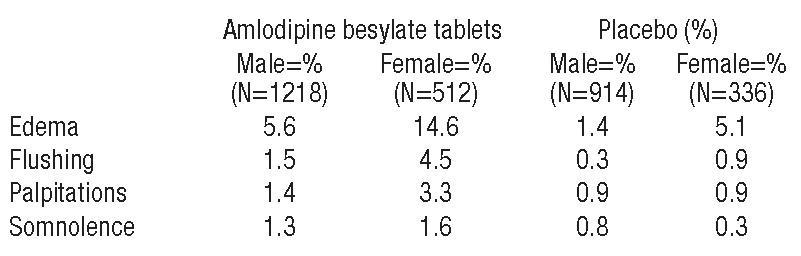
Which drugs may cause syncope?
- Bezafibrate
- Bosentan
- Capreomycin
- Carbidopa-Levodopa
- Dipyridamole
- Enflurane
- Ephedrine
- Iloprost
- Maprotiline
- Nefopam
Is there a cure for cough syncope?
Your treatment options will depend on what is causing your syncope and the results of your evaluation and testing. The goal of treatment is to keep you from having episodes of syncope. Treatment options include: Taking medications or making changes to medications you already take.
What are the most common causes of syncope?
- Ischemic cardiomyopathy (most common structural cardiac etiology of syncope)
- Valvular abnormalities (second most common structural etiology, most commonly aortic stenosis)
- Nonischemic/Dilated cardiomyopathy (third most common structural etiology)
- Hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy
- Aortic dissection
- Cardiac tamponade
- Obstructive cardiac tumors
What causes blacking out when standing up?
Blacking out while standing up is a condition that can occur due to various causes. Commonly known as dizziness or light headedness, blacking out is often experienced by people when raising from a position. While sudden drop in blood pressure is the commonest cause, it is important to know the other causes and ways to prevent it.
What is the most common type of syncope?
What tests are used to determine if you have syncope?
What is the condition called when the blood vessels are smaller?
How to get rid of syncope while sleeping?
What causes neurologic syncope?
What is the name of the condition where you can't stand and lie down?
How common is syncope?
See more
About this website

Here’s Why You Can NOT Delay Treatments for Syncope and Collapse
Syncope and collapse is a medical condition that can turn fatal if not treated soon. Let us go into the details of this disorder in the following article.
Vasovagal syncope - Symptoms and causes - Mayo Clinic
Symptoms. Before you faint due to vasovagal syncope, you may experience some of the following: Pale skin; Lightheadedness; Tunnel vision — your field of vision narrows so that you see only what's in front of you
Neurocardiogenic Syncope Symptoms & Treatment | Baptist Health
What is Neurocardiogenic Syncope? Neurocardiogenic syncope, also known as vasovagal neurocardiogenic syncope, is a fainting spell that occurs when the body overreacts to certain triggers, like intense emotion, the sight of blood, extreme heat, dehydration, a long period of standing or intense pain.
What is considered a pre-syncope?
Getting an injection or having blood drawn (not considered serious) Standing up quickly (a "head rush" is considered pre-syncope) Standing upright for a long time. Sudden and unexpected trauma, stress or pain, such as being hit. Blood donation.
What is the most common form of reflex syncope?
Vasovagal syncope — the common faint — occurs in one third of the population. It is by far the most common form of reflex syncope. Vasovagal syncope is often triggered by a combination of dehydration and upright posture. But it can also have an emotional trigger such as seeing blood ("fainting at the sight of blood").
What is reflex syncope?
Reflex Syncope (Neurally Mediated Syncope, Vasovagal Syncope, Vasodepressor Syncope, the Common Faint) Reflex syncope is the result of a reflex response to some trigger, in which the heart slows or blood vessels dilate (widen). This causes blood pressure to drop, so less blood flows to the brain and fainting (syncope) or near-fainting (pre-syncope) ...
What causes syncope in the heart?
Common causes of cardiac syncope: Arrhythmia and abnormal heart rhythm: During episodes of heart arrhythmia, the heart works inefficiently and not enough oxygenated blood can circulate to the brain. There are many types of cardiac arrhythmias that may cause syncope.
What is post-micturition syncope?
Urinating ( post-micturition syncope: occurs in men while standing to urinate) Eating a meal. Sudden abdominal pain. Blowing a brass instrument or lifting weights. Carotid Sinus Syncope, a response in older adults that occurs when pressure is applied to the carotid artery in the neck.
What is an EKG test?
On-site Diagnostic Tests. Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG): wires taped to various parts of your body to create a graph of your heart’s electrical rhythm. Exercise stress test: ECG recorded while strenuously exercising. Echocardiogram or transesophageal echocardiogram: ultrasound of the heart.
How long do you wear an ECG?
Holter monitor: a portable ECG you wear continuously for one to seven days to record your heart rhythms over time. Event monitor: a portable ECG you wear for one or two months, which records only when triggered by an abnormal heart rhythm or when you manually activate it.
How to avoid syncope?
• Avoid situations likely to induce syncope – for example, standing in a queue, taking a long hot bath, eating a large carbohydrate-rich meal in a warm restaurant, or failing to drink sufficient fluid in a hot nightclub.#N#• Take immediate action at the first warning of an impending collapse. If a collapse is imminent lie down flat propping your legs up on a chair or against a wall or sit down with your head between your knees. Squatting down on ones heels can be very effective and is less likely to attract attention in public . All these manoeuvres help reverse venous pooling of blood in the limbs, swiftly restoring blood flow to the brain and alleviating symptoms. When sufficiently recovered get up carefully. If your symptoms return or worsen squat down, or lie down again.
What is the best treatment for autonomic mediated syncope?
Various medications have been used to treat Autonomic Mediated Syncope (Neurocardiogenic Syncope, Vasovagal Syncope). Beta blockers (Antihypertensive and antianginal drugs) such as Bisoprolol at low dose can be effective.
How to prevent vasovagal syncope?
It may also be helpful in preventing vasovagal syncope. Ensuring adequate intake, as determined by the clear appearance of urine, may help prevent collapses. • Increase your dietary intake of salt if your oral intake is low – 24 hour urinary sodium excretion is a proxy measure.
Which is the strongest drug for autonomic mediated syncope?
SSRIs and Midodrine currently have the strongest scientific evidence. The fact that so many different medications are used in the treatment of Autonomic Mediated Syncope (Neurocardiogenic Syncope, Vasovagal Syncope) indicates that none is entirely effective. Sometimes, a combination of drugs is required.
What tests are needed for syncope?
Other tests, such as exercise stress test, Holter monitor and an echocardiogram, may be needed to rule out other cardiac causes. An ECG also is recommended for children and young adults with syncope. Other noninvasive diagnostic testing may be needed if they're suspected of having congenital heart disease, cardiomyopathy or a heart rhythm disorder. ...
What are the signs of syncope?
People who experience the warning signs of fainting of dizziness, nausea and sweaty palms should sit or lie down. Anyone with syncope should receive an initial evaluation, including detailed physical and history examinations and measurement of blood pressure and heart rate, by a physician.
What causes syncope in the heart?
Cardiac or cardiovascular syncope is caused by various heart conditions, such as bradycardia, tachycardia or certain types of hypotension . It can increase the risk of sudden cardiac death. People suspected of having cardiac syncope but who don't have serious medical conditions may be managed as outpatients.
What is the cause of NMS?
It happens when the part of the nervous system that regulates blood pressure and heart rate malfunctions in response to a trigger, such as emotional stress or pain.
Can heart failure cause syncope?
If evaluation suggests cardiac vascular abnormalities, an ambulatory external or implantable cardiac monitor may be required. Heart failure, atrial fibrillation and other serious cardiac conditions can cause recurrent syncope in older adults, with a sharp increase after age 70.
Can you drive after a syncope?
When it comes to driving after a syncope episode, there are no restrictions for VVS patients who had no fainting spells in the previous year. Still, it may be helpful for healthcare providers to discuss regional driving laws, restrictions and implications with all patients.
What is the best medicine for vasovagal syncope?
A drug called fludrocortisone acetate that's normally used to treat low blood pressure may be helpful in preventing vasovagal syncope. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors also may be used. Therapies. Your doctor may recommend ways to decrease the pooling of blood in your legs.
How to diagnose vasovagal syncope?
Diagnosis. Diagnosing vasovagal syncope often begins with a physical examination. During the physical exam, your doctor will listen to your heart and take your blood pressure. He or she may also massage the main arteries in your neck to see if that causes you to feel faint. Your doctor may also recommend several tests to rule out other possible ...
What tests are done to see if you have a fainting spell?
Blood tests. Your doctor may look for conditions, such as anemia, that can cause or contribute to fainting spells. Tilt table test. If no heart problems appear to cause your fainting, your doctor may suggest that you undergo a tilt table test.
How to tell if you're fainting?
What you can do 1 Write down details of your symptoms, including any triggers that may have caused you to faint. 2 Make a list of any medications, vitamins and supplements you're taking. 3 Write down questions you want to ask your doctor, including questions about potential tests and treatments.
What is the most common type of syncope?
Vasovagal syncope (also called cardio-neurogenic syncope) Vasovagal syncope is the most common type of syncope. It is caused by a sudden drop in blood pressure, which causes a drop in blood flow to the brain. When you stand up, gravity causes blood to settle in the lower part of your body, below your diaphragm.
What tests are used to determine if you have syncope?
Tests to determine causes of syncope include: Laboratory testing: Blood work to check for anemia or metabolic changes. Electrocardiogram (EKG or ECG): A test that records the electrical activity of your heart. Electrodes (small sticky patches) are applied to your skin to collect this information. Exercise stress test: A test ...
What is the condition called when the blood vessels are smaller?
Some patients with vasovagal syncope have a condition called orthostatic hypotension. This condition keeps the blood vessels from getting smaller (as they should) when the patient stands. This causes blood to collect in the legs and leads to a quick drop in blood pressure.
How to get rid of syncope while sleeping?
Elevating the head of your bed while sleeping. You can do this by using extra pillows or by placing risers under the legs of the head of the bed. Avoiding or changing the situations or “triggers” that cause a syncope episode. Biofeedback training to control a fast heartbeat.
What causes neurologic syncope?
Neurologic syncope is caused by a neurological condition such as seizure, stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA). Other less common conditions that lead to neurologic syncope include migraines and normal pressure hydrocephalus
What is the name of the condition where you can't stand and lie down?
Postural syncope (also called postural hypotension) Postural syncope is caused by a sudden drop in blood pressure due to a quick change in position, such as from lying down to standing. Certain medications and dehydration can lead to this condition.
How common is syncope?
It affects 3% of men and 3.5% of women at some point in life. Syncope is more common as you get older and affects up to 6% of people over age 75. The condition can occur at any age and happens in people with and without other medical problems.