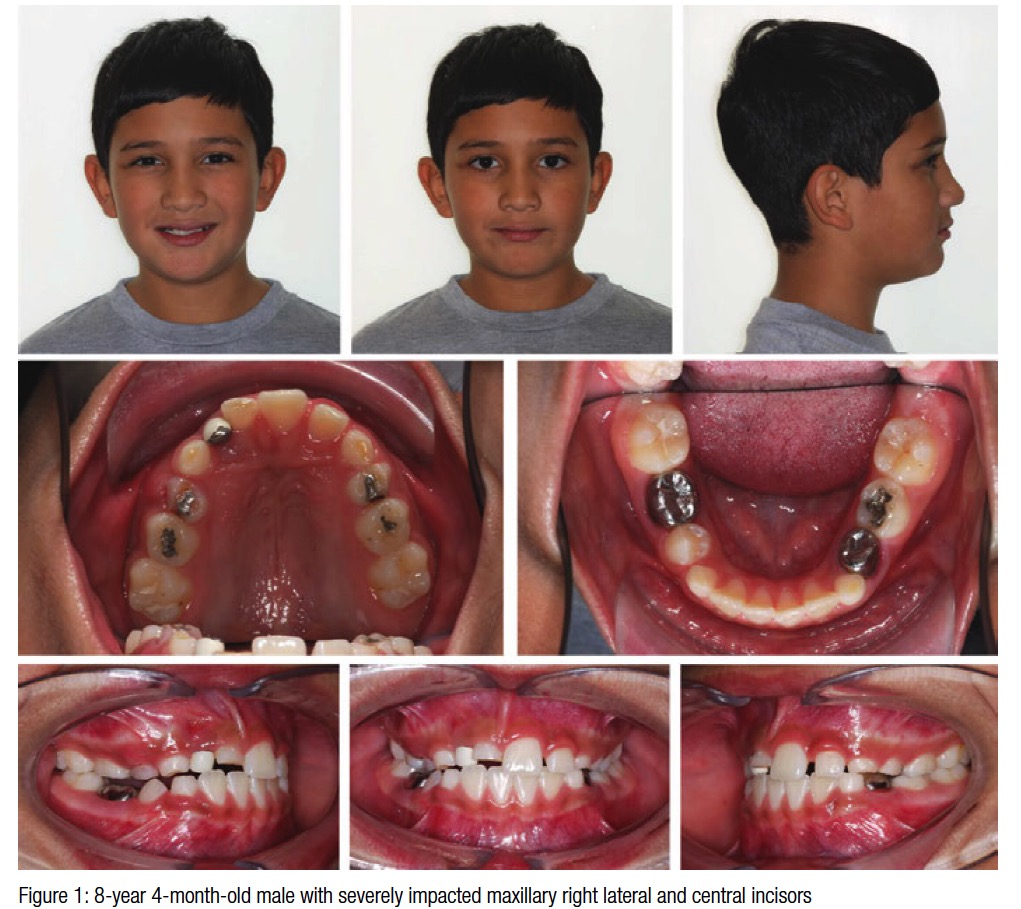
Before starting orthodontic treatment it is important to have status radiographs to ascertain the state of the patient's general dental health. A dental panoramic tomogram is very suitable in this respect, but right and left bimolar projections together with upper and lower occlusal films provide an appropriate alternative.
What is the best clinical practice of radiography in orthodontics?
In summary, careful assessment and the justification of need for a radiographic examination, meticulous technique, quality assurance and understanding the advantages and disadvantages of the different imaging techniques available, are the keys to the best clinical practice of radiography in orthodontics. Clinicians should note:
Can orthodontic treatment be carried out without radiographs?
Adult dentition In patients with a healthy dentition and supporting structures, orthodontic treatment may be carried out without the need for radiographs. History of previous orthodontic treatment needs investigation, and localised intra-oral radiographs may be required.
When were radiographs first used in orthodontics?
2 IN 1994 The British Society for the Study of Orthodontics (BSSO) asked the Standards Committee to develop guidelines for the use of radiographs in orthodontics, which formed the basis for the first edition. This was one of the first published sets of guidelines for dentistry.
What are the different types of radiographs used in dentistry?
The two most common radiographs - although not exclusive - are the panoramic (OPG) and cephalometric views. The OPG provides information about the presence and position of unerupted teeth, the health of the supporting bone around the teeth, jaw joints (TMJ's) sinuses, and the jaw bones (maxilla and mandible).

What radiograph is used for orthodontic treatment?
Intraoral x-rays are the most widely recognized x-ray taken by dental specialist. Bitewings and periodicals are two types of intraoral x-rays. In these images, a dental specialist gets a detailed image of a tooth and it's roots, and overall how healthy it is. These x-rays are generally used to find cavities.
What type of radiograph is most commonly taken in orthodontics?
There are two main types of X-rays used in general dentistry and orthodontics. Intraoral X-rays are taken of the inside of the mouth. Extraoral X-rays are taken outside of the mouth.
Why is cephalometric radiograph used?
It is a useful record prior to treatment and can be used during treatment to assess progress. It is used to assess the aetiology of malocclusion; to determine whether the malocclusion is due to skeletal relationship, dental relationship or both.
What is the best orthodontic treatment?
Best Orthodontic Treatment Options in 2019 By Kellyn Hodges on July 07, 2019#1: Invisalign. Possibly our most popular treatment, Invisalign® straightens the teeth discreetly, without the need for metal brackets, bands, or wires. ... #2: Braces. ... #3: Fastbraces.
What is a panoramic radiograph used for?
A panoramic x-ray allows us view your head, neck, and jaw, and how they work together as a whole, which means we can more easily identify cysts, tumors, growths, jaw abnormalities, and cancer.
What is OPG test?
What is an OPG? X-rays use radiation to take pictures of bones and other parts inside the body. An OPG is a panoramic X-ray of the upper and lower jaws, including the teeth. The OPG unit is specifically designed to rotate around the patient's head during the scan. An OPG will take approximately 20 seconds.
What is the difference between cephalometric and panoramic?
Cephalometric Analysis is an X-ray similar to a panoramic X-ray, in that it has the capability of capturing a full view of your skull and neck. A difference is that it is captured using a side-to-side sweeping motion, instead of the full 360 degree non-stop motion used in panoramic X-rays.
What is the importance of Cephalometrics to orthodontics?
Cephalometrics can help orthodontists determine whether malocclusions are due to skeletal or alveolar deviations, and in patients with skeletal discrepancy, cephalometrics can identify if this is due to dento-alveolar compensation or dysplastic development.
What does OPG mean in dentistry?
An Orthopantomogram x-ray (OPG x-ray) is a wide-view, panoramic x-ray of the patients upper and law jaw, and associated dentition from root to crown, in a single image - which is not possible with periapical or Bite-wing x-rays.
What are the types of orthodontic treatment?
There are 5 main types of braces available today:Metal braces.Ceramic braces.Self-ligating braces.Lingual braces.Clear aligners like Invisalign.
What is the latest orthodontic treatment?
What's New in Orthodontic Treatment: 5 Current Trends to Watch3-D Imaging With CBCT Scanning. ... Temporary Anchorage Devices (TADs) ... Self-Ligating, Clear, and Invisible Braces. ... Customized Smile Design Systems. ... Faster Orthodontic Treatment with PROPEL.
What are the three classifications of orthodontic treatment?
Classification of TeethClass I: Class I is a normal relationship between the upper teeth, lower teeth and jaws or balanced bite. ... Class II: Class II is where the lower first molar is posterior (or more towards the back of the mouth) than the upper first molar. ... Class III:
Why do we gather radiographs?
Radiographs are an important diagnostic tool in assessing an orthodontic condition and in determining a suitable treatment plan. The two most common radiographs - although not exclusive - are the panoramic (OPG) and cephalometric views.
Are radiographs harmful?
You may have questions regarding the safety of x-rays used in orthodontic treatment.
How many x-rays should I expect to have taken?
The OPG and lateral cephalogram are the two most common x-rays gathered at the beginning of treatment. Occasionally other views will be necessary to adequately assess unusual morphology or pathology.
What if I refuse to have x-rays?
It is unlikely that treatment will be initiated unless adequate radiographic records are obtained. There is a very real danger to your teeth, jaws and overall well being if treatment is commenced without thorough diagnostic records.
What are the different types of dental x-rays?
There are 4 common types of dental x-rays: Bitewings. Periapicals. OPG / Panoramic X-ray. CT-Scan. 1. Bitewings are x-rays taken of your back teeth biting together on the left and right sides. These are used to check for tooth decay in between teeth, and bone levels around teeth. They do not show the roots of the teeth.
Why is it important to have an x-ray of your teeth?
First of all it’s important to understand dental x-rays are a useful and important part of dental examination, to ensure the correct diagnosis when there are some signs/symptoms or indications.
What is a periapical x-ray?
Periapicals are x-rays taken of individual teeth – can be 1-2 teeth next to each other, and they show the full length of the tooth – including the root of the tooth. Periapicals are mainly used to check the root / nerve health of a tooth. They are great for detail. 3.
Why is it important to keep x-rays?
X-rays are essential as a diagnostic tool and if you keep a record of them you can avoid having new ones taken too frequently. «.
What is the purpose of X-rays?
X-rays are small doses of radiation that are able to pass through the body then expose an image on a computer or film to show a view of hard tissues of the body. X-rays are great to see bones and calcified objects like teeth. They are not useful to see softer items like cartilage, muscle, tissue.
Can you have orthodontic treatment without x-rays?
The British Orthodontic Society states that for adults with healthy teeth, orthodontic treatment can be carried out without orthodontic x-rays .#N#“In patients with a healthy definition and supporting structures, orthodontic treatment may be carried out without the need for radiographs.”
Can you diagnose tooth decay with an OPG?
You can’t accurately diagnose early tooth decay on an OPG. They are great for general survey. 4. CT Scan – these are a 3D view of the upper and lower jaws. These are great when doing implant surgery and you want to use 3D planning software. They are however high in radiation and so should only be used when needed.
Where is the x-ray placed on a dental radiograph?
For this type of radiograph, the x-ray film is placed horizontally between the teeth, as shown below. Occlusal radiograph – Essentials of Dental Radiography and Radiology. These views are helpful for a variety of reasons:
What is intra oral dental radiograph?
Dental radiographs can broadly be divided in to two categories: Intra-oral – where the x-ray film is inside the mouth. Extra-oral – where the x-ray film is outside the mouth.
Why do we need periapical radiographs?
Periapical radiographs are used for numerous reasons: Assessment of periapical pathology – as in the image above, periapical radiographs can help assess for the presence of periapical infection associated with a tooth. This will typically present as a radiolucent area.
Why do you need a bitewing on a radiograph?
These radiographs are typically routine screening radiographs taken on patients. One bitewing is taken for each side to assess the posterior teeth. These are usually done in a horizontal manner, however they can also be done vertically to gain some more information. Bitewings are useful for 2 main reasons:
What is PA radiograph?
Posteroanterior (PA) Radiographs. These can either be of the skull or of the mandible. PA skull views are helpful in assessing for pathology of the skull, such as Paget’s disease, or fractures of the skull vault.
What side of the face does the oblique lateral x-ray come from?
For an oblique lateral radiograph, the patient sits with the film against the side of their face and the x-ray beam coming obliquely from the opposite side of the face . This will ideally capture both sides of the jaw.
