What is the first line treatment for gonorrhea?
- For persons weighing ≥150 kg (300 lb), 1 g of IM ceftriaxone should be administered.
- If chlamydia coinfection is identified when pharyngeal gonorrhea testing is performed, providers should treat for chlamydia with doxycycline 100 mg orally twice a day for 7 days. ...
- No reliable alternative treatments are available for pharyngeal gonorrhea. ...
What happens after being treated for gonorrhea?
- Conversation Starters from the Start Talking. Stop HIV. campaign – CDC’s Division of HIV/AIDS Prevention
- Talk to Your Partner – STDs & Testing (GYT) external icon
- Telling Your Partner You Have an STD – TeensHealth external icon
How do you cure gonorrhea?
To successfully utilize apple cider vinegar for gonorrhea cure, consider the following steps:
- Add a tablespoon of apple cider vinegar in water while you are taking a bath.
- Immerse yourself in the mixture for around 15-20 minutes.
- Repeat the process for a week.
What is the best medication for gonorrhea?
Make a list of:
- Your symptoms, if you have any, including any that may seem unrelated to the reason for which you scheduled the appointment, and when they began
- All medications, vitamins or other supplements you take, including doses
- Questions to ask your doctor
What was the most commonly used medication for gonorrhea?
At that time, the two most consistently used medications for both acute and chronic gonorrhea were cubebs, an Indonesian variety of pepper of which the dried powdered unripe fruit was used, and balsam of copaiba (or copaiva), which was extracted from a South American tree. In 1859, 151,000 pounds of copaiba balsam were imported into Great Britain, ...
How to treat gonorrhea?
According to the 1874 edition of Dunglison’s Dictionary of Medical Science: “Gonorrhea of every kind, attended with any inflammatory symptoms, is best treated by the antiphlogistic regimen, avoiding every kind of irritation, and keeping the body cool by small doses of salts, and the urine diluted by the mildest fluids.
How many cases of gonorrhea were reported in 1946?
In 1946 four cases of gonorrhea were reported in whom the infection was resistant to “large” amounts of penicillin (0.6 to 1.6 million units). Resistance was confirmed by in vitro testing. A gradual increase in the number of strains of gonococci with increasing resistance to penicillin occurred a decade later (32).
How long does it take for a gonococcus to die?
Heat therapy of gonococcal infection achieved scientific justification in 1932 when investigators at the University of Rochester, NY discovered that, in vitro, 99% of a gonococcus culture is killed by two hours of exposure to 41.5°-42.0° C., although heat resistance varied among strains (15).
How long did sulfanilamide last?
The first reports of the effect of sulfanilamide on gonorrhea appeared in 1937. Treatment at the Johns Hopkins University Clinic lasted four weeks with the divided daily dosage decreasing from 4.8 gm to 1.2 gm per day (total 65.6 gm).
What was the effect of the 1916 Gonococcus shot?
The effects were most consistently beneficial in regard to arthritis. However, the responses were not specific to the gonococcus vaccine.
When did sulfapyridine become available?
Sulfapyridine, soon followed by sulfathiazol, analogues of sulfanilamide, became available in 1940-41. A one week course of sulfapyridine cured three fourths of cases for whom sulfanilamide had failed, as well as 87% of previously untreated patients (26).
What was the first treatment for gonorrhea?
One of the earliest treatments for gonorrhea was the use of mercury. Research shows that surgical tools were used to inject the mercury into the urinary opening. By the 19th century this infection was treated with silver nitrate. However, that was soon discontinued and protargol was used. Also, in the 19th century cubebs were used.
What was used to treat gonorrhea in the 1940s?
Patients were then successfully treated with spectinomycin. Today the treatment used for gonorrhea is the antibiotic ceftriaxone, which is an injection.
How long does it take for gonorrhea to show up after taking antibiotics?
Once you are on antibiotics you should see results in several days. However, it is important to talk to your doctor about how long you should wait before engaging in sexual activity. Following this infection, you are still at risk of getting gonorrhea again.
How long does it take for gonorrhea to show?
Gonorrhea symptoms occur about two weeks after exposure. Symptoms in men include a burning sensation while urinating with a greater frequency to urinate. Men may also experience a discharge from the penis, as well as swelling at the opening of the penis.
When did the first cases of Gonorrhea occur?
August 7, 2017. Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted infection that has dated back to medieval times. However, the earliest records of this disease date back to the 1600s. This disease caused a widespread of infection causing the English parliament to enact a law to prevent the spread.
How to prevent STDs?
Therefore, it is important to protect yourself from this disease and other STDs. Of course, the best way to prevent it is through abstinence. However, if you are sexually active it is important to use a condom and to make sure you are aware if your partners have an STD such as gonorrhea or have been tested.
How to test for gonorrhea?
Testing for gonorrhea is done through a fluid sample in the area with the symptoms, such as the penis or vagina. The doctor may also request to do a blood sample if he or she suspects a blood infection. Another test done will take the sample and place it on a dish.
What was the first treatment for gonorrhea?
The earliest treatment of gonorrhea was with the use of mercury. Earliest findings from an English warship “Mary Rose” show that several special surgical tools were used to inject mercury via the urinary opening.
When did gonorrhea start?
Discovery of the infection and its cause. The exact time when gonorrhea started cannot be ascertained. Earliest records of the disease are found from 1161 when the English parliament enacted a law to ensure that the spread of the infection is decreased and curbed.
When did gonococcus become resistant to penicillin?
In 1980 the first gonococcus isolates were identified that were resistant to penicillin. In 1983 a local epidemic caused by a penicillin resistant strain occurred in North Carolina. Patients were successfully treated with spectinomycin.
Is gonorrhea a sexually transmitted disease?
Gonorrhea History. Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted infection that has been known to mankind since medieval times. It was referred to as the “clap” before the actual cause was discovered.
When did gonorrhea first appear?
This remains the earliest known legal records of the disease and dates back to around 1161 AD. The French king Louis IX passed a similar law in 1256 AD. [ 9] Confusion regarding the relation between gonorrhea and syphilis arose with the arrival of syphilis in Europe in the late 15 th century.
When did sulfonamides start being used for gonorrhea?
In 1937, Dees and Colston introduced sulfonamides in the treatment of gonorrhea. [ 30] . As per John Hopkins University clinic protocol, gonorrhea patients received sulfonamides at a dose of 4.8 grams initially, tapered to 1.2 g/day for 4 weeks. [ 31] .
What is the name of the disease that a person urinates?
Others believe that the name is derived from the ancient treatment of “clapping” an infected penis on either side with a big book to remove pus.
When was ophthalmia neonatorum made a notifiable disease?
Under the public health regulations, ophthalmia neonatorum was made a notifiable disease in England and Wales in 1914. Crede’s method, the time tested procedure for the prevention of ophthalmia neonatorum, is still in practice in some parts of the world with apparent success. [ 13] .
When was the first antibiotic used?
The silver-based treatment was in use till the first antibiotics arrived in the 1940s. [ 28] From the killed gonococci taken from Neisser’s laboratory, the first vaccine was prepared in 1890, which was introduced in 1909. [ 29] . It had a low efficacy and did not propagate extensively.
Is norfloxacin used for gonorrhea?
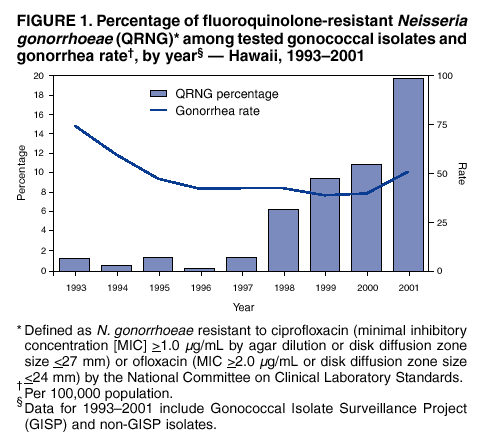
Although norfloxacin and ciprofloxacin were used during the 1980s and 90s, the WHO and centers for disease control (CDC) no longer recommend fluoroquinolones for the treatment of gonorrhea due to drug resistance.
Who said that the issue of seed was a disease?
It is believed that the mention of “an issue of seed” in the Book of Leviticus in the Old Testament and the precautions suggested refers to this disease. [ 1] . Gonorrhea was termed “strangury” by Hippocrates (460–375 BC) who claimed that it resulted from the “pleasures of Venus.”.
How long after treatment for gonorrhea?
Resistance has developed to many previously used antibiotics and higher doses of ceftriaxone are occasionally required. Retesting is recommended three months after treatment. Sexual partners from the last two months should also be treated. Gonorrhea affects about 0.8% of women and 0.6% of men.
What is the most effective antibiotic for gonorrhea?
Antibiotics are used to treat gonorrhea infections. As of 2016, both ceftriaxone by injection and azithromycin by mouth are most effective.
What is a PCR test for gonorrhea?
Tests that use polymerase chain reaction ( PCR, aka nucleic acid amplification) to identify genes unique to N. gonorrhoeae are recommended for screening and diagnosis of gonorrhea infection. These PCR-based tests require a sample of urine, urethral swabs, or cervical/vaginal swabs.
What causes gonorrhoea in pus?
Cause. Neisseria gonorrhoeae in pus from a case of gonorrhoea in a man ( Gram stain) Gonorrhea is caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Previous infection does not confer immunity – a person who has been infected can become infected again by exposure to someone who is infected.
How long does it take for gonorrhea to show symptoms?
The time from exposure to symptoms is usually between two and 14 days, with most symptoms appearing between four and six days after infection, if they appear at all.
How is gonorrhea spread?
Gonorrhea is spread through sexual contact with an infected person. This includes oral, anal, and vaginal sex. It can also spread from a mother to a child during birth. Diagnosis is by testing the urine, urethra in males, or cervix in females.
What are the complications of gonorrhea?
One of the complications of gonorrhea is systemic dissemination resulting in skin pustules or petechia, septic arthritis, meningitis, or endocarditis. This occurs in between 0.6 and 3% of infected women and 0.4 and 0.7% of infected men. In men, inflammation of the epididymis, prostate gland, and urethra can result from untreated gonorrhea.
Why is it important to talk to your doctor about gonorrhea?
If you are pregnant, it is important that you talk to your health care provider so that you get the correct examination, testing, and treatment, as necessary. Treating gonorrhea as soon as possible will make health complications for your baby less likely.
What is gonorrhea in women?
What is gonorrhea? Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted disease (STD) that can infect both men and women. It can cause infections in the genitals, rectum, and throat. It is a very common infection, especially among young people ages 15-24 years.
How to avoid STDs?
The only way to avoid STDs is to not have vaginal, anal, or oral sex. If you are sexually active, you can do the following things to lower your chances of getting gonorrhea: Being in a long-term mutually monogamous relationship with a partner who has been tested and has negative STD test results;
Can you get gonorrhea from sex?
Any sexually active person can get gonorrhea through unprotected vaginal, anal, or oral sex. If you are sexually active, have an honest and open talk with your health care provider and ask whether you should be tested for gonorrhea or other STDs.
Can you take medication for gonorrhea?
It is important that you take all of the medication your doctor prescribes to cure your infection. Medication for gonorrhea should not be shared with anyone. Although medication will stop the infection, it will not undo any permanent damage caused by the disease.
Can you use a urine swab for gonorrhea?
Most of the time, urine can be used to test for gonorrhea. However, if you have had oral and/or anal sex, swabs may be used to collect samples from your throat and/or rectum. In some cases, a swab may be used to collect a sample from a man’s urethra (urine canal) or a woman’s cervix (opening to the womb).
Can gonorrhea cause vaginal bleeding?
Women with gonorrhea are at risk of developing serious complications from the infection, even if they don’t have any symptoms. Symptoms in women can include: Painful or burning sensation when urinating; Increased vaginal discharge; Vaginal bleeding between periods.
What was the USPHS charged with?
Even before availability of modern antimicrobials, the USPHS had been charged with control of syphilis and gonorrhea, as well as other public health threats. In 1918, the United States Congress approved the Chamberlain-Kahn Act, providing for federally funded venereal disease (VD) control and research programs, authorizing federal grants to states for VD control, and giving the government power to quarantine citizens suspected to have STIs [ 8 ]. This act created the Division of Venereal Disease in the USPHS, which ultimately evolved to become the Division of STD Prevention within CDC. Our interviews indicated that federal STI control and research during this time focused predominantly on syphilis, while gonorrhea, though far more common than syphilis, was less highly prioritized, possibly owing to both the lack of proven therapies and the fact that it was apparently considered less of a long-term threat to health [ 8 ].
What are improved detection methods?
Improved detection methods have enhanced estimation of gonorrhea rates at microbially complex sites. Current methods provide increased accuracy of detection but do not provide viable specimens to allow testing for AMR.
Is Neisseria gonorrheae resistant to antibiotics?
Progressively decreasing susceptibility of Neisseria gonorrhoeae to the antibiotics recommended for treatment has raised concerns about the public health threat of antibiotic resistant gonorrhea. This is not a new process, and the organism has reliably developed resistance to all modern antibiotics used for treatment since the dawn of the antibiotic era. The history of changing recommendations for gonorrhea therapy is complex, however, and has been influenced by diagnostic test methods and surveillance. Understanding the impact of these influences may provide insights into current approaches to address this reemerging public health challenge. We reviewed available methods for gonorrhea diagnosis, and public health recommendations for gonorrhea treatment. The literature review was supplemented by qualitative interviews with senior investigators whose research helped shape gonorrhea management strategies over the past 50 years. The process of development of antimicrobial resistance to the antibiotics widely used for treatment seems to be inexorable. Many currently voiced concerns are similar to those raised in the past. The public health threat of increasing antimicrobial resistance by N. gonorrhoeae has been amplified as a result of a smaller pipeline introducing new drugs for gonorrhea treatment. Improved methods for gonorrhea diagnosis have also repeatedly influenced appreciation of the burden of disease caused by N. gonorrhoeae. US Public Health Service leadership has also shaped and improved the management of this important public health problem.
Is gonorrhea a STI?
Gonorrhea has been recognized as a sexually transmitted infection (STI) for centuries and, since the advent of modern antibiotics, has repeatedly demonstrated a capacity to develop resistance to antimicrobials used for treatment. More recently, continued increases in gonococcal antimicrobial resistance (AMR) and a reduced “pipeline” for new antimicrobial development have repeatedly combined to limit availability of readily available therapy for this continuing global public health threat. Increasing resistance was serially countered by increases in the penicillin dose used for treatment or recommendations for alternate antibiotics [ 1–3 ]. Although the publications on sexually transmitted disease surveillance and treatment guidelines from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) provide data on reported gonorrhea-associated morbidity since the 1940s, recent changes in recommended treatment and, over the past 30 years, trends in gonococcal susceptibility [ 1–4 ], there are few summaries of the sequence of earlier changes to treatment practice and guidance.

Discovery of The Infection and Its Cause
The Clap
- Gonorrhoea was referred to as the clap. According to some historians the name came about because the infected person would experience a clapping sensation that appeared suddenly when urinating. Others say that the name originated because in order to remove the pus-like discharge from the penis, the penis had to be clapped on both sides. Still others believe that the name com…
History of Gonorrhea Treatments
- The earliest treatment of gonorrhea was with the use of mercury. Earliest findings from an English warship “Mary Rose” show that several special surgical tools were used to inject mercury via the urinary opening. In the 19th century gonorrhea was treated with the help of silver nitrate. Silver nitrate was soon discontinued and instead protargol was...
Further Reading