
Bacterial STDs are curable, while viral STDs aren’t. Common bacterial STDs include chlamydia
Chlamydia Infection
A common sexually transmitted infection caused by bacteria.
Which STDs stay in your system permanently?
Jan 14, 2019 · Bacterial STDs are curable, while viral STDs aren’t. Common bacterial STDs include chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis. Alternatively, common viral STDs are herpes, HIV, HPV, and hepatitis. Herpes, HIV, and chronic cases of hepatitis will remain in your system permanently after contraction. However, HPV usually won’t.
Do STDs ever come back?
Herein, which STD stays in the body for life? Genital herpes Tingling or burning sensation in the legs, buttocks, or genital area may happen just before the blisters show up. The herpes sores usually disappear within a few days. The virus stays in the body for life, and the sores may return from time to time. There is no cure for HSV.
How long does it take for an STD rash to go away?
Sep 11, 2015 · Trichomoniasis – Trich is caused by a parasitic protozoan that can be eradicated with antibiotics. Syphilis – Syphilis attacks the body in stages. It can often be easily treated with penicillin during the primary and secondary stages. A higher dosage may be required for the latent stage, especially for late latent stage.
Can I get rid of my STD?
Jul 26, 2018 · Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) are contracted from person to person through vaginal, anal, or oral sex. STDs are extremely common. In fact, 20 million new cases are reported in the United ...
Which STD stay in the body after symptoms are treated?
Some viral STDs stay with you for life, such as herpes and HIV. Others, such as hepatitis B and human papillomavirus (HPV), can be prevented with vaccines but cannot be cured.Apr 25, 2016
Can STD stay after treatment?
Treatment for chlamydia, gonorrhea, or another STD may be successful, but it does not protect you from other STDs in the future. In fact, many people become infected with STDs over and over again. This is because they have unprotected sex with partners who have untreated STDs.Nov 9, 2021
How long does STD last after treatment?
RESUMING SEXUAL ACTIVITY STOP having sex with others until you take the medicine, and DO NOT have sex for the next 7 days after taking the medicine. It takes 7 days for the medicine to work in your body and cure Chlamydia infection.
Which STDs stay with you for life?
Of these, 4 are currently curable: syphilis, gonorrhoea, chlamydia and trichomoniasis. The other 4 are viral infections which are incurable: hepatitis B, herpes simplex virus (HSV or herpes), HIV and human papillomavirus (HPV).Nov 22, 2021
How long can chlamydia stay in your body?
Chlamydia can lie dormant in the body for many years causing a low grade infection without symptoms. It could potentially flare up to cause a symptomatic infection, especially if there is an alteration in the persons immune system, such as a severe cold or flu, cancer or some other severe illness.
How do I know if my chlamydia is gone?
When will the signs and symptoms go away?Discharge or pain when you urinate should improve within a week.Bleeding between periods or heavier periods should improve by your next period.Pelvic pain and pain in the testicles should start to improve quickly but may take up to two weeks to go away.Jun 24, 2021
Can chlamydia stay after treatment?
Does chylamedia stay in the body even if its been cured? Nope! Chlamydia is easily cured with antibiotics. Chlamydia is a bacterial infection (like strep throat or an ear infection), which means that once you've been treated and tested negative for it (to make sure the antibiotics worked), it's gone.Sep 17, 2013
How long does gonorrhea take to go away?
If you have any symptoms of gonorrhoea, these will usually improve within a few days, although it may take up to 2 weeks for any pain in your pelvis or testicles to disappear completely. Bleeding between periods or heavy periods should improve by the time of your next period.
Can you still test positive for chlamydia after treatment?
Yes. After you finish all of your medicine, wait three or four months and then get tested again. Chlamydia can be easily cured with antibiotics, and your sexual partners need to be treated, too.Mar 3, 2021
Which of the following STD is not completely curable?
Explanation: Genital herpes is caused by a virus and is not completely curable at present along with hepatitis and HIV-B. Chlamydiasis, Syphilis and Gonorrhoea are bacterial diseases and can be cured completely if detected early and treated.
Can STD be cured permanently?
Viral STDs cannot be cured, but you can manage symptoms with medications. There is a vaccine against hepatitis B, but it will not help if you already have the disease. If you are given antibiotics to treat a STD, it is important that you take all of the drug prescribed to you, even if the symptoms go away.
Which of the STD is not completely curable?
Incurable STDs. Currently, there are 4 sexually transmitted infections (STIs or STDs) that are not curable: herpes (HSV), hepatitis B (HBV), human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), and human papillomavirus (HPV).
What STDs can be treated with antibiotics?
STDs that can be treated and cured with antibiotics or prescriptions include: Chlamydia – Chlamydia is a bacterial STD. It can often be treated with just a single round of antibiotics. Gonorrhea – Like chlamydia, gonorrhea is caused by bacteria that can usually be treated with antibiotics, however, there have recently been some cases ...
How long does hepatitis B last?
Acute Hepatitis B (HBV) – Hepatitis B cases last for about six months before the body clears the virus. Acute Hepatitis C (HCV) – In acute HCV cases, 1 in 5 individuals will clear the virus on their own for unknown reasons, the rest develop chronic HCV.
How long do penis warts last?
Hepatitis A (HAV) – HAV typically only lasts a couple months before the body can get rid of the virus on its own. Some cases last up to six months.
How long does it take for a STD to clear?
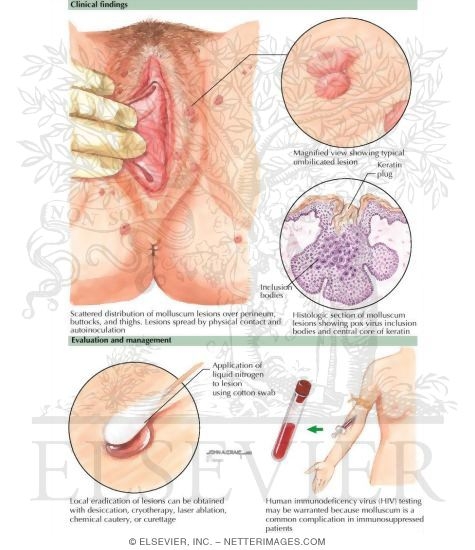
STDs that the body sometimes clears over time on its own include: Molluscum contagiosum – Even though this is a viral STD, the body typically clears itself of this rash-causing virus after approximately 6 to 18 months, but can take as long as four years, according to the CDC.
Why is it important to get tested for STD?
No matter what type of STD you may be worried about, it is important to get tested to know what you are dealing with (if anything) and to seek the appropriate treatment. Treatments, like antibiotics, can cure some sexually transmitted diseases, while others can keep the disease from worsening.
Can HSV cause cold sores?
Oral herpes – Oral herpes (cold sores) are typically caused by the HSV-1 strain of the virus, but can be caused by HSV-2. Herpes goes through unpredictable active and inactive phases. Even when the virus is inactive it can still be spread.
Can STDs be cured?
Sexual Healing: Which STDs Can & Cannot Be Cured. With all of the different STDs out there, it can be difficult to remember which ones can be treated and cured, and which sexually transmitted diseases stay with you for life. STDs are caused by a variety of bacteria, parasites and viruses. There are a few exceptions, ...
How to prevent STDs?
Fortunately, most of the STDs that are curable with antibiotics are also preventable by practicing safe sex. Using condoms, dental dams, and other barriers to make your sex life safer is an effective way to prevent bacterial STDs. However, it's important to use them consistently—for vaginal, anal, and oral intercourse.
What to do if you have a STD?
If you've been treated for an STD and don't want to get another one, the best thing that you can do is change your behaviors to decrease your risk. That means consistently practicing safe sex and always talking to new partners about STD risk before having sex.
Can you fail if you take the wrong medication?
Taking the Incorrect Medication. Keep in mind that your treatment can fail if you're taking the wrong medication. You might be prescribed the wrong drugs due to syndromatic treatment, an efficient, but sometimes inaccurate treatment method in which patients are prescribed STD treatment based on symptoms, rather than testing. ...
Can STDs cause encores?
Certain STDs pose additional problems that can make them likely to have an encore. If you've been diagnosed with any of these, it's important to keep the following in mind.
Can STDs be caused by the same pathogens?
Not all STDs are caused by the same pathogens (infectious organisms). Different illnesses require different treatments. That's why it's so important for your healthcare provider to correctly identify what's causing your infection. That's also why you can't just take any random antibiotic and hope it's going to work.
Is it too late to start a STD test?
STDs aren't necessarily transmitted every time you have sex, so it's never too late to start doing things more safely. The Best At-Home STD Tests.
Can chlamydia come back after treatment?
Research using animal models suggests that chlamydia may be able to hide out in the gut and re-emerge, which could be another reason why chlamydia can come back after treatment. 1 .
How common are STDs?
STDs are extremely common. In fact, 20 million new cases are reported in the United States each year, with 50 percent of these cases generally affecting people between the ages of 15 and 24. The good news is that most STDs are curable and even those without a cure can be effectively managed or minimized with treatment.
What to do if you have hepatitis B?
If you have hepatitis B, your best option is to speak to your doctor about checking your liver and your medication options to lessen symptoms. Immune system modulators and antiviral medications can help slow the virus’s damage to your liver.
Why is it important to get tested for STDs?
For this reason, it’s very important to get tested for STDs on a regular basis for your own safety, the safety of your partner (s), and general public health. The best treatment for STDs will always be prevention. If you have an STD or think you might have one, speak with your doctor to discuss your options.
What is the cause of liver cancer?
Hepatitis B is one of the leading causes of liver cancer. Babies usually receive a vaccine against this infection at birth, but many adults born before 1991 may not have received the vaccine.
How many people have herpes?
Herpes is very common — over 500 million people. are estimated to have herpes worldwide. Herpes is spread through skin-to-skin contact. Many people with herpes may not know they have it because they show no symptoms. However, when there are symptoms, they come in the form of painful sores around the genitals or anus.
What is the treatment for HIV?
The main treatment for HIV is called antiretroviral therapy. These drugs reduce the amount of HIV in the blood to undetectable levels.
Can STDs be cured?
However, there are still four incurable STDs: hepatitis B. herpes. HIV. HPV. Even though these infections can’t be cured, they can be managed with treatment and medication.
What is the rash on the bottom of the feet?
The characteristic rash of secondary syphilis may appear as rough, red, or reddish brown spots both on the palms of the hands and the bottoms of the feet. However, rashes with a different appearance may occur on other parts of the body, sometimes resembling rashes caused by other diseases.
How is syphilis transmitted?
Syphilis is transmitted from person to person by direct contact with a syphilitic sore, known as a chancre. Chancres can occur on or around the external genitals, in the vagina, around the anus , or in the rectum, or in or around the mouth. Transmission of syphilis can occur during vaginal, anal, or oral sex.
What is the primary stage of syphilis?
Primary Stage. The appearance of a single chancre marks the primary (first) stage of syphilis symptoms, but there may be multiple sores. The chancre is usually (but not always) firm, round, and painless. It appears at the location where syphilis entered the body.
How long does a chancre last?
These painless chancres can occur in locations that make them difficult to notice (e.g., the vagina or anus). The chancre lasts 3 to 6 weeks and heals regardless of whether a person is treated or not. However, if the infected person does not receive adequate treatment, the infection progresses to the secondary stage.
What are the symptoms of secondary syphilis?
Rashes associated with secondary syphilis can appear when the primary chancre is healing or several weeks after the chancre has healed. The rash usually does not cause itching. The characteristic rash of secondary syphilis may appear as rough, red, or reddish brown spots both on the palms of the hands and the bottoms of the feet. However, rashes with a different appearance may occur on other parts of the body, sometimes resembling rashes caused by other diseases. Sometimes rashes associated with secondary syphilis are so faint that they are not noticed. Large, raised, gray or white lesions, known as condyloma lata, may develop in warm, moist areas such as the mouth, underarm or groin region. In addition to rashes, symptoms of secondary syphilis may include fever, swollen lymph glands, sore throat, patchy hair loss, headaches, weight loss , muscle aches, and fatigue. The symptoms of secondary syphilis will go away with or without treatment. However, without treatment, the infection will progress to the latent and possibly tertiary stage of disease.
How long does it take for tertiary syphilis to appear?
Tertiary syphilis is rare and develops in a subset of untreated syphilis infections;, it can appear 10–30 years after infection was first acquired, and it can be fatal. Tertiary syphilis can affect multiple organ systems, including the brain, nerves, eyes, heart, blood vessels, liver, bones, and joints.
What is the name of the disease that causes headaches, paralysis, and dementia?
Syphilis can invade the nervous system at any stage of infection, and causes a wide range of symptoms, including headache, altered behavior, difficulty coordinating muscle movements, paralysis, sensory deficits, and dementia. 3 This invasion of the nervous system is called “neurosyphilis.
How to treat a STD?
These include chlamydia, gonorrhea and syphilis. Most bacterial infections can be cured with a simple treatment of antibiotics. This treatment could be administered orally or by injection, depending on what your doctor thinks is the most effective form of treatment. Recently, there has been increasing reports of antibiotic-resistant strains of gonorrhea which have made treating this STD more difficult. These reports have led to an urge by health organizations to confirm the infection exists before administering treatment.
What are the causes of STDs?
Viruses Can Cause STDs. The kind of STD that stays with you for the rest of your life is caused by a virus. These STDs include HIV (human immunodeficiency virus), HPV (human papillomavirus), HSV (herpes simplex virus) and Hepatitis B and C.
What does it mean when you have an STD?
Hearing the news that you have contracted an STD can often seem devastating. Many people think that having an STD means that your life is changed forever. While it is true that some STDs will be with you the rest of your life, there are others that are easily curable.
How many people have STDs?
An estimated 3.7 million people are thought to be infected with this STD, but only about 30% ever develop symptoms. This infection is more common in women than in men and is usually treated with antibiotics. The CDC recommends engaging in the practices of safe sexual intercourse in order to prevent the spread of STDs.
Can a parasite cause a STD?
Parasites Can Cause STDs. Another STD that is completely curable is an infection by parasite. Trichomoniasis is caused by infection with a protozoan parasite called Trichomonas vaginalis. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention lists trichomoniasis as the most common curable STD in the United States.
Is gonorrhea an antibiotic resistant disease?
Recently, there has been increasing reports of antibiotic-resistant strains of gonorrhea which have made treating this STD more difficult. These reports have led to an urge by health organizations to confirm the infection exists before administering treatment.
Can STDs stay in your body?
Since these STDs are viruses they stay in the body for life and can cause symptoms to appear periodically over time. The good news is that treatment exists for all of these infections. That means that even if a person is diagnosed with these illnesses, they can still lead a long and happy life.
How to ensure that dormant STDs receive the proper diagnosis and treatment?
The best way to ensure that dormant STDs receive the proper diagnosis and treatment is regular STD screening. The CDC. Trusted Source. recommends that all sexually active adults with new or multiple sexual partners receive at least yearly testing for most STDs, especially chlamydia and gonorrhea.
Why is STD asymptomatic?
In some cases, an STD may be asymptomatic (not show symptoms) because it’s latent, or lying dormant in your body. Latent STDs can cause someone to remain undiagnosed until symptoms begin to appear. This may put them at risk for long-term complications.
How long does it take for a STD to show up?
For some STDs, the body begins to produce antibodies and symptoms in as little as a few days. For others, it can take weeks or months for symptoms to appear. Here are the ranges of incubation periods for some of the most common STDs. STD.
What is the incubation period for STD?
STD incubation periods. When you first contract an STD, your body needs time to recognize and produce antibodies to the disease. During this time period, known as the incubation period, you may not experience any symptoms. If you test for an STD too early and the incubation period is not over yet, you may test negative for the disease ...
What are the risks of STDs?
Some of the potential risks of untreated STDs include: 1 pelvic inflammatory disease and infertility in women, from untreated#N#Trusted Source#N#chlamydia and gonorrhea 2 cervical cancer in women, from untreated HPV 3 pregnancy and birth-related risks, from untreated bacterial STDs, HIV, and hepatitis B 4 organ damage, dementia, paralysis, or death, from untreated syphilis
How to diagnose STDs?
After the incubation period has passed, most STDs can be diagnosed via antibody-specific blood tests. Some STDs are also accompanied by lesions and can be diagnose d via swab, culture, or urine tests as well. While retesting is recommended for bacterial STDs, some STDs are lifelong viral infections.
Why is early diagnosis important?
Early diagnosis and treatment of STDs is important for taking care of your sexual health. While it’s important not to test too early for STDs, knowing the incubation period of the most common infections can help you determine when to seek medical help.

Treatment
- There are effective treatments available for a number of sexually transmitted diseases (STDs). Chlamydia, gonorrhea, syphilis, and trichomoniasis can all be treated and cured reasonably easily with antibiotics. However, having your STD treated is not a guarantee that it will never come back. There are several reasons why simply finding treatment fo...
Diagnosis
- That's why it's so important for your doctor to correctly identify what's causing your infection before she prescribes antibiotics. That's also why you can't just take any random antibiotic and hope it's going to work.
Risks
- If your doctor prescribes you antibiotics, it's incredibly important to take the whole prescription. That's true even if you feel better before you're done. Failing to finish your antibiotics might not only keep your STD from being cured. It might also make it far more difficult to treat your STD when your doctor tries to do so next time (antibiotic resistance). This is a serious concern, partic…
Prognosis
- This is a big one. Being successfully treated for chlamydia, gonorrhea, or another STD does not mean that you can't get it again. In fact, many people become infected with STDs over and over again because they continue to have unprotected sex with partners who have untreated STDs. Certain STDs pose additional problems that can make them likely to have an encore. If you've be…
Epidemiology
- Around the world, trichomoniasis is the most common curable STD. However, with the standard single-dose treatment, repeat infections occur somewhat frequently. Fortunately, research has shown that recurrence occurs around half as frequently with multi-dose treatments for trichomoniasis. Multi-dose trichomoniasis treatment is now the standard regimen for women wi…
Prevention
- No one wants to see an STD come back after treatment. Fortunately, most of the STDs that are curable with antibiotics are also preventable by practicing safe sex. Using condoms, dental dams, and other barriers to make your sex life safer is a very effective way to prevent bacterial STDs. However, it's important to use them consistently, and for vaginal, anal, and oral intercourse. Whil…