What are the harmful effects of radioactive isotopes?
topes commonly used for this purpose are cobalt-60 and cesium-137. Radiation treatment of malignant growths is not, of course, a novel procedure; both radium im plants and X-rays generated at medium voltages (up to 250 kV) have been used all over the world for many years. However, large scale production of radio
Why are isotopes useful in the treatment of cancer?
Radioisotope therapy can treat a wide variety of cancers, including bone metastases, brain cancer, thyroid cancer, bile duct cancer, liver cancer, and neuroblastoma. Radioisotope therapy can also be useful as an adjuvant, or assisting, therapy when combined with …
What are the beneficial uses of radioactive isotopes?
The radioactive isotope used in the treatment of cancer is : (a) plutonium-239.
What are some medical uses for radioactive isotopes?
Radioactive isotopes in cancer treatment. Radioactive isotopes in cancer treatment. Radioactive isotopes in cancer treatment Strahlentherapie Sonderb. 1953;29:52-60. Author J BECKER. PMID: 13226110 No abstract available. MeSH terms Isotopes / therapeutic use* Neoplasms / therapy* ...
Why UAB
UAB Radiation Oncology offers a wide range of advanced treatment techniques in radiation therapy including triggered imaging radiosurgery, Gamma Knife surgery, medical dosimetry, Three-Dimensional Conformal Radiation Therapy, Brachytherapy, External Beam Radiation Therapy, Image-Guided Radiotherapy, Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy, radioisotope therapy, Stereotactic body radiation therapy, Total Body Irradiation, and Total Skin Irradiation..
CLINICAL TRIALS
UAB is an active participant in research and clinical trials. We encourage you to speak to your physician about research and clinical trial options and browse the link below for more information.
How to treat RAI?
For RAI therapy to be most effective, you must have a high level of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH or thyrotropin) in the blood. This hormone is what makes thyroid tissue (and cancer cells) take up radioactive iodine. If your thyroid has been removed, there are a couple of ways to raise TSH levels before being treated with RAI: 1 One way is to stop taking thyroid hormone pills for several weeks. This causes very low thyroid hormone levels (hypothyroidism), which makes the pituitary gland to release more TSH. This intentional hypothyroidism is temporary, but it often causes symptoms like tiredness, depression, weight gain, constipation, muscle aches, and reduced concentration. 2 Another way is to get an injection (shot) of thyrotropin (Thyrogen), which can make withholding thyroid hormone for a long period of time unnecessary. This drug is given daily for 2 days, followed by RAI on the 3 rd day.
How long after radiation therapy can you go home?
Depending on the dose of radioiodine used and where you are being treated, you might need to be in the hospital for a few days after treatment, staying in a special isolation room to prevent others from being exposed to radiation. Some people may not need to be hospitalized. Once you are allowed to go home after treatment, you will be given instructions on how to protect others from radiation exposure and how long you need to take these precautions. These instructions may vary slightly by treatment center. Be sure you understand the instructions before you leave the hospital.
Can hypothyroidism cause constipation?
This intentional hypothyroidism is temporar y, but it often causes symptoms like tiredness, depression, weight gain, constipation, muscle aches, and reduced concentration. Another way is to get an injection (shot) of thyrotropin (Thyrogen), which can make withholding thyroid hormone for a long period of time unnecessary.
Does radioactive iodine help with thyroid cancer?
Radioactive iodine therapy helps people live longer if they have papillary or follicular thyroid cancer (differentiated thyroid cancer) that has spread to the neck or other body parts, and it is now standard practice in such cases. But the benefits of RAI therapy are less clear for people with small cancers of the thyroid gland ...
What are radioactive sources used for?
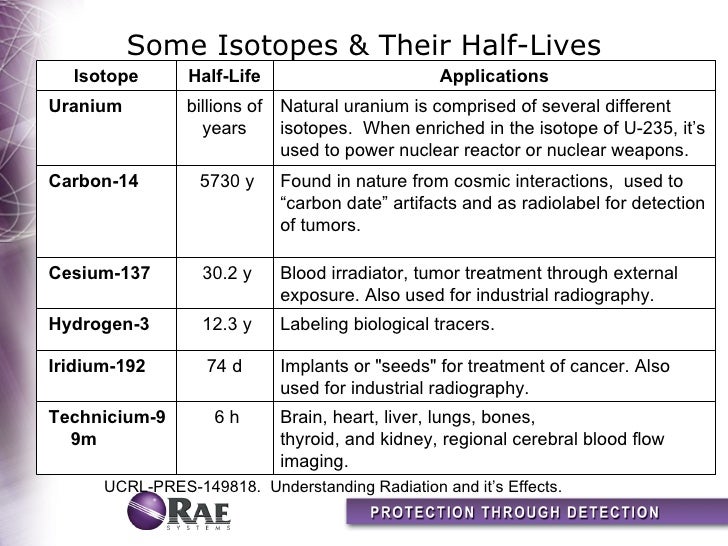
Hospitals and medical facilities are among the largest users of radioactive sources, typically for teletherapy and brachytherapy applications. Until the 1950s, the only significant radioactive sources produced were the radium-226 sources that were used for brachytherapy. Most of the old radium sources used in brachytherapy have been replaced by cobalt-60, cesium-137 and iridium192
Can radiation therapy cause side effects?
Any medical treatment may cause side effects or put you at risk for a more serious and/or permanent complication. You may experience a few, none, or (very rarely) all of these side effects. Most will disappear or lessen with time. Also, if other types of treatment are given in conjunction with radiation therapy, side effects may be more frequent and/or more severe than if radiation therapy alone had been given.