Medication
Treating Prostate Cancer 1 Thinking about taking part in a clinical trial. 2 Considering complementary and alternative methods. 3 Help getting through cancer treatment. Your cancer care team will be your first source... 4 Choosing to stop treatment or choosing no treatment at all.
Procedures
There are different types of treatment for patients with prostate cancer. Radiation therapy and radiopharmaceutical therapy There are treatments for bone pain caused by bone metastases or hormone therapy. New types of treatment are being tested in clinical trials.
Therapy
“For many men, prostate cancer never affects their lives,” said Christopher L. Runz, DO, attending urologist at University of Maryland Shore Regional Health. “Active surveillance means we actively watch the cancer and make sure it stays low-grade, which means the cancer may potentially never spread.”
Self-care
The FDA has approved degarelix (Firmagon), given by monthly injection, to treat advanced prostate cancer. One side effect of this drug is that it may cause a severe allergic reaction. An oral LHRH antagonist, relugolix (Orgovyx), is also approved by the FDA for the treatment of advanced prostate cancer.
Nutrition
How to treat prostate cancer?
What are the different types of prostate cancer treatment?
Can prostate cancer be treated with active surveillance?
What is the best drug to treat advanced prostate cancer?
Which of the following are treatment options for prostate cancer?
Depending on each case, treatment options for men with prostate cancer might include:Observation or Active Surveillance for Prostate Cancer.Surgery for Prostate Cancer.Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer.Cryotherapy for Prostate Cancer.Hormone Therapy for Prostate Cancer.Chemotherapy for Prostate Cancer.More items...
What surgery is not done for prostate cancer?
Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) (It is not used to try to cure the cancer.) During this operation, the surgeon removes the inner part of the prostate gland that surrounds the urethra (the tube through which urine leaves the bladder). The skin is not cut with this surgery.
What are the treatments for early prostate cancer?
Radiation and surgery are the main treatments for early-stage prostate cancer. But other options include: Cryosurgery. This treatment uses very cold gas to freeze and kill cancer cells.
What is the most common procedure for prostate cancer?
The most common surgery for prostate cancer removes the entire prostate gland using a procedure called radical prostatectomy.
What is the most common prostate surgery?
Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP). This is the most common surgery to treat BPH. Your doctor removes portions of the prostate that are affecting your urine flow.
Is chemotherapy used for prostate cancer?
Types of Chemotherapy Drugs The most common chemotherapy drug for prostate cancer is docetaxel (Taxotere), which is usually given with prednisone, a steroid medicine. After starting docetaxel, many men experience the improvements in disease-related symptoms, including pain, fatigue and loss of energy.
How many types of treatment are there?
Three principal types of medical treatment Curative – to cure a patient of an illness. Palliative – to relieve symptoms from an illness. Preventative – to avoid the onset of an illness.
What is the best treatment for advanced prostate cancer?
Endocrine Therapy and Prostate Cancer Hormone (endocrine) therapy, known as androgen ablation or androgen suppression therapy, is the main treatment for advanced prostate cancer.
What is the best treatment for prostate cancer radiation or surgery?
Both radiation and surgery are equally effective treatments to cure prostate cancer." The choice of which treatment is best is up to individual patients and their care teams, Dr. King says. "Make sure you talk with a surgeon and a radiation oncologist before you make your decision.
How do you treat prostate?
The options include:Alpha blockers. These medications relax bladder neck muscles and muscle fibers in the prostate, making urination easier. ... 5-alpha reductase inhibitors. These medications shrink your prostate by preventing hormonal changes that cause prostate growth. ... Combination drug therapy. ... Tadalafil (Cialis).
Does a prostatectomy cure prostate cancer?
Radical prostatectomy is an operation to remove the prostate gland and tissues surrounding it. This usually includes the seminal vesicles and some nearby lymph nodes. Radical prostatectomy can cure prostate cancer in men whose cancer is limited to the prostate gland.
What is TURP treatment for prostate?
A transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) is a surgical procedure that involves cutting away a section of the prostate. The prostate is a small gland in the pelvis only found in men. It's located between the penis and bladder, and surrounds the urethra (the tube that carries urine from the bladder to the penis).
Which Treatments Are Used For Prostate Cancer?
Depending on each case, treatment options for men with prostate cancer might include: 1. Watchful waiting or active surveillance 2. Surgery 3. Radi...
Which Doctors Treat Prostate Cancer?
The main types of doctors who treat prostate cancer include: 1. Urologists: surgeons who treat diseases of the urinary system and male reproductive...
Making Treatment Decisions
It’s important to discuss all of your treatment options, including their goals and possible side effects, with your doctors to help make the decisi...
Help Getting Through Treatment
Your cancer care team will be your first source of information and support, but there are other resources for help when you need it. Hospital- or c...
What is the best way to monitor prostate cancer?
Closely monitoring the prostate cancer by performing prostate specific antigen (PSA) and digital rectal exam (DRE) tests and prostate biopsies regularly , and treating the cancer only if it grows or causes symptoms. Surgery.
What is the procedure to remove prostate cancer?
Surgery. A prostatectomy is an operation where doctors remove the prostate. Radical prostatectomy removes the prostate as well as the surrounding tissue. Radiation therapy. Using high-energy rays (similar to X-rays) to kill the cancer. There are two types of radiation therapy—. External radiation therapy.
How does ultrasound help with cancer?
High-intensity focused ultrasound. This therapy directs high-energy sound waves (ultrasound) at the cancer to kill cancer cells.
What is complementary medicine?
Complementary and alternative medicine are medicines and health practices that are not standard cancer treatments. Complementary medicine is used in addition to standard treatments, and alternative medicine is used instead of standard treatments. Meditation, yoga, and supplements like vitamins and herbs are some examples.
Is it safe to take supplements with complementary medicine?
Meditation, yoga, and supplements like vitamins and herbs are some examples. Many kinds of complementary and alternative medicine have not been tested scientifically and may not be safe. Talk to your doctor about the risks and benefits before you start any kind of complementary or alternative medicine.
What is the Gleason score for prostate removal?
Surgical prostate removal, or prostatectomy, is an option for men with a Gleason Score of 7 or higher when the cancer has not spread beyond the prostate. Most surgeries are performed robotically using the Da Vinci surgical system.
What to do if you have a high Gleason score?
Other Treatment Options. If the cancer has a very high Gleason Score and has spread to other areas of the body, chemotherapy and immunotherapy may be suggested. Genetic testing of the cancer is also recommended, as it may be able to predict whether a Gleason Score 6 or 7 tumor will later become aggressive.
How long does radiation therapy last?
Patients receive treatment five days a week for six weeks.
What does active surveillance mean?
Runz, DO, attending urologist at University of Maryland Shore Regional Health. “Active surveillance means we actively watch the cancer and make sure it stays low-grade, which means the cancer may potentially never spread.”.
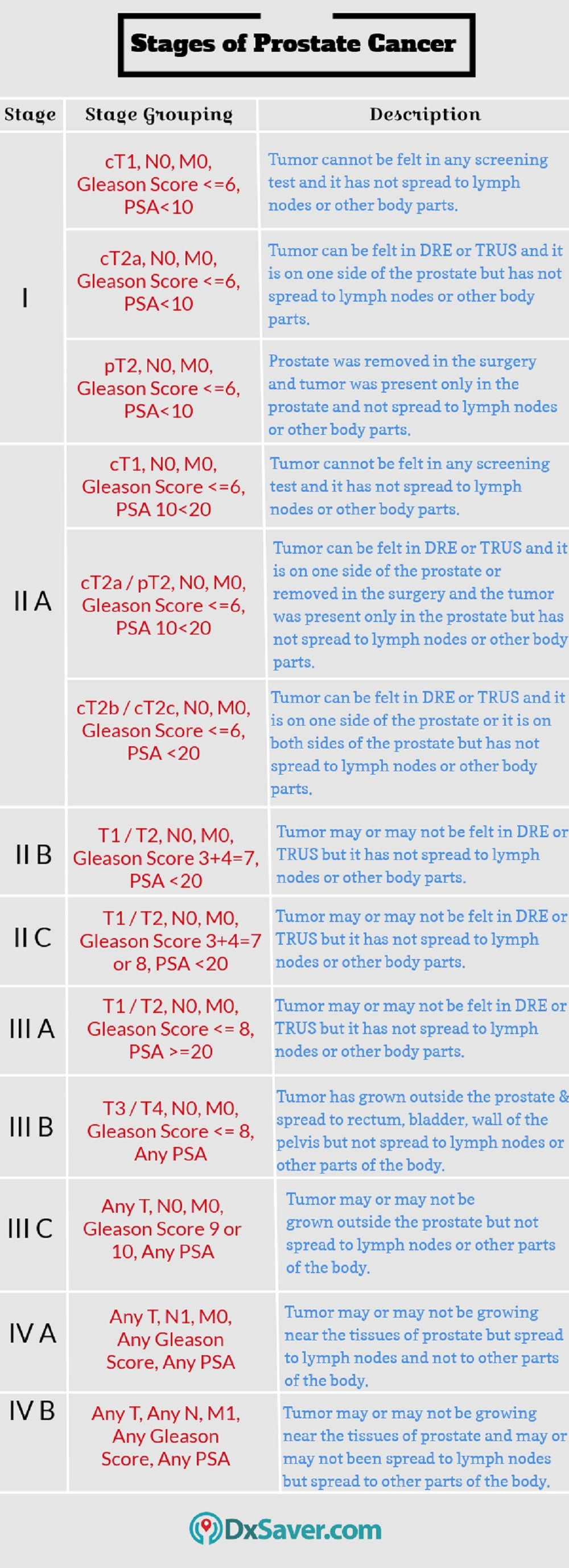
What is the best stage for prostate cancer?
Most cancers are graded from stage 1 to 4 in level of severity, ...
Can radiation cause erectile dysfunction?
However, because the areas around the prostate are also exposed to radiation, the neurovascular bundles also get radiated. This can cause unpredictable erectile function, including a total loss of the ability to achieve and maintain an erection. Radiation is a good option for older men and those unable to have surgery.
What is the purpose of a transrectal biopsy?
A biopsy is done to diagnose prostate cancer and find out the grade of the cancer (Gleason score). A transrectal biopsy is used to diagnose prostate cancer. A transrectal biopsy is the removal of tissue from the prostate by inserting a thin needle through the rectum and into the prostate.
What is a high Gleason score?
The two grades are then added to get a Gleason score. The Gleason score can range from 6 to 10. The higher the Gleason score, the more likely the cancer will grow and spread quickly. A Gleason score of 6 is a low-grade cancer; a score of 7 is a medium-grade cancer; and a score of 8, 9, or 10 is a high-grade cancer.
What is done after prostate cancer diagnosis?
After prostate cancer has been diagnosed, tests are done to find out if cancer cells have spread within the prostate or to other parts of the body.
What is the most common cancer in older men?
Anatomy of the male reproductive and urinary systems, showing the prostate, testicles, bladder, and other organs. Prostate cancer is most common in older men. In the U.S., about 1 out of 5 men will be diagnosed with prostate cancer.
What are the signs of prostate cancer?
Signs of prostate cancer include a weak flow of urine or frequent urination. Tests that examine the prostate and blood are used to diagnose prostate cancer.
Why is it important to know the stage of prostate cancer?
The information gathered from the staging process determines the stage of the disease. It is important to know the stage in order to plan treatment. The results of the tests used to diagnose prostate cancer are often also used to stage the disease. (See the General Information section .)
What does grade 3 mean in cancer?
For example, if the most common tissue pattern is grade 3 and the secondary pattern is grade 4, it means that most of the cancer is grade 3 and less of the cancer is grade 4. The grades are added for a Gleason score of 7, and it is a medium-grade cancer.
How does chemotherapy help prostate cancer?
Chemotherapy may help those with advanced or castration-resistant prostate cancer and those with newly diagnosed or castration-sensitive metastatic prostate cancer.
How long does it take for prostate cancer to grow?
Early-stage prostate cancer usually grows very slowly and may take years to cause any symptoms or other health problems, if it ever does at all. As a result, active surveillance or watchful waiting may be recommended. Radiation therapy (external-beam or brachytherapy) or surgery may also be suggested, as well as treatment in clinical trials. For those with a higher Gleason score, the cancer may be faster growing, so radical prostatectomy and radiation therapy are often recommended. Your doctor will consider your age and general health before recommending a treatment plan.
What to do if prostate cancer gets worse?
If the cancer is found to be worsening, treatment will begin. Active surveillance is usually preferred for those with very-low-risk and low-risk prostate cancer that can be treated with surgery or radiation therapy if it shows signs of getting worse.
How to treat prostate cancer with radioactive substance?
Radium-223 (Xofigo) is a radioactive substance used to treat castration-resistant prostate cancer that has spread to the bone. Radium-223 is an alpha-emitter radionucleotide that mimics calcium and targets areas in the bone where the cancer is causing changes. This treatment delivers radiation particles directly to tumors found in the bone, limiting damage to healthy tissue, including the bone marrow, where normal blood cells are made. Radium-223 is given by intravenous injection (IV) once a month for 6 months. This treatment is given by a radiation oncologist or a nuclear medicine doctor. Your medical oncologist should continue to follow your progress during this treatment to make sure the treatment is helping and that any potential side effects are managed. Treatment with radium-233 does not dependably lower PSA, so patients should not expect to see big decreases in PSA levels during treatment and, in fact, often PSA levels may rise.
How long does it take for a person to get a definitive treatment for prostate cancer?
People with intermediate-risk prostate cancer should receive hormonal therapy for at least 4 to 6 months. Those with high-risk prostate cancer should receive it for 24 to 36 months.
What is it called when you talk to your doctor about prostate cancer?
In addition, it is important to discuss your doctor's experience with treating prostate cancer. These types of talks are called "shared decision making .". Shared decision making is when you and your doctors work together to choose treatments that fit the goals of your care.
What is standard of care for prostate cancer?
This section explains the types of treatments that are the standard of care for prostate cancer. “Standard of care” means the best treatments known. When making treatment plan decisions, you are encouraged to consider clinical trials as an option.
What does it mean when your PSA is high?
An increase in PSA level may indicate that a man’s cancer has started growing again. A PSA level that continues to increase while hormone therapy is successfully keeping androgen levels extremely low is an indicator that a man’s prostate cancer has become resistant to the hormone therapy that is currently being used.
What is the most common treatment for prostate cancer?
Treatments that reduce androgen production by the testicles are the most commonly used hormone therapies for prostate cancer and the first type of hormone therapy that most men with prostate cancer receive. This form of hormone therapy (also called androgen deprivation therapy, or ADT) includes:
What are the two things that are needed for prostate cancer?
Androgens are also necessary for prostate cancers to grow. Androgens promote the growth of both normal and cancerous prostate cells by binding to and activating the androgen receptor, a protein that is expressed in prostate cells ( 1 ). Once activated, the androgen receptor stimulates the expression of specific genes that cause prostate cells ...
What is the LHRH agonist?
LHRH agonists are given by injection or are implanted under the skin. Four LHRH agonists are approved to treat prostate cancer in the United States: leuprolide (Lupron), goserelin (Zoladex), triptorelin (Trelstar), and histrelin (Vantas).
What are the most abundant androgens in men?
The most abundant androgens in men are testosterone and dihydrotestosterone ( DHT). Androgens are required for normal growth and function of the prostate, a gland in the male reproductive system that helps make semen. Androgens are also necessary for prostate cancers to grow.
What are the hormones that control the development and maintenance of male characteristics?
Hormones are substances that are made by glands in the body. Hormones circulate in the bloodstream and control the actions of certain cells or organs. Androgens (male sex hormones) are a class of hormones that control the development and maintenance of male characteristics. The most abundant androgens in men are testosterone ...
Where are androgens produced?
Most of the remaining androgens are produced by the adrenal glands . Androgens are taken up by prostate cells, where they either bind to the androgen receptor directly or are converted to dihydrotestosterone (DHT), which has a greater binding affinity for the androgen receptor than testosterone.
