
Table 1
| Tradename | Material | Drug | Company | Indication |
| Doxil® | Liposome-PEG | Doxorubicin | Janssen | MBC, metastatic ovarian cancer |
| Eligard® | PLGA | Leuprolide acetate | Tolmar | Prostate Cancer |
| Abraxane® | Albumin | Paclitaxel | Celgene | Metastatic breast cancer |
| Genexol PM® | mPEG-PLA | Paclitaxel | Samyang Corporation | Metastatic breast cancer |
How nanoparticles could change the way we treat cancer?
5 rows · Dec 05, 2021 · Based on carbon, these are divided into: 1) graphene quantum dots, 2) nanodiamond quantum dots, and ...
What is the best cure for cancer?
A wide range of nanomaterials based on organic, inorganic, lipid, or glycan compounds, as well as on synthetic polymers has been utilized for the development and improvement of new cancer therapeutics. In this study, we discuss the role of NPs in treating cancer among different drug delivery methods for cancer therapy.
What are the options for cancer treatment?
Aside from the advantages they offer in treatment, nanoparticles are also emerging to be valuable diagnostic entities. This article highlights the various ways nanotechnology is being used to improve the treatment and management of cancer. We also discuss the opportunities and obstacles in this area and provide an up to date review of progress ...
What medications treat cancer?
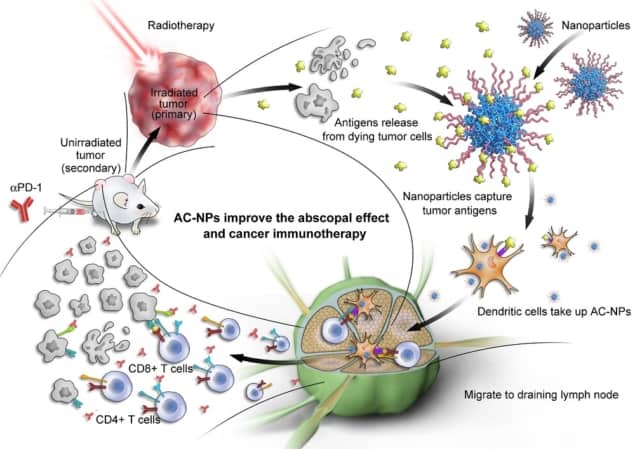
What nanoparticles are used in chemotherapy?
Researchers at the University of Tornoto have demonstrated the use of manganese dioxide nanoparticles designed to concentrate in a tumor and generate oxygen can increase the effectiveness of the chemotherapy drug doxorubicin.
What are nanoparticles in cancer?
Nanotechnology offers the means to target chemotherapies directly and selectively to cancerous cells and neoplasms, guide in surgical resection of tumors, and enhance the therapeutic efficacy of radiation-based and other current treatment modalities.Aug 8, 2017
How are nanoparticles used in cancer diagnosis and treatment?
Nanoparticles can selectively target cancer biomarkers and cancer cells, allowing more sensitive diagnosis; early detection requiring minimal amount of tissue, monitoring of the progress of therapy and tumor burden over time, and destruction of solely the cancer cells.May 13, 2012
Can nanoparticles cure cancer?
Nanoparticles are a promising treatment option for cancers that are resistant to common therapies. In a new study that demonstrates an innovative and non-invasive approach to cancer treatment, Northwestern Medicine scientists successfully used magnetic nanoparticles to damage tumor cells in animal models.
How do nanoparticles target cancer cells?
The drug molecules carried by nanoparticle are released in the extracellular matrix and diffuse throughout the tumor tissue. The particles carry surface ligands to facilitate active targeting of particles to receptors present on target cell or tissue.Aug 8, 2017
When was nanotechnology used for cancer?
In the 1980s, Maeda and colleagues observed the enhanced accumulation of nanoparticles in the tumor site due to the altered structure of tumor vasculature (Matsumura and Maeda, 1986).Sep 30, 2013
How are nanoshells used in cancer detection?
Once the nanoshells are attached to the cancerous cells, only laser light is needed to treat the cancer. Near infrared (NIR) light passes through the body and reaches the gold nanoshell The tuned gold nanoshell receives the NIR light and converts the light energy into heat, killing the cancer cells [8].
Can nanobots be used to cure cancer?
Currently, nanobots are programed to recognize 12 different types of cancer cells and can attack them with amazing selectivity and precision. Unlike chemotherapy and radiation therapy, which destroys healthy cells in addition to cancer cells, nanobots release cancer-fighting drugs directly into the malignant tumor.
Why are nanoparticles important?
Nanoparticles allow for a greater range of benefits for drug delivery and therapy. One of the largest portions of nanomedicine research is focused on anti-cancer drugs, since the targeting capabilities of nanoparticles make them extremely versatile for anti-cancer medicine.
What are the properties of nanoparticles?
Nanoparticles have an extremely versatile set of properties that range from diagnostic to therapeutic. Imaging technology has kept up in the race with nanotechnology because of its utility. Diagnosing problems is just as important as solving them. Nanoparticles can both diagnose and treat diseases at the same time; this dual ability is called “theranostics”. Some theranostic NPs include liposomes, emulsions, and nanogels.
How does nanotechnology help cancer?
The traditional use of nanotechnology in cancer therapeutics has been to improve the pharmacokinetics and reduce the systemic toxicities of chemotherapies through the selective targeting and delivery of these anticancer drugs to tumor tissues.
Why are nanocarriers used in cancer treatment?
These therapeutics are used in many cases to target ‘undruggable’ cancer proteins. Additionally, the increased stability of genetic therapies delivered by nanocarriers, and often combined with controlled release, has been shown to prolong their effects.
What is nanotechnology used for?
Additional uses of nanotechnology for immunotherapy include immune depots placed in or near tumors for in situ vaccination and artificial antigen presenting cells. These and other approaches will advance and be refined as our understanding of cancer immunotherapy deepens.
What are the benefits of PDT?
The primary benefits to the patient would be local delivery of PDT to deep tissue tumor targets, an alternative therapy for cancer cells that have become radiotherapy resistant, and reduction in toxicity (e.g., light sensitivity) common to traditional PDT.
What is immunotherapy for cancer?
Immunotherapy is a promising new front in cancer treatment encompassing a number of approaches, including checkpoint inhibition and cellular therapies. Although results for some patients have been spectacular, only a minority of patients being treated for just a subset of cancers experience durable responses to these therapies. Expanding the benefits of immunotherapy requires a greater understanding of tumor-host immune system interactions. New technologies for molecular and functional analysis of single cells are being used to interrogate tumor and immune cells and elucidate molecular indicators and functional immune responses to therapy. To this end, nano-enabled devices and materials are being leveraged to sort, image, and characterize T cells in the Alliance’s NanoSystems Biology Cancer Center.
What is the treatment for superficial tumors?
Another type of therapy that relies upon external electromagnetic radiation is photodynamic therapy (PDT). It is an effective anticancer procedure for superficial tumor that relies on tumor localization of a photosensitizer followed by light activation to generate cytotoxic reactive oxygen species (ROS).
What are the ligands used in nanoparticles?
At the same time, the relatively large surface area of nanoparticle can be functionalized with ligands, including small molecules, DNA or RNA strands, peptides, aptamers or antibodies. These ligands can be used for therapeutic effect or to direct nanoparticle fate in vivo.
What is gold nanoparticle?
Gold nanoparticles are emerging as promising agents for cancer therapy and are being investigated as drug carriers, photothermal agents, contrast agents and radiosensitisers. This review introduces the field of nanotechnology with a focus on recent gold nanoparticle research which has led to early-phase clinical trials.
What is plasmid model?
The DNA plasmid model is a relatively simple system that allows the study of radiation-induced DNA damage and chemical-free radical effects [56]. Plasmid DNA refers to double stranded extrachromosomal DNA which ranges from a few hundred to a few thousand base pairs in length and is normally present in bacteria.
Is GNP oxidized or nonoxidized?
GNPs, however, exist in a non-oxidised state (Au [0]). GNPs are not new; in the 19th century, Michael Faraday [7] published the first scientific paper on GNP synthesis, describing the production of colloidal gold by the reduction of aurochloric acid by phosphorous.
