What is excessive exposure therapy?
Exposure therapy is a psychological treatment that was developed to help people confront their fears. When people are fearful of something, they tend to avoid the feared objects, activities or situations. Although this avoidance might help reduce feelings of fear in the short term, over the long term it can make the fear become even worse.
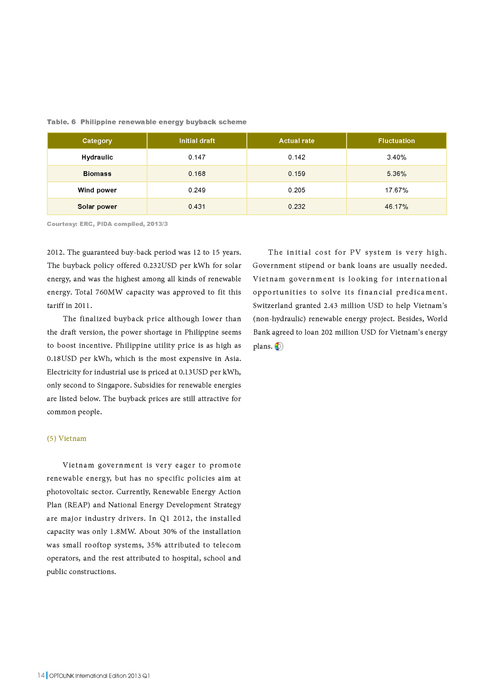
What are the limitations of exposure therapy?
Despite these limitations, exposure therapy is worth considering as a treatment option, as research supports its effectiveness. In fact, one of the limitations of exposure therapy is that it is not utilized enough.
How effective is exposure therapy to treat phobias?
A 2016 study found that people who received exposure therapy to treat phobias had fewer symptoms not only immediately after treatment but eight years later as well, suggesting that exposure therapy has long-term benefits. 3 Facing your fears can be difficult, so exposure therapy can be uncomfortable and challenging.
What is an example of exposure in psychology?
In vivo exposure: Directly facing a feared object, situation or activity in real life. For example, someone with a fear of snakes might be instructed to handle a snake, or someone with social anxiety might be instructed to give a speech in front of an audience.

Which of the following is a type of exposure therapy?
There are two different kinds of Exposure Therapy, including: Flooding — this type of Exposure Therapy involves rapid exposure to feared situations. Systematic Desensitization, also known as Progressive Exposure — this involves gradual exposure coupled with relaxation exercises when anxiety levels become too great.
Which best describes exposure therapy?
Exposure therapy is a psychological treatment that was developed to help people confront their fears. When people are fearful of something, they tend to avoid the feared objects, activities or situations.
Is exposure therapy a CBT?
A form of CBT, exposure therapy is a process for reducing fear and anxiety responses. In therapy, a person is gradually exposed to a feared situation or object, learning to become less sensitive over time. This type of therapy has been found to be particularly effective for obsessive-compulsive disorder and phobias.
Which of the following is not a goal of psychotherapy?
Particularly, one aspect that is not considered a goal of psychotherapy is learning to repress one's emotions (c).
What are the three types of exposure therapy?
During exposure therapy, a therapist guides you through the process of confronting whatever causes you anxiety. There are three types of exposure therapy: in vivo, imaginal, and flooding.
How do you do exposure therapy?
Make a list. Make a list of situations, places or objects that you fear. ... Build a Fear Ladder. Once you have made a list, arrange things from the least scary to the most scary. ... Facing fears (exposure) Starting with the situation that causes the least anxiety, repeatedly engage in.Practise. ... Reward brave behaviour.
Is EMDR exposure therapy?
EMDR therapy sets up a learning state that allows these experiences to be stored appropriately in the brain. This is the main difference between exposure therapy and EMDR; in other words, the individual is not re-exposed to the trauma.
Is ERP exposure therapy?
Exposure with Response Prevention (ERP) is a specific type of Exposure Therapy designed to treat Obsessive Compulsive Disorder. In ERP, people change their behavior in two ways. They approach anxiety-provoking situations instead of avoiding them (which is exposure).
When should you not use exposure therapy?
The PE manual (Foa et al., 2007) specifies several clinically determined contraindications for treatment: imminent threat of suicidal or homicidal behavior, recent (past 3 months) serious self-injurious behavior, and current psychosis.
Which of the following are goals of psychotherapy?
Psychotherapy goals include the following:Adjustment to injury or medical conditions.Improving emotional regulation.Social skills development.Managing excessive stress and/or tension.Improving communication skills.Wellness and personal growth.Dealing with difficult life decisions.
How many types of therapy are there?
Types of Therapy and How They Work. The American Psychological Association (APA) recognizes five different approaches to counseling: psychoanalysis, behavioral therapy, cognitive therapy, humanistic therapy and integrative or holistic therapy.
What is psychodynamic therapy used to treat?
WASHINGTON—Psychodynamic psychotherapy is effective for a wide range of mental health symptoms, including depression, anxiety, panic and stress-related physical ailments, and the benefits of the therapy grow after treatment has ended, according to new research published by the American Psychological Association.
What are the optimum conditions for eradication of a disease?
C: The optimum conditions for eradication of a disease include the absence of animal reservoirs, the absence of long-term carrier states, and the development of potent long term protection through natural infection or vaccination.
Why is screening acceptable?
Misses those who have false negative results because when a negative test occurs, the testing process is over for the immediate future. 4.Screening is acceptable in terms of harms, costs, an patient acceptance. Harms must be judged by looking at the entire testing strategy, not just the initial test.
What is a feasible screening strategy?
3.There is a feasible testing strategy for screening. Usually requires identification of a high risk population. Requires a strategy for using 2 or more tests to distinguish false positives/negatives. False positive: individuals who have positive results on a screening test, but do not turn out to have the disease.
What are the conditions that exposure therapy can help with?
These are some of the conditions and anxiety disorders exposure therapy can help treat: Phobias. Panic disorder. Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) Social anxiety disorder. Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) OCD. How to Practice Exposure Therapy for the Fear of Public Speaking.
What is exposure therapy?
Exposure therapy is a form of behavioral therapy designed to help you face your fears . When you’re scared of a specific object or activity, you may avoid it. For instance, if you’re afraid of enclosed spaces, you may avoid taking the elevator, especially if it’s crowded. While avoiding it can help keep your fear at bay in the short term, ...
Why is exposure therapy important?
Known as a therapeutic rapport, it is vital to exposure therapy because you need to feel safe and supported as you confront your worst fears.
How does exposure therapy help with fear?
Emotional processing: This form of therapy can help you explore and understand the source of your fear. It can also help you replace your instinctive response with more realistic thoughts and beliefs about the feared situation and make you more comfortable with fear and anxiety. Self-efficacy: Over time, exposure therapy can help you realize ...
What is systematic desensitization?
Systematic desensitization: Your therapist may employ systematic desensitization methods to help you relax and get comfortable with each step of this process. These methods can include relaxation exercises like meditation, deep breathing, guided imagery, and progressive muscle relaxation.
What is virtual reality exposure?
Virtual reality exposure is a more novel approach that allows you to confront your fears using virtual reality. If, for example, you have a fear of flying, you may benefit from videos that simulate flying before going on a vacation that involves air travel. A to Z: List of Phobias, From the Strange to the Common.
What is in vivo exposure?
In vivo exposure involves directly approaching a feared stimulus or situation in real time. For instance, if an adolescent is afraid to be away from their parents, this would mean practicing to gradually separate from the parents in various situations (with guidance from a clinician and consent from the parents).
What are the different types of exposure therapy?
Exposure therapy has been scientifically demonstrated to be a helpful treatment or treatment component for a range of problems, including: 1 Phobias 2 Panic Disorder 3 Social Anxiety Disorder 4 Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder 5 Posttraumatic Stress Disorder 6 Generalized Anxiety Disorder
Why do psychologists recommend exposure therapy?
In such situations, a psychologist might recommend a program of exposure therapy in order to help break the pattern of avoidance and fear. In this form of therapy, psychologists create a safe environment in which to “expose” individuals to the things they fear and avoid.
Why is exposure therapy important?
The exposure to the feared objects, activities or situations in a safe environment helps reduce fear and decrease avoidance. Exposure therapy has been scientifically demonstrated to be a helpful treatment or treatment component for a range of problems, including: There are several variations of exposure therapy.
What is in vivo exposure?
In vivo exposure: Directly facing a feared object, situation or activity in real life. For example, someone with a fear of snakes might be instructed to handle a snake, or someone with social anxiety might be instructed to give a speech in front of an audience.
How does exposure help with anxiety?
Extinction: Exposure can help weaken previously learned associations between feared objects, activities or situations and bad outcomes. Self-efficacy: Exposure can help show the client that he/she is capable of confronting his/her fears and can manage the feelings of anxiety.
What is interoceptive exposure?
Interoceptive exposure: Deliberately bringing on physical sensations that are harmless, yet feared. For example, someone with Panic Disorder might be instructed to run in place in order to make his or her heart speed up, and therefore learn that this sensation is not dangerous.
What is exposure fear hierarchy?
These include: Graded exposure: The psychologist helps the client construct an exposure fear hierarchy, in which feared objects, activities or situations are ranked according to difficulty. They begin with mildly or moderately difficult exposures, then progress to harder ones.