
What is a sewage treatment plant?
A sewage treatment plant is designed and constructed to best suit the need of the facility; whether be industry, ships or regular sewers in urban cities. The sewer stored can be treated with mainly two major ways; chemically or biologically.
Which chemical is used in wastewater treatment plant?
The next chemical used in wastewater treatment plant is sodium aluminate. Sodium aluminate is a chemical belongs to inorganic compound. The liquid form of it works well as phosphorus remover. Wastewater often contains phosphorus that is a kind of phosporic calcium able to create hard substance on environment.
What type of pump is used in sewage treatment plant?
Many sewage treatment plants use centrifugal pumps to transfer the nitrified mixed liquor from the aeration zone to the anoxic zone for denitrification. These pumps are often referred to as Internal Mixed Liquor Recycle (IMLR) pumps.
Which EPA regulation covers sewage treatment plants?
EPA sets basic national wastewater standards: The "Secondary Treatment Regulation" applies to municipal sewage treatment plants, and the " Effluent guidelines " which are regulations for categories of industrial facilities. ^ a b c "Sanitation Systems – Sanitation Technologies – Activated sludge".
Which chemical is used in water treatment plant?
The most commonly used chemicals for water treatment process are: Algicide. Chlorine. Chlorine dioxide.
What substances are found in sewage?
What's in sewage sludgePolychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs);Chlorinated pesticides--DDT, dieldrin, aldrin, endrin, chlordane, heptachlor, lindane, mirex, kepone, 2,4,5-T, 2,4-D;Chlorinated compounds such as dioxins;Polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons;Heavy metals--arsenic, cadmium, chromium, lead, mercury;More items...
Which chemical most commonly used in wastewater treatment?
Certain basic or alkaline chemicals used to raise wastewater pH are below: CaO (calcium oxide or lime), MgO (magnesium oxide), Ca (OH) (calcium hydroxide, a hydrated form of lime) or Mg (OH) (magnesium hydroxide) are the most commonly used chemicals because of availability, low cost, and high capacity.
What are the chemicals used for treatment process?
Types of Wastewater Treatment ChemicalsCoagulants. ... Odor Control. ... Flocculants. ... Defoamers. ... Organic Polymers. ... Reducing Agents. ... Sludge Conditioners. ... Cleaners and Degreasers.More items...•
What is sewage treatment?
wastewater treatment, also called sewage treatment, the removal of impurities from wastewater, or sewage, before it reaches aquifers or natural bodies of water such as rivers, lakes, estuaries, and oceans.
What are the 3 types of sewage treatment?
There are three main stages of the wastewater treatment process, aptly known as primary, secondary and tertiary water treatment.
What chemicals are added in wastewater treatment?
Specialized chemicals such as chlorine, hydrogen peroxide, sodium chlorite, and sodium hypochlorite (bleach) act as agents that disinfect, sanitize, and assist in the purification of wastewater at treatment facilities.
Which acid is used in wastewater treatment?
Sulfuric AcidSodium Hypochlorite — more commonly known as bleach, this chemical is often used to eliminate viruses and bacteria during the disinfection stage. Sulfuric Acid — sulfuric acid is the most commonly used acid in the world. It is frequently used to bring the pH level of wastewater back to normal.
Which chemicals are added in sewage treatment plant for the process of flocculation?
Ferric Chloride works as a flocculant and coagulant. It is versatile in the water treatment industry and is an alternative to ferric sulfate.
What is wastewater treatment plant?
The term "sewage treatment plant" (or "sewage treatment works" in some countries) is nowadays often replaced with the term wastewater treatment plant or wastewater treatment station . Strictly speaking, the latter is a broader term that can also refer to industrial wastewater.
Where can sewage be treated?
Sewage can be treated close to where the sewage is created , which may be called a "decentralized" system or even an "on-site" system (in septic tanks, biofilters or aerobic treatment systems ). Alternatively, sewage can be collected and transported by a network of pipes and pump stations to a municipal treatment plant.
Why is wastewater treated?
The pretreatment has the following aims: to remove constituents that may pose risks to the sewerage system and its workers; prevent toxic or inhibitory compounds to the microorganisms in the biological stage in the municipal treatment plant; hinder beneficial use of the produced sewage sludge; or that will still be present in the final effluent from the treatment plant. : 59 Some industrial wastewater may contain pollutants which cannot be removed by sewage treatment plants. Also, variable flow of industrial waste associated with production cycles may upset the population dynamics of biological treatment units.
What is wastewater used for?
Physical, chemical, and biological processes are used to remove contaminants and produce treated wastewater (or treated effluent) that is safe enough for release into the environment.
What is municipal wastewater treatment?
Sewage treatment (or domestic wastewater treatment, municipal wastewater treatment) is a type of wastewater treatment which aims to remove contaminants from sewage.
How much of the world's wastewater is treated?
At the global level, an estimated 52% of municipal wastewater is treated. However, wastewater treatment rates are highly unequal for different countries around the world. For example, while high-income countries treat approximately 74% of their municipal wastewater, developing countries treat an average of just 4.2%.
How does sewage water go through a bar screen?
The influent in sewage water passes through a bar screen to remove all large objects like cans, rags, sticks, plastic packets, etc. carried in the sewage stream. This is most commonly done with an automated mechanically raked bar screen in modern plants serving large populations, while in smaller or less modern plants, a manually cleaned screen may be used. The raking action of a mechanical bar screen is typically paced according to the accumulation on the bar screens and/or flow rate. The solids are collected and later disposed in a landfill, or incinerated. Bar screens or mesh screens of varying sizes may be used to optimize solids removal. If gross solids are not removed, they become entrained in pipes and moving parts of the treatment plant, and can cause substantial damage and inefficiency in the process. : 9
What is the smell of sewage treatment?
Ans - Odors emitted by sewage treatment are typically a sign of an anaerobic or "septic" condition. Early stages of processing will tend to supply foul-smelling gases, with sulfide being commonest in generating complaints. Carbon reactors, a contact media with bio-slimes, less doses of chlorine, or circulating fluids to biologically capture and metabolize the noxious gases at plants with large processes in urban areas are the processes that are used to fade away the foul odor. Other methods of odor control exist, including addition of iron salts, peroxide, nitrate, etc. to manage hydrogen sulfide levels. High-density solids pumps are used for minimizing the odor by conveying sludge through hermetic closed pipework.
Why is sewage treatment important?
The sewage treatment is important to scale back the toxicity of sewage and maintain a secure and healthy environment , also as it promotes human welfare.
What is the smell of sewage?
Odors emitted by sewage treatment are typically a sign of an anaerobic or "septic" condition. Early stages of processing will tend to supply foul-smelling gases, with sulfide being commonest in generating complaints. Carbon reactors, a contact media with bio-slimes, less doses of chlorine, or circulating fluids to biologically capture and metabolize the noxious gases at plants with large processes in urban areas are the processes that are used to fade away the foul odor. Other methods of odor control exist, including addition of iron salts, peroxide , nitrate, etc. to manage hydrogen sulfide levels. High-density solids pumps are used for minimizing the odor by conveying sludge through hermetic closed pipework.
How does wastewater treatment work?
There are many processes that are used in the wastewater treatment plant that are designed to copy the natural treatment processes that occur within the environment , whether that environment may be a natural water body or not. Bacteria within the environment will consume organic contaminants if not overloaded,although this may lead to the reduction of the amount of oxygen within the water and should significantly change the general ecology of the receiving water. Organic contaminants work as a food for the neighbouring bacterial populations and therefore the numbers of disease-causing microorganisms are reduced by natural environmental conditions like predation or exposure to ultraviolet .
How is electricity generated from wastewater?
Electricity from wastewater can also be generated by Microbial fuel cells. From the wastewater treatment plant microbial fuel cells utilize the organic matter.During digestion, organic matters are converted into the straight molecule and release the CO2 and electrons. Those electrons are absorbed by the electrode and used as the source of electricity.
Where are biomasses collected?
Biomasses (Biowastes) are collected at the biogas plant and therefore the slurry is fed. Biomasses are rich in organic matter. Some of the bacteria inside the biogas plant anaerobically These bacteria can digest the biomasses which are present within the slurry and sewage. During digestion, an enormous amount of mixture of gases is released inside the tank. The mixture of these gases is called biogas. Biogas is removed from the biogas plant through a separate outlet.
Is wastewater treatment required?
Consequently, in cases where the receiving environment provides a high level of dilution, a high degree of wastewater treatment might not be required. However, recent evidence has demonstrated that very low levels of specific contaminants in wastewater, including hormones (from farming and residue from human hormonal contraception methods) and artificial materials such as phthalates that mimic hormones in their action, can have hit or miss adverse impact on the natural biota and potentially on humans if the water is reused for drinking water. As per the law in the US and EU, uncontrolled discharges of wastewater to the environment aren't permitted under law, and strict water quality requirements are to be met, as clean water is essential. A significant threat within the coming decades are going to be the increasing uncontrolled discharges of wastewater within rapidly developing countries.
What is wastewater treatment plant?
Wastewater treatment plant itself is a process of removing waste and dirts. This also works as a system to offer soluble and environmentally result of industrial waste. The contaminants in the sewage are removed and in turn produced safer wastewater for the environment. In order to do so, this treatment needs some chemicals as listed in the list ...
What is the first chemical in wastewater treatment?
Aluminum Sulfate. The first chemical in wastewater treatment plant is aluminum sulfate. Aluminum sulfate in wastewater plant acts as purifier of the wastewater. The chemical itself is soluble and easily reacts to the chemicals in wastewater. As a result, it produces protein antigens that break insoluble and hazardous chemicals.
What is the function of polymer in wastewater treatment?
The function of polymer is to coagulate any solids dirts and work in diluted water in order to free these materials from suspension. In order to use polymer in wastewater treatment, people need to dilute polymer with water with a concentration around 0,5 percent.
What is the most important element in water purification?
Also read: Harmful Effects of Oxidizing Chemicals for Environmental Health. Sodium Aluminate. The next chemical used in wastewater treatment plant is sodium aluminate. Sodium aluminate is a chemical belongs to inorganic compound.
What can lower the pH in water?
If the ph is higher, people can use hydrochloric acid as one of the compounds to lower the ph in water.
What chemicals lower pH?
While some chemicals work to elevate ph level, there are also chemicals to lower it. One of them is hydrochloric acid. While the chemical has many uses in industry, it also works for wastewater treatment. Its function is to lower the ph of the wastewater.
Is ferric chloride good for sewage?
This substance is very good for sewage treatment due to its effectiveness to deal with the heavy chemicals in most industry waste. To use ferric chloride, pour the liquid form of it in the dose mentioned on the label. Leave it until its corrosive effect wipes out the metal and heavy substance.
Why Treat Wastewater?
It's a matter of caring for our environment and for our own health. There are a lot of good reasons why keeping our water clean is an important priority:
Wastewater treatment
The major aim of wastewater treatment is to remove as much of the suspended solids as possible before the remaining water, called effluent, is discharged back to the environment. As solid material decays, it uses up oxygen, which is needed by the plants and animals living in the water.
How is sludge treated?
The sludge that is removed from the settling tanks and the scum that is skimmed off the top during the primary steps are treated separately from the water. Anaerobic bacteria (anaerobic bacteria do not require oxygen) feed off of the sludge for 10 to 20 days at temperatures around 38 degrees Celsius. This process decreases the odour and organic matter of the sludge, and creates a highly combustible gas of methane and carbon dioxide, which can be used as fuel to heat the treatment plant. Finally, the sludge is sent to a centrifuge, like the one shown in the picture below. A centrifuge is a machine that spins very quickly, forcing the liquid to separate from the solid. The liquid can then be processed with the wastewater and the solid is used as fertilizer on fields.
How does wastewater treatment work?
In small communities, wastewater treatment facilities may consist of individual septic systems, simple collection systems that directly discharge effluent to surface waters, or municipal lagoons that are emptied annually. These facilities usually treat and disperse the waste as close as possible to its source, thus minimizing operational costs and maintenance requirements. The longer the waste can sit in a lagoon before being discharged, the less likely it will be to contaminate drinking water sources. Some communities store the waste in lagoons, but others release the waste directly into water sources.
How to reduce pressure on septic system?
Following some water conservation practices can greatly reduce pressure on your septic system. For more information about conserving water, see the fact sheet about Water Consumption. Here are a few things that you can do to care for your septic system: 1 Do not use your drain or toilet as a garbage disposal; avoid putting dental floss, diapers, coffee grounds and paper towel down the drain, as they can clog up your septic system. 2 Spread your loads of laundry out over the week. When too much water is added to the septic tank, it does not have time to treat wastes, and you could be flooding your drainfield with wastewater. 3 Plant grass on your drainfield, but keep trees and shrubs away from it, because roots can clog the system and cause damage. 4 Do not drive on your drainfield, because this can compact the soil and damage the septic system components.
Why is oxygen important in wastewater treatment?
The oxygen helps the bacteria to digest the pollutants faster. The water is then taken to settling tanks where the sludge again settles, leaving the water 90 to 95 percent free of pollutants. The picture below shows the settling tanks in the Winnipeg Wastewater Treatment Plant.
Why is commercial wastewater not sent to public wastewater treatment plants?
Commercial and industrial waste is not sent directly to public wastewater treatment plants, because the public wastewater treatment system cannot effectively remove all of the contaminants. Wastewater from commercial and industrial processes is usually divided into the following four categories and dealt with accordingly:
What are the different levels of wastewater treatment?
There are several levels of wastewater treatment; these are primary, secondary and tertiary levels of treatment. Most municipal wastewater treatment facilities use primary and secondary levels of treatment, and some also use tertiary treatments.
Why do cities dump raw sewage?
Some cities choose to dump raw sewage into the oceans and rivers, because it is cheaper than effective treatment . A report published by Sierra Legal found that, of 22 Canadian cities, Victoria, Dawson City, Montreal, Saint John, Halifax and St. John’s dump some or all of their raw sewage directly into water bodies. While not all of the sewage is dumped directly into the oceans, these six cities produce 400 million litres of raw sewage each day! Montreal dumps around 3.6 billion litres of raw sewage into the St. Lawrence River each year, and Victoria is the only large Canadian city to dump all of its waste into the ocean without any attempt to improve the system. The city of Victoria dumps more than 34 billion litres of raw sewage into waterways each year, and still claims that their actions are not harming the environment! Halifax and St. John’s have plans to construct wastewater treatment facilities, but in the meantime, are still discharging 65.7 billion litres and 33 billion litres, respectively, of raw sewage into the Atlantic Ocean. For more information about water pollution, see the Water Pollution fact sheet, or the Operation Water Pollution lesson plans and resources.
What is wastewater treatment plant?
A wastewater treatment plant basically just for filtering, aerating, depositing, then discharge into the natural environment (wetland), then let it get into the wider environment such as the river and ocean to be “deluded” into the environment which is actually accumulating there --- as scientists found out.
What is biological wastewater treatment?
Biological wastewater treatment consists of two phases, secondary and tertiary. In secondary treatment, microorganisms in the wastewater are forced to actively consume organic matter so as to reduce the Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD) of the water. Thus when the water is released into a lake or river, the chance of eutrophication has been greatly reduced. Sometimes the water is chlorinated to reduce numbers of viable pathogens. The water, after secondary treatment, may be passed through a tertiary phase in which additional purification steps are conducted to the point the water is potable (drinkable).
How can we stop pollution?
The solution is to totally stop polluting by changing the way of our life and production; but not keep polluting while trying to “depollute” it. Pollution is a thermodynamically irreversible process, therefore, the effect of pollution cannot be reversed. Depollute chemical pollution is impossible, therefore the only way to rescue our ecosystem is to stop polluting, strictly. Pollution as part of the environment destruction is fundamentally not a technical issue therefore no fundamental technical solution.
What are the levels of SOP?
First you have to determine the objectives of the SOP, for the wwtp (read waste water treatment plant), there are 4 levels that are currently practice at our place: 1. Overall machineries and equipment operation 2. Guidance to Operators 3. Guidance to Supervisors 4. Performance monitoring of the plant
Is detergent removed from wastewater treatment plants?
Getting back to your original question- how is detergent removed at wastewater treatment plants. The simple answer is that it isn’t!
Can plants remove phosphorus?
However, if the inflow into a facility contains a lot of phosphorus and effluent restrictions are tight, a plants may require additional phosphorus removal. This can be achieved either by adding chemicals or biological processes designed specifically for that purpose.
Is it possible to remove chemical pollution from wastewater?
It is thermodynamically impossible for any wastewater treatment plant to remove or depollute the mixed chemical pollution in the wastewater, and therefore, it is impossible for it to functionally and economically do so regardless what the science and technology to be used for it.

Overview
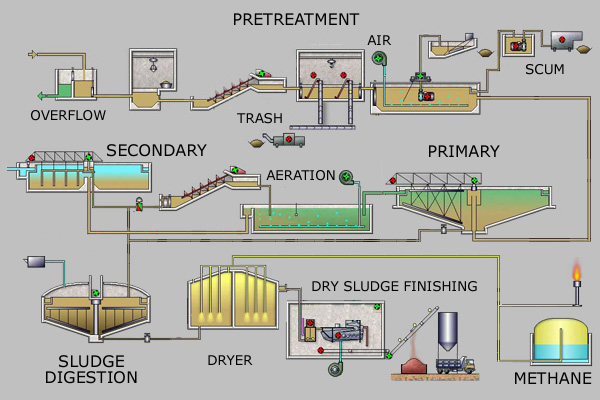
Available process steps
Sewage treatment often involves two main stages, called primary and secondary treatment, while advanced treatment also incorporates a tertiary treatment stage with polishing processes. Different types of sewage treatment may utilize some or all of the process steps listed below.
Preliminary treatment (sometimes called pretreatment) removes coarse mater…
Terminology
The term "sewage treatment plant" (STP) (or "sewage treatment works" in some countries) is nowadays often replaced with the term wastewater treatment plant (WWTP). Strictly speaking, the latter is a broader term that can also refer to industrial wastewater.
The terms "water recycling center" or "water reclamation plants" are also in use.
Purposes and overview
The overall aim of treating sewage is to produce an effluent that can be discharged to the environment while causing as little water pollution as possible, or to produce an effluent that can be reused in a useful manner. This is achieved by removing contaminants from the sewage. It is a form of waste management.
With regards to biological treatment of sewage, the treatment objectives can include various de…
Types of treatment processes
Sewage can be treated close to where the sewage is created, which may be called a "decentralized" system or even an "on-site" system (on-site sewage facility, septic tanks, etc.). Alternatively, sewage can be collected and transported by a network of pipes and pump stations to a municipal treatment plant. This is called a "centralized" system (see also sewerage and pipes and inf…
Design aspects
The "per person organic matter load" is a parameter used in the design of sewage treatment plants. This concept is known as population equivalent (PE). The base value used for PE can vary from one country to another. Commonly used definitions used worldwide are: 1 PE equates to 60 gram of BOD per person per day, and it also equals 200 liters of sewage per day. This concept is also used as a comparison parameter to express the strength of industrial wastewater compare…
Environmental impacts
Sewage treatment plants can have significant effects on the biotic status of receiving waters and can cause some water pollution, especially if the treatment process used is only basic. For example, for sewage treatment plants without nutrient removal, eutrophication of receiving water bodies can be a problem.
Reuse
Increasingly, people use treated or even untreated sewage for irrigation to produce crops. Cities provide lucrative markets for fresh produce, so are attractive to farmers. Because agriculture has to compete for increasingly scarce water resources with industry and municipal users, there is often no alternative for farmers but to use water polluted with sewage directly to water …