What is the equivalent treatment of heat to reduce bacteria?
is the use of heat to reduce numbers of pathogenic/spoilage bacteria in a food item to a safe level. Which are essentially equivalent treatments? - Dry 200°C heat for 1.5 hours; wet 121°C heat for 15 minutes - Dry 160°C heat for 1.0 hour; wet 200°C heat for 30 minutes - Dry 121°C heat for 1.5 hours; wet 200°C heat for 15 minutes
Which of the following compounds is no longer used to sterilize water?
sterilization Compounds of tin, mercury, arsenic, and copper are no longer used to prevent microbial growth in cooling water primarily because - antibiotics are cheaper.
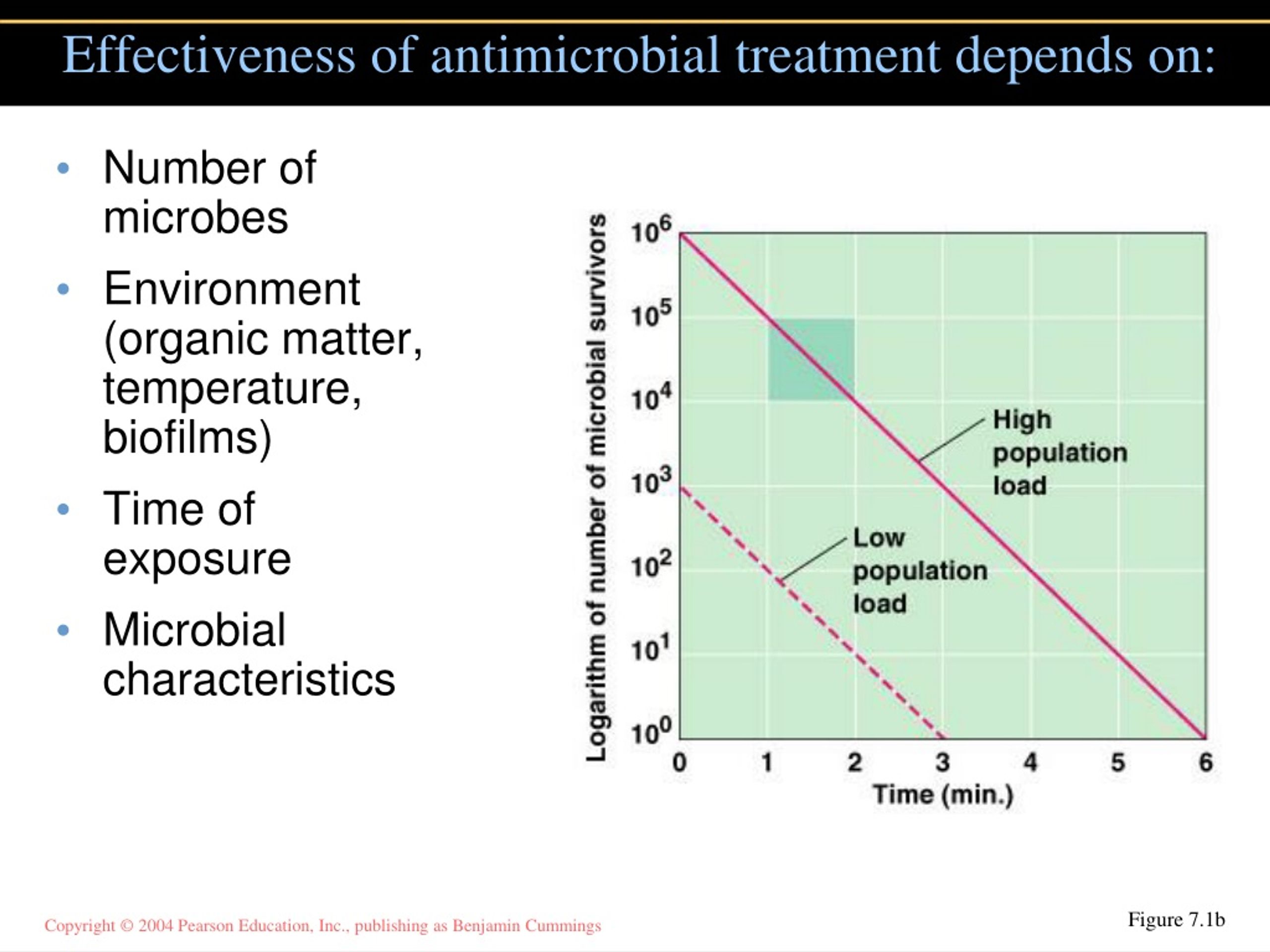
How many minutes would it take to kill 100000 organisms?
If a process kills 90% of the organisms per minute, how many minutes would it take to kill all organisms when starting with 100,000 organisms? - 6 minutes - 3 minutes - 2 minutes
Why is T/f false boiling not reliable for sterilization?
T/F False Boiling is not reliable for sterilization because - heat-sensitive instruments may be destroyed. - water boils at a higher temperature at lower altitudes. - heat-resistant endospores are unaffected. - viruses are more sensitive to heat than bacteria. - most pathogens are heat stable heat-resistant endospores are unaffected

Why is boiling not used as a sterilization method in a clinical setting?
Additionally, boiling may be less effective at higher altitudes, where the boiling point of water is lower and the boiling time needed to kill microbes is therefore longer. For these reasons, boiling is not considered a useful sterilization technique in the laboratory or clinical setting.
When treated with heat or chemicals bacteria will?
Upon heat treatment, bacteria die at a constant proportion. The more bacteria ones starts with, the longer it will take to kill them all. Heat treatment is an effective method for sterilization or disinfection of all materials. Boiling is very effective at removing most common waterborne pathogens.
Which of the following are the standard conditions for pasteurization?
Pasteurization of milk, widely practiced in several countries, notably the United States, requires temperatures of about 63 °C (145 °F) maintained for 30 minutes or, alternatively, heating to a higher temperature, 72 °C (162 °F), and holding for 15 seconds (and yet higher temperatures for shorter periods of time).
What temperature of moist heat will eliminate most bacterial endospores?
When placed under 15 pounds of pressure, the boiling point of water is raised to 121°C, a temperature sufficient to kill bacterial endospores.
Can boiling water destroy endospores?
Boiling is one of the oldest methods of moist-heat control of microbes, and it is typically quite effective at killing vegetative cells and some viruses. However, boiling is less effective at killing endospores; some endospores are able to survive up to 20 hours of boiling.
Which of the following methods will not sterilize?
Solution : Sedimentation is not a sterilization method. It is used to remove suspended solid matter.
Hence, the correct option is (d) . Step by step solution by experts to help you in doubt clearance & scoring excellent marks in exams.
Why is there a need to pasteurize the milk for at least 30 minutes?
With pasteurization, not only are pathogenic microorganisms killed but also a wide range of spoilage organisms are destroyed. Typical pasteurization conditions should be as follows: Not less than 62.8 °C or more than 65.6 °C for at least 30 min (holder method)
What are the 3 types of pasteurization?
Different Types of Thermal Processing MethodsThermization: Heat the milk to between 57°C to 68°C and hold for 15 minutes. ... Batch pasteurization: Also known as low-temperature long time (LTLT) pasteurization. ... Flash pasteurization: Also known as high-temperature short time (HTST) pasteurization.More items...•
What products are pasteurized?
Commonly pasteurized foodseggs and egg products.juice.alcoholic and fermented beverages (beer, wine, cider, kombucha)dairy products (milk, cheese, butter, ice cream, yogurt, cream)frozen desserts.imitation meats and deli meat.nuts (almonds, peanuts)flour and its products (bread, cereal, etc.)
Can endospores be killed?
While resistant to extreme heat and radiation, endospores can be destroyed by burning or by autoclaving. Endospores are able to survive boiling at 100°C for hours, although the longer the number of hours the fewer that will survive.
What temperature kills bacterial spores?
Most microbial cells will die at a temperature of 100 ºC. However, some bacterial spores will survive this and need temperatures around 130ºC to kill them.
Which of the following moist heat destroys microbes?
Autoclaves. Autoclaves rely on moist-heat sterilization. They are used to raise temperatures above the boiling point of water to sterilize items such as surgical equipment from vegetative cells, viruses, and especially endospores, which are known to survive boiling temperatures, without damaging the items.
What is the process of sterilizing food?
Pasteurization. - is the use of heat to sterilize food products. - is a process that uses intense cold to kill microorganisms on foods. - is the use of heat to reduce numbers of pathogenic/spoilage bacteria in a food item to a safe level.
What is the function of nitrites in processed foods?
The most important function of nitrites in processed foods is to. - prevent browning. - inhibit the germination of Clostridium botulinum endospores. - prevent carcinogen formation. - make the food more acidic. - destroy cell membranes of potential pathogens. inhibit the germination of Clostridium botulinum endospores.
