Blockers of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS), that is, renin inhibitors, angiotensin (Ang)-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, Ang II type 1 receptor antagonists, and mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists, are a cornerstone in the treatment of hypertension.
What is the role of the renin-angiotensin system in Hypertension (HTN)?
The systemic role of the renin-angiotensin system (RAS) in the regulation of blood pressure and volume homeostasis and in the pathophysiology of hypertension (HTN) has been targeted for many decades1).
How does angiotensin II regulate blood pressure?
It regulates blood pressure by sending messages to the brain and the kidneys to help raise blood pressure. Angiotensin II stimulates an area in the brain called the "thirst center" to help increase blood pressure.
How does the renin angiotensin system work?
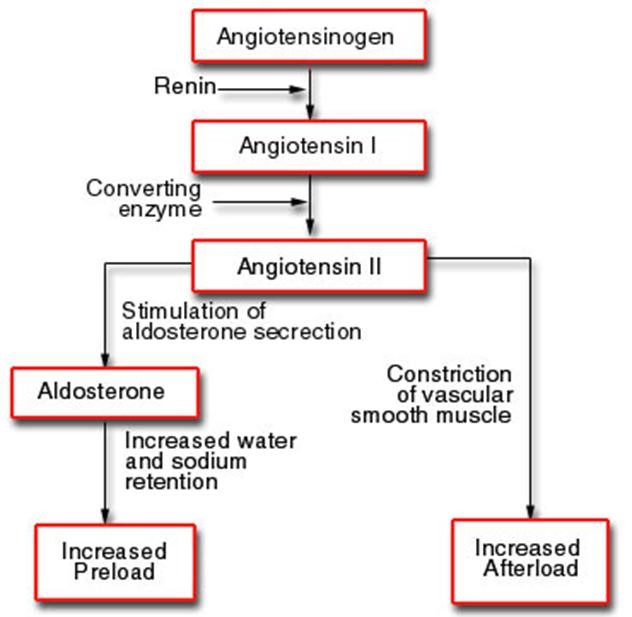
How the Renin-Angiotensin System Works. It has another important function as well—stimulating the release of aldosterone. Aldosterone is a very powerful vasoconstrictor that causes large increases in blood pressure but is more important because it can actually change the baseline filtering activity of the kidneys.
What is the role of the kidneys in the control of hypertension?
Abstract The kidneys play a fundamental role in the long-term control of arterial pressure by regulating sodium balance and extracellular fluid volume. The renin-angiotensin system (RAS) is at the center of the regulation of hypertension and progressive renal injury.

What are the drugs affecting renin-angiotensin system?
ACE-inhibitors (benazepril, captopril, cilazapril, delapril, enalapril, fosinopril, imidapril, lisinopril, moexipril, perindopril, quinapril, ramipril, spirapril, trandolapril or zofenopril) and the direct renin inhibitor aliskiren block the actions of specific enzymes involved in the production of angiotensin II in ...
What specific drugs could be have been developed to treat hypertension by targeting the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system?
Examples include candesartan, eprosartan, irbesartan, losartan, olmesartan and telmisartan. AA blocks the action of aldosterone on mineralocorticoid receptors. Spironolactone was the first member of the class.
What four classes of antihypertensive drugs target the effects of renin?
Site of action of four classes of antihypertensive drugs that block the renin-angiotensin system: beta-blockers, angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers, and the direct renin inhibitor.
How do ACE inhibitors affect renin?
ACE (Angiotensin-converting enzyme) inhibitors are known to raise renin and lower aldosterone levels, thereby causing false-negative ARR results.
What drugs are angiotensin receptor blockers?
Examples of angiotensin II receptor blockers include:Azilsartan (Edarbi)Candesartan (Atacand)Eprosartan.Irbesartan (Avapro)Losartan (Cozaar)Olmesartan (Benicar)Telmisartan (Micardis)Valsartan (Diovan)
What drugs are direct renin inhibitors?
A direct renin inhibitor used to manage hypertension....Renin-Inhibitors.DrugTargetTypeEnalkirenRenintargetRemikirenRenintargetAliskirenRenintargetAliskirenCytochrome P450 3A4enzyme1 more row
How do renin inhibitors treat hypertension?
How It Works. Direct renin inhibitors block the enzyme renin from triggering a process that helps regulate blood pressure. As a result, blood vessels relax and widen, making it easier for blood to flow through the vessels, which lowers blood pressure.
Do ARBs increase renin?
In the intact animal, acute administration of angiotensin II converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEI) or angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARB) causes a prompt and large increase in plasma renin concentration (PRC), reflecting stimulation of renin secretion.
How is high renin hypertension treated?
Renal hypertension (high renin/high aldosterone) is best treated with angiotensin receptor antagonists; primary aldosteronism (low renin/high aldosterone) is best treated with aldosterone antagonists (spironolactone or eplerenone); and hypertension due to overactivity of the renal epithelial sodium channel (low renin/ ...
Which ACE inhibitor is best for hypertension?
When considering factors such as increased ejection fraction, stroke volume, and decreasing mean arterial pressure, our results suggest that enalapril was the most effective ACE inhibitor.
What is renin angiotensin aldosterone inhibitor?
The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) plays a pivotal role in the pathogenesis of hypertension (HTN). Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEIs) and angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) are first line anti-HTN drug classes that are potent, effective and largely safe.
What do ARBs do?
ARBs work by blocking receptors that the hormone acts on, specifically AT1 receptors, which are found in the heart, blood vessels and kidneys. Blocking the action of angiotensin II helps to lower blood pressure and prevent damage to the heart and kidneys.
What is the renin-angiotensin system?
Updated on July 08, 2021. The renin-angiotensin system (RAS), is a group of related hormones that act together to regulate blood pressure and control inflammation. It is called a system because each part influences the other parts and all are necessary for the whole to function correctly.
Which pathway controls blood pressure and body fluid?
Angiotensin- (1-9) While the classical RAS pathway controls blood pressure and body fluid, it also has a complementary negative effect on the body that promotes inflammation. Some of the inflammatory responses of the classical RAS pathway include: 10. Blood vessel narrowing, or constriction.
What is the purpose of ACE inhibitors?
ACE inhibitors, which stop the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II , other drugs work by targeting different parts of the system. 8. Angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs), prevent angiotensin II from binding to blood vessels and causing vasoconstriction.
How to treat high blood pressure?
10 Angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs), for example, prevent angiotensin II from binding to blood vessels and causing vasoconstriction. Water pills, or diuretics , are another treatment for high blood pressure that helps to get rid of fluid by helping the body excrete water and sodium through urination.
Which hormone is responsible for reabsorbing water from urine?
This hormone travels from the brain to the kidneys and tells the kidneys to reabsorb water from the urine. 5. Angiotensin II also acts directly on the kidneys to further help increase blood pressure and blood flow by telling the kidneys to: Constrict its small blood vessels to help increase the blood pressure.
How do water pills help with high blood pressure?
Water pills, or diuretics, which help to get rid of fluid by telling the body excrete water and sodium through urination. While we have a better understanding of how to manage chronic high blood pressure, the fine details of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system are still being discovered.
Does angiotensin 2 stimulate the sympathetic nervous system?
Angiotensin II also stimulates the sympathetic nervous system by increasing the release of norepinephrine. Norepinephrine is a hormone that is associated with the " fight-or-flight response ," which is activated during stressful situations. In the RAA system, norepinephrine causes the heart to pump more quickly and forcefully to increase the circulating volume of blood to increase the blood pressure. 5
