What is HIV antiretroviral therapy?
4 rows · Apr 11, 2022 · Ridofranz / Getty Images. Antiretroviral drugs are used to treat HIV infection. They work by ...
How many antiretroviral drugs are there for HIV infection?
HIV medicine is called antiretroviral therapy (ART). There is no effective cure for HIV. But with proper medical care, you can control HIV. Most people can get the virus under control within six months. Taking HIV medicine does not prevent transmission of other sexually transmitted diseases. When should I start treatment?
Which antiviral drugs directly target the virus?
Mar 29, 2019 · HIV is a type of virus called a retrovirus, and the combination of drugs used to treat it is called antiretroviral therapy (ART). ART is recommended for all people living with HIV, regardless of how long they’ve had the virus or how healthy they are. ART must be taken every day, exactly as your health care provider prescribes.
What are the different types of drugs to combat HIV?
During the past six years Zidovudine has been the main antiviral drug directed against HIV. The indications for its use have slowly been extended and a reduced dose has limited the side effects. The therapeutical gain is a survival benefit of three to nine months.

What antiviral drugs are used for HIV?
Currently, there are eight FDA-approved NRTIs: abacavir (ABC, Ziagen), didanosine (ddI, Videx), emtricitabine (FTC, Emtriva), lamivudine (3TC, Epivir), stavudine (d4T, Zerit), zalcitabine (ddC, Hivid), zidovudine (AZT, Retrovir), and Tenofovir disoprovil fumarate (TDF, Viread), a nucleotide RT inhibitor (Fig.
What is the best antiviral for HIV?
FDA-Approved HIV MedicinesDrug ClassGeneric Name (Other names and acronyms)Brand NameNRTIs block reverse transcriptase, an enzyme HIV needs to make copies of itself.abacavir (abacavir sulfate, ABC)Ziagenemtricitabine (FTC)Emtrivalamivudine (3TC)Epivirtenofovir disoproxil fumarate (tenofovir DF, TDF)Viread55 more rows
What is Lamivudine used for?
Lamivudine (Epivir-HBV) is used to treat hepatitis B infection. Lamivudine is in a class of medications called nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs). It works by decreasing the amount of HIV and hepatitis B in the blood.
What is HIV treatment?
HIV treatment involves taking medicine that reduces the amount of HIV in your body. HIV medicine is called antiretroviral therapy (ART). There is n...
When should I start treatment?
Start Treatment As Soon As Possible After Diagnosis HIV medicine is recommended for all people with HIV, regardless of how long they’ve had the vir...
What if I delay treatment?
HIV will continue to harm your immune system. This will put you at higher risk for developing AIDS. Learn more about AIDS and opportunistic infecti...
What are the benefits of taking my HIV medicine every day as prescribed?
Treatment Reduces the Amount of HIV in the Blood The amount of HIV in the blood is called viral load. Taking your HIV medicine as prescribed will h...
Does HIV medicine cause side effects?
HIV medicine can cause side effects in some people. However, not everyone experiences side effects. The most common side effects are Nausea and vom...
Will HIV treatment interfere with my hormone therapy?
There are no known drug interactions between HIV medicine and hormone therapy. Talk to your health care provider if you are worried about taking HI...
What if my treatment is not working?
Your health care provider may change your prescription. A change is not unusual because the same treatment does not affect everyone in the same way.
Sticking to my treatment plan is hard. How can I deal with the challenges?
Tell your health care provider right away if you’re having trouble sticking to your plan. Together you can identify the reasons you’re skipping med...
Why is it important to take HIV medication?
Taking HIV medication consistently, as prescribed, helps prevent drug resistance. Drug resistance develops when people with HIV are inconsistent with taking their HIV medication as prescribed. The virus can change (mutate) and will no longer respond to certain HIV medication. If you develop drug resistance, it will limit your options ...
How does treatment help prevent HIV?
Having an undetectable viral load may also help prevent transmission from injection drug use.
What does it mean when your HIV is suppressed?
Viral suppression is defined as having less than 200 copies of HIV per milliliter of blood. HIV medicine can make the viral load so low that a test can’t detect it (called an undetectable viral load ). If your viral load goes down after starting HIV treatment, that means treatment is working.
What is the amount of HIV in the blood called?
The amount of HIV in the blood is called viral load . Taking your HIV medicine as prescribed will help keep your viral load low and your CD4 cell count high. HIV medicine can make the viral load very low (called viral suppression ). Viral suppression is defined as having less than 200 copies of HIV per milliliter of blood.
How long does it take for a mother to give her baby HIV?
If a mother with HIV takes HIV medicine as prescribed throughout pregnancy, labor, and delivery and gives HIV medicine to her baby for 4 to 6 weeks after birth, the risk of transmitting HIV to her baby can be 1% or less.
How long does it take to get rid of HIV?
There is no effective cure for HIV. But with proper medical care, you can control HIV. Most people can get the virus under control within six months. Taking HIV medicine does not prevent transmission ...
Does HIV harm the immune system?
HIV will continue to harm your immune system. This will put you at higher risk for developing AIDS. Learn more about AIDS and opportunistic infections. This will put you at higher risk for transmitting HIV to your sexual and injection partners.
Why do you prescribe HIV?
Your health care provider may prescribe medicines to prevent certain infections. HIV treatment is most likely to be successful when you know what to expect and are committed to taking your medicines exactly as prescribed.
What is the treatment for HIV?
HIV treatment involves taking medicines that slow the progression of the virus in your body. HIV is a type of virus called a retrovirus, and the combination of drugs used to treat it is called antiretroviral therapy (ART). ART is recommended for all people living with HIV, regardless of how long they’ve had the virus or how healthy they are.
What is drug resistance in HIV?
What Is HIV Drug Resistance? Drug resistance can be a cause of treatment failure for people living with HIV. As HIV multiplies in the body, it sometimes mutates (changes form) and produces variations of itself. Variations of HIV that develop while a person is taking ART can lead to drug-resistant strains of HIV.
How long do HIV side effects last?
Some side effects can occur once you start a medicine and may only last a few days or weeks.
How soon can you start ART for HIV?
Treatment guidelines from the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services recommend that a person living with HIV begin ART as soon as possible after diagnosis. Starting ART slows the progression of HIV and can keep you healthy for many years.
Is HIV treatment a prevention?
There is also a major prevention benefit. People living with HIV who take HIV medication daily as prescribed and get and keep an undetectable viral load have effectively no risk of sexually transmitting HIV to their HIV-negative partners. This is called treatment as prevention.
Can HIV be drug resistant?
A person can initially be infected with drug-resistant HIV or develop drug-resistant HIV after starting HIV medicines. Drug-resistant HIV also can spread from person to person. Drug-resistance testing identifies which, if any, HIV medicines won’t be effective against your specific strain of HIV.
What is the name of the drug that stops HIV from making copies of itself?
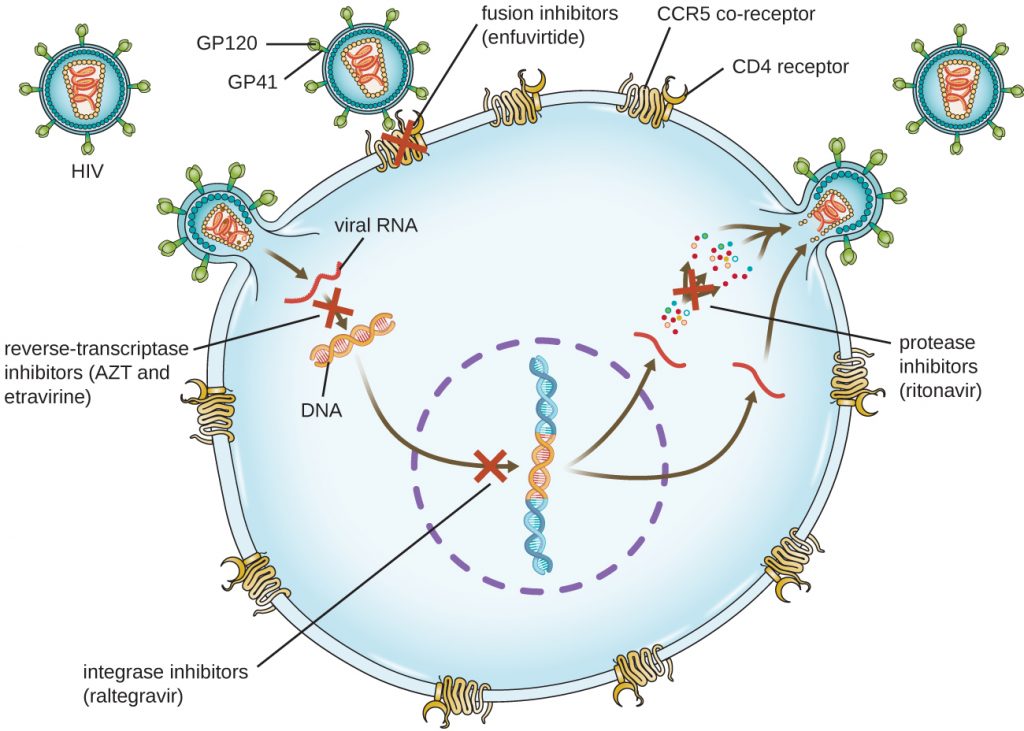
Ritonavir or RTV (Norvir) Saquinavir or SQV ( Invirase, Fortovase) Tipranavir or TPV ( Aptivus) Integrase Inhibitors. These stop HIV from making copies of itself by blocking a key protein that allows the virus to put its DNA into the healthy cell's DNA. They're also called integrase strand transfer inhibitors (INSTIs).
What is the drug that stops HIV from attaching to the CD4 T cells?
It targets the glycoprotein 120 on the surface of the virus, stopping it from being able to attach itself to the CD4 T-cells of your body’s immune system. CCR5 Antagonist. Maraviroc, or MVC ( Selzentry ), also stops HIV before it gets inside a healthy cell, but in a different way than fusion inhibitors.
What is the name of the drug that is a fusion inhibitor?
Bictegravir or BIC (combined with other drugs as Biktarvy) Dolutegravir or DTG ( Tivicay) Elvitegravir or EVG ( Vitekta) Ralte gravir or RAL ( Isentress) Fusion Inhibitors. Unlike NRTIs, NNRTIs, PIs, and INSTIs, which work on infected cells, these drugs block HIV from getting inside healthy cells.
Why do you need to tell your doctor about your medication?
Because these "drug boosters" can increase the levels of other drugs and cause potential harm, you should always tell your doctor about the medicines you are taking. Fixed-Dose Combinations. Some drug manufacturers put together specific medicines into a single pill so they're easier to take, including: Continued.
What infections are treated with antibiotics?
Bacterial infections like tuberculosis or pneumonia, treated with antibiotics. Fungal infections like thrush or pneumocystis pneumonia, treated with anti-fungal meds. Parasitic infections like toxoplasmosis, which may require long-term treatment in people with HIV.
What are the most common infections that can be caused by HIV?
These include: Viral infections like herpes and shingles, treated with rest and antiviral meds. Bacterial infections like tuberculosis or pneumonia, treated with antibiotics.
What is the best PrEP for HIV?
PrEP medications for HIV include Truvada and Descovy. People who inject drugs are often at higher risk for HIV, especially if they share needles or other tools. Gay and bisexual men are at higher risk from sexual activity, but heterosexual men and women can also get it from sexual activity.
What is the drug used to treat HIV?
Ivermectin. Ivermectin is an antiparasitic drug that is being evaluated to treat COVID-19. Lopinavir/Ritonavir and Other HIV Protease Inhibitors. Protease inhibitors are antiretroviral drugs for HIV that were studied as treatments for COVID-19. Table: Characteristics of Antiviral Agents.
What is Remdesivir used for?
Remdesivir is a nucleotide analogue prodrug that is approved to treat COVID-19 in certain patients. Chloroquine or Hydroxychloroquine With or Without Azithromycin. Chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine are antimalarial drugs that were studied to treat COVID-19. Ivermectin.
What are the drugs that are used to treat HIV?
Other types of drugs designed to combat HIV include CCR5 antagonists and post-attachment inhibitors, which block different types of molecules on the immune cell surface to prevent HIV from entering the cells, and integrase inhibitors, which block the ability of HIV to replicate. Pharmacokinetic enhancers, although not antiviral drugs themselves, ...
What is the name of the drug that converts viral RNA into DNA?
Anti-HIV drugs. Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), the virus that causes AIDS, is a retrovirus. Like other retroviruses, HIV contains reverse transcriptase, an enzyme that converts viral RNA into DNA. This DNA is integrated into the DNA of the host cell, where it replicates.
Why are interferons important?
The interferons are of interest because they have broad-spectrum antiviral activity and because they inhibit the growth of cancer tissue. However, the use of interferon is limited by adverse effects, a relative lack of efficacy, and the requirement for local or intravenous administration.
What is the treatment for respiratory syncytial virus?
The only pharmacological therapy available for treatment of the infection is the nucleoside analogue ribavirin, which can be administered orally, parenterally, or by inhalation.
How is ribavirin activated?
Ribavirin must also be activated by phosphorylation in order to be effective. An injectable humanized monoclonal antibody is available for prevention of RSV infection in high-risk infants and children. It provides passive immunity and must by given by intramuscular injection once a month during RSV season.
What is the challenge of RT inhibitors?
A significant challenge with the use of RT inhibitors is the development of resistance; because HIV replicates continuously at a very high rate, there are many chances for mutation and hence the emergence of a virus resistant to many drugs.
What are interferons used for?
Interferon results in the production of a protein that prevents the synthesis of viral components from the viral nucleic acid template . The interferons are of interest because they have broad-spectrum antiviral activity and because they inhibit the growth of cancer tissue. However, the use of interferon is limited by adverse effects, a relative lack of efficacy, and the requirement for local or intravenous administration.
