with a drain tube, bipolar drainage of the cavity and the main bile duct, padding, omental plombage, drainage of the cavity by anastomosis with the stomach/jejunum, pericysto-biliar drainage. It should also be mentioned that hepatic transplantation might be a treatment option when at least 25-30% of the total hepatic parenchymal volume cannot be saved, or in the case of para- or post-hydatic hepatic cirrhosis [10]. The opening of the cystic cavity must be preceded by the inactivation of the parasite with a hypertonic saline solution, ethyl alcohol, hydrogen peroxide or Albendazole. It is also necessary to isolate the cyst from the rest of the peritoneal cavity, either by wrapping the adjacent areas with dressings soaked in anthelmintic substances or by applying adherent cones to the cyst using the icing technique or suction [11]. Resolving the remaining cavity is the primary challenge of the open surgical approach. In a study belonging to Mousavi et al., it is concluded that omental plumbing is superior to the drainage of the remaining cavity as it reduces the risk of seeding the peritoneum with germs [12].
When were hepatic hydatid cysts admitted?
The majority of the cases of hepatic hydatid cyst in this study were admitted in 2015, mentioning the fact that only the cases treated at the first visit were taken into account.
What is hydatic disease?
The hydatic disease is a severe, potentially lethal disease caused by Echinococcus granulosus larvae. The infection with E. granulosus should be seen as a challenge both from a medical and economic point of view [1].
Where does hydatic cyst occur?
The hydatic cyst occurs by accidental infection of the human with the eggs of Echinococcus granulosus, followed by the development of the larvae, most commonly in the liver (50-70% of cases), and less commonly in the lungs, spleen, kidneys and brain [5-7].
Where is hydatic disease found?
Introduction:the hydatic disease, caused by the larvae of Echinococcus granulosus, is a serious disease, potentially lethal, which can be found anywhere in the world, but especially in endemic areas such as the Mediterranean Basin, Australia, New Zealand, North Africa, Eastern Europe, the Balkans, Middle East and South America. The hydatic cyst is mainly found in the liver (75% of the cases), being asymptomatic in most cases and discovered accidentally on a routine abdominal ultrasound or an ultrasound performed for diagnosing other pathologies. The hepatic hydatid cyst therapy is multimodal, including medical, surgical, and, lately, minimally invasive techniques.
Is hepatic hydatid cyst heterogeneous?
Conclusions:patients with hepatic hydatid cyst form a heterogeneous group, semiology being poor and unspecific. Among the laboratory examinations, eosinophilia is a sign of concern but is present in less than half of the patients. Imaging findings are the basis for the diagnosis of hepatic hydatid cysts. Surgical treatment remains the “gold standard” in therapy, but minimally invasive methods with high applicability, less frequent complications and lower hospital requirements are starting to gain ground.
Which cytolysis syndrome was the least detected?
Hepatic cytolysis syndrome, investigated through serum transaminases (AST and ALT), was most often identified. Excretory biliary syndrome or cholestatic syndrome was evaluated by measuring the serum alkaline phosphatase and serum bilirubin values. It was the least detected. Coagulation tests were used to investigate the hepatic insufficiency syndrome and were modified in 31 patients.
How to remove parasites from cyst?
The basic steps of the procedure are eradication of the parasite by mechanical removal, sterilization of the cyst cavity by injection of a scolicidal agent, and protection of the surrounding tissues and cavities.
How long does it take for a cyst to return to the scolicidal system?
The PAIR technique is performed using either ultrasound or computed tomography (CT) guidance, involves aspiration of the cyst contents via a special cannula, followed by injection of a scolicidal agent for at least 15 minutes, and then reaspiration of the cystic contents. This is repeated until the return is clear.
Is hydatid cyst inpatient or outpatient?
Inpatient care for individuals who have had surgical resection of their hydatid cyst (s) is similar to that for any other surgical procedure on the affected organ.
Can sodium chloride be used to fill a cyst?
The cavity is then filled with isotonic sodium chloride solution and closed. Rarely, the omentum is needed to fill the cavity. The cyst fluid is inspected for bile staining at the end of the evacuation and irrigation process. The inside of the cyst is inspected, and any bile duct communication is sutured. In case of infected cysts with biliary communication, closed suction drainage is required. Regardless of whether an open or a laparoscopic approach is chosen, these basic principles must be followed in order to ensure the safety of the procedure.
Can a liver cyst rupture?
Indications: Large liver cysts with multiple daughter cysts; superficially located single liver cysts that may rupture (traumatically or spontaneously); liver cysts with biliary tree communication or pressure effects on vital organs or structures; infected cysts; and cysts in lungs, brain, kidneys, eyes, bones, and all other organs are indications for surgery.
Is surgery the only cure for CE?
In CE, surgery remains the primary treatment and the only hope for complete cure. Better forms of chemotherapy and newer methods, such as the puncture, aspiration, injection, and reaspiration (PAIR) technique are now available but need to be tested. Currently, indications for these modes of therapy are restricted.
Can a pair be performed on a liver cyst?
The PAIR technique can be performed on liver, bone, and kidney cysts but should not be performed on lung and brain cysts. The cysts should be larger than 5 cm in diameter and type I or II according to the Gharbi ultrasound classification of liver cysts (ie, type I is purely cystic; type II is purely cystic plus hydatid sand; type III has the membrane undulating in the cystic cavity; and type IV has peripheral or diffuse distribution of coarse echoes in a complex and heterogeneous mass). PAIR can be performed on type III cysts as long as it is not a honeycomb cyst.