What is the treatment of bacterial and viral infections?
Treatment of Bacterial and Viral Infections. The discovery of antibiotics for bacterial infections is considered one of the most important breakthroughs in medical history. Unfortunately, bacteria are very adaptable, and the overuse of antibiotics has made many of them resistant to antibiotics.
Why is it important to differentiate between bacterial and viral infections?
This is important to understand, because bacterial and viral infections must be treated differently. Misusing antibiotics to treat viral infections contributes to the problem of antibiotic resistance.
Are antibiotics effective against viruses?
Antibiotics are not effective against viruses, and many leading organizations now recommend against using antibiotics unless there is clear evidence of a bacterial infection. Since the beginning of the 20th century, vaccines have been developed.
What's the difference between antivirals and antibiotics?
"Viruses are treated by antiviral agents while bacteria are treated by antibacterial agents (antibiotics)," says Dr. Bailey. Antivirals can't treat bacteria, and antibiotics can't treat viruses due to the different structure of the organisms.
How does the treatment of bacterial diseases and viruses differ?
In some cases, bacterial infections may be treated with antibiotics. They stem from viruses, which consist of multiple cells. Viruses feed off of healthy cells in the body, sometimes killing their host cells as they multiply. Certain types of viral infections are treated with antiviral medications.
How can you tell difference between viral and bacterial infection?
Bacterial infections are caused by bacteria, while viral infections are caused by viruses....Bacterial InfectionsSymptoms persist longer than the expected 10-14 days a virus tends to last.Fever is higher than one might typically expect from a virus.Fever gets worse a few days into the illness rather than improving.
Do antibiotics treat viral infections?
Viruses are germs different from bacteria. They cause infections, such as colds and flu. However, antibiotics do not treat infections caused by viruses. For more information on common illnesses and when antibiotics are and aren't needed, visit Common Illnesses.
What is the treatment for bacteria?
Most bacterial infections can be effectively treated with antibiotics. They either kill bacteria or stop them multiplying. This helps the body's immune system to fight the bacteria. Your doctor's choice of antibiotic will depend on the bacteria that is causing the infection.
Why don't we use antibiotics for viral infections?
We don’t use antibiotics for viral infections because it does not speed the recovery and we could be introducing you to side effects and problems related to the medicine.
What are the symptoms of a viral infection?
If it’s a viral illness, typically symptoms are shorter lasting and classically the symptoms include fever, chills, sore throat, nasal congestion, runny nose, cough, and a lot of times you can have some body aches.
What is the best medicine to take for a sore throat?
So some of the best things you can take over-the-counter are anti-inflammatory medicines, things like ibuprofen or Tylenol. What that does is it helps with body aches, fevers, chills, sore throat, and other aches and pains related to the illness.
Why are bacterial and viral infections dissimilar?
But bacterial and viral infections are dissimilar in many other important respects, most of them due to the organisms' structural differences and the way they respond to medications.
What are the two types of infections?
Bacterial and Viral Infections. Bacterial and viral infections have many things in common. Both types of infections are caused by microbes -- bacteria and viruses, respectively -- and spread by things such as: Coughing and sneezing. Contact with infected people, especially through kissing and sex.
Why are antibiotics important?
The discovery of antibiotics for bacterial infections is considered one of the most important breakthroughs in medical history. Unfortunately, bacteria are very adaptable, and the overuse of antibiotics has made many of them resistant to antibiotics. This has created serious problems, especially in hospital settings.
Why are viral infections so difficult to treat?
But the treatment of viral infections has proved more challenging, primarily because viruses are relatively tiny and reproduce inside cells. For some viral diseases, such as herpes simplex virus infections, HIV/AIDS, and influenza, antiviral medications have become available.
What are the symptoms of a viral infection?
Bacterial and viral infections can cause similar symptoms such as coughing and sneezing, fever, inflammation, vomiting, diarrhea, fatigue, and cramping -- all of which are ways the immune system tries to rid the body of infectious organisms. But bacterial and viral infections are dissimilar in many other important respects, ...
How long have bacteria been around?
Fossilized records show that bacteria have existed for about 3.5 billion years, and bacteria can survive in different environments, including extreme heat and cold, radioactive waste, and the human body.
What are the causes of acute infection?
Coughing and sneezing. Contact with infected people, especially through kissing and sex. Contact with contaminated surfaces, food, and water. Contact with infected creatures, including pets, livestock, and insects such as fleas and ticks. Microbes can also cause: Acute infections, which are short-lived.
Why is it important to understand the difference between a virus and a bacteria?
This is important to understand, because bacterial and viral infections must be treated differently. Misusing antibiotics to treat viral infections contributes to the problem of antibiotic resistance .
What is the difference between a virus and a bacterium?
Bacteria and viruses are too tiny to be seen by the naked eye, can cause similar symptoms and are often spread in the same way, but that’s where the similarities end. A bacterium is a single, but complex, cell.
What are some examples of bacterial infections?
Examples of bacterial infections include whooping cough, strep throat, ear infection and urinary tract infection (UTI). Viral infections include the common cold, flu, most coughs and bronchitis, chickenpox and HIV/AIDS. It can be difficult to know what causes an infection, because viral and bacterial infections can cause similar symptoms.
What is the best way to stop viral reproduction?
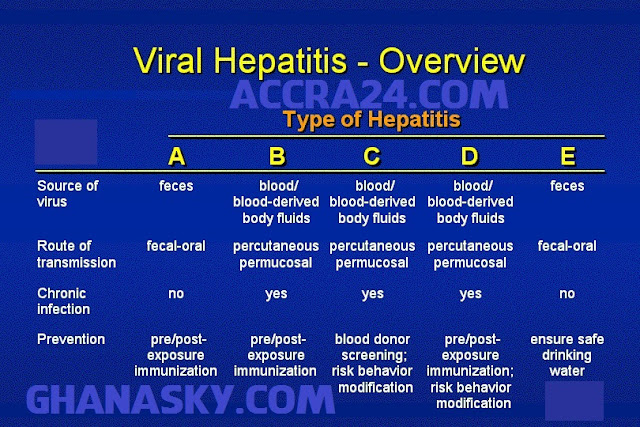
stopping viral reproduction using antiviral medicines, such as medicines for HIV/AIDS and cold sores. preventing infection in the first place, such as vaccines for flu and hepatitis. Remember: Antibiotics won’t work for viral infections.
Can a swab be used to find out what infection you have?
It can be difficult to know what causes an infection, because viral and bacterial infections can cause similar symptoms. Your doctor may need a sample of your urine, stool or blood, or a swab from your nose or throat to see what sort of infection you have.
Can bacteria survive on their own?
It can survive on its own, inside or outside the body. Most bacteria aren’t harmful. In fact, we have many bacteria on and inside our body, especially in the gut to help digest food. Viruses are smaller and are not cells. Unlike bacteria, they need a host such as a human or animal to multiply.
Can antibiotics kill bacteria?
Doctors usually treat bacterial infections with antibiotics. They either kill bacteria or stop them multiplying. But since antibiotic resistance is a growing problem, antibiotics may be prescribed only for serious bacterial infections.
How to prevent infection?
However, some infections are untreatable. The best way to prevent infection is to practice good hygiene. Vaccines are an effective method for preventing certain viruses, such as measles, mumps, and polio. A person should visit their doctor if they suspect they may have an infection.
How to diagnose a viral infection?
In order to diagnose a bacterial or viral infection, a doctor will ask a person about their medical history and symptoms. The doctor may then order tests to look for signs of bacteria or viruses in the person’s blood or urine, or from a throat or nasal swab.
What are the different types of microorganisms?
Bacteria, viruses, and fungi are different types of microorganisms. Pathogens are microorganisms that have the potential to cause illness or disease. Bacterial pathogens cause bacterial infections, whereas viral pathogens cause viral infections. Sometimes, both bacteria and viruses can cause illness. Examples include pneumonia and meningitis.
Where do Viridans group streptococci live?
Viridans group streptococci. V iridans group streptococci most commonly exist in the mouth, gut, and genital region. Severe infections can occur if the bacteria enter other parts of the body. A Viridans group streptococci infection that enters the bloodstream can infect the inner lining of the heart.
What are the benefits of bacteria?
helping people to digest food. providing vitamins. getting rid of cells that could cause disease. Less than 1% of bacterial species can cause bacterial infections. Such infections occur when the bacteria enter the body and invade the body’s immune system, where they quickly multiply and produce harmful toxins.
How many types of staph are there?
There are more than 30 types of Staphylococcus, or staph, bacteria. Most staph infections are due to the species Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus). This bacteria lives on the skin or inside the nose and can enter the body through an open wound.
Where does group B strep live?
Group B strep. Group B strep, such as Streptococcus agalactiae usually live harmlessly inside the digestive system and female genital tract. Group B strep most commonly affects newborns. This is because the bacteria can pass from mother to fetus in the womb.
What is the difference between a viral infection and a bacterial infection?
What's the difference between a bacterial infection and a viral infection? As you might think, bacterial infections are caused by bacteria, and viral infections are caused by viruses. Perhaps the most important distinction between bacteria and viruses is that antibiotic drugs usually kill bacteria, but they aren't effective against viruses.
Can viruses survive?
Viruses. Viruses are even smaller than bacteria and require living hosts — such as people, plants or animals — to multiply. Otherwise, they can't survive. When a virus enters your body, it invades some of your cells and takes over the cell machinery, redirecting it to produce the virus.
Can bacteria cause a person to die?
Most bacteria cause no harm to people, but there are exceptions. Infections caused by bacteria include: Strep throat. Tuberculosis. Urinary tract infections. Inappropriate use of antibiotics has helped create bacterial diseases that are resistant to treatment with different types of antibiotic medications.
What are viruses and bacteria?
Viruses are tiny organisms made of genetic material called nucleic acid— either DNA or RNA —that is enclosed within a protein capsule, Charles Bailey, MD, medical director for infection prevention at Providence St. Joseph Hospital and Providence Mission Hospital in Orange County, California, tells Health.
Protecting yourself from viruses and bacteria
First, let's break down how the germs are spread. Depending on the type, viruses can spread through:
Viral vs. bacterial infections
While bacteria and viruses are different in terms of molecular structure, they can cause infections that have similar symptoms, such as coughing, sneezing, fever, vomiting, diarrhea, fatigue, and cramping. But symptoms vary depending on the specific infection and how severe it is.
Treating viral and bacterial infections
If you're infected with a virus or bacterium and become sick, you might need some treatment. But how viruses and bacteria respond to medication is another difference between them.
How do viruses and bacteria differ in their mode of infection?
Because of their distinct biochemistry, it should come as no surprise that bacteria and viruses differ in how they cause infection. Viruses infect a host cell and then multiply by the thousands, leaving the host cell and infecting other cells of the body.
What is the difference between a virus and a bacteria?
Viruses are only "active" within host cells which they need to reproduce, while bacteria are single-celled organisms that produce their own energy and can reproduce on their own. Bacteria serve many vital roles in nature outside of being infectious. Systemic diseases caused by viral infection include influenza, measles, polio, AIDS, and COVID-19. ...
What is pathogenic infection?
Pathogenic bacteria have a more varied operation and will often infect when the right opportunity arises, so called opportunistic infection . The infection caused by pathogenic bacteria is usually confined to a part of the body, described as a localized infection.
How big are bacteria compared to viruses?
The smallest bacteria are about 0.4 micron (one millionth of a meter) in diameter while viruses range in size from 0.02 to 0.25 micron. This makes most viruses submicroscopic, unable to be seen in an ordinary light microscope.
How do bacteria live?
Bacteria, on the other hand, are living organisms that consist of single cell that can generate energy, make its own food, move, and reproduce (typically by binary fission ). This allows bacteria to live in many places—soil, water, plants, and the human body—and serve many purposes.
Is a virus a living organism?
Viruses are not living organisms, bacteria are. Viruses only grow and reproduce inside of the host cells they infect. When found outside of these living cells, viruses are dormant. Their “life” therefore requires the hijacking of the biochemical activities of a living cell. Bacteria, on the other hand, are living organisms that consist of single cell that can generate energy, make its own food, move, and reproduce (typically by binary fission ). This allows bacteria to live in many places—soil, water, plants, and the human body—and serve many purposes. They serve many vital roles in nature by decomposing organic matter (maybe not that vital to anyone who's forgotten leftovers in the back of the fridge) and by converting nitrogen, through nitrogen fixation, to chemicals usable by plants. Bacteria even know how to work as a team through something called quorum sensing.

Overview
- Influenza, also known as the \"flu\", is a respiratory infection caused by viruses. The flu differs in several ways from the common cold. Symptoms of the flu include body chills, fever, headache, muscle ache and sore throat. Unlike many other viral respiratory infections, the flu can cause severe illness and life-threatening complications in many people. The flu is contracted in the sa…
Treatment
- Many viral infections resolve on their own without treatment. Other times, treatment of viral infections focuses on symptom relief, not fighting the virus. For example, cold medicine helps alleviate the pain and congestion associated with the cold, but it doesn't act directly on the cold virus. There are some medications that work directly on viruses. These are called antiviral medic…
- The best way of treating human viruses will depend on the strength of the individuals immune system, their overall health status, age, the severity of the condition, and the type of viruses involved. Minor illnesses caused by viral infections usually only require symptomatic treatment, while more severe conditions may require advanced medical treatment and sometimes even lif…
- Your surgeon can provide antibiotics and any other therapies that are necessary to prevent the infection from spreading.
- For most viruses, treatment is for the symptoms, such as using over-the-counter pain relievers to ease pain and reduce fever, rest for fatigue, etc., until the virus is gone. But the viruses themselves are not easy to treat. For example, treatment for hepatitis C, a liver disease, involves a strict medication regimen that can take from several weeks up to a few months before the virus is cle…
Signs And Symptoms
- Viral skin infections can range from mild to severe and often produce a rash. Examples of viral skin infections include:
- Viral infections come with a variety of symptoms ranging from mild to severe. Symptoms may vary depending on what part of the body is affected, type of viruses, age, and overall health of the affected person. Children often contract viral infections, as children spend time around other children who have colds, and this makes it more likely that the cold will be passed on to them. A …
- The signs and symptoms of a viral infection depend on what virus you have and how it affects your body. Here are a few examples:Influenza: 1. Fever 2. Muscle ache 3. Cough 4. Sore throat 5. HeadacheMeningitis: 1. Stiff neck 2. Headache 3. Fever 4. Nausea and vomiting 5. Rash 6. Sensitivity to light (photophobia) 7. ConfusionMalaria: 1. Fever 2. Headache 3. Chills 4. Poor app…
- Infections may start almost anywhere. Common places where infections can start include: 1. The mouth 2. The skin 3. The lungs 4. The urinary tract 5. The rectum 6. The genitalsSigns of infection include: 1. A fever, which is a temperature of 100.5°F (38°C) or higher 2. Chills or sweating 3. Sore throat, sores in the mouth, or a toothache 4. Abdominal pain 5. Pain near the anus 6. Pain or bur…
Prevention
- Frequent hand-washing, covering the nose and mouth when coughing or sneezing, and avoiding contact with infected individuals can all reduce the spread of respiratory infections. Disinfecting hard surfaces and not touching the eyes, nose, and mouth can help reduce transmission as well. The best way to avoid viral skin infections is to avoid skin-to-skin contact (especially areas that …
- Start an exercise regimen, like walking, biking with the family or swimming. Take it easy on the body at first and allow breaks. Walking 20 minutes a day, without over-exertion, can help keep the body healthy and get back into optimum shape after a viral infection. The body is resilient and will continue to thrive in the right circumstances. Taking care of the immune system after a virus wil…
- The good news is that prevention of all of these problems can be as simple as washing hands frequently and using hand sanitizer when a sink is not available. Hand washing is the best way to prevent infection, and while there are other tactics that can also reduce risk, keeping hands clean continues to be the best way to stay healthy after surgery.
- Viruses are spread in different ways, depending on the virus. Hepatitis C, a liver disease, is spread through body fluid. On the other hand, influenza can be spread by coming in contact with the virus that has been left behind on an object, like a phone, or through droplets in the air, if someone with the flu sneezes or coughs in front of you. Not all viral infections can be prevented, but you can re…
Definition
- Contagiousness refers to the ability of a virus to be transmitted from one person (or host) to another. Viral infections are contagious for varying periods of time depending on the virus. An incubation period refers to the time between exposure to a virus (or other pathogen) and the emergence of symptoms. The contagious period of a virus is not necessarily the same as the in…
Causes
- A viral infection is a proliferation of a harmful virus inside the body. Viruses cannot reproduce without the assistance of a host. Viruses infect a host by introducing their genetic material into the cells and hijacking the cell's internal machinery to make more virus particles. With an active viral infection, a virus makes copies of itself and bursts the host cell (killing it) to set the newly-f…
Examples
- Respiratory viral infections affect the lungs, nose, and throat. These viruses are most commonly spread by inhaling droplets containing virus particles. Examples include:
- Viruses “hijack” normal, living cells in your body. They use these cells to replicate and multiply, eventually destroying the host cell – this is what makes you sick. Unlike bacterial infections that respond to antibiotics, viral infections are not so easy to treat. Many, like colds, run their course and your body heals on its own, but others, like HIV, do not.Some of the more common viruses i…
Diagnosis
- The diagnosis of a viral infection is usually based on the physical symptoms and the history of the illness. A condition such as influenza, which is caused by a virus, is generally easy to diagnose because most people are familiar with the symptoms. Other types of viral infections may be harder to diagnose and various tests may have to be performed.
Classification
- Both viral and bacterial infections cause sickness; however, there is a difference between them. A viral infection is any type of infection that is caused by a virus, which is even smaller than bacteria and is encapsulated by a protective coating, so it is more difficult to kill than bacteria. Viral infections involve a dormant virus getting into a living cell and re-writing the cell's genetic codes …
Risks
- While an infection in an incision or the urinary tract are the most common infections after having surgery, it is also possible to have pneumonia, a serious lung infection. Surgery patients are at a higher risk than the average person to develop pneumonia, so the development of a cough in the days following the procedure should not be ignored. Likewise, severe diarrhea should not be ign…