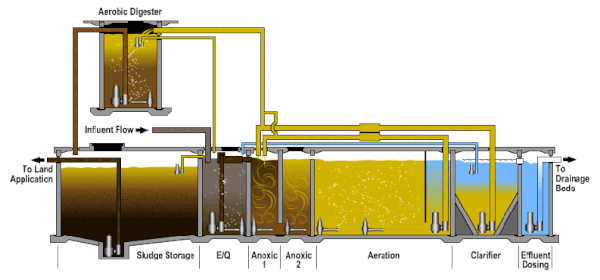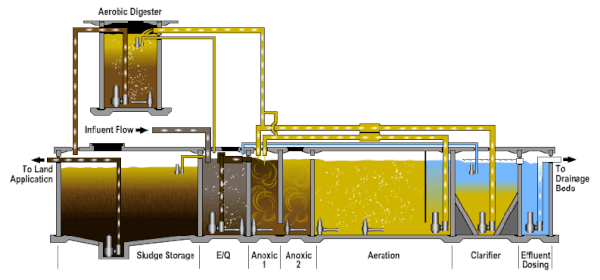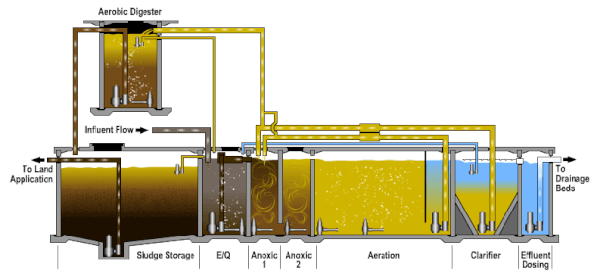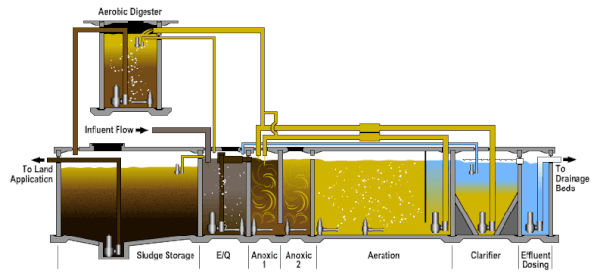
Primary treatment basically involves the process of sedimentation or settling. In the normal process of sewage treatment, sedimentation is usually carried out twice-once before the secondary treatment, referred to as primary sedimentation, and then after the secondary treatment is complete, a process known as secondary sedimentation.
Full Answer
What are the different levels of wastewater treatment?
There are several levels of wastewater treatment; these are primary, secondary and tertiary levels of treatment. Most municipal wastewater treatment facilities use primary and secondary levels of treatment, and some also use tertiary treatments.
What are the basic components of a wastewater treatment plant?
The type and order of treatment may vary from one treatment plant to another, but this diagram of the Ottawa-Carleton wastewater treatment plant illustrates the basic components. The primary level of treatment uses screens and settling tanks to remove the majority of solids.
Which process is most widely used for the treatment of sewage?
Among these, the complete-mix anaerobic digestion process is most widely used for the treatment of sewage. Anaerobic digestion is mostly useful for the stabilization of concentrated sludge’s that are produced on the treatment of industrial sewage.
What is the process of wastewater treatment?
The physical process of wastewater treatment begins with screening out large items that have found their way into the sewer system, and if not removed, can damage pumps and impede water flow. A bar screen is usually used to remove large items from the influent and ultimately taken to a landfill. Water Quality and the Clean Water Rule

What is the correct order of steps in waste water treatment?
Treatment StepsStep 1: Screening and Pumping. ... Step 2: Grit Removal. ... Step 3: Primary Settling. ... Step 4: Aeration / Activated Sludge. ... Step 5: Secondary Settling. ... Step 6: Filtration. ... Step 7: Disinfection. ... Step 8: Oxygen Uptake.
What are the 4 stages of wastewater treatment?
4-Step Wastewater Sludge Treatment ProcessStep 1 – Sludge Thickening. The first step in the sewage sludge treatment plan is called thickening. ... Step 2 – Sludge Digestion. After amassing all the solids from the sewage sludge begins the sludge digestion process. ... Step 3 – Dewatering. ... Step 4 – Disposal.
What are the 3 steps to wastewater treatment?
There are three main stages of the wastewater treatment process, aptly known as primary, secondary and tertiary water treatment. In some applications, more advanced treatment is required, known as quaternary water treatment.
What is the first stage of wastewater treatment?
sedimentationPrimary treatment (stage 1) Primary wastewater treatment involves sedimentation. This is when wastewater is temporarily held in large sedimentation tanks to remove settleable solids. With gravity, heavier solids sink to the bottom while lighter solids rise to the top.
What are the 3 stages of wastewater treatment PDF?
Wastewater is treated in 3 phases: primary (solid removal), secondary (bacterial decomposition), and tertiary (extra filtration).
What methods are used for the treatment of wastewater?
The treatment of wastewater is accomplished by four basic methods or techniques; physical, mechanical, biological and chemical. Physical methods of treatment include the use of tanks and other structures designed to contain and control the flow of wastewater to promote the removal of contaminants.
What is the final step in wastewater treatment?
The last step of primary treatment involves sedimentation, which causes the physical settling of matter. Sedimentation often uses chemicals like flocculants and coagulants.
What is the second stage of water treatment?
Secondary Treatment The secondary stage of treatment removes about 85 percent of the organic matter in sewage by making use of the bacteria in it. The principal secondary treatment techniques used in secondary treatment are the trickling filter and the activated sludge process.
Stage One — Bar Screening
Stage Two — Screening
- Removal of grit by flowing the influent over/through a grit chamber. Fine grit that finds its way into the influent needs to be removed to prevent the damage of pumps and equipment downstream (or impact water flow). Too small to be screened out, this grit needs to be removed from the grit chamber. There are several types of grit chambers (horizontal, aerated or vortex) which control t…
Stage Three — Primary Clarifier
- Initial separation of solid organic matter from wastewater. Solids known as organics/sludge sink to the bottom of the tank and are pumped to a sludge digestor or sludge processing area, dried and hauled away. Proper settling rates are a key indicator for how well the clarifier is operating. Adjusting flow rate into the clarifier can help the operator adjust the settling rates and efficiency…
Stage Five — Secondary Clarifier
- Treated wastewater is pumped into a secondary clarifier to allow any remaining organic sediment to settle out of treated water flow. As the influent exits the aeration process, it flows into a secondary clarifier where, like the primary clarifier, any very small solids (or fines) sink to the bottom of the tank. These small solids are called activated sludge and consist mostly of active …
Stage Six — Chlorination
- Chlorine is added to kill any remaining bacteria in the contact chamber. With the enhanced concentration of bacteria as part of the aeration stage, there is a need to test the outgoing effluent for bacteria presence or absence and to disinfect the water. This ensures that higher than specified concentrations of bacteria are not released into the environment. Chlorinationis the m…
Stage Seven — Water Analysis & Testing
- Testing for proper pH level, ammonia, nitrates, phosphates, dissolved oxygen, and residual chlorine levels to conform to the plant’s NPDES permit are critical to the plant’s performance. Although testingis continuous throughout the wastewater treatment process to ensure optimal water flow, clarification and aeration, final testing is done to make sure the effluent leaving the p…
Stage Eight — Effluent Disposal
- After meeting all permit specifications, clean water is reintroduced into the environment. Although testingis continuous throughout the wastewater treatment process to ensure optimal water flow, clarification and aeration, final testing is done to make sure the effluent leaving the plant meets permit specifications. Plants that don`t meet permit discharge levels are subject to fines and po…