Medication
Melanoma is the deadliest form of skin cancer. In the early stages, melanoma can be treated successfully with surgery alone and survival rates are high, but after metastasis survival rates drop significantly. Therefore, early and correct diagnosis is key for ensuring patients have the best possible prognosis.
Procedures
Drugs Approved for Melanoma 1 Aldesleukin. 2 Binimetinib. 3 Braftovi (Encorafenib) 4 Cobimetinib. 5 Cotellic (Cobimetinib) 6 ... (more items)
Therapy
Because immunotherapy and targeted therapy have been more effective at treating melanoma, chemotherapy is used much less often. A chemotherapy regimen, or schedule, usually consists of a set number of cycles given over a specific time.
Nutrition
Melanoma is an incredibly virulent disease. It is a heterogenous and complex disease, which can make it difficult to diagnose and treat. Understanding the mechanisms that lead to melanomagenesis and allow melanomas to evade the immune system will give us new strategies for diagnosis and treating the disease.
What is melanoma and how is it treated?
What is the best drug for melanoma?
How often is chemotherapy used to treat melanoma?
Why is melanoma difficult to diagnose and treat?

What is the first treatment for melanoma?
Treating stage I melanoma Stage I melanoma is typically treated by wide excision (surgery to remove the melanoma as well as a margin of normal skin around it). The width of the margin depends on the thickness and location of the melanoma. Most often, no other treatment is needed.
Which of the following is malignant melanoma?
Malignant Melanoma is a common skin cancer that arises from the melanin cells within the upper layer of the skin (epidermis) or from similar cells that may be found in moles (nevi). This type of skin cancer may send down roots into deeper layers of the skin.
What is the latest treatment for melanoma?
In 2016, the FDA approved the combination of nivolumab and ipilimumab as a frontline therapy for patients with metastatic or inoperable melanoma. In 2022, the FDA approved a second combination, nivolumab and relatlimab, as a frontline therapy for patients with metastatic or inoperable melanoma.
What is the best treatment for malignant tumors?
Treatment options range from medical treatments such as chemotherapy, radiation or targeted drug therapy, to surgical treatments. In many cases, medical treatments are used in addition to surgery.
What is meant by malignant melanoma?
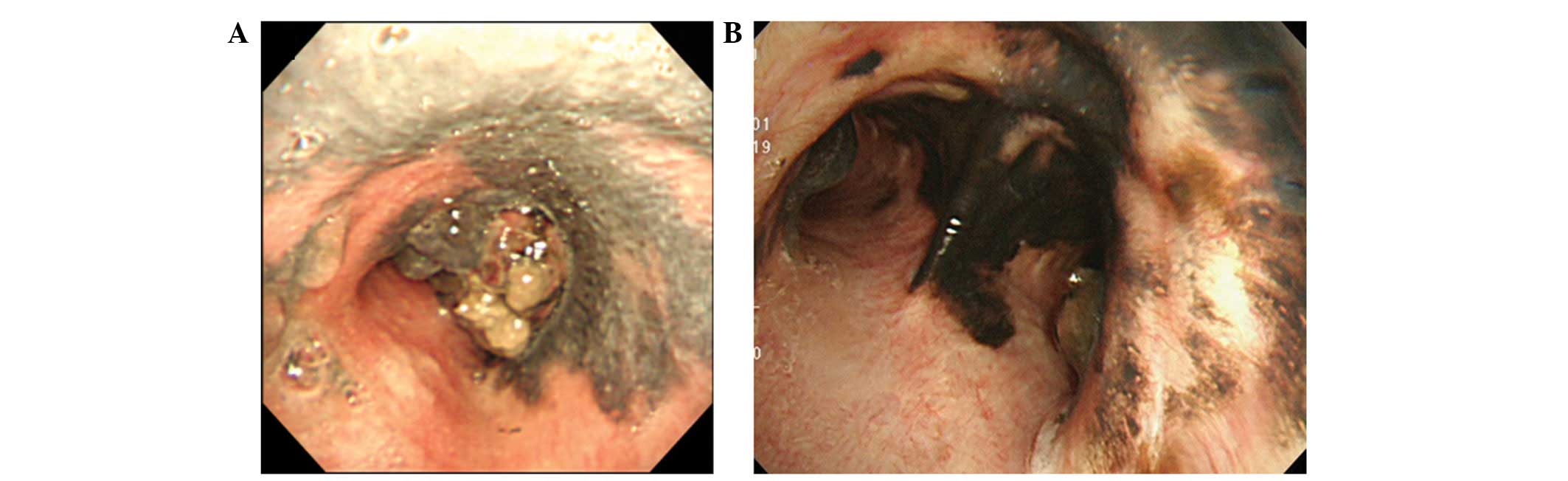
Malignant melanoma (see the image below) is a neoplasm of melanocytes or a neoplasm of the cells that develop from melanocytes. Although it was once considered uncommon, the annual incidence has increased dramatically over the past few decades.
Is a melanoma malignant?
Melanoma is a cancer that begins in the melanocytes. Other names for this cancer include malignant melanoma and cutaneous melanoma. Most melanoma cells still make melanin, so melanoma tumors are usually brown or black.
Is chemotherapy used to treat melanoma?
Chemo might be used to treat advanced melanoma after other treatments have been tried, but it's not often used as the first treatment because newer forms of immunotherapy and targeted drugs are typically more effective.
How can malignant melanoma be prevented?
Tips to Reduce Your Risk for Melanoma:Never Intentionally Expose Your Skin to the Sun. There is no such thing as a 'healthy' tan.Wear Sunscreen. Make sunscreen a daily habit. ... Wear Protective Clothing. ... Avoid Peak Rays. ... Don't Use Tanning Beds. ... Protect Children.
What is the treatment for stage 4 melanoma?
Doctors may use traditional methods to treat stage 4 melanoma. These include surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. Newer methods of treatment for stage 4 melanoma include immunotherapy and targeted therapy.
How many types of treatment are there?
Three principal types of medical treatment Curative – to cure a patient of an illness. Palliative – to relieve symptoms from an illness. Preventative – to avoid the onset of an illness.
Which are the different methods of treatment that we depend on?
Types of Treatment MethodsTargeted Therapies: A targeted therapy is designed to treat only the cancer cells and minimize damage to normal, healthy cells. ... Chemotherapy: ... Surgery: ... Radiation Therapies: ... Biological Therapy: ... Hormonal Therapy:
Why do we use chemotherapy?
Chemo is considered a systemic treatment because the drugs travels throughout the body, and can kill cancer cells that have spread (metastasized) to parts of the body far away from the original (primary) tumor. This makes it different from treatments like surgery and radiation.
Treatment by Stage
For patients with stage I and stage IA (≤1 mm thick, no ulceration, mitotic rate < 1/mm 2 with no adverse features) melanoma, treatment recommendations include wide-excision surgery
Treatment for Disease Progression Following Ipilimumab and BRAF Inhibitor Treatment
Treatment options for unresectable or metastatic melanoma and disease progression following ipilimumab treatment are as follows:
Oncolytic Immunotherapy
Talimogene laherparepvec (Imlygic) is a genetically modified oncolytic viral therapy indicated for the local treatment of unresectable cutaneous, subcutaneous, and nodal lesions in patients with melanoma recurrence after initial surgery {ref17}
How to treat early stage melanoma?
Treatment for early-stage melanomas usually includes surgery to remove the melanoma. A very thin melanoma may be removed entirely during the biopsy and require no further treatment. Otherwise, your surgeon will remove the cancer as well as a border of normal skin and a layer of tissue beneath the skin.
How to cope with melanoma?
Here are some ideas to help you cope: Learn enough about melanoma to make decisions about your care. Ask your doctor about your cancer, including your treatment options and, if you like, your prognosis. As you learn more about cancer, you may become more confident in making treatment decisions. Keep friends and family close.
How to treat melanoma that has spread beyond the skin?
Treating melanomas that have spread beyond the skin. If melanoma has spread beyond the skin, treatment options may include: Surgery to remove affected lymph nodes. If melanoma has spread to nearby lymph nodes, your surgeon may remove the affected nodes.
What is the procedure to remove melanoma from lymph nodes?
If there's a risk that the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes, your doctor may recommend a procedure known as a sentinel node biopsy. During a sentinel node biopsy, a dye is injected in the area where your melanoma was removed. The dye flows to the nearby lymph nodes.
What is the stage of melanoma?
Melanoma is staged using the Roman numerals 0 through IV. At stage 0 and stage I, a melanoma is small and has a very successful treatment rate. But the higher the numeral, the lower the chances of a full recovery. By stage IV, the cancer has spread beyond your skin to other organs, such as your lungs or liver.
How does thickness affect melanoma?
The thickness of a melanoma helps doctors decide on a treatment plan. In general, the thicker the tumor, the more serious the disease. Thinner melanomas may only require surgery to remove the cancer and some normal tissue around it.
What is used to close the site of a biopsy?
During an excisional biopsy, the doctor removes an entire lump or an entire area of abnormal skin, including a portion of normal skin. Stitches are generally used to close the biopsy site after this procedure.
How to treat melanoma on skin?
Wide excision. The main treatment for melanoma is surgical removal, or excision, of the primary melanoma on the skin. The extent of the surgery depends on the thickness of the melanoma. Most melanomas are found when they are less than 1.0 mm thick, and outpatient surgery is often the only treatment needed.
What are the factors that determine the treatment of melanoma?
Treatment recommendations depend on many factors, including the thickness of the primary melanoma, whether the cancer has spread, the stage of the melanoma, the presence of specific genetic changes in melanoma cells, rate of melanoma growth, and the patient’s other medical conditions.
How to treat stage 2 melanoma?
The standard treatment for stage II melanoma is surgery to remove the tumor and some of the healthy tissue around it. While this surgery is being done, lymph node mapping and sentinel lymph node biopsy may also be done. In some people with stage II melanoma, treatment with interferon may be recommended after surgery to lower the chances of the cancer coming back. Treatment in a clinical trial for stage II melanoma may also be an option. Ask your doctor about what clinical trials may be available for you.
How is stage 1 melanoma treated?
Stage I melanoma is usually treated with surgical removal of the tumor and some of the healthy tissue around it . The doctor may recommend lymph node mapping, and some lymph nodes may be removed.
What is the procedure to remove a tumor?
Surgery. Surgery is the removal of the tumor and some surrounding healthy tissue during an operation. This procedure is usually performed by a surgical oncologist. Surgery is the main treatment for people with local melanoma and most people with regional melanoma.
Does nivolumab shrink melanoma?
Both nivolumab and pembrolizumab have been shown to shrink melanoma for 25% to 45% of patients with un resectable or stage IV melanoma, depending on when the treatment is given. Both drugs also have been shown to reduce the risk of the cancer coming back after surgery for stage III melanoma.
What kind of doctor treats melanoma?
For a person with melanoma, this team may include these doctors: Dermatologist: A doctor who specializes in diseases and conditions of the skin. Surgical oncologist: A doctor who specializes in treating cancer with surgery. Medical oncologist: A doctor who specializes in treating cancer with medication.
What is the treatment for melanoma?
Several innovative treatments for melanoma are offered at MD Anderson, and many of them were discovered here. Your personalized melanoma skin cancer treatment may include: Lymphatic mapping and sentinel node biopsy. Minimally invasive isolated limb perfusion, which delivers cancer drugs directly to the arm or leg if melanoma has spread.
What is the procedure to remove a melanoma?
The surgeon carefully cuts out the melanoma and a predetermined area around it. The amount of skin that is removed and the degree of scarring depend on the tumor thickness of the melanoma. Most patients usually do not need more treatment.
How long does it take to heal from a melanoma?
The area may require stitches, and recovery can take a few weeks. The severity of the scar depends on the size, depth and location of the melanoma.
Can melanoma recur?
The chance of recurrence is greater if the melanoma was thick or had spread to nearby tissue. Your family members also should have regular checks for melanoma. To increase the chance of finding a new or recurrent melanoma as early as possible, follow your doctor's schedule for regular checkups.
Can you get a melanoma after treatment?
Follow-up After Treatment. If you have had a melanoma, you are at higher risk of developing new melanomas than someone who has never had a melanoma. You may be at risk of the cancer coming back in nearby skin or in other parts of the body.
Can radiation therapy be used for melanoma?
In collaboration with skilled radiation oncologists, cancer radiation therapy may be used as a component of your melanoma treatment plan. Radiation therapy may sometimes be combined with chemotherapy.
Is melanoma a one size fits all cancer?
Melanoma is not a “one-size-fits-all” type of cancer. The molecular and cellular changes are different for each person. The experts at MD Anderson tailor your treatment to be sure you receive the most advanced therapies with the least impact on your body. We have an extensive menu of choices to treat all stages and types of melanoma skin cancer.
What is the stage of melanoma?
Stages of melanoma. Stage 0. Also called melanoma in situ, this means the cancer occurs in the top layer of skin. Stage 1. The cancer is found only in the skin, but the tumor has grown thicker. In stage 1A, the skin covering the melanoma remains intact.
What does a doctor look for in a melanoma report?
The doctor is looking for cancer cells. What this doctor sees while looking at your tissue will be explained in the pathology report, including whether cancer cells were seen. If melanoma cells are seen, the report will include many important details, including: How deeply the melanoma tumor has grown into the skin.
How do you know if you have skin cancer?
Having a skin biopsy is the only way to know for sure whether you have skin cancer. The tissue that your dermatologist removes will be sent to a lab, where a doctor, such as a dermatopathologist, will examine it under a high-powered microscope. The doctor is looking for cancer cells.
How thick is melanoma?
The melanoma has grown thick, with the thickness ranging from 1.01 millimeters to greater than 4.0 millimeters. While thick, the cancer has not grown deeper than the skin or spread to nearby skin. Stage 3. The melanoma has spread to either: • One or more nearby lymph node (often called a lymph gland) • Nearby skin.
What is the survival rate of melanoma?
Survival rate is “the percentage of people who will be alive within a certain time period, such as 5 years, after being diagnosed with a certain stage of melanoma. Each stage of melanoma has its own survival rate. Before you search for the melanoma survival rates, it’s important to keep the following facts in mind:
What is the procedure to remove cancer cells?
Removing some normal-looking skin helps to remove stray cancer cells. What your dermatologist removes will be looked at under a microscope. This time the doctor is looking for cancer cells in the normal-looking skin.
What is it called when you have a spot on your skin?
This can be done during an office visit and is called a skin biopsy. This is a simple procedure, which a dermatologist can quickly, safely, and easily perform.
ABSTRACT
Melanoma is the deadliest form of skin cancer. In the early stages, melanoma can be treated successfully with surgery alone and survival rates are high, but after metastasis survival rates drop significantly. Therefore, early and correct diagnosis is key for ensuring patients have the best possible prognosis.
Introduction
At the basal level of the epidermis sit the melanocytes, which produce the UV absorbing pigment melanin. Melanocytes make up a minority cell population in the epidermis, with only 1500 melanocytes per square millimeter, and divide infrequently, less than twice per year.
History of melanoma
Melanoma is generally thought of as a modern disease exacerbated by migration of fair skinned people to areas nearer the equator and by modern sun-seeking behavior. However, although melanoma incidence rates have certainly skyrocketed in modern times, melanoma is an ancient disease that has been documented throughout history.
Molecular defects
When melanoma was first recognized as a disease in the 1800s it was classified based on where the tumor arose. In the 1960s melanomas began to be classified based on histologic patterns.
Diagnosis and prognosis of melanoma
The early classification of melanoma was based on where the tumor arose from (existing nevus, acquired melanocytic lesion, blemish free skin), but in the 1960s a prominent dermatologist, Wallace Clark, suggested that melanoma ought to be classified based on histological features instead, thus revolutionizing the way melanoma was diagnosed.
Treatment
Surgical removal of the tumor and surrounding healthy tissue is the primary treatment for localized melanoma, and sentinel lymph node biopsy is performed in patients whose tumors are greater than 0.8 mm thick or are thinner than this but ulcerated (stage pT1b or greater).
Conclusion
Melanoma is an incredibly virulent disease. It is a heterogenous and complex disease, which can make it difficult to diagnose and treat. Understanding the mechanisms that lead to melanomagenesis and allow melanomas to evade the immune system will give us new strategies for diagnosis and treating the disease.

Diagnosis
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Coping and Support
Specialist to consult
Preparing For Your Appointment